Abstract
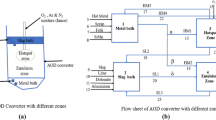
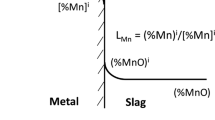
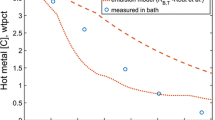
The importance of emulsion zone formation in the basic oxygen steelmaking (BOF) process lies in its crucial role in enhancing refining efficiency. This study provides a comprehensive theoretical analysis of refining in BOF steelmaking, empowering steelmakers to optimize emulsion zone formation. By examining the contributions of decarburization, desiliconization, and dephosphorization from the emulsion zone, the study systematically investigates refining phenomena in distinct sections of the BOF converter, interconnected through recirculation streams. By utilizing FactSageTM and its macro-facilities, transient variations in metal and slag compositions, alongside varying terminal phosphorus levels for diverse emulsion zone dimensions, are quantified. Model findings highlight that emulsion and hotspot zones play roles in decarburization and desiliconization, while dephosphorization exclusively occurs within the emulsion zone. The model’s projections for carbon, silicon, and phosphorus removals (wt pct) and metal bath temperature concur with data obtained from plant trials. This comprehensive analysis enhances our understanding of the BOF steelmaking process, enabling steelmakers to fabricate the required emulsion zone strategically for optimal refining efficiency.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Ogasawara, Y. Miki, Y. Uchida, and N. Kikuchi: ISIJ Int., 2013, vol. 53, pp. 1786–93.
F. Pahlevani, S.Y. Kitamura, H. Shibata, and N. Maruoka: ISIJ Int., 2010, vol. 50, pp. 822–29.
X.R. Wu, P. Wang, L.S. Li, Z.J. Wu, and R.H. Chen: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2011, vol. 38, pp. 185–88.
S. Barui, S. Mukherjee, A. Srivastava, and K. Chattopadhyay: Metals, 2019, vol. 9, pp. 1–8.
M. Iwasaki and M. Matsuo: Nippon Steel Tech. Rep., 2011, vol. 391, pp. 88–93.
M. Kumakura: Nippon Steel Tech. Rep., 2012, vol. 394, pp. 4–11.
M. Iwasaki and M. Matsuo: Nippon Steel Tech. Rep., 2012, vol. 394, pp. 26–32.
T. Hashimoto, H. Iiboshi, and K. Kumar: Nippon Steel Tech. Rep., 2012, vol. 394, pp. 84–90.
M. Kobayashi, K. Isobe, and M. Arai: Nippon Steel Tech. Rep., 2012, vol. 394, pp. 119–24.
X.M. Yang, J.Y. Li, G.M. Chai, D.P. Duan, and J. Zhang: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2017, vol. 44, p. 437.
X.M. Yang, C.B. Shi, M. Zhang, J.P. Duan, and J.A. Zhang: Met. Mater. Trans. B., 2011, vol. 42, pp. 951–76.
F. He and L. Zhang: J. Process. Control., 2018, vol. 66, pp. 51–58.
H. Sun, J. Yang, W. Yang, and R. Zhang: Steel Res. int., 2023, vol. 94, pp. 1–21.
E. Turkdogan and J. Pearson: ISIJ, 1953, vol. 175, pp. 398–401.
E. Turkdogan and J. Pearson: J. Iron Steel Inst., 1954, vol. 176, pp. 59–63.
G. Chen and S. He: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2015, vol. 42, pp. 433–38.
T. Ikeda and T. Matsuo: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1982, vol. 22, pp. 495–503.
G. Ye, J. Yang, and Rh. Zhang: Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater., 2021, vol. 28, pp. 66–75.
X. Yang, F.M. Sun, J.L. Yang, F. Liu, F.K.S. Cheng, and J.H. Wang: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2013, vol. 20, p. 41.
B. Deo and R. Boom: Fundamentals of Steel Making Metallurgy, Prentice Hall International, Upper Saddle River, 1993.
K.S Coley, E.Chen, and M. Pomeroy: in: Proceedings of the Extraction and Processing Division Symposium on Pyrometallurgy, San Diego, 16–20 June 2014, p. 289
E. Chen and K.S. Coley: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2010, vol. 37, pp. 541–45.
K. Gu, N. Dogan, and K.S. Coley: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2017, vol. 48, pp. 2343–53.
K. Gu, N. Dogan, and K.S. Coley: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 1119–35.
Z. Tian, B. Li, X. Zhang, and Z. Jiang: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2009, vol. 16, pp. 6–14.
W. Wu, S. Dai, and Y. Liu: J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2017, vol. 24, pp. 908–15.
A. Basu, A.K. Lahiri, and S. Seetharaman: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2007, vol. 38B, pp. 357–66.
A.N. Assis, M. Tayeb, S. Sridhar, and R.J. Fruehan: Metals, 2019, vol. 9, pp. 1–2.
Y. Zhou, R. Zhu, H. Wang, and H. Zhang: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2021, vol. 48, pp. 570–78.
P. Kozakevitch: Study of Basic Phosphate Slag Foams, International Congress of Oxygen Steelmaking, Le Touquet, 1963.
H.W. Meyer, W.F. Porter, G.C. Smith, and J. Szekely: JOM, 1968, vol. 20, pp. 35–42.
S. Okano, J. Matsuno, H. Ooi, K. Tsuruoka, T. Koshikawa, and A. Okazaki: International Conference on Science and Technology of Iron and Steel, Iron and Steel Institute, Tokyo, 1971, pp. 227–31.
D.J. Price: Process Engineering of Pyrometallurgy Symposium, IMM, London, 1974.
A. Chatterjee, N.O. Lindfors, and J.A. Weste: Ironmak. Steelmak., 1976, vol. 3, pp. 21–32.
B.K Rout, G.A Brooks, M.A. Rhamdhani, in: Proceedings of the AISTech 2015 Iron and Steel Technology Conference, Cleveland, 4–7 May 2015; vol. 3, pp. 3225–37.
B.K. Rout, G.A. Brooks, M.A. Rhamdhani, Z. Li, F.N.H. Schrama, and A. Overbosch: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2018, vol. 49, pp. 1022–1033.
N. Dogan, G.A. Brooks, and M.A. Rhamdhani: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 1102–1109.
N. Dogan, G.A. Brooks, and M.A. Rhamdhani: ISIJ Int., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 1093–1101.
P. Singha and A.K. Shukla: Metals, 2022, vol. 12, pp. 1–7.
D.G.C. Robertson, B. Deo, and S. Ohguchi: Ironmak. Steelmak., 1984, vol. 11, pp. 41–56.
FactSage: Center for Research in Chemical Thermodynamics, Polytechnique de Montreal, Canada. Available online: www. factsage.com (accessed on 1 Feb 2023).
FactSage Documentation: version 7.3, 2021.
K.J. Graham and G.A. Irons: Iron Steel Technol, 2009, vol. 6, pp. 164–73.
P. Singha: Ironmak. Steelmak., 2023, vol. 22, pp. 884–93.
Acknowledgments
The author wishes to thank JSW Steel Ltd., India, for providing the plant data used to validate the models developed in this work.
Funding
No funding is available for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singha, P. Contribution of Emulsion Zone in Refining of Basic Oxygen Steelmaking Converter. Metall Mater Trans B (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03117-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-024-03117-y