Abstract
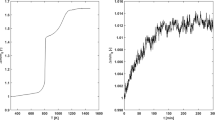
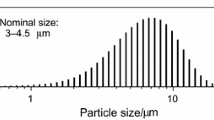
This paper analyzes the oxidation law of metal particles and proposes a new oxidation reaction rate model, based on measurements of thermogravimetric-mass spectrometer (TG-MS), X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The model is named EBM (egg broken model) with a formula of exponential law. According to the model, the aluminum particles do not react in a spherical shape, but crack and the melted metal inside flows out to form a new nonspherical surface and the reaction rate is still determined by the surface area. The model is verified with heating rates of 5°C/min, 10°C/min and 25°C/min, and with particle size of 1–2 µm, 8–9 µm and 20–22 µm. Many models are based on spherical hypothesis and the new model gives a different physical illustration to explain oxidation progress of metal particles. The new model gives an exponential law, which fits the experimental data well, and it may be useful to understand oxidation mechanism of metal particles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pang A., Li X., The law of innovation and development of solid propellant technology. Law of Innovation and Development of Solid Propellant Technology, 2015, 23: 3–6. (in Chinese)
Yu D., Zhuo J.K., Yao Q., Research progress on ignition and combustion properties of Boron particles. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2014, 1: 20.
Buttler W.T., Lamoreaux S.K., Schulze R.K., et al., Ejecta transport, breakup and conversion. Journal of Dynamic Behavior of Materials, 2017, 3(5): 334–345.
Wang J.H., Liu J.Z., Thermal oxidation characteristics of micron-sized aluminum particles. Chinese Journal of Energetic Materials, 2017, 8: 667–674.
Irvin G., Richard A., Combustion (Fourth Edition). Elsevier Inc, 2008, pp. 495–505.
Law C.K., Combustion Physics. Cambridge university press, 2006, pp. 652–658.
Edward L., Dreizin M.S., Correlating ignition mechanisms of aluminum-based reactive materials with thermoanalytical measurements. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2015, 50: 81–105.
Kong C.D., Study on combustion mechanism and kinetics of metallic Aluminum nanoparticles. Ph.D dissertation. Beijing, Tsinghua University, 2015. (in Chinese)
Granier J.J., Pantoya M.L., Laser ignition of nanocomposite thermites. Combustion and Flame, 2004, 138: 373–383.
Rai A., Park K., Zhou L., Zachariah M.R., Understanding the mechanism of aluminium nanoparticle oxidation. Combustion Theory and Modelling, 2006, 10: 843–859.
Trunov M.A., Schoenitz M., Zhu X., Dreizin E.L., Effect of polymorphic phase transformations in Al2O3 film on oxidation kinetics of aluminum powders. Combustion and Flame, 2005, 140: 310–318.
Watson K.W., Pantoya M.L., Levitas V.I., Fast reactions with nano- and micrometer aluminum: A study on oxidation versus fluorination. Combustion and Flame, 2008, 155: 619–634.
Levitas V.I., Pantoya M.L., Dean S., Melt dispersion mechanism for fast reaction of aluminum nano- and micron-scale particles: Flame propagation and SEM studies. Combustion and Flame, 2014, 161: 1668–1677.
Henz B.J., Hawa T., Zachariah M.R., On the role of built-in electric fields on the ignition of oxide coated nanoaluminum: Ion mobility versus Fickian diffusion. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 107(2): 024901.
Levitas V.I., Pantoya M.L., Watson K.W., Melt-dispersion mechanism for fast reaction of aluminum particles: Extension for micron scale particles and fluorination. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(20): 201917.
Levitas V.I., Pantoya M.L., Dikici B., Melt dispersion versus diffusive oxidation mechanism for aluminum nanoparticles: Critical experiments and controlling parameters. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(1): 011921.
Xia H., Wei K., Equivalent characteristic spectrum analysis in TG-MS system. Thermochimica Acta, 2015, 602: 15–21.
Cui Y.L., Wang B.R., Kong W.J., Analysis of oxidation characteristics of micron-sized aluminum powder at different heating rates. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2018, 39: 1147–1153.
Rufino B., Coulet M.V., Bouchet R., Isnard O., Denoyel R., Structural changes and thermal properties of aluminium micro- and nano-powders. Acta Materialia, 2010, 58: 4224–4232.
Coulet M.V., Rufino B., Esposito P.H., Neisius T., Isnard O., Denoyel R., Oxidation mechanism of aluminum nanopowders. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2015, 119: 25063–25070.
Trunov M.A., Schoenitz M., Dreizin E.L., Effect of polymorphic phase transformations in alumina layer on ignition of aluminium particles. Combustion and Flame, 2006, 104: 603–623.
Levitas V.I., Asay B.W., Son S.F., Pantoya M., Mechanochemical mechanism for fast reaction of metastable intermolecular composites based on dispersion of liquid metal. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 101: 083524.
Godsave G., Studies of the combustion of drops in a fuel spray-the burning of single drops of fuel. Symposium on Combustion, 1953, 4(1): 818–830.
Yang H., Yoon W., Modeling of aluminum particle combustion with emphasis on the oxide effects and variable transport properties. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2010, 24: 909–921.
Velasco F., Guzman S., Moral C., Oxidation of micro-sized aluminium particles: Hollow alumina spheres. Oxidation of Metals, 2013, 80(3): 403–422.
Acknowledgement
The study was financially supported by the joint fund of National Natural Science Foundation and China Academy of Engineering Physics (NSAF) under grant No. U1530157. The authors greatly appreciate the support provided by the grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, W., Wang, Y., Cui, Y. et al. A New Nonspherical Oxidation Model of Metal Particles. J. Therm. Sci. 32, 812–821 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-023-1734-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-023-1734-2