Abstract
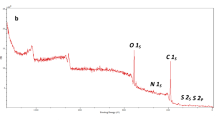
Textile industries are one of the leading environmental pollutants by releasing harmful dye effluents. In many textile distrts, the amount of excess color in treated textile effluent that exceeds regulatory limitations is still being a major concern. The combining usage of nanomaterials and polymer material to solve these issues using various techniques. In this research, graphene oxide–copper oxide (GO–CuO) nanomaterial have been incorporated into cellulose-acetate (CA), poly-ether sulfone (PES) blend polymer by using phase inversion process to fabricate thin film nanocomposite (TFN) membrane for removal of dye pollutant. The physiochemical properties of prepared TFN materials were studied by Fourier transform infra-red spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffractometer (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA), and mechanical strength analysis. Dye adsorption experiments were performed with four typical water-soluble organic dyes methylene blue (MB), rhodamine blue (Rh. B), methyl orange (MO) and Congo red (CR). After reaching adsorption equilibrium, the composite membrane final removal effectiveness for MB 92.42%, Rh. B 89.39%, CR 68.39%, and MO 58.82% respectively. As a result, the fabricated TFN material proves to be an effective adsorbent material for cationic dye molecules. Also, when the fabricated material was tested with textile industry effluent sample, all physio-chemical properties exhibited a considerable decrease in concentrations when compared to the real textile effluent concentration. The treated effluents permitted for a relatively greater growth and germination index of Tropical amaranth roots than the textile effluent, this demonstrates that phytotoxicity testing was also successful. The most effective temperature, concentration and pH were found to be 273 K, 1 × 10−5 M and pH 9. The fabricated TFN membrane material (GO–CuO @ CA–PES) can be recommended for water treatment applications.
Graphical abstract




















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data were used to support this study.
References
Ali I, Asim M, Khan TA (2012) Low-cost adsorbents for the removal of organic pollutants from wastewater. J Environ Manage 113:170–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.08.028
Amin MR, Chowdhury MA, Kowser MA (2019) Characterization and performance analysis of composite bioplastics synthesized using titanium dioxide nanoparticles with corn starch. Heliyon 5(8):p.e02009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02009
Arthanareeswaran G, Kumar SA (2010) Effect of additives concentration on performance of cellulose acetate and polyethersulfone blend membranes. J Porous Mater 17:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-009-9319-y
Banu R, Salvi N, Gupta S et al (2022) A Facile Synthesis of GO/CuO Nanocomposite with Enhancing Photocatalytic Activity for the Degradation of Azure-B Dye and Its Antimicrobial Behavior. Arab J Sci Eng 47:365–378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-021-05421-0
Bhattacharya G, Sas S, Wadhwa S et al (2017) Aloe vera assisted facile green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical and dye removal applications. RSC Adv 7:26680–26688. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra02828h
Bruzzoniti MC, Appendini M, Onida B et al (2018) Regenerable, innovative porous silicon-based polymer-derived ceramics for removal of methylene blue and rhodamine B from textile and environmental waters. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:10619–10629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1367-x
Chai PV, Law JY, Mahmoudi E, Mohammad AW (2020) Development of iron oxide decorated graphene oxide (Fe3O4/GO) PSf mixed-matrix membrane for enhanced antifouling behavior. J Water Process Eng 38:101673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101673
De Souza ZSB, Silva MP, Fraga TJM, Motta Sobrinho MA (2021) A comparative study of photo-Fenton process assisted by natural sunlight, UV-A, or visible LED light irradiation for degradation of real textile wastewater: factorial designs, kinetics, cost assessment, and phytotoxicity studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:23912–23928. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-12106-y
Dlamini DS, Tesha JM, Vilakati GD et al (2020) A critical review of selected membrane- and powder-based adsorbents for water treatment: Sustainability and effectiveness. J Clean Prod 277:123497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123497
Dutta DP, Nath S (2018) Low-cost synthesis of SiO2/C nanocomposite from corn cobs and its adsorption of uranium (VI), chromium (VI) and cationic dyes from wastewater. J Mol Liq 269:140–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.08.028
Dutta S, Gupta B, Srivastava SK, Gupta AK (2021) Recent advances on the removal of dyes from wastewater using various adsorbents: A critical review. Mater Adv 2:4497–4531. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ma00354b
Elgarahy AM, Elwakeel KZ, Elshoubaky GA, Mohammad SH (2019a) Untapped Sepia Shell–Based Composite for the Sorption of Cationic and Anionic Dyes. Water Air Soil Pollut 230(9):1–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-019-4247-1
Elgarahy AM, Elwakeel KZ, Elshoubaky GA, Mohammad SH (2019b) Microwave-accelerated sorption of cationic dyes onto green marine algal biomass. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:22704–22722. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05417-2
Elgarahy AM, Elwakeel KZ, Mohammad SH, Elshoubaky GA (2021) A critical review of biosorption of dyes, heavy metals and metalloids from wastewater as an efficient and green process. Clean Eng Technol 4:100209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100209
Elgarahy AM, Akhdhar A, Al-Bogami AS, Elwakeel KZ (2022) Magnetically separable solid phase extractor for static anionic dyes adsorption from aqueous solutions. Surf Interfaces 30:101962. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfin.2022.101962
Elwakeel KZ (2009) Removal of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solutions using magnetic chitosan resins. J Hazard Mater 167:383–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.01.051
Elwakeel KZ (2010) Environmental application of chitosan resins for the treatment of water and wastewater: A review. J Dispers Sci Technol 31:273–288. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932690903167178
Elwakeel KZ, Rekaby M (2011) Efficient removal of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous media using glycidyl methacrylate resin modified with tetraethelenepentamine. J Hazard Mater 188:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.003
Elwakeel KZ, Abd El-Ghaffar MA, El-kousy SM, El-Shorbagy HG (2012) Synthesis of new ammonium chitosan derivatives and their application for dye removal from aqueous media. Chem Eng J 203:458–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.001
Elwakeel KZ, Abd El-Ghaffar MA, El-Kousy SM, El-Shorbagy HG (2013) Enhanced Remediation of Reactive Black 5 from Aqueous Media Using New Chitosan Ion Exchangers. J Dispers Sci Technol 34:1008–1019. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2012.695943
Elwakeel KZ, El-Bindary AA, El-Sonbati AZ, Hawas AR (2016a) Adsorption of toxic acidic dye from aqueous solution onto diethylenetriamine functionalized magnetic glycidyl methacrylate-N, N′-methylenebisacrylamide. RSC Adv 6:3350–3361. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra24035b
Elwakeel KZ, El-Bindary AA, Ismail A, Morshidy AM (2016b) Sorptive removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R from aqueous solution by diethylenetriamine functionalized magnetic macro-reticular hybrid material. RSC Adv 6:22395–22410. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra26508h
ELwakeel KZ, El-Kousy S, El-Shorbagy HG, El-Ghaffar MAA (2016c) Comparison between the removal of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solutions by 3-amino-1,2,4 triazole,5-thiol and melamine grafted chitosan prepared through four different routes. J Environ Chem Eng 4:733–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.12.015
Elwakeel KZ, El-Bindary AA, Ismail A, Morshidy AM (2017a) Magnetic chitosan grafted with polymerized thiourea for remazol brilliant blue R recovery: Effects of uptake conditions. J Dispers Sci Technol 38:943–952. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2016.1216436
Elwakeel KZ, Elgarahy AM, Mohammad SH (2017b) Use of beach bivalve shells located at Port Said coast (Egypt) as a green approach for methylene blue removal. J Environ Chem Eng 5:578–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.12.032
Elwakeel KZ, Elgarahy AM, Elshoubaky GA, Mohammad SH (2020) Microwave assist sorption of crystal violet and Congo red dyes onto amphoteric sorbent based on upcycled Sepia shells. J Environ Heal Sci Eng 18:35–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-019-00435-1
Elwakeel KZ, Elgarahy AM, Al-Bogami AS et al (2021) 2-Mercaptobenzimidazole-functionalized chitosan for enhanced removal of methylene blue: Batch and column studies. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105609
Erol K (2016) DNA adsorption via Co (II) immobilized cryogels. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem 53:629–635. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2016.1212310
Erol K (2017a) Polychelated cryogels: hemoglobin adsorption from human blood. Artif Cells, Nanomed Biotechnol 45:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2016.1215326
Erol K (2017b) Synthesis, Characterization and Chromatographic Applications of Antimicrobial Cryogels. Hacettepe J Biol Chem 2:187–195. https://doi.org/10.15671/hjbc.2017b.151
Erol K (2017c) The Adsorption of Calmoduline via Nicotinamide-Immobilized Poly (HEMA-GMA) Cryogels. 4:133–148
Erol K, Uzun L (2017) Two-step polymerization approach for synthesis of macroporous surface ion-imprinted cryogels. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem 54:867–875. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2017.1342519
Erol B, Erol K, Gökmeşe E (2019) The effect of the chelator characteristics on insulin adsorption in immobilized metal affinity chromatography. Process Biochem 83:104–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2019.05.009
Erol K, Yıldız E, Alacabey İ et al (2019) Magnetic diatomite for pesticide removal from aqueous solution via hydrophobic interactions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:33631–33641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06423-0
Erol K, Bolat M, Tatar D et al (2020) Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial application of silver nanoparticle embedded composite cryogels. J Mol Struct 1200:127060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127060
Erol K, Bülter MB, Köse DA, Can HK (2021a) Water-soluble polymeric particle embedded cryogels: Synthesis, characterisation and adsorption of haemoglobin. J Polym Eng 41:671–680. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2020-0285
Erol K, Tatar D, Veyisoǧlu A, Tokatll A (2021b) Antimicrobial magnetic poly (GMA) microparticles: Synthesis, characterization and lysozyme immobilization. J Polym Eng 41:144–154. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2020-0191
Fahmi MZ, Wathoniyyah M, Khasanah M et al (2018) Incorporation of graphene oxide in polyethersulfone mixed matrix membranes to enhance hemodialysis membrane performance. RSC Adv 8:931–937. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra11247e
Fei P, Liao L, Cheng B, Song J (2017) Quantitative analysis of cellulose acetate with a high degree of substitution by FTIR and its application. Anal Methods 9:6194–6201. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ay02165h
Ganesan K, Jothi VK, Natarajan A et al (2020) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles decorated with graphene oxide for anticancer activity and catalytic applications. Arab J Chem 13:6802–6814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.06.033
Gowriboy N, Kalaivizhi R (2022) Optical properties containing of bioinspired Ag2O nanoparticles anchored on CA/PES polymer membrane shows an effective adsorbent material. Optik 259:168935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2022.168935
Gowriboy N, Kalaivizhi R, Sivasankari S (2021) Green Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles Decorated into CA/PES Polymer as an Effective Dye Adsorbent. Polymer Sci - Series B 63:322–331. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1560090421030076
Gzara L, Ahmad Rehan Z, Khan SB et al (2016) Preparation and characterization of PES-cobalt nanocomposite membranes with enhanced anti-fouling properties and performances. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 65:405–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.04.012
Habibi S, Nematollahzadeh A (2016) Enhanced Water Flux through Ultrafiltration Polysulfone Membrane via Addition-Removal of Silica Nano-Particles: Synth Charact 43556:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.43556
Hassan H, Salama A, El-ziaty AK, El-Sakhawy M (2019) New chitosan/silica/zinc oxide nanocomposite as adsorbent for dye removal. Int J Biol Macromol 131:520–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.03.087
Hoang BN, Nguyen TT, Bui QPT et al (2020) Enhanced selective adsorption of cation organic dyes on polyvinyl alcohol/agar/maltodextrin water-resistance biomembrane. J Appl Polym Sci 137:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.48904
Idris A, Ahmad I (2011) Survival and Sustainability. Surviv Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-95991-5
Jamil A, Zulfiqar M, Arshad U et al (2020) Development and Performance Evaluation of Cellulose Acetate-Bentonite Mixed Matrix Membranes for CO2Separation. Adv Polym Technol Dec 14:2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8855577
Kalaivizhi R, Rajeswari S, Suhana H et al (2018) Preparation of polymer blend membranes based on cellulose acetate and quaternized polyethersulfone for ultrafiltration. Int J Green Pharm 12:123–128
Khaled B, Nassira Z, Imene H (2020) Eco-friendly synthesis of self-regenerative low-cost biosorbent by the incorporation of CuO: a photocatalyst sensitive to visible light irradiation for azo dye removal. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:31074–31091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09364-1
Kiran SA, Arthanareeswaran G, Thuyavan YL, Ismail AF (2015) Influence of bentonite in polymer membranes for effective treatment of car wash effluent to protect the ecosystem. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 121:186–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.04.001
Kireç O, Alacabey I, Erol K, Alkan H (2021) Removal of 17β-estradiol from aqueous systems with hydrophobic microspheres. J Polym Eng 41:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1515/polyeng-2020-0150
Leelavathi H, Abirami N, Muralidharan R et al (2021) Sunlight-assisted degradation of textile pollutants and phytotoxicity evaluation using mesoporous ZnO/g-C3N4catalyst. RSC Adv 11:26800–26812. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra03806k
Li J, Yuan S, Zhu J, Van der Bruggen B (2019) High-flux, antibacterial composite membranes via polydopamine-assisted PEI-TiO2/Ag modification for dye removal. Chem Eng J 373:275–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.05.048
Mahlangu OT, Nackaerts R, Thwala JM et al (2017) Hydrophilic fouling-resistant GO-ZnO/PES membranes for wastewater reclamation. J Memb Sci 524:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.11.018
Mansor ES, Ali H, Abdel-Karim A (2020) Efficient and reusable polyethylene oxide/polyaniline composite membrane for dye adsorption and filtration. Colloids Interface Sci Commun 39:100314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2020.100314
Mercante LA, Facure MHM, Locilento DA et al (2017) Solution blow spun PMMA nanofibers wrapped with reduced graphene oxide as an efficient dye adsorbent. New J Chem 41:9087–9094. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj01703k
Mofradi M, Karimi H, Ghaedi M (2020) Hydrophilic polymeric membrane supported on silver nanoparticle surface decorated polyester textile: Toward enhancement of water flux and dye removal. Chinese J Chem Eng 28:901–912. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2019.09.011
Mosaffa E, Ghafuri H, Esmaili Zand HR (2019) Improvement on physical properties of polyethersulfone membranes modified by poly(1-vinylpyrrolidone) grafted magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles. Appl Organomet Chem 33:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/aoc.4639
Ng HKM, Leo CP (2019) Translucent and adsorptive PVA thin film containing microfibrillated cellulose intercalated with TiO2 nanoparticles for dye removal. Colloids Surf a Physicochem Eng Asp 578:23590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.123590
Palanivel B, Vaiyazhipalayam Murugaiyan S, Marimuthu T (2020) Synthesis and characterization of GO/FeSO4 composites for the effective removal of Hg2+ and Cd2+ ions from the synthetic effluent. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:20621–20628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05994-2
Parsamanesh M, Mansourpanah Y, Dadkhah Tehrani A (2021) Improving the efficacy of PES-based mixed matrix membranes incorporated with citric acid–amylose-modified MWCNTs for HA removal from water. Polym Bull 78:1293–1311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-020-03162-y
Pu S, Xue S, Yang Z et al (2018) In situ co-precipitation preparation of a superparamagnetic graphene oxide/Fe3O4 nanocomposite as an adsorbent for wastewater purification: synthesis, characterization, kinetics, and isotherm studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:17310–17320. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-1872-y
Radziuk D, Mikhnavets L, Tkach A et al (2018) Sonochemically Assembled Photoluminescent Copper-Modified Graphene Oxide Microspheres. Langmuir 34:8599–8610. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b01557
Ramanujam AS, Kaleekkal NJ, Kumar PS (2020) Preparation and characterization of proton exchange polyvinylidene fluoride membranes incorporated with sulfonated mesoporous carbon/SPEEK nanocomposite. SN Appl Sci 2(4):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-2464-2
Ravichandran S, Radhakrishnan J, Sengodan P, Rajendran R (2022) Biosynthesis of copper oxide nanoparticle from clerodendrum phlomidis and their decoration with graphene oxide for photocatalytic and supercapacitor application. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:9403–9411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07340-0
Sarode HA, Barai DP, Bhanvase BA et al (2020) Investigation on preparation of graphene oxide-CuO nanocomposite based nanofluids with the aid of ultrasound assisted method for intensified heat transfer properties. Mater Chem Phys 251:123102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2020.123102
Shi C, Lv C, Wu L, Hou X (2017) Porous chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite membrane for dyes static and dynamic removal from aqueous solution. J Hazard Mater 338:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.05.022
Sivasankari S, Kalaivizhi R, Gowriboy N (2021) Cellulose Acetate (CA) Membrane Tailored with Fe3O4@ZnO Core Shell Nanoparticles: Fabrication, Structural analysis and Its Adsorption Analysis. Chem Select 6:2350–2359. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202004689
Sridevi DV, Sundaravadivel E, Kanagaraj P (2019) Influence of Fe doping on structural, physicochemical and biological properties of CdSe nanoparticles. Mater Sci Semicond Process 101:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2019.05.031
Suleman MS, Lau KK, Yeong YF (2016) Characterization and Performance Evaluation of PDMS/PSF Membrane for CO2/CH4 Separation under the Effect of Swelling. Procedia Eng 148:176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2016.06.525
Sun Z, Xu Z, Zhou Y et al (2019) Effects of different scrap iron as anode in Fe-C micro-electrolysis system for textile wastewater degradation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:26869–26882. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05931-3
Vishveshvar K, Aravind Krishnan MV, Haribabu K, Vishnuprasad S (2018) Green Synthesis of Copper Oxide Nanoparticles Using Ixiro coccinea Plant Leaves and its Characterization. Bionanoscience 8:554–558. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12668-018-0508-5
Xie Q, Zhang S, Xiao Z et al (2017) Preparation and characterization of novel alkali-resistant nanofiltration membranes with enhanced permeation and antifouling properties: the effects of functionalized graphene nanosheets. RSC Adv 7:18755–18764. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra00928c
Xu C, Chen W, Gao H et al (2020) Cellulose nanocrystal/silver (CNC/Ag) thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes with multifunctional properties. Environ Sci Nano 7:803–816. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9en01367a
Yadav S, Shakya K, Gupta A et al (2022) A review on degradation of organic dyes by using metal oxide semiconductors. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20818-6
Yakout AA, Shaker MA, Elwakeel KZ, Alshitari W (2019) Lauryl sulfate@magnetic graphene oxide nanosorbent for fast methylene blue recovery from aqueous solutions. J Dispers Sci Technol 40:707–715. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2018.1477604
Zakaria Z, Kamarudin SK, Timmiati SN, Masdar MS (2019) New composite membrane poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide for direct ethanol–proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J Appl Polym Sci 136:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.46928
Zhao J, Nguyen DCT, Areerob Y, Oh WC (2019) Novel synthesis of nano needle-like Cu 2 O-GO-TiO 2 and CuO-GO-TiO 2 for the high photocatalytic performance of anionic and cationic pollutants. Solid State Sci 91:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.03.019
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Department of Chemistry, SRM Institute of Science and Technology for providing the financial support through the University Fellowship Scheme.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Gowriboy Natesan: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft. Kalaivizhi Rajappan: supervision, investigation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Compliance of ethical Standards: The author declares that there are no conflicts of interest in this study.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
I give consent to publish my work, with images and respective tables for the esteemed journal.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor Tito Roberto Cadaval Jr.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Natesan, G., Rajappan, K. GO–CuO nanocomposites assimilated into CA–PES polymer membrane in adsorptive removal of organic dyes from wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 42658–42678 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21821-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-21821-7