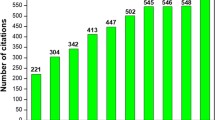
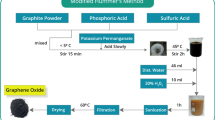
Abstract
The discharge of organic dye pollutants in natural water bodies has put forward a big challenge of providing clean water to a large part of the population. As the population is increasing with time, only underground water is not sufficient to complete the water requirements of everyone everywhere. Purification of wastewater and its reuse is the only way to fulfill the water needs. Nanotechnology has been used very efficiently for wastewater treatment via photocatalytic degradation of dye molecules. In the past few years, a lot of investigations have been done to enhance the photocatalytic activity of metal oxide semiconductors for water purification. In this review, we have discussed the different methods of synthesis of various metal oxide semiconductor nanoparticles, energy band gap, their role as efficient photocatalysts, radiations used for photocatalytic reactions, and their degradation efficiency to degrade the dye pollutants. We have also discussed the nanocomposites of metal oxide with graphene. These nanocomposites have been utilized as the efficient photocatalyst due to unique characteristics of graphene such as extended range of light absorption, separation of charges, and high capacity of adsorption of the dye pollutants.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Adekunle AS, Oyekunle JAO, Durosinmi LM, Oluwafemi OS, Olayanju DS, Akinola AS, Obisesan OR, Akinyele OF, Ajayeoba A (2020) Potential of cobalt and cobalt oxide nanoparticles as nanocatalyst towards dyes degradation in wastewater. Nano-Struct Nano-Objects 21:100405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoso.2019.100405
Ali Z, Chaudhry M N, Niaz N A, Khalid N R (2013) Significant effect of graphene on catalytic degradation of methylene blue by pure and Ce doped TiO2 at nanoscale. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 8(4):1525–1534. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259240951
Amritha A, Sundararajan M, Rejith RG, Mohammed-Aslam MA (2019) La-Ce doped TiO2 nanocrystals: a review on synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity. SN Appl Sci 1:1441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-019-1455-7
Ansari SA, Khan MM, Ansari MO, Lee J, Cho MH (2013) Biogenic synthesis, photocatalytic, and photoelectrochemical performance of Ag–ZnO nanocomposite. J Phys Chem C 117:27023–27030. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp410063p
Anwar DI, Mulyadi D (2015) Synthesis of Fe-TiO2 composite as a photocatalyst for degradation of methylene blue. Procedia Chem 17:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proche.2015.12.131
Arabzadeh A, Salimi A (2016) One dimensional CdS nanowire@TiO2 nanoparticles core-shell as highperformance photocatalyst for fast degradation of dye pollutants under visible and sunlight irradiation. J Colloid Interface Sci 479:43–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.06.036
Arshad A, Iqbal J, Siddiq M, Ali MU, Ali A, Shabbir H, Nazeer UB, Saleem MS (2017) Solar light triggered catalytic performance of graphene-CuO nanocomposite for waste water treatment. Ceram Int 43(14):10654–10660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.03.165
Arteaga-Diaz SJ, Meramo-Hurtado SI, León-Pulido J, Zuorro A, González-Delgado AD (2019) Environmental assessment of large scale production of magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles via coprecipitation. Appl Sci 9:1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9081682
Assefi P, Ghaedi M, Ansari A, Habibi MH, Momeni MS (2014) Artificial neural network optimization for removal of hazardous dye Eosin Y from aqueous solution using Co2O3-NP-AC: Isotherm and kinetics study. J Indust Engin Chem 20(5):2905–2913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.11.027
Ayyappan S, Philip J, Raj B (2009) A facile method to control the size and magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater Chem Phys 115(2–3):712–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.02.005
Balakrishnan G, Velavan R, Batoo KM, Raslanc EH (2020) Microstructure, optical and photocatalytic properties of MgO nanoparticles. Results Phys 16:103013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2020.103013
Banu R, Salvi N, Ameta C, Ameta R, Punjabi P B (2019) Visible light driven photocatalytic degradation of brilliant green dye using graphene oxide / copper oxide binary composite. IJC-B 58B(02):157- 166. http://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/45781
Basith MA, Ahsan R, Zarinand I, Jalil MA (2018) Enhanced photocatalytic dye degradation and hydrogen production ability of Bi25FeO40-rGO nanocomposite and mechanism insight. Sci Rep 8(2018):11090. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-29402-w
Bhargava R, Khan S, Ahmad N, Ansari MMN (2018) Investigation of structural, optical and electrical properties of Co3O4 nanoparticles. AIP Conf Proc 1953:030034. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5032369
Bolade OP, Williams AK, Benson NK (2020) Green synthesis of iron-based nanomaterials for environmental remediation: A review. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 13:100279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2019.100279
Boumediene M, Benaïssa H, George B, Molina S, Merlin A (2015) Characterization of two cellulosic waste materials (orange and almond peels) and their use for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. Maderas Cienc Tecnol 17(1):69–84. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-221X2015005000008
Cao N, Zhang YS (2015) Study of reduced graphene oxide preparation by Hummers’ method and related characterization. J Nanomater 2015:168125. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/168125
Chaudhary M, Walker TR (2019) River Ganga pollution: causes and failed management plans (correspondence on Dwivedi et al. 2018. Ganga water pollution: a potential health threat to inhabitants of Ganga basin. Environment International 117: 327–338). Environ. Int. 126:202–206.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.02.033
Chauhan M, Kaur N, Bansal P, Kumar R, Srinivasan S (2020) Ram Chaudhary G (2020) Proficient photocatalytic and sonocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants using CuO nanoparticles. J Nanomater 2020:6123178. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6123178
CM Bezerra de Araujo, Oliveira do Nascimento G F, Bezerra da Costa G R, Santos da Silva K, Salgueiro Baptisttella A M, Ghislandi M G, Alves da Motta Sobrinho M, (2019) Adsorptive removal of dye from real textile wastewater using graphene oxide produced via modifications of hummers method. Chem Eng Commun 206(11):1375–1387. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2018.1534232
Dehghanghadikolaei A, Ansary J, Ghoreishi R (2008) Sol-gel process applications: a mini-review. Proc. Nat. Res. Soc. 2:02008. https://doi.org/10.11605/j.pnrs.201802008
Dewi N, Yulizar Y, Apriandanu D (2019) Green synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles using Euphorbia heterophylla L. leaves extract: characterization and photocatalytic activity. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 509:012105. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/509/1/012105
Díez-García MI, Manzi-Orezzoli V, Jankulovska M, Anandan S, Bonete P, Gómez R, Lana-Villarreala T (2015) Effects of ultrasound irradiation on the synthesis of metal oxide nanostructures. Phys Procedia 63:85–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2015.03.014
Dlugosz O, Staroń A, Brzoza P, Banach M (2021) Synergistic effect of sorption and photocatalysis on the degree of dye removal in single and multicomponent systems on ZnO-SnO2. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18044-7
Dunca AM (2018) Water pollution and water quality assessment of major transboundary rivers from Banat (Romania). J Chem 2018:9073763. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9073763
Durmus Z, Kurt BZ, Durmus A (2019) Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide/zinc oxide (GO/ZnO) nanocomposite and its utilization for photocatalytic degradation of basic Fuchsin dye. Chem Select 4(1):271–278. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201803635
Dwivedi S, Mishra S, Tripathi RD (2018) Ganga water pollution: a potential health threat to inhabitants of Ganga basin Environ. Environ Inter 117:327–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.05.015
Ertl G, Knözinger H, Weitkamp J (1999) Preparation of Solid Catalysts. Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527619528
Esteves LM, Smarzaro JL, Caytuero A, Oliveira HA, Passos FB (2019) Catalyst preparation methods to reduce contaminants in a high-yield purification process of multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Braz J Chem Eng 36(4):1587–1600. https://doi.org/10.1590/0104-6632.20190364s20190251
Ferreira-Leitão VS, de Carvalho MEA, Bon EPS (2007) Lignin peroxidase efficiency for methylene blue decolouration: comparison to reported methods. Dyes Pigm 74(1):230–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2006.02.002
Fine GF, Cavanagh LM, Afonja A, Binions R (2010) Metal oxide semi-conductor gas sensors in environmental monitoring. Sensors 10:5469–5502. https://doi.org/10.3390/s100605469
Fujishima A, Zhang X, Tryk DA (2008) TiO2 photocatalysis and related surface phenomena. Surf Sci Rep 63:515–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfrep.2008.10.001
Ghaedi M, Daneshfar A, Ahmadi A, Momeni MS (2015) Artificial neural network-genetic algorithm based optimization for the adsorption of phenol red (PR) onto gold and titanium dioxide nanoparticles loaded on activated carbon. J Indust Engin Chem 21:587–598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.03.024
Ghumro SS, Lal B, Pirzada T (2022) Visible-light-driven carbon-doped TiO2-based nanocatalysts for enhanced activity toward microbes and removal of dye. ACS Omega 7:4333–4341. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c06112
Golmohammadi M, Honarmand M, Esmaeili A (2022) Biosynthesis of ZnO nanoparticles supported on bentonite and the evaluation of its photocatalytic activity. Mater Res Bull 149:111714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2021.111714
Guo B, Li C, Yuan ZY (2010) Nanostructured Co3O4 materials: synthesis, characterization, and electrochemical behaviors as anode reactants in rechargeable lithium ion batteries. J Phys Chem C 114:12805–12817. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp103705q
Guo S, Zhang G, Guo Y, Yu JC (2013) Graphene oxide-Fe2O3 hybrid material as highly efficient heterogeneous catalyst for degradation of organic contaminants. Carbon 60:437–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.04.058
Han C, Liu J, Yang W, Wu Q, Yang H, Xue X (2017) Photocatalytic activity of CaTiO3 synthesized by solid state, sol–gel and hydrothermal methods. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 81:806–813. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4261-3
Haseena S, Jayamani N, Shanavas S, Duraimurugan J, Haija MA, Kumar GS, Kumar AS, Prabhuraj T, Maadeswaran P, Acevedo R (2022) Bio-synthesize of photocatalytic Fe2O3 nanoparticles using Leucas aspera and Jatropha podagrica leaf extract for an effective removal of textile dye pollutants. Optik 249:168275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2021.168275
Hashim FS, Alkaim AF, Mahdi SM, Alkhayatt AHO (2019) Solid-phase synthesis of mesoporous ZnO using lignin-amine template and its photocatalytic properties. Compos Commun 16:111–116
Hashimoto K, Irie H, Fujishima A (2005) TiO2 photocatalysis: a historical overview and future prospects. Jpn J Appl Phys 44(12):8269. https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.44.8269
Hayashi H, Hakuta Y (2010) Hydrothermal synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles in supercritical water. Materials 3:3794–3817. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma3073794
Hitkari G, Sandhya S, Gajanan P, Shrivash MK, Kumar D (2018) Synthesis of chromium doped cobalt oxide (Cr:Co3O4) nanoparticles by co-precipitation method and enhanced photocatalytic properties in the visible region. J Material Sci Eng 7(1):1000419. https://doi.org/10.4172/2169-0022.1000419
Hu YC, Dai CL, Hsu CC (2014) Titanium dioxide nanoparticle humidity microsensors integrated with circuitry on-a-chip. Sensors 14:4177–4188. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140304177
Huang Y, Zhang X, Zhang K, Lu P, Zhang D (2018) Facile fabrication of sandwich-like BiOI/AgI/g-C3N4 composites for efficient photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange and reduction of Cr(VI). J Nanoparticle Res 20:328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-018-4431-z
Ikram M, Inayat T, Haider A, Ul-Hamid A, Haider J, Nabgan W, Saeed A, Shahbaz A, Hayat S, Ul-Ain K, Butt AR (2021) Graphene oxide-doped MgO nanostructures for highly efficient dye degradation and bactericidal action. Nanoscale Res Lett 16:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-021-03516-z
Iravani S, Varma RS (2020) Sustainable synthesis of cobalt and cobalt oxide nanoparticles and their catalytic and biomedical applications. Green Chem 22:2643–2661. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0gc00885k
Jaffari Z, Lam S, Sin JC (2019) Boosting visible light photocatalytic and antibacterial performance by decoration of silver on magnetic spindle-like bismuth ferrite. Mater Sci Semicond Process 101:103–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2019.05.036
Jahanger MI, Shad NA, Sajid MM, Akhtar K, Javed Y, Ullah A, Hassan MA, Sarwar MH, Sarwar M, Sillanpää M (2022) Aqueous photodegradation of methyl orange and antimicrobial activity against E. coli and S. aureus bacteria using pH modifed MgO nanomaterials. React Kinet Mech Catal 135:499–510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02145-y
Jakani M, Campet G, Claverie J, Fichou D, Pouliquen J, Kossanyi J (1985) Photoelectrochemical properties of zinc oxide doped with 3d elements. J Solid State Chem 56:269–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-4596(85)90176-8
Jilani A, Othman MHD, Ansari MO, Hussain SZ, Ismail AF, Khan IU, Inamuddin (2018) Graphene and its derivatives: synthesis, modifcations, and applications in wastewater treatment. Environ Chem Lett 16(10):1301–1323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-018-0755-2
Jodlowski PJ, Jedrzejczyk RJ, Chelebda DK, Dziedzicka A, Kuterasinski L, Gancarczyk A, Sitarz M (2017) Non noble metal oxide catalysts for methane catalytic combustion: sonochemical systhesis and characterisation. Nanomaterials 7(7):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7070174
Karthikeyan C, Arunachalam P, Ramachandran K, Al-Mayouf AM, Karuppuchamy S (2020) Recent advances in semiconductor metal oxides with enhanced methods for solar photocatalytic applications. J Alloys Compd 828:1542813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154281
Khairol NF, Sapawe N, Danish M (2019) Excellent performance integrated both adsorption and photocatalytic reaction toward degradation of Congo Red by CuO/eggshell. Mater Today Proce 19:1340–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.11.147
Khalid N R, Ahmed E, Ahmad M, Khawar R (2015) Co-doping effect of carbon and yttrium on photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles for methyl orange degradation. J. Ovonic Res. 11(3):107–112. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280996786
Khan M, Tahir MN, Adil SF, Khan HU, Rafiq M, Siddiqui H, Al-warthan AA, Tremel W (2015) Graphene based metal and metal oxide nanocomposites: synthesis, properties and their applications. J Mater Chem A 3:18753–18808. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta02240a
Konios D, Stylianakis MM, Stratakis E, Kymakis E (2014) Dispersion behaviour of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. J Colloid Interface Sci 430:108–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.05.033
Kumar RV, Diamant Y, Gedanken A (2000) Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of nanometer-size transition metal oxides from metal acetate. Chem Mater 12:2301–2305. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm000166z
Kumar A, Kumari S, Parmanand SSK (2022) Constructing the nanomixture of guar gum and Fe3O4 for photocatalytic degradation of dyes and heavy metal. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 33:2643–2653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-07472-3
Lam SM, Jaffari ZH, Sin JC (2018) Hydrothermal synthesis of coral-like palladiumdoped BiFeO3 nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic and magnetic properties. Mater Lett 224:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2018.04.058
Liang J, Liu J, Xie Q, Bai S, Yu W, Qian Y (2005) Hydrothermal growth and optical properties of doughnut-shaped ZnO microparticle. J Phys Chem B 109:9463–9467. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp050485j
Lin Y, Hong R, Chen H, Zhang D, Xu J (2020) Green synthesis of ZnO-GO composites for the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J Nanomater 2020:4147357. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4147357
Lou X, Han J, Chu W, Wang X, Cheng Q (2007) Synthesis and photocatalytic property of Co3O4 nanorods. Mater Sci Eng B 137:268–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2006.12.002
Machado ÊL, Dambros VS, Kist LT, Alcayaga Lobo EA, Tedesco SB, Moro CC (2012) Use of ozonization for the treatment of dye wastewaters containing rhodamine B in the agate industry. Water Air Soil Pollut 223:1753–1764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-011-0980-9
Mageshwari K, Nataraj D, Pal T, Sathyamoorthy R, Park J (2015) Improved photocatalytic activity of ZnO coupled CuO nanocomposites synthesized by reflux condensation method. J Alloys Compd 625:362–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.11.109
Mallampati R, Valiyaveettil S (2015) Co-precipitation with calcium carbonate – a fast and nontoxic method for removal of nanopollutants from water. RSC Adv 5:11023–11028. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA14292F
Martinez S, Sanchez C, Santa K, Mena ERL, Orozco-Guare E, Garc-Guaderrama M (2018) N-doped TiO2 nanoparticles obtained by a facile coprecipitation method at low temperature. Ceram Int 44(5):5273–5283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.12.140
Minguez-Bacho I, Courté M, Fan HJ, Fichou D (2015) Conformal Cu2S-coated Cu2O nanostructures grown by ion exchange reaction and their photoelectrochemical properties. Nanotechnology 26:185401. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/26/18/185401
Mohamed MM, Ghanemb M, Khairya M, Naguiba E, Alotaibib H (2019) Zinc oxide incorporated carbon nanotubes or graphene oxide nanohybrids for enhanced sonophotocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Appl Surf Sci 487:539–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.135
Mohan S, Sivakumar B, Kulangara RV, Subramanian B (2016) Visible light driven photocatalytic efficiency of rGO-Ag-BiFeO3Ternary nanohybrids on the decontamination of dye-polluted water: An amalgamation of 1D, 2D and 3D systems. Chem Select 1:6961–6971. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201601275
Nafiey A, Addad A, Sieber B, Chastanet G, Barras A, Szunerits S, Boukherroub R (2017) Reduced graphene oxide decorated with Co3O4 nanoparticles (rGO-Co3O4) nanocomposite: a reusable catalyst for highly efficient reduction of 4- nitrophenol, and Cr(VI) and dye removal from aqueous solutions. Chem Eng J 322:375–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.039
Nathan VK, Vijayan J, Parvathi A (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of synthetic dyes using iron (III) oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O3 –NPs) synthesized using Rhizophora mucronata Lam. IET Nanobiotechnol IET Nanobiotechnol 13(2):120–123. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-nbt.2018.5230
Nautiyal CS (2009) Self-purificatory Ganga water facilitates death of pathogenic Escherichia coli O157: H7. Curr Microbiol 58(1):25–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-008-9260-3
Niu F, Chen D, Qin L, Gao T, Zhang N, S. Wang S, Chen Z, Wang J, Sun X, Huang Y (2015) Synthesis of Pt/BiFeO3 heterostructured photocatalysts for highly efficient visible-light photocatalytic performances. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 143:386–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2015.07.008
Pan A, Bin WuH, Yu L, Zhu T, David Lou X W (2012) Synthesis of hierarchical three-dimensional vanadium oxide microstructures as high-capacity cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:3874–3879. https://doi.org/10.1021/am3012593
Panahian Y, Arsalani N (2017) Synthesis of hedgehoglike F-TiO2(B)/CNT nanocomposites for sonophotocatalytic and photocatalytic degradation of malachite green (MG) under visible light: kinetic study. J Phys Chem A 121:5614–5624. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpca.7b02580
Parashar M, Shukla VK, Singh R (2020) Metal oxides nanoparticles via sol–gel method: a review on synthesis, characterization and applications. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 31:3729–3749. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-02994-8
Pathak TK, Kroon RE, Swart HC (2018) Photocatalytic and biological applications of Ag and Au doped ZnO nanomaterial synthesized by combustion. Vacuum 157:508–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2018.09.020
Patra AS, Gogoi G, Qureshi M (2018) Ordered−disordered BaZrO3−δ hollow nanosphere/carbon dot hybrid nanocomposite: a new visible-light-driven efficient composite photocatalyst for hydrogen production and dye degradation. ACS Omega 3:10980–10991. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b01577
Petrella A, Petrella M, Boghetich G, Mastrorilli P, Petruzzelli V, Ranieri E, Petruzzelli D (2013) Laboratory scale unit for 1306 A. Petrella et al. photocatalytic removal of organic micro-pollutants from water and wastewater. Methyl Orange degradation. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(6):2201–2208
Petrella A, Boghetich G, Petrella M, Mastrorilli P, Petruzzelli V, Petruzzelli D (2014) Photocatalytic degradation of azo dyes. Pilot plant investigation. Ind Eng Chem Res 53(7):2566–2571
Petrella A, Mascolo G, Murgolo S, Petruzzelli V, Ranieri E, Spasiano D, Petruzzelli D (2016) Photocatalytic oxidation of organic micro-pollutants: pilot plant investigation and mechanistic aspects of the degradation reaction. Chem Eng Commun 203:1298–1307. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2016.1188292
Ponraj C, Vinitha G, Daniel J (2017) A review on the visible light active BiFeO3 nanostructures as suitable photocatalyst in the degradation of different textile dyes. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 7:110–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2017.02.001
Poolwong J, Kiatboonyarit T, Achiwawanich S, Butburee T, Khemthong P, Kityakarn S ( 2021 )Three-dimensional hierarchical porous TiO2 for enhanced adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of remazol dye, Nanomaterials 11(7):1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11071715
Qu X, Alvarez P, Li Q (2013) Applications of nanotechnology in water and wastewater treatment. Water Res 47:3931–3946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.09.058
Rabani I, Bathula C, Zafar R, Tahir MS, Park YJ, Kim HS, Naushad M, Seo YS (2022) Visible light-driven photocatalytic rapid degradation of organic contaminants engaging manganese dioxide-incorporated iron oxide three dimensional nanoflowers. J Colloid Interface Sci 608:2347–2357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.10.149
Rahman MR, Rashid MM, Islam MM, Akanda MM (2019) Electrical and chemical properties of graphene over composite materials: a technical review. Mat Sci Res 16(2):142–163. https://doi.org/10.13005/msri/160208
Rajaramanan T, Shanmugaratnam S, Gurunanthanan V, Yohi S, Velauthapillai D, Ravirajan P, Senthilnanthanan M (2021) Cost effective solvothermal method to synthesize Zn-doped TiO2 nanomaterials for photovoltaic and photocatalytic degradation applications. Catalysts 11(6):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal11060690
Rao K G, Ashok C, Rao K V, Chakra S (2014) Structural properties of MgO nanoparticles: synthesized by co-precipitation technique. Int J Sci Res 2319–7064
Ratnam MV, Karthikeyan C, Rao KN, Meena V (2020) Magnesium oxide nanoparticles for effective photocatalytic degradation of methyl red dye in aqueous solutions: optimization studies using response surface methodology. Mater Today Proce 26(2):2308–2313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.498
Ren X, Yang H, Gen S, Zhou J, Yang T, Zhang X, Cheng Z Sun S (2016) Controlled growth of LaFeO3 nanoparticles on reduced graphene oxide for highly efficient photocatalysis. Nanoscale 8:752. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5nr06338h
Ridzuan S (2021) Inequality and water pollution in India. Water Policy 23(4):985–999. https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2021.057
Ristic M, Music S, Ivanda M, Popovic S (2005) Sol–gel synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline ZnO powders. J Alloys Compd 397(1–2):L1–L4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2005.01.045
Roshan A, Vaezi M, Shokuhfar A, Rajabali Z (2011) Synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles via sonochemical method and their characterization. Particuology 9(1):95–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2010.05.013
Saravan R, Muthukumaran M, Mubashera SM, Abinaya M, Varun Prasath P, Parthiban R, Mohammad F, Oh WC, Sagadevan S (2020) Evaluation of the photocatalytic efficiency of cobalt oxide nanoparticles towards the degradation of crystal violet and methylene violet dyes. Optik 207:164428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164428
Selvamani M, Krishnamoorthy G, Ramadoss M, Kumar P (2016) Ag@Ag8W4O16 nanoroasted rice beads with photocatalytic, antibacterial and anticancer activity. Mater Sci Eng C 60:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.11.002
Selvamania T, Abdullah SA, Asirib M, Maruthamuthuc P, Ashokkumar M (2021) Preparation of MgTi2O5 nanoparticles for sonophotocatalytic degradation of triphenylmethane dyes. Ultrason Sonochem 75:105585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105585
Shanthi RV, Kayalvizhi R, Abel MJ, Neyvasagam K (2022) MgO nanoparticles with altered structural and optical properties by doping (Er3+) rare earth element for improved photocatalytic activity. Appl Phys A 128:133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05141-0
Sharma SD, Singh D, Saini KK, Kant C, Sharma V, Jain SC, Sharma CP (2006) Sol–gel-derived super-hydrophilic nickel doped TiO2 film as active photo-catalyst. Appl Catal A-Gen 314(1):40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2006.07.029
Sharma M, Chaudhry S (2015) Impact of industrial pollution on Yamuna River: a review. ICEM 2010:512–521. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.3632.8401
Sharma M, Pathak M, Kapoor P N (2018) The sol-gel method: pathway to ultrapure and homogeneous mixed metal oxide nanoparticles. Asian J. Chem. 30(7):1405–1412. https://doi.org/10.14233/ajchem.2018.20845
Sietsma JRA, Jos van Dillen A, de Jongh PE, de Jong KP (2006) Application of ordered mesoporous materials as model supports to study catalyst preparation by impregnation and drying. Stud Surf Sci Catal 162:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2991(06)80895-5
Singh V, Joung D, Zhai L, Das S, Khondaker SI, Seal S (2011) Graphene based materials: past, present and future. Prog Mater Sci 56(8):1178–1271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2011.03.003
Sun Z, Chen Y, Ke Q, Yang Y, Yuan J (2002) Photocatalytic degradation of cationic azo dye by TiO2/bentonite nanocomposite. J Photochem Photobiol a: Chem 149:169–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1010-6030(01)00649-9
Sun G, Dong B, Cao M, Wei B, Hu C (2011) Hierarchical dendrite-like magnetic materials of Fe3O4, γ-Fe2O3, and Fe with high performance of microwave absorption. Chem Mater 23:1587–1593. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm103441u
Suslick KS (1990) Sonochemistry Science 247(4949):1439–1445. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.247.4949.1439
Tao J, Zhang M, Gao X, Zhao H, Ren Z, Li D, Li J, Zhang R, Liu Y, Zhai Y (2019) Photocatalyst Co3O4/red phosphorus for efficient degradation of malachite green under visible light irradiation. Mater Chem Phys 240:122185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122185
Taouratia R, Khaddora M, Laghzala A, Kasmib AE (2020) Facile one-step synthesis of highly efficient single oxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic application. Sci Afr 8:e00305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00305
Teoh WY, Amal R, Scott J (2012) Progress in heterogenours photocatalysis: from classical radical chemistry to engineering nanomaterials and solar reactors. J Phys Chem Lett 3:629–639. https://doi.org/10.1021/jz3000646
Tyagi P K, Singh R, Vats S, Kumar D, Tyagi S (2012) Nanomaterials use in wastewater treatment. ICNCS'2012 2012:65–69
Vandarkuzhali S, Pugazhenthiran N, Mangalaraja R V, Sathishkumar P, Viswanathan B, Anandan S (2018) Ultrasmall plasmonic nanoparticles decorated hierarchical mesoporous TiO2 as an efficient photocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of textile dyes. ACS Omega 3:983. http://pubs.acs.org/journal/acsodf
Vasiljevic ZZ, Dojcinovic MP, Vujancevic JD, Jankovic-Castvan I, Ognjanovic M, Tadic NB, Stojadinovic S, Brankovic GO, Nikolic MV (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue under natural sunlight using iron titanate nanoparticles prepared by a modified sol–gel method. R Soc Open Sci 7:200708. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.200708
Vennela A B, Mangalaraj D, Muthukumarasamy N, Agilan S, Hemalatha K V (2019) Structural and optical properties of Co3O4 nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel technique for photocatalytic application. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 14:3535–3552. https://doi.org/10.20964/2019.04.40
Wang L, Ali J, Zhang C, Mailhot G, Pan G (2020) Simultaneously enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of TiO2/Ag composite nanofibers for wastewater purification. J Environ Chem Eng 8(1):102104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.12.057
Wu W, Jiangc C, Roy VAL (2015) Recent progress in magnetic iron oxide–semiconductor composite nanomaterials as Promising photocatalysts. Nanoscale 7:38–58. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr04244a
Yadav S, Yadav J, Kumar M, Saini K (2022) Synthesis and characterization of nickel oxide/ cobalt oxide nanocomposite for effective degradation of methylene blue and their comparative electrochemical study as electrode material for supercapacitor application. Int J Hydrog Energy https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.02.011
Yan W, Rao H, Wei T, Hua L, Jun C (2013) Reduced graphene oxide–cuprous oxide composite via facial deposition for photocatalytic dye-degradation. J Alloys Compd 568:26–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.03.019
Yang G, Park SJ (2019) Conventional and microwave hydrothermal synthesis and application of functional materials: a review. Materials 12(7):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12071177
Yao C, Lin J, Li L, Qu Y, Jiang K, Hu Z, Xu N, Sun J, Wu J (2020) Sandwiched CdS/Au/ZnO nanorods with enhanced ultraviolet and visible photochemical and photoelectrochemical properties via semiconductor and metal cosensitizing. J Phys Chem C 124(20):10941–10950. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c00997
Zaleska A (2008) Doped-TiO2: A Review. Recent Pat Eng 2(3):157–164. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221208786306289
Zhang Y, Deng B, Zhang T, Gao D, Xu AW (2010) Shape effects of Cu2O polyhedral microcrystals on photocatalytic activity. J Phys Chem C 114:5073–5079. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp9110037
Zhang X, Wang B, Wang X, Xiao X, Dai Z, Wu W, Zheng J, Ren F, Jiang C (2015) Preparation of M@BiFeO3 nanocomposites (M= Ag, Au) bowl arrays with enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. J Am Ceram Soc 98:2255–2263. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.13543
Zhu M, Zhai C, Fujitsuka M, Majima T (2018) Noble metal-free near-infrared-driven photocatalyst for hydrogen production based on 2D hybrid of black phosphorus/WS2. Appl Catal B 221:645–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.09.063
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our special thanks and gratitude to the D S Kothari Centre for Research and Innovation in Science Education, Miranda House, University of Delhi, for granting us the permission to take part in the summer workshop and inspiration.
Funding
Sapna Yadav would like to express her great appreciation to the CSIR, New Delhi, for JRF (CSIR, File No. 08/700/(0004)/2019-EMR-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, Kalawati Saini; methodology, Sapna Yadav and Kriti Shakya; writing-original draft preparation, Sapna Yadav, Aarushi Gupta, Divya Singh, Anjana R Chandran, Anjali V A, Kanika Goyal, and Nutan Rani; writing-review and editing, Sapna Yadav; reference editing, Kalawati Saini; supervision and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
All the authors consented to participate in the drafting of this review.
Consent for publication
All of the authors consented to publish this review.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor Guilherme L. Dotto
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, S., Shakya, K., Gupta, A. et al. A review on degradation of organic dyes by using metal oxide semiconductors. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30, 71912–71932 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20818-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-20818-6