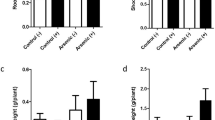
Abstract
Due to increased industrialization, arsenic (As) in the soil has become a serious issue for wheat production since past few decades. We investigated the role of Azospirillum brasilense and trans-zeatin riboside (tZR) in the mitigation of arsenic toxicity in wheat for 2 years (2018–2019 and 2019–2020) in pot experiments. Wheat plants grown in soil artificially spiked with arsenic (50, 70, and 100 μM) was left alone or amended with A. brasilense, tZR, or their combination as mitigation strategies. A treatment without arsenic or amendments was maintained as control. Arsenic-induced physiological damages were noticed in the wheat plants. Detrimental effects on the plant physiological functions, such as disruption of cell membrane stability, reduced water uptake, and stomatal functions, were noticed with increase in As toxicity. Application of biological amendments reversed the effects of As toxicity by increasing wheat plant growth rate, leaf area, and photosynthesis and also yield. Therefore, application of tZR and wheat seed inoculation with A. brasilense could be a sustainable and environmentally friendly strategy to mitigate arsenic-induced crop physiological damages.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbas G, Murtaza B, Bibi I, Shahid M, Niazi NK, Khan MI, Amjad M, Hussain M, Natasha, (2018) Arsenic uptake, toxicity, detoxification, and speciation in plants: physiological, biochemical, and molecular aspects. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:59
Ahsan N, Lee DG, Kim KH, Alam I, Lee SH, Lee KW, Lee H, Lee BH (2010) Analysis of arsenic stress-induced differentially expressed proteins in rice leaves by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis coupled with mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 78:224–231
Anjum SA, Tanveer M, Hussain S, Ashraf U, Khan I, Wang L (2017) Alteration in growth, leaf gas exchange, and photosynthetic pigments of maize plants under combined cadmium and arsenic stress. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:13
Armendariz AL, Talano MA, Oller ALW, Medina MI, Agostini E (2015) Effect of arsenic on tolerance mechanisms of two plant growth-promoting bacteria used as biological inoculants. J Environ Sci 33:203–210
Armendariz AL, Talano MA, Nicotra MFO, Escudero L, Breser ML, Porporatto C, Agostini E (2019) Impact of double inoculation with Bradyrhizobium japonicum E109 and Azospirillum brasilense Az39 on soybean plants grown under arsenic stress. Plant Physiol Biochem 138:26–35
Awasthi S, Chauhan R, Srivastava S, Tripathi RD (2017) The journey of arsenic from soil to grain in rice. Front Plant Sci 8:1007
Banerjee M, Banerjee N, Bhattacharjee P, Mondal S, Lythgoe PR, Martínez M, Pan J, Polya DA, Giri AK (2013) High arsenic in rice is associated with elevated genotoxic effects in humans. Sci Rep 3:1–8
Barr H, Weatherley P (1962) A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficit in leaves. Aust J Biol Sci 15:413–428
Bar-Tal A, Yermiyahu U, Beraud J, Keinan M, Rosenberg R, Zohar D, Rosen V, Fine P (2004) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium uptake by wheat and their distribution in soil following successive, annual compost applications. J Environ Qual 33:1855–1865
Bashan Y, Bustillos J, Leyva L, Hernandez J-P, Bacilio M (2006) Increase in auxiliary photoprotective photosynthetic pigments in wheat seedlings induced by Azospirillum brasilense. Biol Fertil Soils 42:279–285
Belluck D, Benjamin S, Baveye P, Sampson J, Johnson B (2003) Widespread arsenic contamination of soils in residential areas and public spaces: an emerging regulatory or medical crisis? Int J Toxicol 22:109–128
Besset-Manzoni Y, Rieusset L, Joly P, Comte G, Prigent-Combaret C (2018) Exploiting rhizosphere microbial cooperation for developing sustainable agriculture strategies. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:29953–29970
Boleta EHM, Shintate Galindo F, Jalal A, Santini JMK, Rodrigues WL, Lima BHD, Arf O, Silva MRD, Buzetti S, Teixeira Filho MCM (2020) Inoculation with growth-promoting bacteria Azospirillum brasilense and its effects on productivity and nutritional accumulation of wheat cultivars. Front Sustain Food Syst 4:265
Cakmak I, Strbac D, Marschner H (1993) Activities of hydrogen peroxide-scavenging enzymes in germinating wheat seeds. J Exp Bot 44:127–132
Cassán F, Coniglio A, López G, Molina R, Nievas S, Carlan CL, Donadío F, Torres D, Rosas S, Pedrosa FO, Souza ED, Zorita M, de-Bashan L, Mora V, (2020) Everything you must know about Azospirillum and its impact on agriculture and beyond. Biol Fertil Soils 56:461–479
Cecagno R, Fritsch TE, Schrank IS (2015) The plant growth-promoting bacteria Azospirillum amazonense: genomic versatility and phytohormone pathway. BioMed Res Int 2015:898592. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/898592
Chandrakar V, Naithani SC, Keshavkant S (2016) Arsenic-induced metabolic disturbances and their mitigation mechanisms in crop plants: A review. Biologia 71:367–377
Chang Z, Liu Y, Dong H, Teng K, Han L, Zhang X (2016) Effects of cytokinin and nitrogen on drought tolerance of creeping bentgrass. PloS one 11:e0154005
Chen P, Wang H-Y, Zheng R-L, Zhang B, Sun G-X (2018) Long-term effects of biochar on rice production and stabilisation of cadmium and arsenic levels in contaminated paddy soils. Earth Environ Sci Trans R Soc Edinb 109:415–420
Chen P, Zhang H-M, Yao B-M, Chen S-C, Sun G-X, Zhu Y-G (2020) Bioavailable arsenic and amorphous iron oxides provide reliable predictions for arsenic transfer in soil-wheat system. J Hazard Mater 383:121160
Dhindsa RS, Matowe W (1981) Drought tolerance in two mosses: correlated with enzymatic defence against lipid peroxidation. J Exp Bot 32:79–91
Etesami H, Adl SM (2020) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and their action mechanisms in availability of nutrients to plants. Phyto-Microbiome in Stress Regulation, pp 147–203.
Fahad S, Hussain S, Bano A, Saud S, Hassan S, Shan D, Khan FA, Khan F, Chen Y, Wu C, Tabassum MA, Chun MX, Afzal M, Jan M, Jan MT, Huang J (2015) Potential role of phytohormones and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria in abiotic stresses: consequences for changing environment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4907–4921
Finnegan P, Chen W (2012) Arsenic toxicity: the effects on plant metabolism. Front Physiol 3:182
Fukami J, Nogueira MA, Araujo RS, Hungria M (2016) Accessing inoculation methods of maize and wheat with Azospirillum brasilense. AMB Express 6:1–13
Gangwar S, Singh VP, Prasad SM, Maurya JN (2010) Modulation of manganese toxicity in Pisum sativum L. seedlings by kinetin. Sci Hortic 126:467–474
Gangwar S, Singh VP, Tripathi DK, Chauhan DK, Prasad SM, Maurya JN (2014) Chapter 10 - plant responses to metal stress: the emerging role of plant growth hormones in toxicity alleviation. In: Ahmad P, Rasool S (eds) Emerging technologies and management of crop stress tolerance. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 215–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-800875-1.00010-7
Gardner F, Pearce R, Mitchell R (1985) Physiology of crop plants. Iowa State Univ. Press, Ames, IA. Physiology of crop plants Iowa State Univ Press, Ames, IA.
Genkov T, Tsoneva P, Ivanova I (1997) Effect of cytokinins on photosynthetic pigments and chlorophyllase activity in in vitro cultures of axillary buds of Dianthus caryophyllus L. J Plant Growth Regul 16:169–172
Ghorbani B, Tafteh M, Roudbari N, Pishkar L, Zhang W, Wu C. 2021. Piriformospora indica augments arsenic tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) by immobilizing arsenic in roots and improving iron translocation to shoots. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 209: 111793.
Guarino F, Miranda A, Castiglione S, Cicatelli A (2020) Arsenic phytovolatilization and epigenetic modifications in Arundo donax L. assisted by a PGPR consortium. Chemosphere 251:126310.
Gujjar RS, Banyen P, Chuekong W, Worakan P, Roytrakul S, Supaibulwatana K (2020) A synthetic cytokinin improves photosynthesis in rice under drought stress by modulating the abundance of proteins related to stomatal conductance, chlorophyll contents, and Rubisco activity. Plants 9:1106
Gupta G, Parihar SS, Ahirwar NK, Snehi SK, Singh V (2015) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR): current and future prospects for development of sustainable agriculture. J Microb Biochem Technol 7:096–102
Gupta D, Tiwari S, Razafindrabe B, Chatterjee S (2017) Arsenic contamination in the environment: the issues and solutions. In: Gupta D, Chatterjee S (eds) Arsenic contamination in the environment: the Issues and Solutions. Springer International Publishing AG, Cham, Switzerland, pp 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54356-7_1
Gusman GS, Oliveira JA, Farnese FS, Cambraia J (2013) Arsenate and arsenite: the toxic effects on photosynthesis and growth of lettuce plants. Acta Physiol Plant 35:1201–1209
Havlová M, Dobrev PI, Motyka V, Štorchová H, Libus J, Dobrá J, MALBECK J, Gaudinová A, Vanková R, (2008) The role of cytokinins in responses to water deficit in tobacco plants over-expressing trans-zeatin O-glucosyltransferase gene under 35S or SAG12 promoters. Plant Cell Environ 31:341–353
Hönig M, Plíhalová L, Husičková A, Nisler J, Doležal K (2018) Role of cytokinins in senescence, antioxidant defence and photosynthesis. Int J Mol Sci 19:4045
Hu L, Wang Z, Huang B (2013) Effects of cytokinin and potassium on stomatal and photosynthetic recovery of Kentucky bluegrass from drought stress. Crop Sci 53:221–231
Hu Y, Li J, Lou B, Wu R, Wang G, Lu C, Wang H, Pi J, Xu Y (2020) The role of reactive oxygen species in arsenic toxicity. Biomolecules 10:240
Hungria M, Campo RJ, Souza EM, Pedrosa FO (2010) Inoculation with selected strains of Azospirillum brasilense and A. lipoferum improves yields of maize and wheat in Brazil. Plant Soil 331:413–425
Islam FS, Gault AG, Boothman C, Polya DA, Charnock JM, Chatterjee D, Lloyd JR (2004) Role of metal-reducing bacteria in arsenic release from Bengal delta sediments. Nature 430:68–71
Javid MG, Sorooshzadeh A, Sanavy SAMM, Allahdadi I, Moradi F (2011) Effects of the exogenous application of auxin and cytokinin on carbohydrate accumulation in grains of rice under salt stress. Plant Growth Regul 65:305–313
Khan E, Gupta M (2018) Arsenic–silicon priming of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seeds influence mineral nutrient uptake and biochemical responses through modulation of Lsi-1, Lsi-2, Lsi-6 and nutrient transporter genes. Sci Rep 8:1–16
Khan I, Ahmad A, Iqbal M (2009) Modulation of antioxidant defence system for arsenic detoxification in Indian mustard. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:626–634
Kumar A, Meena VS (2019) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for agricultural sustainability. Springer, Berlin
Letham D, Palni L (1983) The biosynthesis and metabolism of cytokinins. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 34:163–197
Liu Q, Zheng C, Hu C, Tan Q, Sun X, Su J (2012) Effects of high concentrations of soil arsenic on the growth of winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L) and rape (Brassica napus). Plant Soil Environ 58:22–27
Liu F, Xing S, Ma H, Du Z, Ma B (2013) Cytokinin-producing, plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria that confer resistance to drought stress in Platycladus orientalis container seedlings. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:9155–9164
Liu C-W, Chen Y-Y, Kao Y-H, Maji S-K (2014) Bioaccumulation and translocation of arsenic in the ecosystem of the Guandu Wetland. Taiwan Wetlands 34:129–140
Maghsoudi K, Arvin MJ, Ashraf M (2020) Mitigation of arsenic toxicity in wheat by the exogenously applied salicylic acid, 24-Epi-brassinolide and silicon. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 20:577–588
Mahanty T, Bhattacharjee S, Goswami M, Bhattacharyya P, Das B, Ghosh A, Tribedi P (2017) Biofertilizers: a potential approach for sustainable agriculture development. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:3315–3335
Mishra RK, Kumar J, Srivastava PK, Bashri G, Prasad SM (2016) PSII photochemistry, oxidative damage and anti-oxidative enzymes in arsenate-stressed Oryza sativa L. seedlings. Chem Ecol 33:34–50
Mishra RK, Mishra G, Singh R, Parihar P, Kumar J, Srivastava PK, Prasad SM (2021) Managing arsenic (V) toxicity by phosphate supplementation in rice seedlings: modulations in AsA-GSH cycle and other antioxidant enzymes. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-16587-3
Miteva E, Merakchiyska M (2002) Response of chloroplasts and photosynthetic mechanism of bean plants to excess arsenic in soil. Bulg J Agr Sci 8:151–156
Mitra A, Chatterjee S, Moogouei R, Gupta DK (2017) Arsenic accumulation in rice and probable mitigation approaches: a review. Agronomy 7:67
Naeem M, Aftab T, Ansari AA, Khan MMA (2021) Carrageenan oligomers and salicylic acid act in tandem to escalate artemisinin production by suppressing arsenic uptake and oxidative stress in Artemisia annua (sweet wormwood) cultivated in high arsenic soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-13241-w
Nakano Y, Asada K (1981) Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate-specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. Plant Cell Physiol 22:867–880
Pandey C, Gupta M (2015) Selenium and auxin mitigates arsenic stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by combining the role of stress indicators, modulators and genotoxicity assay. J Hazard Mater 287:384–391
Pigna M, Cozzolino V, Giandonato Caporale A, Mora M, Di Meo V, Jara A, Violante A (2010) Effects of phosphorus fertilization on arsenic uptake by wheat grown in polluted soils. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10:428–442
Rafiq M, Shahid M, Shamshad S, Khalid S, Niazi NK, Abbas G, Saeed M, Ali M, Murtaza B (2018) A comparative study to evaluate efficiency of EDTA and calcium in alleviating arsenic toxicity to germinating and young Vicia faba L. seedlings. J Soil Sediment 18:2271–2281
Roberto FF, Barnes JM, Bruhn DF (2002) Evaluation of a GFP reporter gene construct for environmental arsenic detection. Talanta 58:181–188
Rowe JH, Topping JF, Liu J, Lindsey K (2016) Abscisic acid regulates root growth under osmotic stress conditions via an interacting hormonal network with cytokinin, ethylene and auxin. New Phytol 211:225–239
Roy S, Parveen Z, Huq SI (2012) Effect of arsenic on the nutrient uptake pattern of Amaranthus. Dhaka Univ J Biol Sci 21:87–96
Samea-Andabjadid S, Ghassemi-Golezani K, Nasrollahzadeh S, Najafi N (2018) Exogenous salicylic acid and cytokinin alter sugar accumulation, antioxidants and membrane stability of faba bean. Acta Biol Hung 69:86–96
Schäfer M, Brütting C, Meza-Canales ID, Großkinsky DK, Vankova R, Baldwin IT, Meldau S (2015) The role of cis-zeatin-type cytokinins in plant growth regulation and mediating responses to environmental interactions. J Exp Bot 66:4873–4884
Schiller LG, Magnitskiy S (2019) Efecto de la aplicación de trans-zeatina ribósido sobre el crecimiento de banano (Musa AAA Simmonds) cv. Williams en etapa juvenile. Rev Colomb Cienc Hortic 13: 2.
Shahid M, Dumat C, Khalid S, Schreck E, Xiong T, Niazi NK (2017) Foliar heavy metal uptake, toxicity and detoxification in plants: A comparison of foliar and root metal uptake. J Hazard Mater 325:36–58
Sharma I (2012) Arsenic induced oxidative stress in plants. Biologia 67:447–453
Shewry PR (2009) Wheat. J Exp Bot 60:1537–1553
Silva ER, Zoz J, Oliveira CES, Zuffo AM, Steiner F, Zoz T, Vendruscolo EP (2019) Can co-inoculation of Bradyrhizobium and Azospirillum alleviate adverse effects of drought stress on soybean (Glycine max L. Merrill.)? Arch Microbiol 201:325–335
Singh N, Ma LQ, Srivastava M, Rathinasabapathi B (2006) Metabolic adaptations to arsenic-induced oxidative stress in Pteris vittata L and Pteris ensiformis L. Plant Sci 170:274–282
Singh HP, Batish DR, Kohli RK, Arora K (2007) Arsenic-induced root growth inhibition in mung bean (Phaseolus aureus Roxb.) is due to oxidative stress resulting from enhanced lipid peroxidation. Plant Growth Regul 53:65–73
Srivastava S, Suprasanna P, Tripathi RD (2020) Safeguarding rice from arsenic contamination through the adoption of chemo-agronomic measures. In: Srivastava S (ed) Arsenic in drinking water and food. Springer, Singapore, pp 411–424. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8587-2_16
Stancheva I, Kaloyanova N, Atanasova E (1999) Effect of copper and arsenic on the yield and plastid pigment content of rice inoculated with Azospirillum brasilense. Soil Sci Agrochem Ecol 39:140–143
Stoeva N, Bineva T (2003) Oxidative changes and photosynthesis in oat plants grown in As-contaminated soil. Bulg J Plant Physiol 29:87–95
Stoeva N, Berova M, Zlatev Z (2004) Physiological Response of Maize to Arsenic Contamination Biol Plant 47:449–452
Stoeva N, Berova M, Zlatev Z (2005) Effect of arsenic on some physiological parameters in bean plants. Biol Plant 49:293–296
Sullivan CY, Ross WM (1979) Selecting for drought and heat resistance in grain sorghum. In: Mussell H, Staples RC (eds) Stress physiology in crop plants. John Wiley & Sons, New York, USA, pp 263–281
Talukdar D (2013) Arsenic-induced changes in growth and antioxidant metabolism of fenugreek. Russ J Plant Physiol 60:652–660
Tu T, Zheng S, Ren P, Meng X, Zhao J, Chen Q, Li C (2021) Coordinated cytokinin signaling and auxin biosynthesis mediates arsenate-induced root growth inhibition. Plant Physiol 185:1166–1181
Tugarova AV, Mamchenkova PV, Khanadeev VA, Kamnev AA (2020) Selenite reduction by the rhizobacterium Azospirillum brasilense, synthesis of extracellular selenium nanoparticles and their characterisation. N Biotechnol 58:17–24
Ullah I, Ali N, Durrani S, Shabaz MA, Hafeez A, Ameer H, Ishfaq M, Fayyaz MR, Rehman A, Waheed A (2018) Effect of different nitrogen levels on growth, yield and yield contributing attributes of wheat. Int J Sci Eng Res 9:595–602
Upadhyay MK, Shukla A, Yadav P, Srivastava S (2019) A review of arsenic in crops, vegetables, animals and food products. Food Chem 276:608–618
Vezza ME, Nicotra MFO, Agostini E, Talano MA (2020) Biochemical and molecular characterization of arsenic response from Azospirillum brasilense Cd, a bacterial strain used as plant inoculant. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:2287–2300
Wu Z, Ren H, McGrath SP, Wu P, Zhao F-J (2011) Investigating the contribution of the phosphate transport pathway to arsenic accumulation in rice. Plant Physiol 157:498–508
Zaheer MS, Raza MAS, Saleem MF, Erinle KO, Iqbal R, Ahmad S (2019a) Effect of rhizobacteria and cytokinins application on wheat growth and yield under normal vs drought conditions. Comm Soil Sci Plant Anal 50:2521–2533
Zaheer MS, Raza MAS, Saleem MF, Khan IH, Ahmad S, Iqbal R, Manevski K (2019b) Investigating the effect of Azospirillum brasilense and Rhizobium pisi on agronomic traits of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Arch Agron Soil Sci 65:1554–1564
Zeffa DM, Perini LJ, Silva MB, de Sousa NV, Scapim CA, de Oliveira ALM, Júnior ATA, Gonçalves LSA (2019) Azospirillum brasilense promotes increases in growth and nitrogen use efficiency of maize genotypes. PloS one 14:e0215332.
Zhao F-J, Stroud JL, Eagling T, Dunham SJ, McGrath SP, Shewry PR (2010) Accumulation, distribution, and speciation of arsenic in wheat grain. Environ Sci Technol 44:5464–5468
Zhu X, Cao Q, Sun L, Yang X, Yang W, Zhang H (2018) Stomatal conductance and morphology of arbuscular mycorrhizal wheat plants response to elevated co2 and NaCl Stress. Front Plant Sci 9:1363
Acknowledgements
The technical support for this study was gratefully provided by the Regional Agriculture Research Institute in Bahawalpur and Ayub Agricultural Research Institute in Faisalabad. Provision of resources from Islamia University Bahawalpur, Pakistan, and Khwaja Fareed University of Engineering and Information Technology Rahim Yar Khan, Pakistan, is also greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.H. Ali planned and supervised the experiment, M.S. Zaheer & M. Nawaz involved in planning and execution of experiment, K.O. Erinle and S.H. Wani participated in write up of manuscript and review. O.G. Okon, M.M. Waqas & M.A. Bodlah participated in the discussion of the study and field trails, A. Raza participated in the methodology and discussion of the study, J. Iqbal & M.A. Nadeem Review the manuscript and improve the technical and English language.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All animal handling and euthanasia procedures were approved by the University. The authors confirm that ethical standards were addressed.
Consent to participate
The authors confirm the volunteer’s declaration of consent.
Consent for publication
The authors confirm the volunteer’s consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Gangrong Shi
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaheer, M.S., Ali, H.H., Erinle, K.O. et al. Inoculation of Azospirillum brasilense and exogenous application of trans-zeatin riboside alleviates arsenic induced physiological damages in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Environ Sci Pollut Res 29, 33909–33919 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18106-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-18106-w