Abstract
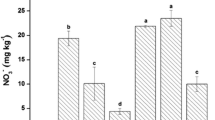
Lead (Pb) and copper (Cu) contamination in croplands pose severe health hazards and environmental concerns throughout soil-food chain transfer. In the present study, BCR, TCLP, CaCl2, and SBET techniques were employed to evaluate the simultaneous effectiveness of rice straw (RS) and its derived biochar (BC), multiwall carbon nanotube (MWCNT), and single superphosphate (SSP) to immobilize the Pb and Cu in co-contaminated soil. The BCR sequential extraction results suggested that with increasing BC and SSP amount, the acid-soluble fractions decreased while oxidizable and residual proportions of Pb and Cu were increased significantly. Compared to SSP, the application of BC amendment substantially modified partitioning of Cu from easily exchangeable phase to less bioavailable residual bound fraction. The immobilized Pb and Cu were mainly transformed to reducible forms. The TCLP and CaCl2-extracted Pb and Cu were reduced significantly by the addition of BC compared to RS and MWCNT, whereas the bio-accessibility of Pb significantly reduced with RS addition. SSP showed better results for Pb immobilization while marginal for Cu in co-contaminated soil. Overall, the addition of BC offered the best results and could be effective in both Pb and Cu immobilization thereby reducing their mobility and bioavailability in the co-contaminated soil.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bilgic S, Caliskan N (2001) An investigation of some Schiff bases as corrosion inhibitors for austenitic chromium and nickel steel in H2SO4. J Appl Electrochem 31:79–83
Bian R, Chen D, Liu X, Cui L, Li L, Pan G, Xie D, Zheng J, Zhang X, Zheng J, Chang A (2013) Biochar soil amendment as a solution to prevent Cd-tainted rice from China: results from a cross-site field experiment. Ecol Eng 58:378–383
Bolan NS, Naidu R, Syers JK, Tillman RW (1999) Surface charge and solute interactions in soils. Adv Agron 67:88–141
Cao X, Ma L, Gao B, Harris W (2009a) Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environ Sci Technol 43:3285–3291
Cao X, Liang Y, Zhao L, Le H (2013) Mobility of Pb, Cu, and Zn in the phosphorus-amended contaminated soils under simulated landfill and rainfall conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5913–5921
Cao X, Al W, Ma L, Li B, Yang Y (2009b) Immobilization of Zn, Cu, and Pb in contaminated soils using phosphate rock and phosphoric acid. J Hazard Mater 164:555–564
Cao X, Dermatas D, Xu X, Shen G (2008) Immobilization of lead in shooting range soils by means of cement, quicklime, and phosphate amendments. Environ Sci Pollut Res 15:120–127. doi:10.1065/espr2007.05.416
Cao RX, Ma LQ, Chen M, Singh SP, Harris WG (2003) Phosphate-induced metal immobilization in a contaminated site. Environ Pollut 122:19–28
Cao XD, Ma LQ, Rhue DR, Appel CS (2004) Mechanisms of lead, copper, and zinc retention by phosphate rock. Environ Pollut 131(3):435–444
Chan KY,Van Zwieten L, Meszaros I, Downie A, Joseph S (2007) Agronomic val-ues of greenwate biochar as a soil amendment. Aust J Soil Res 45:629–634
Chen X, Chen G, Chen L, Chen Y, Lehmann J, McBride MB, Hay AG (2011) Adsorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution. Bioresource Technol 102:8877–8884
Cui Y, Du X, Weng L, Van Riemsdijk WH (2010) Assessment of in situ immobilization of lead (Pb) and arsenic (As) in contaminated soils with phosphate and iron: solubility and bioaccessibility. Water Air Soil Poll 213:95–104
Cui YS, Du X, Weng LP, Zhu YG (2008) Effects of rice straw on the speciation of cadmium (Cd) and copper (Cu) in soils. Geoderma 146:370–377
Dzombak DA, Morel FMM (1990) Surface complexation modeling, in: hydrous ferric oxide. Wiley, New York
Fang Y, Cao X, Zhao L (2012) Effects of phosphorus amendments and plantgrowth on the mobility of Pb, Cu, and Zn in a multi-metal-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1659–1667. doi:10.1007/s11356-011-0674-2
Hmid A, Al Chami Z, Sillen W, De Vocht A, Vangronsveld J (2015) Olive mill waste biochar: a promising soil amendment for metal immobilization in contaminated soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1444–1456
Houben D, Evrard L, Sonnet P (2013) Mobility, bioavailability and pH-dependent leaching of cadmium, zinc and lead in a contaminated soil amended with biochar. Chemosphere 92:1450–1457
Jiang J, Xu R (2013) Application of crop straw derived biochars to Cu(II) contaminated Ultisol: Evaluating role of alkali and organic functional groups in Cu(II) immobilization. Bioresource Technol 133:537–545
Jiang J, Xu R, Jiang TY, Li Z (2012a) Immobilization of Cu(II), Pb(II) and Cd(II) by the addition of rice straw derived biochar to a simulated polluted Ultisol. J Hazard Mater 229:145–150
Jiang TY, Jiang J, Xu RK, Li Z (2012b) Adsorption of Pb(II) on variable charge soils amended with rice-straw derived biochar. Chemosphere 89:249–256
Josko I, Oleszczuk P, Pranagal J, Lehmann J, Xing B, Cornelissen G (2013) Effect of biochars, activated carbon and multiwalled carbon nanotubes on phytotoxicity of sediment contaminated by inorganic and organic pollutants. Ecol Eng 60:50–59
Kim HS, Kim KR, Kim HJ, Yoon JH, Yang JE, Ok YS, Owens G, Kim KH (2015) Effect of biochar on heavy metal immobilization and uptake by lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) in agricultural soil. Environ Earth Sci doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4116-1
Lehmann J (2007) Bio-energy in the black. Front Ecol Environ 5:381–387
Liang Y, Cao X, Zhao L, Arellano E (2014) Biochar and phosphate-induced immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated soil and water: implication on simultaneous remediation of contaminated soil and groundwater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:4665–4674
Lindsay WL (1979) Chemical equilibria in soils. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New York
Lu RK (1999) Analytical methods for soil agrochemistry. Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Lu K, Yang X, Shen J, Robinson B, Huang H, Liu D, Bolan N, Pei J, Wang H (2014) Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the bioavailability of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn to Sedum plumbizincicola. Agri Ecosyst Environ 191:124–132
Lyklema L (1995) Fundamentals of interface and colloid science: solid–liquid interfaces, vol II. Academic Press, New York
Ma LQ, Rao GN (1997) Effects of phosphate rock on sequential chemical extraction of lead in contaminated soils. J. Environ Qual 26:788–794
Miretzky P, Fernandez-Cirelli A (2008) Phosphates for Pb immobilization in soils: a review. Environ Chem Lett 6:121–133
Moon DH, Park JW, Chang YY, Ok YS, Lee SS, Ahmad M, Koutsospyros A, Park JH, Baek K (2013) Immobilization of lead in contaminated firing range soil using biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:8464–8471
Mousa W, Soliman S, El-Bialy A, Shier HA (2013) Removal of some heavy metals from aqueous solution using rice straw. J Appl Sci Res 9:1696–1701
Mubaraka N, Daniela S, Khalid M, Tana J (2012) Comparative study of functionalize and non-functionalized carbon nanotube for removal of copper from polluted water. Int J Chem Environ Eng 3(5)
Nawar N, Ebrahim M, Sami E ( 2013) Removal of heavy metals Fe3+, Mn2+, Zn2+, Pb2+ and Cd2+ from wastewater by using rice straw as low cost adsorbent. Acad J Interdiscipl Stud 2(6). doi:10.5901/ajis.2013.v2n6p85
Namgay T, Singh B, Singh BP (2010) Influence of biochar application to soil on the availability of As, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn to maize (Zea mays L.). Aust J Soil Res 48:638–647
Park JH, Choppala GK, Bolan NS, Chung JW, Chuasavathi T (2011) Biochar reduces the bioavailability and phytotoxicity of heavy metals. Plant Soil 348:439–451
Rauret G, Lopez-Sanchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson C, Ure A, Quevauviller P (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monitor 1:57–61
Rizwan MS, Imtiaz M, Chhajro MA, Huang G, Fu Q, Zhu J, Aziz O, Hu H (2016) Influence of pyrolytic and non-pyrolytic rice and castor straws on the .immobilization of Pb and Cu in contaminated soil. Environ Technol (doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1158870)
Ryan JA, Zhang P, Hesterberg D, Chou J, Sayers DE (2001) Formation of chloropyromorphite in a lead-contaminated soil amended with hydroxyapatite. Environ Sci Technol 35:3798–3803
Salam MA, Zhrani GA, Kosa SA (2012) Simultaneous removal of copper(II), lead(II), zinc(II) and cadmium(II) from aqueous solutions by multi-walled carbon nanotubes C. R Chimie 15:398–408
Samsuri AW, Sadegh-Zadeh F, Seh-Bardan BJ (2014) Characterization of biochars produced from oil palm and rice husks and their adsorption capacities for heavy metals. Int J Environ Sci Tech 11:967–976
Sergio T, Bosso, Enzweiler J, Rômulo S, Angelica (2008) Lead bioaccessibility in soil and mine wastes after immobilization with phosphate. Water Air Soil Pollut 195:257–273. doi 10.1007/s11270-008-9744-6
Stafiej A, Pyrzynska K (2007) Adsorption of heavy metal ions with carbon nanotubes. Sep Purif Technol 58:49–52
Tang XY, Zhu YG, Chen SB, Tang LL, Chen XP (2004) Assessment of the effectiveness of different phosphorus fertilizers to remediate Pb-contaminated soil using in vitro test. Environ Int 30:531–537
Uchimiya M, Chang S, Klasson KT (2011a) Screening biochars for heavy metal retention in soil: role of oxygen functional groups. J Hazard Mater 190:432–441
Uchimiya M, Klasson KT, Wartelle LH, Lima IM (2011b) Influence of soil properties on heavy metal sequestration by biochar amendment: 1. Copper sorption isotherms and the release of cations. Chemosphere 82:1431–1437
USEPA (1992) Test methods for evaluating solid waste, physical/chemical methods. US Environmental Pollution Agency USA, Washington, DC
Wang B, Xie Z, Chen J, Jiang J, Su Q (2008) Effects of field application of phosphate fertilizers on the availability and uptake of lead, zinc and cadmium by cabbage (Brassica chinensis L.) in a mining tailing contaminated soil. J Environ Sci-China 20:1109–1117
Wei HX, Zong HY, Shan CY (2010) Effect of bone char addition on the fractionation and bio-accessibility of Pb and Zn in combined contaminated soil. Acta Ecol Sin 30:118–122. doi:10.1016/j.chnaes.2010.03.012
Wu WH, Xie ZM, Xu JM, Wang F, Shi JC, Zhou RB, Jin ZF (2013) Immobilization of trace metals by phosphates in contaminated soil near lead/zinc mine tailings evaluated by sequential extraction and TCLP. J Soils Sediments 13:1386–1395. doi:10.1007/s11368-013-0751-x
Wuana R, Yiase S, Iorungwa P, Iorungwa M (2013) Evaluation of copper and lead immobilization in contaminated soil by single, sequential and kinetic leaching tests. Afr J Environ Sci Technol 7:249–258
Xu X, Cao X, Zhao L, Wang H, Yu H, Gao B (2013) Removal of Cu, Zn, and Cd from aqueous solutions by the dairy manure-derived biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:358–368
Yuan JH, Xu RK, Zhang H (2011) The forms of alkalis in the biochar produced from crop residues at different temperatures. Bioresource Technol 102:3488–3497
Acknowledgments
The study was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (41371470) and National Sci-Tech Support Plan (2015BAD05B02). The authors gratefully acknowledge to Gao Ruili and Guangguang Guo for help during laboratory work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rizwan, M.S., Imtiaz, M., Huang, G. et al. Immobilization of Pb and Cu in polluted soil by superphosphate, multi-walled carbon nanotube, rice straw and its derived biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23, 15532–15543 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6695-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6695-0