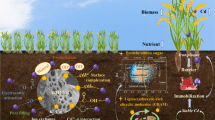
Abstract
Long-term wastewater irrigation or solid waste disposal has resulted in the heavy metal contamination in both soil and groundwater. It is often separately implemented for remediation of contaminated soil or groundwater at a specific site. The main objective of this study was to demonstrate the hypothesis of simultaneous remediation of both heavy metal contaminated soil and groundwater by integrating the chemical immobilization and pump-and-treat methods. To accomplish the objective, three experiments were conducted, i.e., an incubation experiment was first conducted to determine how dairy-manure-derived biochar and phosphate rock tailing induced immobilization of Cd in the Cd-contaminated soils; second, a batch sorption experiment was carried out to determine whether the pre-amended contaminated soil still had the ability to retain Pb, Zn and Cd from aqueous solution. BCR sequential extraction as well as XRD and SEM analysis were conducted to explore the possible retention mechanism; and last, a laboratory-scale model test was undertaken by leaching the Pb, Zn, and Cd contaminated groundwater through the pre-amended contaminated soils to demonstrate how the heavy metals in both contaminated soil and groundwater were simultaneously retained and immobilized. The incubation experiment showed that the phosphate biochar were effective in immobilizing soil Cd with Cd concentration in TCLP (toxicity characteristics leaching procedure) extract reduced by 19.6 % and 13.7 %, respectively. The batch sorption experiment revealed that the pre-amended soil still had ability to retain Pb, Zn, and Cd from aqueous solution. The phosphate-induced metal retention was mainly due to the metal–phosphate precipitation, while both sorption and precipitation were responsible for the metal stabilization in the biochar amendment. The laboratory-scale test demonstrated that the soil amended with phosphate removed groundwater Pb, Zn, and Cd by 96.4 %, 44.6 %, and 49.2 %, respectively, and the soil amended with biochar removed groundwater Pb, Zn, and Cd by 97.4 %, 53.4 %, and 54.5 %, respectively. Meanwhile, the metals from both groundwater and soil itself were immobilized with the amendments, with the leachability of the three metals in the CaCl2 and TCLP extracts being reduced by up to 98.1 % and 62.7 %, respectively. Our results indicate that the integrated chemical immobilization and pump-and-treat method developed in this study provides a novel way for simultaneous remediation of both metal-contaminated soil and groundwater.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) (2000) Annual book of ASTM standards. Soil and Rock. vol. 4.08
Beesley L, Moreno-Jimenez E, Gomez-Eyles JL (2010) Effects of biochar and greenwaste compost amendments on mobility, bioavailability and toxicity of inorganic and organic contaminants in a multi-element polluted soil. Environ Pollut 158:2282–2287
Beesley L, Marmiroli M (2011) The immobilisation and retention of soluble arsenic, cadmium and zinc by biochar. Environ Pollut 159:474–480
Beesley L, Moreno-Jimenez E, Gomez-Eyles JL, Harris E, Robinson B, Sizmur T (2011) A review of biochars' potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 159:3269–3282
Caliman FA, Robu BM, Smaranda C, Pavel VL, Gavrilescu M (2011) Soil and groundwater cleanup: benefits and limits of emerging technologies. Clean Technol Environ Policy 13:241–268
Cao XD, Harris W (2010) Properties of dairy-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use in remediation. Bioresour Technol 101:5222–5228
Cao XD, Ma LN, Liang Y, Gao B, Harris W (2011) Simultaneous immobilization of lead and atrazine in contaminated soils using dairy-manure biochar. Environ Sci Technol 45:4884–4889
Cao XD, Liang Y, Zhao L, Le HY (2013) Mobility of Pb, Cu, and Zn in the phosphorus-amended contaminated soils under simulated landfill and rainfall conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5913–5921
Castillo MLA, Alonso EV, Cordero MTS, Pavon JMC, de Torres AG (2011) Fractionation of heavy metals in sediment by using microwave assisted sequential extraction procedure and determination by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Microchem J 98:234–239
Chen GQ, Zeng GM, Du CY, Huang DL, Tang L, Wang LA, Shen GL (2010) Transfer of heavy metals from compost to red soil and groundwater under simulated rainfall conditions. J Hazard Mater 181:211–216
China Environmental Quality Standard for Groundwater (GB/T 14848–1993) (1993) China National Standardization Management Committee, China, Beijing
China Environmental Quality Standard for Soil (GB15618-1995) (1995) China National Standardization Management Committee, China, Beijing
China Hygienic Standard for Grains (GB2715-2005) (2005) Ministry of Health in China and China National Standardization Management Committee, China, Beijing
Davezza M, Fabbri D, Prevot AB, Pramauro E (2011) Removal of alkylphenols from polluted sites using surfactant-assisted soil washing and photocatalysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:783–789
Diels L, Vanbroekhoven K (2008) Remediation of metal and metalloid contaminated groundwater. In: Annable MD, Teodorescu M, Hlavinek P, Diels L (ed) Methods and techniques for cleaning-up contaminated sites. NATO Science for Peace and Security Series C-Environmental Security, pp 1–23
El Khalil H, El Hamiani O, Bitton G, Ouazzani N, Boularbah A (2008) Heavy metal contamination from mining sites in South Morocco: monitoring metal content and toxicity of soil runoff and groundwater. Environ Monit Assess 136:147–160
Fang YY, Cao XD, Zhao L (2012) Effects of phosphorus amendments and plant growth on the mobility of Pb, Cu, and Zn in a multi-metal-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res 19:1659–1667
Forsyth PA, Sudicky EA (1998) Discrete wellbore simulations of pump-and-treat strategies for remediation of LNAPL-contaminated aquifers. J Contam Hydrol 31:57–81
Guo GL, Zhou QX (2006) Evaluation of heavy metal contamination in Phaeozem of northeast China. Environ Geochem Health 28:331–340
Hashimoto Y, Takaoka M, Oshita K, Tanida H (2009) Incomplete transformations of Pb to pyromorphite by phosphate-induced immobilization investigated by X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy. Chemosphere 76:616–622
Horckmans L, Swennen R, Deckers J (2007) Retention and release of Zn and Cd in spodic horizons as determined by pH(stat) analysis and single extractions. Sci Total Environ 376:86–99
Jiang TY, Jiang J, Xu RK, Li Z (2012) Adsorption of Pb(II) on variable charge soils amended with rice-straw derived biochar. Chemosphere 89:249–256
Kumpiene J, Lagerkvist A, Maurice C (2008) Stabilization of As, Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn in soil using amendments — a review. Waste Manage 28:215–225
Memon R, Schroder P (2009) Implications of metal accumulation mechanisms to phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16:162–175
Miretzky P, Fernandez-Cirelli A (2008) Phosphates for Pb immobilization in soils: a review. Environ Chem Lett 6:121–133
Niu L, Yang F, Xu C, Yang H, Liu W (2013) Status of metal accumulation in farmland soils across China: from distribution to risk assessment. Environ Pollut 176:55–62
Olsen SR, Sommers LE (1982) Phosphorus. In: Page AL et al (eds) Methods of soil analyses: Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, pp 403–430
Raicevic S, Kaludjerovic-Radoicic T, Zouboulis AI (2005) In situ stabilization of toxic metals in polluted soils using phosphates: theoretical prediction and experimental verification. J Hazard Mater 117:41–53
Reichenauer TG, Germida JJ (2008) Phytoremediation of organic contaminants in soil and groundwater. Chemsuschem 1:708–717
Rivett MO, Chapman SW, Allen-King RM, Feenstra S, Cherry JA (2006) Pump-and-treat remediation of chlorinated solvent contamination at a controlled field-experiment site. Environ Sci Technol 40:6770–6781
Thawornchaisit U, Polprasert C (2009) Evaluation of phosphate fertilizers for the stabilization of cadmium in highly contaminated soils. J Hazard Mater 165:1109–1113
Uchimiya M, Chang S, Klasson KT (2011) Screening biochars for heavy metal retention in soil: Role of oxygen functional groups. J Hazard Mater 190:432–441
USEPA (1992) Method 1311: test methods for evaluating solid waste, physical/chemical methods. SW-846 3rd edn. US Environmental Pollution Agency, USA, Washington, DC
USEPA (1986) Test methods for evaluating solid waste, laboratory manual physical/chemicalmethods, vol.1A, 3rd edn. SW-846, USA. Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Waterlot C, Pruvot C, Ciesielski H, Douay F (2011) Effects of a phosphorus amendment and the pH of water used for watering on the mobility and phytoavailability of Cd, Pb, and Zn in highly contaminated kitchen garden soils. Ecol Eng 37:1081–1093
Wu XL, Yang YL, Tang QF, Xu Q, Liu XD, Huang YY, Yin XC (2011) Ecological risk assessment and source analysis of heavy metals in river water, groundwater along river banks and river sediments in Shenyang. Chin J Ecol 30:438–447
Xu XY, Cao XD, Zhao L (2013) Comparison of rice husk- and dairy manure-derived biochars for simultaneously removing heavy metals from aqueous solutions: role of mineral components in biochars. Chemosphere 92:955–961
Yang XM, Beckmann D, Fiorenza S, Niedermeier C (2005) Field study of pulsed air sparging for remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated soil and groundwater. Environ Sci Technol 39:7279–7286
Zhao LYL, Schulin R, Nowack B (2009a) Cu and Zn mobilization in soil columns percolated by different irrigation solutions. Environ Pollut 157:823–833
Zhao XM, Dong DM, Hua XY, Dong SF (2009b) Investigation of the transport and fate of Pb, Cd, Cr(VI), and As(V) in soil zones derived from moderately contaminated farmland in Northeast, China. J Hazard Mater 170:570–577
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21077072, 21107070, 21377081), Shanghai Pujiang Talent Project (No. 11PJ1404600), and Suzhou Science and Technology Support Program (No. SS201230).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Zhihong Xu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, Y., Cao, X., Zhao, L. et al. Biochar- and phosphate-induced immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated soil and water: implication on simultaneous remediation of contaminated soil and groundwater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21, 4665–4674 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2423-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-013-2423-1