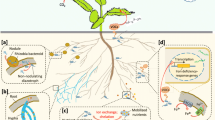
Abstract
We highlighted some of the key problems associated with the use of beneficial microorganisms for improving adaptation of plants to soils, polluted with heavy metals (HMs), especially Cd. Inoculation of pea line SGE and its Cd-tolerant mutant SGECdt with nodule bacteria Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae demonstrated that nodulation process may be disturbed at Cd concentrations below threshold toxicity levels for each partner and the plant genotype plays a major role in nodulation under Cd stress. A comparative mathematical analysis of available information about Cd tolerance, accumulation of HMs (Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Sr and Zn), response to mycorrhizal fungus Glomus sp. and 15 phenotypic traits of 99 pea varieties revealed that (1) the Cd-sensitive varieties were more efficient in exploring the protective potential of symbiosis to compensate their deficit in Cd tolerance and (2) correlations between the studied traits exist and can be helpful for selection of plant-microbe systems adapted to polluted soils. In pot experiment with 11 varieties of Indian mustard, the plant growth-promoting effect of rhizobacterium Variovorax paradoxus 5C-2 negatively correlated with Cd tolerance and shoot Cd concentration of the plants grown in Cd-supplemented soil. In an outdoor pot experiment, inoculation of willow with the ectomycorrhizal fungus Pisolithus tinctorius and a cocktail of rhizobacteria stimulated root exudation, decreased soil pH and increased Cd mobilization in soil and Cd uptake by plants, but decreased plant growth at a moderate contamination level (25 mg Cd kg−1). Opposite effects were observed in highly contaminated soil (77 mg Cd kg−1). We propose a preliminary systematic framework of interactions between these factors that determine the success of microbial inoculation aimed at improving crop performance on HM-polluted soils or enhancing phytoremediation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Shanab, R. A., Angle, J. S., & Chaney, R. L. (2006). Bacterial inoculants affecting nickel uptake by Alyssum murale from low, moderate and high Ni soils. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 38(9), 2882–2889.
Ahmad, I., Hayat, S., Ahmad, A., Inam, A., & Samiullah, A. (2001). Metal and antibiotic resistance traits in Bradyrhizobium sp. (cajanus) isolated from soil receiving oil refinery wastewater. World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology, 17(4), 379–384.
Antipchuk, A. F., Rangelova, V. N., & Tantsiurenko, E. V. (2002). Species and strain sensitivity of diasotrophs to heavy metals. Mikrobiolohichnyi Zhurnal, 64(3), 44–51.
Antonovics, J., & Bradshaw, A. D. (1970). Evolution of closely adjacent plant populations. VIII. Cline patterns in Anthoxanthum odoratum across a mine boundary. Heredity, 25, 349–358.
Basta, N. T., Gradwohl, R., Snethen, K. L., & Schroder, J. L. (2001). Chemical immobilization of lead, zinc, and cadmium in smelter-contaminated soils using biosolids and rock phosphate. Journal of Environmental Quality, 30(4), 1222–1230.
Baum, C., Hrynkiewicz, K., Leinweber, P., & Meißner, R. (2006). Heavy-metal mobilization and uptake by mycorrhizal and nonmycorrhizal willows (Salix x dasyclados). Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 169(4), 516–522.
Belimov, A. A., Safronova, V. I., Sergeyeva, T. A., Egorova, T. N., Matveyeva, V. A., Tsyganov, V. E., Borisov, A. Y., Tikhonovich, I. A., Kluge, C., Preisfeld, A., Dietz, K.-J., & Stepanok, V. V. (2001). Characterisation of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria isolated from polluted soils and containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 47(7), 642–652.
Belimov, A. A., Safronova, V. I., Tsyganov, V. E., Borisov, A. Y., Kozhemyakov, A. P., Stepanok, V. V., Martenson, A. M., Gianinazzi-Pearson, V., & Tikhonovich, I. A. (2003a). Genetic variability in tolerance to cadmium and accumulation of heavy metals in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Euphytica, 131(1), 25–35.
Belimov, A. A., Safronova, V. I., Tsyganov, V. E., Borisov, A. Y., Stepanok, V. V., Naumkina, T. S., & Serdyuk, V. P. (2003b). Garden pea: tolerance to cadmium and uptake of heavy metals from soil by pea plants. In Catalogue of the World Collection of VIR, 729 (p. 23). St.-Petersburg: VIR Press.
Belimov, A. A., Kunakova, A. M., Safronova, V. I., Stepanok, V. V., Yudkin, L. Y., Alekseev, Y. V., & Kozhemyakov, A. P. (2004). Employment of rhizobacteria for the inoculation of barley plants cultivated in soil contaminated with lead and cadmium. Microbiology (Microbiologiya), 73(1), 99–106.
Belimov, A. A., Hontzeas, N., Safronova, V. I., Demchinskaya, S. V., Piluzza, G., Bullitta, S., & Glick, B. R. (2005). Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 37(2), 241–250.
Belimov, A. A., Safronova, V. I., Demchinskayaa, S. V., & Dzyuba, O. O. (2007). Intraspecific variability of cadmium tolerance in hydroponically grown Indian mustard (Brassica juncea (L.) Czern.) seedlings. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 29(5), 473–478.
Belimov, A. A., Dodd, I. C., Safronova, V. I., Malkov, N. V., Davies, W. J., Tikhonovich, I. A. (2015). The cadmium tolerant pea (Pisum sativum L.) mutant SGECdt is more sensitive to mercury: assessing plant water relations. Journal of Experimental Botany, doi:10.1093/jxb/eru536.
Borisov, A. Y., Tsyganov, V. E., Shtark, O. Y., Jacobi, L. M., Naumkina, T. S., Serdyuk, V. P., & Vishnyakova, M. A. (2002). Pea: symbiotic effectiveness. In Catalogue of the World Collection of VIR, 728 (p. 29). St.-Petersburg: VIR Press.
Braud, A., Jézéquel, K., Bazot, S., & Lebeau, T. (2009). Enhanced phytoextraction of an agricultural Cr- and Pb-contaminated soil by bioaugmentation with siderophore-producing bacteria. Chemosphere, 74(2), 280–286.
Burd, G. I., Dixon, D. G., & Glick, B. R. (1998). A plant growth promoting bacterium that decreases nickel toxicity in plant seedlings. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 64(10), 3663–3668.
Cardoso, P. F., Molina, S. M. G., Pereira, G. J. G., Vitoria, A. P., & Azevedo, R. A. (2002). Response of rice inbred lines to cadmium exposure. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 25(5), 927–944.
Citterio, S., Prato, N., Fumagalli, P., Aina, R., Massa, N., Santagostino, A., Sgorbati, S., & Berta, G. (2005). The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae induces growth and metal accumulation changes in Cannabis sativa L. Chemosphere, 59(1), 21–29.
Dary, M., Chamber-Pérez, M., Palomares, A. J., & Pajuelo, E. (2010). “In situ” phytostabilisation of heavy metal polluted soils using Lupinus luteus inoculated with metal resistant plant-growth promoting rhizobacteria. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 177(1–3), 323–330.
Dos Santos Utmazian, M. N., & Wenzel, W. W. (2007). Cadmium and zinc accumulation in willow and poplar species grown on polluted soils. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 170(2), 265–272.
Dos Santos Utmazian, M. N., Wieshammer, G., Vega, R., & Wenzel, W. W. (2007a). Hydroponic screening for metal resistance and accumulation of cadmium and zinc in willows and poplars. Environmental Pollution, 148(1), 155–165.
Dos Santos Utmazian, M. N., Schweiger, P., Sommer, P., Gorfer, M., Strauss, J., & Wenzel, W. W. (2007b). Influence of Cadophora finlandica and other microbial treatments on cadmium and zinc uptake in willows grown on polluted soils. Plant, Soil and Environment, 53(4), 158–166.
Duan, J., Muller, K. M., Charles, T. C., & Glick, B. R. (2009). 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase genes in rhizobia from southern Saskatchewan. Microbial Ecology, 57(3), 423–436.
Fatnassi, I. C., Chiboub, M., Saadani, O., Jebara, M., & Jebara, S. H. (2015). Phytostabilization of moderate copper contaminated soils using co-inoculation of Vicia faba with plant growth promoting bacteria. Journal of Basic Microbiology, 55(3), 303–311.
Gadd, G. M. (2004). Microbial influence on metal mobility and application to bioremediation. Geoderma, 122(2–4), 109–119.
Gepts, P. (2002). A comparison between crop domestication, classical plant breeding, and genetic engineering. Crop Science, 42(6), 1780–1790.
Glick, B. R. (2010). Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation. Biotechnology Advances, 28(3), 367–374.
Guefrachi, I., Rejili, M., Mahdhi, M., & Mars, M. (2013). Assessing genotypic diversity and symbiotic efficiency of five rhizobial legume interactions under cadmium stress for soil phytoremediation. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 15(10), 938–951.
Hao, X., Taghavi, S., Xie, P., Orbach, M. J., Alwathnani, H. A., Rensing, C., & Wei, G. (2014). Phytoremediation of heavy and transition metals aided by legume-rhizobia symbiosis. International Journal of Phytoremediation, 16(2), 179–202.
Hildebrandt, U., Regvar, M., & Bothe, H. (2007). Arbuscular mycorrhiza and heavy metal tolerance. Phytochemistry, 68(1), 139–46.
Huff, D. R., & Wu, L. (1985). Phenotypic correlation between metal tolerance and morphology in Festuca rubra L. Crop Science, 25(5), 787–789.
Jacobi, L. M., Kukalev, A. S., Ushakov, K. V., Tsyganov, V. E., Naumkina, T. S., Provorov, N. A., Borisov, A. Y., & Tikhonovich, I. A. (2000). Polymorphism of garden pea (Pisum sativum L.) for the efficiency of symbiosis with endomycorrhizal fungus Glomus sp. under the conditions of rhizobia inoculation. Agricultural Biology, 3, 94–102 (In Russian).
Janousková, M., Pavlıková, D., & Macek Vosátka, M. (2005). Arbuscular mycorrhiza decreases cadmium phytoextraction by transgenic tobacco with inserted metallothionein. Plant and Soil, 272(1), 29–40.
Jing, Y., He, Z., & Yang, X. (2007). Role of soil rhizobacteria in phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE B, 8(3), 192–207.
Kamnev, А. А., & Van der Lelie, D. (2000). Chemical and biological parameters as tools to evaluate and improve heavy metal phytoremediation. Bioscience Reports, 20(4), 239–258.
Khan, A. G. (2005). Role of soil microbes in the rhizospheres of plants growing on trace metal contaminated soils in phytoremediation. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 18(4), 355–364.
Kidd, P. S., Diez, J., & Martinez, C. M. (2004). Tolerance and bioaccumulation of heavy metals in five populations of Cistus ladanifer L. subsp. ladanifer. Plant and Soil, 258(1–2), 189–205.
Kuffner, M., Puschenreiter, M., Wieshammer, G., Gorfer, M., & Sessitsch, A. (2008). Rhizosphere bacteria affect growth and metal uptake of heavy metal accumulating willows. Plant and Soil, 304(1–2), 35–44.
Leyval, C., Turnau, K., & Haselwandter, K. (1997). Effect of heavy metal pollution on mycorrhizal colonization and function: physiological, ecological and applied aspects. Mycorrhiza, 7(3), 139–153.
Lindberg, S., & Greger, M. (2002). Plant genotypic differences under metal deficient and enriched conditions. In M. N. V. Prasad & K. Stralska (Eds.), Physiology and biochemistry of metal toxicity and tolerance in plants (pp. 357–393). Dordrecht: Kluwer.
Ma, W., Guinel, F. C., & Glick, B. R. (2003). Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase promotes nodulation of pea plants. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 69(8), 4396–4402.
Ma, Y., Rajkumar, M., & Freitas, H. (2009). Inoculation of plant growth promoting bacterium Achromobacter xylosoxidans strain Ax10 for the improvement of copper phytoextraction by Brassica juncea. Journal of Environmental Management, 90(2), 831–837.
Ma, Y., Prasad, M. N. V., Rajkumar, M., & Freitas, H. (2011). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and endophytes accelerate phytoremediation of metalliferous soils. Biotechnology Advances, 29(2), 248–258.
Ma, Y., Rajkumar, M., Rocha, I., Oliveira, R. S., & Freitas, H. (2015). Serpentine bacteria influence metal translocation and bioconcentration of Brassica juncea and Ricinus communis grown in multi-metal polluted soils. Frontiers in Plant Science, 5, 757.
McLaughlin, M. J., Bell, M. J., Wright, G. C., & Cruickshank, J. (1997). Inter- and intra-specific variation in accumulation of cadmium by peanut, soybean, and navy bean. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research, 48(8), 1151–1160.
Metwally, A., Safronova, V. I., Belimov, A. A., & Dietz, K.-J. (2005). Genotypic variation of the response to cadmium toxicity in Pisum sativum L. Journal of Experimental Botany, 56(409), 167–178.
Nascimento, F. X., Brigido, C., Glick, B. R., & Oliveira, S. (2012). ACC deaminase genes are conserved among Mesorhizobium species able to nodulate the same host plant. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 336(1), 26–37.
Neubauer, U., Furrer, G., & Schulin, R. (2002). Heavy metal sorption on soil minerals affected by the siderophore desferrioxamine B: the role of Fe(III) (hydr)oxides and dissolved Fe(III). European Journal of Soil Science, 53(1), 45–55.
Neumarnn, H., Bode-Kirchhoff, A., Madeheim, A., & Wetzel, A. (1998). Toxicity testing of heavy metals with the Rhizobium-Legume symbiosis: high sensitivity to cadmium and arsenic compounds. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 5(1), 28–36.
Pereira, S. I. A., Lima, A. I. G., & Figueira, E. M. A. P. (2006). Screening possible mechanisms mediating cadmium resistance in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae isolated from contaminated Portuguese soils. Microbial Ecology, 52(2), 176–186.
Provorov, N. A., & Tikhonovich, I. A. (2003). Genetic resources for improving nitrogen fixation in legume-rhizobia symbiosis. Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution, 50(1), 89–99.
Puschenreiter, M., Türkta, M., Sommer, P., Wieshammer, G., Laaha, G., Wenzel, W. W., & Hauser, M. T. (2010). Differentiation of metallicolous and non-metallicolous Salix caprea populations based on phenotypic characteristics and nuclear microsatellite (SSR) markers. Plant, Cell & Environment, 33(10), 1641–1655.
Reed, M. L., Warner, B. G., & Glick, B. R. (2005). Plant growth-promoting bacteria facilitate the growth of the common reed Phragmites australis in the presence of copper or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Current Microbiology, 51(6), 425–429.
Safronova, V. I., Stepanok, V. V., Engqvist, G. L., Alekseyev, Y. V., & Belimov, A. A. (2006). Root-associated bacteria containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase improve growth and nutrient uptake by pea genotypes cultivated in cadmium supplemented soil. Biology and Fertility of Soils, 42(3), 267–272.
Safronova, V. I., Piluzza, G., Bullitta, S., & Belimov, A. A. (2011). Use of legume-microbe symbioses for phytoremediation of heavy metal polluted soils: advantages and potential problems. In I. A. Golubev (Ed.), Handbook of phytoremediation (pp. 443–469). New York: Nova Science Publishers, Inc.
Safronova, V. I., Piluzza, G., Zinovkina, N. Y., Kimeklis, A. K., Belimov, A. A., & Bullitta, S. (2012). Relationships between pasture legumes, rhizobacteria an nodule bacteria in heavy metal polluted mine waste of SW Sardinia. Symbiosis, 58(1–3), 149–159.
Saleem, M., Arshad, M., Hussain, S., & Bhatti, A. S. (2007). Perspective of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) containing ACC deaminase in stress agriculture. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 34(10), 635–648.
Sell, J., Kayser, A., Schulin, R., & Brunner, I. (2005). Contribution of ectomycorrhizal fungi to cadmium uptake of poplars and willows from a heavily polluted soil. Plant and Soil, 277(1–2), 245–253.
Seuntjens, P., Nowack, B., & Schulin, R. (2004). Root-zone modeling of heavy metal uptake and leaching in the presence of organic ligands. Plant and Soil, 265(1–2), 61–73.
Tikhonovich, I. A., & Provorov, N. A. (2009). From plant–microbe interactions to symbiogenetics: a universal paradigm for the interspecies genetic integration. Annals of Applied Biology, 154(3), 341–350.
Tsyganov, V. E., Belimov, A. A., Borisov, A. Y., Safronova, V. I., Georgi, M., Dietz, K.-J., & Tikhonovich, I. A. (2007). A chemically induced new pea (Pisum sativum L.) mutant SGECdt with increased tolerance to and accumulation of cadmium. Annals of Botany, 99(2), 227–237.
Wang, F. Y., Lin, X. G., & Yin, R. (2007). Role of microbial inoculation and chitosan in phytoextraction of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cd by Elsholtzia splendens—a field case. Environmental Pollution, 147(1), 248–255.
Wani, P. A., & Khan, M. S. (2013). Nickel detoxification and plant growth promotion by multi metal resistant plant growth promoting Rhizobium species RL9. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 91(1), 117–124.
Wenzel, W. W. (2009). Rhizosphere processes and management in plant-assisted bioremediation (phytoremediation) of soils. Plant and Soil, 321(1–2), 385–408.
Wetzel, A., & Werner, D. (1995). Ecotoxicological evaluation of contaminated soil using the legume root nodule symbiosis as effect parameter. Environmental Toxicology and Water Quality, 10(2), 127–133.
Wu, C. H., Wood, T. K., Mulchandani, A., & Chen, W. (2006). Engineering of plant–microbe symbiosis for rhizoremediation of heavy metals. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 72(2), 1129–1134.
Zaidi, S., Usmani, S., Singh, B. R., & Musarrat, J. (2006). Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere, 64(6), 991–997.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Mrs. Demchinskaya S.V. for the assistance in the experiments with Indian mustard. The work on Indian mustard was supported by the Russian Foundation of Basic Research (06-04-49486-a and 09-04-01614-a). The work on pea, nodule bacteria and mathematical simulation of interactions between pea and AMF was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (14-16-00137).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belimov, A.A., Puhalsky, I.V., Safronova, V.I. et al. Role of Plant Genotype and Soil Conditions in Symbiotic Plant-Microbe Interactions for Adaptation of Plants to Cadmium-Polluted Soils. Water Air Soil Pollut 226, 264 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2537-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2537-9