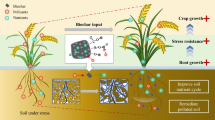
Abstract
Background and Aims
The optimal management of plant nutrition is an effective strategy for sustainable agriculture under various conditions. Soil drying is one of the main limiting factors for plant nutrient acquisition. Plants imposed to these limitations have evolved several strategies such as modifying root-to-shoot ratio, modifying their root anatomy, modifying microbial diversity, and engineering their surrounding soil via rhizodeposition and rhizosheath formation. Rhizosheath is referred to as the soil that remained attached to the root system after being removed from the soil and shacked. Here we reviewed the processes contributing to rhizosheath formation and the mechanisms underlying how it affected the plant's ability to uptake water and nutrients.
Methods
To shed light on the unexplored aspects of rhizosheath and identify potential research directions, we conducted a comprehensive review of the relevant literature on the mechanisms of rhizosheath formation and its impacts on water and nutrient uptake.
Results
The results showed that the presence of mucilage, root hairs and dry-rewetting cycles play a vital role in the formation and strength of rhizosheath. Rhizosheath enables plants to adapt to their environment by keeping the soil and roots hydraulically connected during a soil drying cycle and promoting water and nutrients uptake at the roots-soil interface.
Conclusion
It is concluded that the rhizosheath is the most chemically and biologically active part of the soil. Breeding plants to strengthen their ability to form stable rhizosheath may be one solution to achieving a sustainable agricultural system and maintaining agricultural production under drought stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available upon request to the corresponding author.
References
Abis L, Loubet B, Ciuraru R, Lafouge F, Houot S, Nowak V, Tripied J, Dequiedt S, Maron PA, Sadet-Bourgeteau S (2020) Reduced microbial diversity induces larger volatile organic compound emissions from soils. Sci Rep 10:1–15
Adu MO, Asare PA, Yawson DO, Ackah FK, Amoah KK, Nyarko MA, Andoh DA (2017) Quantifying variations in rhizosheath and root system phenotypes of landraces and improved varieties of juvenile maize. Rhizosphere 3:29–39
Ahmad F, Ashraf N, Da-Chuan Y, Jabeen H, Anwar S, Wahla AQ, Iqbal S (2019) Application of a novel bacterial consortium BDAM for bioremediation of bispyribac sodium in wheat vegetated soil. J Hazard Mater 374:58–65
Ahmed MA, Kroener E, Holz M, Zarebanadkouki M, Carminati A (2014) Mucilage exudation facilitates root water uptake in dry soils. Funct Plant Biol 41:1129–1137
Alami Y, Achouak W, Marol C, Heulin T (2000) Rhizosphere soil aggregation and plant growth promotion of sunflowers by an exopolysaccharide-producing Rhizobium sp. strain isolated from sunflower roots. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3393–3398
Albalasmeh AA, Ghezzehei TA (2014) Interplay between soil drying and root exudation in rhizosheath development. Plant Soil 374:739–751
Alp D, Bulantekin Ö (2021) The microbiological quality of various foods dried by applying different drying methods: a review. Eur Food Res Technol 247:1333–1343
Amato M, Bochicchio R, Mele G, Labella R, Rossi R (2018) Soil structure and stability in the spermosphere of myxosdiaspore chia (Salvia hispanica L.). Soil Res 57:546–558
Aminiyan MM, Rahman MM, Rodríguez-Seijo A, Hajiali Begloo R, Cheraghi M, Aminiyan FM (2022) Elucidating of potentially toxic elements contamination in topsoils around a copper smelter: Spatial distribution, partitioning and risk estimation. Environ Geochem Health 44:1795–1811
Andrade G (2008) Role of Functional Groups of Microorganisms on the Rhizosphere Microcosm Dynamics. In: Varma A, Abbott L, Werner D, Hampp R (eds). Plant Surf Microbiol. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74051-3_4
Ashraf M, Hasnain S, Berge O, Mahmood T (2004) Inoculating wheat seedlings with exopolysaccharide-producing bacteria restricts sodium uptake and stimulates plant growth under salt stress. Biol Fertil Soils 40:157–162
Ashraf M, Hasnain S, Berge O (2006) Effect of exo-polysaccharides producing bacterial inoculation on growth of roots of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plants grown in a salt-affected soil. Int J Environ Sci Technol 3:43–51
Aslam MM, Karanja JK, Dodd IC, Waseem M, Weifeng X (2022) Rhizosheath: An adaptive root trait to improve plant tolerance to phosphorus and water deficits? Plant Cell Environ 45:2861–2874
Aslam MM, Karanja JK, Yuan W, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Xu W (2021) Phosphorus uptake is associated with the rhizosheath formation of mature cluster roots in white lupin under soil drying and phosphorus deficiency. Plant Physiol Biochem 166:531–539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.06.022
Bacher H, Sharaby Y, Walia H, Peleg Z (2022) Modifying root-to-shoot ratio improves root water influxes in wheat under drought stress. J Exp Bot 73:1643–1654
Basirat M, Mousavi SM, Abbaszadeh S, Ebrahimi M, Zarebanadkouki M (2019) The rhizosheath: a potential root trait helping plants to tolerate drought stress. Plant Soil 445:565–575
Belimov A, Ulianich P, Syrova D, Shaposhnikov A, Safronova V, Dodd I (2022) Modulation of tomato root architecture and root hair traits by Pseudomonas brassicacearum and Variovorax paradoxus containing 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase. Biol Plant 66:228–239
Benard P, Zarebanadkouki M, Brax M, Kaltenbach R, Jerjen I, Marone F, Couradeau E, Felde VJ, Kaestner A, Carminati A (2019a) Microhydrological niches in soils: How mucilage and EPS alter the biophysical properties of the rhizosphere and other biological hotspots. Vadose Zone J 18:1–10
Benard P, Zarebanadkouki M, Carminati A (2019b) Physics and hydraulics of the rhizosphere network. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 182:5–8
Benard P, Schepers JR, Crosta M, Zarebanadkouki M, Carminati A (2021) Physics of viscous bridges in soil biological hotspots. Water Resour Res 57:e2021WR030052
Bergmann D, Zehfus M, Zierer L, Smith B, Gabel M (2009) Grass rhizosheaths: associated bacterial communities and potential for nitrogen fixation. W N Am Nat 69:105–114
Bidondo LF, Bompadre J, Pergola M, Silvani V, Colombo R, Bracamonte F, Godeas A (2012) Differential interaction between two Glomus intraradices strains and a phosphate solubilizing bacterium in maize rhizosphere. Pedobiologia 55:227–232
Bochicchio R, Labella R, Vitti A, Nuzzaci M, Logozzo G, Amato M (2022) Root morphology, allometric relations and rhizosheath of ancient and modern tetraploid wheats (Triticum durum Desf.) in response to inoculation with Trichoderma harzianum T-22. Plants 11:159
Borie F, Rubio R, Morales A (2008) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and soil aggregation. Revista de la ciencia del suelo y nutrición vegetal 8:9–18
Brax M, Schaumann GE, Diehl D (2019) Gel formation mechanism and gel properties controlled by Ca2+ in chia seed mucilage and model substances. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 182:92–103
Bristow CE, Campbell G, Wullstein L, Neilson R (1985) Water uptake and storage by rhizosheaths of Oryzopsis hymenoides: a numerical simulation. Physiol Plant 65:228–232
Brown L, George T, Thompson J, Wright G, Lyon J, Dupuy L, Hubbard S, White P (2012) What are the implications of variation in root hair length on tolerance to phosphorus deficiency in combination with water stress in barley (Hordeum vulgare)? Ann Bot 110:319–328
Brown LK, George TS, Neugebauer K, White PJ (2017) The rhizosheath–a potential trait for future agricultural sustainability occurs in orders throughout the angiosperms. Plant Soil 418:115–128
Bucci SJ, Scholz FG, Goldstein G, Meinzer FC, Franco AC, Campanello PI, Villalobos-Vega R, Bustamante M, Miralles-Wilhelm F (2006) Nutrient availability constrains the hydraulic architecture and water relations of savannah trees. Plant Cell Environ 29:2153–2167
Burak E, Quinton JN, Dodd IC (2021) Root hairs are the most important root trait for rhizosheath formation of barley (Hordeum vulgare), maize (Zea mays) and Lotus japonicus (Gifu). Ann Bot 128(1):45–57
Capitani MI, Ixtaina VY, Nolasco SM, Tomás MC (2013) Microstructure, chemical composition and mucilage exudation of chia (Salvia hispanica L.) nutlets from Argentina. J Sci Food Agric 93:3856–3862
Carminati A, Vetterlein D (2013) Plasticity of rhizosphere hydraulic properties as a key for efficient utilization of scarce resources. Ann Bot 112:277–290
Carminati A, Moradi AB, Vetterlein D, Vontobel P, Lehmann E, Weller U, Vogel H-J, Oswald SE (2010) Dynamics of soil water content in the rhizosphere. Plant Soil 332:163–176
Carminati A, Schneider CL, Moradi AB, Zarebanadkouki M, Vetterlein D, Vogel H-J, Hildebrandt A, Weller U, Schüler L, Oswald SE (2011) How the rhizosphere may favor water availability to roots. Vadose Zone J 10:988–998
Carminati A, Benard P, Ahmed MA, Zarebanadkouki M (2017) Liquid bridges at the root-soil interface. Plant Soil 417:1–15
Chen Y, Chen C, Zhou Q, Hu J, Lei Y, Liu W (2021) Specific rhizobacteria responsible in the rhizosheath system of Kengyilia hirsuta. Front Plant Sci 12:785971–785971
Chen Y, Yao Z, Sun Y, Wang E, Tian C, Sun Y, Liu J, Sun C, Tian L (2022) Current studies of the effects of drought stress on root exudates and rhizosphere microbiomes of crop plant species. Int J Mol Sci 23:2374
Cheraghi M, Motesharezadeh B, Alikhani HA, Mousavi SM (2023a) Optimal management of plant nutrition in tomato (Lycopersicon esculent Mill) by using biologic, organic and inorganic fertilizers. J Plant Nutr 46:1560–1579
Cheraghi M, Motesharezadeh B, Mousavi SM, Ma Q, Ahmadabadi Z (2023b) Silicon (Si): a regulator nutrient for optimum growth of wheat under salinity and drought stresses-a review. J Plant Growth Regul:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-023-10959-4
Contesto C, Desbrosses G, Lefoulon C, Béna G, Borel F, Galland M, Gamet L, Varoquaux F, Touraine B (2008) Effects of rhizobacterial ACC deaminase activity on Arabidopsis indicate that ethylene mediates local root responses to plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Plant Sci 175:178–189
Costa OY, Raaijmakers JM, Kuramae EE (2018) Microbial extracellular polymeric substances: ecological function and impact on soil aggregation. Front Microbiol 9:1636
Danin A (1996) Plant adaptations to environmental stresses in desert dunes. Plants of desert dunes. Springer
Daryanto S, Wang L, Jacinthe P-A (2016) Global synthesis of drought effects on maize and wheat production. PLoS ONE 11:e0156362
De la Fuente CC, Simonin M, King E, Moulin L, Bennett MJ, Castrillo G, Laplaze L (2020) An extended root phenotype: the rhizosphere, its formation and impacts on plant fitness. Plant J 103:951–964
De la Fuente CC, Diouf M, Ndour P, Debieu M, Grondin A, Passot S, Champion A, Barrachina C, Pratlong M, Gantet P (2022) Genetic control of rhizosheath formation in pearl millet. Sci Rep 12:1–13
Delhaize E, Gruber BD, Ryan PR (2007) The roles of organic anion permeases in aluminium resistance and mineral nutrition. FEBS Lett 581:2255–2262
Delhaize E, James RA, Ryan PR (2012) Aluminium tolerance of root hairs underlies genotypic differences in rhizosheath size of wheat (Triticum aestivum) grown on acid soil. New Phytol 195:609–619
Dodd IC, Diatloff E (2016) Enhanced root growth of the brb (bald root barley) mutant in drying soil allows similar shoot physiological responses to soil water deficit as wild-type plants. Funct Plant Biol 43:199–206
Esmaeelipoor Jahromi O, Knott M, Mysore Janakiram RK, Rahim R, Kroener E (2022) Pore‐scale simulation of mucilage drainage. Vadose Zone J:e20218. https://doi.org/10.1002/vzj2.20218
Etesami H (2021) Potential advantage of rhizosheath microbiome, in contrast to rhizosphere microbiome, to improve drought tolerance in crops. Rhizosphere 20:100439
Fathi A, Tari DB (2016) Effect of drought stress and its mechanism in plants. Int J Life Sci 10:1–6
Fernandez AL, Sheaffer CC, Wyse DL, Staley C, Gould TJ, Sadowsky MJ (2016) Associations between soil bacterial community structure and nutrient cycling functions in long-term organic farm soils following cover crop and organic fertilizer amendment. Sci Total Environ 566:949–959
Galloway AF, Pedersen MJ, Merry B, Marcus SE, Blacker J, Benning LG, Field KJ, Knox JP (2018) Xyloglucan is released by plants and promotes soil particle aggregation. New Phytol 217:1128–1136
Galloway AF, Akhtar J, Burak E, Marcus SE, Field KJ, Dodd IC, Knox P (2022) Altered properties and structures of root exudate polysaccharides in a root hairless mutant of barley. Plant Physiol 190:1214–1227
Gardner W, Parbery D, Barber D (1982) The acquisition of phosphorus by Lupinus albus LI Some characteristics of the soil/root interface. Plant Soil 70:107–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02374754
George TS, Brown LK, Ramsay L, White PJ, Newton AC, Bengough AG, Russell J, Thomas WT (2014) Understanding the genetic control and physiological traits associated with rhizosheath production by barley (H ordeum vulgare). New Phytol 203:195–205
Gregory PJ (2006) Roots, rhizosphere and soil: the route to a better understanding of soil science? Eur J Soil Sci 57:2–12
Grunert O, Robles-Aguilar AA, Hernandez-Sanabria E, Schrey SD, Reheul D, Van Labeke M-C, Vlaeminck SE, Vandekerckhove TG, Mysara M, Monsieurs P (2019) Tomato plants rather than fertilizers drive microbial community structure in horticultural growing media. Sci Rep 9:1–15
Hale M, Moore L (1980) Factors affecting root exudation II: 1970–1978. Adv Agron 31:93–124
Haling RE, Richardson AE, Culvenor RA, Lambers H, Simpson RJ (2010) Root morphology, root-hair development and rhizosheath formation on perennial grass seedlings is influenced by soil acidity. Plant Soil 335:457–468
Haling RE, Brown LK, Bengough AG, Young IM, Hallett PD, White PJ, George TS (2013) Root hairs improve root penetration, root–soil contact, and phosphorus acquisition in soils of different strength. J Exp Bot 64:3711–3721
Haling RE, Brown LK, Bengough AG, Valentine TA, White PJ, Young IM, George TS (2014) Root hair length and rhizosheath mass depend on soil porosity, strength and water content in barley genotypes. Planta 239:643–651
Hartman S (2020) Trapped in the rhizosheath: root-bacterial interactions modulate ethylene signaling. Am Soc Plant Biol 183(2):443–444. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.20.00379
Hartnett DC, Wilson GW, Ott JP, Setshogo M (2013) Variation in root system traits among African semi-arid savanna grasses: Implications for drought tolerance. Austral Ecol 38:383–392
He H, Wu M, Su R, Zhang Z, Chang C, Peng Q, Dong Z, Pang J, Lambers H (2021) Strong phosphorus (P)-zinc (Zn) interactions in a calcareous soil-alfalfa system suggest that rational P fertilization should be considered for Zn biofortification on Zn-deficient soils and phytoremediation of Zn-contaminated soils. Plant Soil 461:119–134
Hendriks P-W, Ryan PR, Hands P, Rolland V, Gurusinghe S, Weston LA, Rebetzke GJ, Delhaize E (2022) Selection for early shoot vigour in wheat increases root hair length but reduces epidermal cell size of roots and leaves. J Exp Bot 73:2499–2510
Holz M, Zarebanadkouki M, Kaestner A, Kuzyakov Y, Carminati A (2018a) Rhizodeposition under drought is controlled by root growth rate and rhizosphere water content. Plant Soil 423:429–442
Holz M, Zarebanadkouki M, Kuzyakov Y, Pausch J, Carminati A (2018b) Root hairs increase root exudation and carbon input into soil. Ann Bot 121:61–69
Honvault N, Houben D, Firmin S, Meglouli H, Laruelle F, Fontaine J, Lounès-Hadj Sahraoui A, Coutu A, Lambers H, Faucon MP (2021) Interactions between belowground traits and rhizosheath fungal and bacterial communities for phosphorus acquisition. Funct Ecol. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13823
Huang B, North GB, Nobel PS (1993) Soil sheaths, photosynthate distribution to roots, and rhizosphere water relations for Opuntia ficus-indica. Int J Plant Sci 154:425–431
Huang J, Liu W, Deng M, Wang X, Wang Z, Yang L, Liu L (2020) Allocation and turnover of rhizodeposited carbon in different soil microbial groups. Soil Biol Biochem 150:107973
Hussain HA, Men S, Hussain S, Chen Y, Ali S, Zhang S, Zhang K, Li Y, Xu Q, Liao C (2019) Interactive effects of drought and heat stresses on morpho-physiological attributes, yield, nutrient uptake and oxidative status in maize hybrids. Sci Rep 9:1–12
James RA, Weligama C, Verbyla K, Ryan PR, Rebetzke GJ, Rattey A, Richardson AE, Delhaize E (2016) Rhizosheaths on wheat grown in acid soils: phosphorus acquisition efficiency and genetic control. J Exp Bot 67:3709–3718
Jungk AO (2002) Dynamics of nutrient movement at the soil-root interface. Plant roots. CRC Press
Karanja JK, Aslam MM, Qian Z, Yankey R, Dodd IC (2021) Weifeng X (2021) Abscisic acid mediates drought-enhanced rhizosheath formation in tomato. Front Plant Sci 12:658787. eCollection 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2021.658787
Koehler T, Schaum C, Tung S-Y, Steiner F, Tyborski N, Wild AJ, Akale A, Pausch J, Lueders T, Wolfrum S (2023) Above and belowground traits impacting transpiration decline during soil drying in 48 maize (Zea mays) genotypes. Ann Bot 131:373–386
Kong D, Wang J, Yang F, Shao P (2018) Rhizosheaths stimulate short-term root decomposition in a semiarid grassland. Sci Total Environ 640:1297–1301
Kroener E, Zarebanadkouki M, Kaestner A, Carminati A (2014) Nonequilibrium water dynamics in the rhizosphere: How mucilage affects water flow in soils. Water Resour Res 50:6479–6495
Liu X, Zhang W, Wang X, Cai Y, Chang J (2015) Root–soil air gap and resistance to water flow at the soil–root interface of Robinia pseudoacacia. Tree Physiol 35:1343–1355
Liu T-Y, Chen M-X, Zhang Y, Zhu F-Y, Liu Y-G, Tian Y, Fernie AR, Ye N, Zhang J (2019) Comparative metabolite profiling of two switchgrass ecotypes reveals differences in drought stress responses and rhizosheath weight. Planta 250:1355–1369
Liu TY, Ye N, Wang X, Das D, Tan Y, You X, Long M, Hu T, Dai L, Zhang J (2021) Drought stress and plant ecotype drive microbiome recruitment in switchgrass rhizosheath. J Integr Plant Biol 63:1753–1774
Liu S, Li J, Ji X, Fang Y (2022) Influence of root distribution patterns on soil dynamic characteristics. Sci Rep 12:1–14
Lynch JP, Chimungu JG, Brown KM (2014) Root anatomical phenes associated with water acquisition from drying soil: targets for crop improvement. J Exp Bot 65:6155–6166
Lynch JP, Strock CF, Schneider HM, Sidhu JS, Ajmera I, Galindo-Castañeda T, Klein SP, Hanlon MT (2021) Root anatomy and soil resource capture. Plant Soil 466:21–63
Ma X, Liu Y, Zarebanadkouki M, Razavi BS, Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y (2018) Spatiotemporal patterns of enzyme activities in the rhizosphere: effects of plant growth and root morphology. Biol Fertil Soils 54:819–828
Mahmood T, Mehnaz S, Fleischmann F, Ali R, Hashmi Z, Iqbal Z (2014) Soil sterilization effects on root growth and formation of rhizosheaths in wheat seedlings. Pedobiologia 57:123–130
Marasco R, Mosqueira MJ, Fusi M, Ramond J-B, Merlino G, Booth JM, Maggs-Kölling G, Cowan DA, Daffonchio D (2018) Rhizosheath microbial community assembly of sympatric desert speargrasses is independent of the plant host. Microbiome 6:1–18
Marin M, Feeney D, Brown L, Naveed M, Ruiz S, Koebernick N, Bengough AG, Hallett P, Roose T, Puértolas J (2021) Significance of root hairs for plant performance under contrasting field conditions and water deficit. Ann Bot 128:1–16
Marschner P, Rengel Z (2023) Nutrient availability in soils. Marschner’s mineral nutrition of plants. Elsevier
McCully ME (1999) Roots in soil: unearthing the complexities of roots and their rhizospheres. Annu Rev Plant Biol 50:695
McCully M, Boyer J (1997) The expansion of maize root-cap mucilage during hydration. 3. Changes in water potential and water content. Physiol Plant 99:169–177
Miller R, Jastrow J (1990) Hierarchy of root and mycorrhizal fungal interactions with soil aggregation. Soil Biol Biochem 22:579–584
Minemba D, Martin BC, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Gleeson DB (2020) Phosphate fertiliser alters carboxylates and bacterial communities in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) rhizosheaths. Plant Soil 454:245–260
Mo X, Wang M, Wang Y, Zhang P, Zhang A, Kong D, Zeng H, Wang J (2022) High content and distinct spectroscopic characteristics of water-extractable organic matter in rhizosheath soils in a semiarid grassland. Rhizosphere 23:100553
Moradi AB, Carminati A, Vetterlein D, Vontobel P, Lehmann E, Weller U, Hopmans JW, Vogel HJ, Oswald SE (2011) Three-dimensional visualization and quantification of water content in the rhizosphere. New Phytol 192:653–663
Morel JL, Habib L, Plantureux S, Guckert A (1991) Influence of maize root mucilage on soil aggregate stability. Plant Soil 136:111–119
Moshiri F, Ebrahimi H, Ardakani MR, Rejali F, Mousavi SM (2019) Biogeochemical distribution of Pb and Zn forms in two calcareous soils affected by mycorrhizal symbiosis and alfalfa rhizosphere. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 179:241–248
Mousavi SM, Motesharezadeh B, Hosseini HM, Alikhani H, Zolfaghari AA (2018) Root-induced changes of Zn and Pb dynamics in the rhizosphere of sunflower with different plant growth promoting treatments in a heavily contaminated soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:206–16
Mousavi SM, Srivastava AK, Cheraghi M (2023) Soil health and crop response of biochar: an updated analysis. Arch Agron Soil Sci 69:1085–1110
Nambiar E (1976) The uptake of zinc-65 by oats in relation to soil water content and root growth. Soil Res 14:67–74
Ndour PMS, Heulin T, Achouak W, Laplaze L, Cournac L (2020) The rhizosheath: from desert plants adaptation to crop breeding. Plant Soil 456:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04700-3
Newcomb CJ, Qafoku NP, Grate JW, Bailey VL, De Yoreo JJ (2017) Developing a molecular picture of soil organic matter–mineral interactions by quantifying organo–mineral binding. Nat Commun 8(1):396
Nilsen-Nygaard J, Hattrem MN, Draget KI (2016) Propylene glycol alginate (PGA) gelled foams: A systematic study of surface activity and gelling properties as a function of degree of esterification. Food Hydrocolloids 57:80–91
North GB, Nobel PS (1997) Drought-induced changes in soil contact and hydraulic conductivity for roots of Opuntia ficus-indica with and without rhizosheaths. Plant Soil 191:249–258
Opoku VA, Yawson DO, Asare PA, Afutu E, Kotochi MC, Amoah KK, Adu MO (2022) Root hair and rhizosheath traits contribute to genetic variation and phosphorus use efficiency in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp). Rhizosphere 21:100463
Othman AA, Amer WM, Fayez M, Hegazi N (2004) Rhizosheath of Sinai desert plants is a potential repository for associative diazotrophs. Microbiol Res 159:285–293
Pang J, Ryan MH, Siddique KH, Simpson RJ (2017) Unwrapping the rhizosheath. Plant Soil 418:129–139
Peterson RL, Farquhar ML (1996) Root hairs: specialized tubular cells extending root surfaces. Bot Rev 62:1–40
Pinton R, Varanini Z, Nannipieri P (2000) The rhizosphere as a site of biochemical interactions among soil components, plants, and microorganisms. The rhizosphere. CRC Press
Prendergast-Miller M, Duvall M, Sohi S (2014) Biochar–root interactions are mediated by biochar nutrient content and impacts on soil nutrient availability. Eur J Soil Sci 65:173–185
Price SR (1911) The roots of some North African desert-grasses. New Phytol 10:328–340
Rabbi SM, Tighe MK, Flavel RJ, Kaiser BN, Guppy CN, Zhang X, Young IM (2018) Plant roots redesign the rhizosphere to alter the three-dimensional physical architecture and water dynamics. New Phytol 219:542–550
Rabbi SM, Warren CR, Macdonald C, Trethowan RM, Young IM (2022) Soil-root interaction in the rhizosheath regulates the water uptake of wheat. Rhizosphere 21:100462, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rhisph.2021.100462
Rabbi SM, Warren CR, Macdonald C, Trethowan RM, Young IM (2021) Soil-root interaction in the rhizosheath regulates the water uptake of wheat. Rhizosphere:100462
Raynaud X, Leadley PW (2004) Soil characteristics play a key role in modeling nutrient competition in plant communities. Ecology 85:2200–2214
Razavi BS, Zarebanadkouki M, Blagodatskaya E, Kuzyakov Y (2016) Rhizosphere shape of lentil and maize: spatial distribution of enzyme activities. Soil Biol Biochem 96:229–237
Roberson EB, Firestone MK (1992) Relationship between desiccation and exopolysaccharide production in a soil Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1284–1291
Rovira AD (1969) Plant root exudates. Bot Rev 35:35–57
Ryan MH, Kidd DR, Sandral GA, Yang Z, Lambers H, Culvenor RA, Stefanski A, Nichols PG, Haling RE, Simpson RJ (2016) High variation in the percentage of root length colonised by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi among 139 lines representing the species subterranean clover (Trifolium subterraneum). Appl Soil Ecol 98:221–232
Sasaki T, Yamamoto Y, Ezaki B, Katsuhara M, Ahn SJ, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Matsumoto H (2004) A wheat gene encoding an aluminum-activated malate transporter. Plant J 37:645–653
Schmidt R, Etalo DW, De Jager V, Gerards S, Zweers H, De Boer W, Garbeva P (2016) Microbial small talk: volatiles in fungal–bacterial interactions. Front Microbiol 6:1495
Shane MW, McCully ME, Canny MJ, Pate JS, Huang C, Ngo H, Lambers H (2010) Seasonal water relations of Lyginia barbata (Southern rush) in relation to root xylem development and summer dormancy of root apices. New Phytol 185:1025–1037
Sharma M, Pang J, Wen Z, De Borda A, Kim HS, Liu Y, Lambers H, Ryan MH, Siddique KH (2021) A significant increase in rhizosheath carboxylates and greater specific root length in response to terminal drought is associated with greater relative phosphorus acquisition in chickpea. Plant Soil 460:51–68
Song L, Pan Z, Dai Y, Chen L, Zhang L, Liao Q, Yu X, Guo H, Zhou G (2020) Characterization and comparison of the bacterial communities of rhizosphere and bulk soils from cadmium-polluted wheat fields. PeerJ 8:e10302
Unno Y, Okubo K, Wasaki J, Shinano T, Osaki M (2005) Plant growth promotion abilities and microscale bacterial dynamics in the rhizosphere of Lupin analysed by phytate utilization ability. Environ Microbiol 7:396–404
Van Veelen A, Koebernick N, Scotson CS, McKay-Fletcher D, Huthwelker T, Borca CN, Mosselmans JFW, Roose T (2020) Root-induced soil deformation influences Fe, S and P: rhizosphere chemistry investigated using synchrotron XRF and XANES. New Phytol 225:1476–1490
Vives-Peris V, de Ollas C, Gómez-Cadenas A, Pérez-Clemente RM (2020) Root exudates: from plant to rhizosphere and beyond. Plant Cell Rep 39:3–17
Volkens G (1887) Die Flora der aegyptisch-arabischen Wüste auf Grundlage anatomisch-physiologischer Forschungen. Borntraeger
Walker TS, Bais HP, Grotewold E, Vivanco JM (2003) Root exudation and rhizosphere biology. Plant Physiol 132:44–51
Wang H, Inukai Y, Yamauchi A (2006) Root development and nutrient uptake. Crit Rev Plant Sci 25:279–301
Watt M, McCully M, Jeffree C (1993) Plant and bacterial mucilages of the maize rhizosphere: comparison of their soil binding properties and histochemistry in a model system. Plant Soil 151:151–165
Watt M, McCully ME, Canny MJ (1994) Formation and stabilization of rhizosheaths of Zea mays L. (Effect of soil water content). Plant Physiol 106:179–186
Wei M, Xue-Xian L, Chun-Jian L (2011) Modulation of soil particle size and nutrient availability in the maize rhizosheath. Pedosphere 21:483–490
Wen Z, Pang J, Tueux G, Liu Y, Shen J, Ryan MH, Lambers H, Siddique KH (2020) Contrasting patterns in biomass allocation, root morphology and mycorrhizal symbiosis for phosphorus acquisition among 20 chickpea genotypes with different amounts of rhizosheath carboxylates. Funct Ecol 34:1311–1324
Wen Z, Pang J, Ryan MH, Shen J, Siddique KH, Lambers H (2021) In addition to foliar manganese concentration, both iron and zinc provide proxies for rhizosheath carboxylates in chickpea under low phosphorus supply. Plant Soil 465:31–46
Whalley WR, Riseley B, Leeds-Harrison PB, Bird NR, Leech PK, Adderley WP (2005) Structural differences between bulk and rhizosphere soil. Eur J Soil Sci 56:353–360
Williams A, de Vries FT (2020) Plant root exudation under drought: implications for ecosystem functioning. New Phytol 225:1899–1905
Williams A, Langridge H, Straathof AL, Muhamadali H, Hollywood KA, Goodacre R, de Vries FT (2022) Root functional traits explain root exudation rate and composition across a range of grassland species. J Ecol 110(1):21–33
Wu A, Fang Y, Liu S, Wang H, Xu B, Zhang S, Deng X, Palta JA, Siddique KH, Chen Y (2021) Root morphology and rhizosheath acid phosphatase activity in legume and graminoid species respond differently to low phosphorus supply. Rhizosphere 19:100391
Wullstein L (1980) Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) associated with rhizosheaths of Indian ricegrass used in stabilization of the Slick Rock, Colorado tailings pile. Rangel. Ecol 33:204–206.
York LM, Carminati A, Mooney SJ, Ritz K, Bennett MJ (2016) The holistic rhizosphere: integrating zones, processes, and semantics in the soil influenced by roots. J Exp Bot 67:3629–3643
Young I (1995) Variation in moisture contents between bulk soil and the rhizosheath of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. cv. Wembley). New Phytol 130:135–139
Yu RP, Li XX, Xiao ZH, Lambers H, Li L (2020) Phosphorus facilitation and covariation of root traits in steppe species. New Phytol 226:1285–1298
Yuan J, Zhao M, Li R, Huang Q, Raza W, Rensing C, Shen Q (2017) Microbial volatile compounds alter the soil microbial community. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:22485–22493
Zarebanadkouki M, Kim YX, Carminati A (2013) Where do roots take up water? Neutron radiography of water flow into the roots of transpiring plants growing in soil. New Phytol 199:1034–1044
Zarebanadkouki M, Fink T, Benard P, Banfield CC (2019) Mucilage facilitates nutrient diffusion in the drying rhizosphere. Vadose Zone Journal 18:1–13
Zarebanadkouki M, Kuzyakov Y, Carminati A (2016) A new method to enhance rhizosheath formation. Publication: EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts; Bibcode: 2016EGUGA..18..325A. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016EGUGA..18..325A/abstract
Zargar SM, Gupta N, Nazir M, Mahajan R, Malik FA, Sofi NR, Shikari AB, Salgotra R (2017) Impact of drought on photosynthesis: Molecular perspective. Plant Gene 11:154–159
Zhang Y, Du H, Gui Y, Xu F, Liu J, Zhang J, Xu W (2020a) Moderate water stress in rice induces rhizosheath formation associated with abscisic acid and auxin responses. J Exp Bot 71:2740–2751
Zhang Y, Du H, Xu F, Ding Y, Gui Y, Zhang J, Xu W (2020b) Root-bacteria associations boost rhizosheath formation in moderately dry soil through ethylene responses. Plant Physiol 183:780–792
Zhang Y, Xu F, Ding Y, Du H, Zhang Q, Dang X, Cao Y, Dodd IC, Xu W (2021a) Abscisic acid mediates barley rhizosheath formation under mild soil drying by promoting root hair growth and auxin response. Plant Cell Environ 44:1935–1945
Zhang Z, Su R, Chang C, Cheng X, Peng Q, Lambers H, He H (2021b) Effects of oxytetracycline on plant growth, phosphorus uptake, and carboxylates in the rhizosheath of alfalfa. Plant Soil 461:501–515
Zou Y-N, Chen X, Srivastava A, Wang P, Xiang L, Wu Q-S (2016) Changes in rhizosphere properties of trifoliate orange in response to mycorrhization and sod culture. Appl Soil Ecol 107:307–312
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their sincere gratitude to the two anonymous reviewers who provided valuable feedback on the first version of our manuscript. Their insightful comments and constructive recommendations and suggestions were fundamental in shaping the final version of this work.
Funding
“The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to reviewing the literature, writing, and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
“The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.”
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Andrea Schnepf.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheraghi, M., Mousavi, S.M. & Zarebanadkouki, M. Functions of rhizosheath on facilitating the uptake of water and nutrients under drought stress: A review. Plant Soil 491, 239–263 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06126-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-023-06126-z