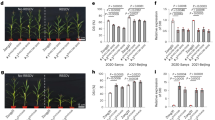
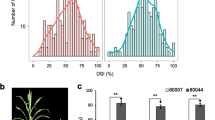
Abstract
Maize rough dwarf disease (MRDD) caused by pathogenic viruses in the genus Fijivirus in the family Reoviridae is one of the most destructive diseases in maize. The pyramiding of effective resistance genes into maize varieties is a potential approach to reduce the damage resulting from the disease. Two major quantitative trait loci (QTLs) (qMrdd2 and qMrdd8) have been previously identified. The resistance genes ZmGLK36 and ZmGDIα-hel have also been cloned with the functional markers Indel-26 and IDP25K, respectively. In this study, ZmGLK36 and ZmGDIα-hel were introgressed to improve MRDD resistance of maize lines (Zheng58, Chang7-2, B73, Mo17, and their derived hybrids Zhengdan958 and B73 × Mo17) via marker-assisted selection (MAS). The converted lines and their derived hybrids, carrying one or two genes, were evaluated for MRDD resistance using artificial inoculation methods. The double-gene pyramiding lines and their derived hybrids exhibited increased resistance to MRDD compared to the monogenic lines and the respective hybrids. The genetic backgrounds of the converted lines were highly similar (90.85–98.58%) to the recurrent parents. In addition, agronomic trait evaluation demonstrated that pyramiding lines with one or two genes and their derived hybrids were not significantly different from the recurrent parents and their hybrids under nonpathogenic stress, including period traits (tasseling, pollen shedding, and silking), yield traits (ear length, grain weight per ear and 100-kernel weight) and quality traits (protein and starch content). There were differences in plant architecture traits between the improved lines and their hybrids. This study illustrated the successful development of gene pyramiding for improving MRDD resistance by advancing the breeding process.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data are enclosed either in the main text or as supplementary materials. Other data can be requested from the corresponding author.
References
Chen YC, Hu CC, Chang FY et al (2021) Marker-assisted development and evaluation of monogenic lines of rice cv. Kaohsiung 145 carrying blast resistance genes. Plant Dis 105(12):3858–3868
Chen G, Zhang B, Ding J et al (2022) Cloning southern corn rust resistant gene RppK and its cognate gene AvrRppK from Puccinia polysora. Nat Commun 13(1):4392
Chen P, Gao G, Lou G et al (2023) Improvement of rice blast resistance in TGMS line HD9802S through optimized anther culture and molecular marker-assisted selection. Int J Mol Sci 24(19):14446
Das G, Patra JK, Baek KH (2017) Insight into MAS: A molecular tool for development of stress resistant and quality of rice through gene stacking. Front Plant Sci 8:985
Deng C, Leonard A, Cahill J et al (2022) The RppC-AvrRppC NLR-effector interaction mediates the resistance to southern corn rust in maize. Mol Plant 15(5):904–912
Fang C, Wang Z, Wang P et al (2021) Heterosis derived from nonadditive effects of the BnFLC homologs coordinates early flowering and high yield in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Front Plant Sci 12:798371
Gautam T, Dhillon GS, Saripalli G et al (2020) Marker-assisted pyramiding of genes/QTL for grain quality and rust resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Breed 40(5):49
Han XH, Chen TM, Yue RQ et al (2019) A rice black-streaked dwarf virus replication curve model to evaluate maize rough dwarf disease resistance. Plant Dis 103(5):868–873
Han JN, Wang MJ, Zhao XC et al (2020) Establishment and Optimization of a Near-Infrared Model of Maize Starch Content. Crop Sci 28(6):81–87 (in Chinese)
Han G, Yan H, Gu T et al (2023) Identification of a wheat powdery mildew dominant resistance gene in the Pm5 Locus for high-throughput marker-assisted selection. Plant Dis 107(2):450–456
He L, Zou L, Huang Q et al (2020) Development of InDel markers of Bph3 and pyramiding of four brown planthopper resistance genes into an elite rice variety. Mol Breed 40(10):95
Hu W, Fu L, Gao D et al (2023) Marker-assisted selection to pyramid Fusarium head blight resistance loci Fhb1 and Fhb2 in the high-quality soft wheat cultivar Yangmai 15. J of Integr Agr 22(2):360–370
Jena KK, Kim SM (2010) Current status of brown planthopper (BPH) resistance and genetics. Rice 3(2–3):161–171
Jiang H, Feng Y, Bao L et al (2012) Improving blast resistance of Jin 23B and its hybrid rice by marker-assisted gene pyramiding. Mol Breed 30(4):1679–1688
Kumari M, Rai AK, Devanna BN et al (2017) Co-transformation mediated stacking of blast resistance genes Pi54 and Pi54rh in rice provides broad spectrum resistance against Magnaportheoryzae. Plant Cell Rep 36(11):1747–1755
Li R, Song W, Wang B et al (2018) Identification of a locus conferring dominant resistance to maize rough dwarf disease in maize. Sci Rep 8(1):3248
Li M, Pan X, Li H (2022a) Pyramiding of gn1a, gs3, and ipa1 exhibits complementary and additive effects on rice yield. Int J Mol Sci 23(20):12478
Li X, Lin F, Li C et al (2022b) Golden 2-like transcription factor contributes to the major QTL against rice black-streaked dwarf virus disease. Theor Appl Genet 135(12):4233–4243
Liu C, Hua J, Liu C et al (2016) Fine mapping of a quantitative trait locus conferring resistance to maize rough dwarf disease. Theor Appl Genet 129(12):2333–2342
Liu Q, Deng S, Liu B et al (2020) A helitron-induced RabGDIα variant causes quantitative recessive resistance to maize rough dwarf disease. Nat Commun 11(1):495
Liu C, Kong M, Yang F et al (2022) Targeted generation of null mutants in ZmGDIα confers resistance against maize rough dwarf disease without agronomic penalty. Plant Biotechnol J 20(5):803–805
Luan J, Wang F, Li Y et al (2012) Mapping quantitative trait loci conferring resistance to rice black-streaked virus in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 125(4):781–791
Mi J, Yang D, Chen Y et al (2018) Accelerated molecular breeding of a novel P/TGMS line with broad-spectrum resistance to rice blast and bacterial blight in two-line hybrid rice. Rice 11(1):11
Miah G, Rafii MY, Ismail MR et al (2013) A review of microsatellite markers and their applications in rice breeding programs to improve blast disease resistance. Int J Mol Sci 14(11):22499–22528
Peng P, Jiang H, Luo L et al (2023) Pyramiding of multiple genes to improve rice blast resistance of photo-thermo sensitive male sterile line, without yield penalty in hybrid rice production. Plants-Basel 12(6):1389
Qiu Y, Guo J, Jing S et al (2010) High-resolution mapping of the brown planthopper resistance gene Bph6 in rice and characterizing its resistance in the 9311 and Nipponbare near isogenic backgrounds. Theor Appl Genet 121(8):1601–1611
Rathnayake AS, Allué J, Llugany M et al (2014) High quality DNA obtained from a single seed of Vitis vinifera L. using rapid DNA extraction method. Am J Plant Sci 05(13):2023–2030
Reinke R, Kim SM, Kim BK (2018) Developing japonica rice introgression lines with multiple resistance genes for brown planthopper, bacterial blight, rice blast, and rice stripe virus using molecular breeding. Mol Genet Genomics 293(6):1565–1575
Sharma A, Srivastava P, Mavi GS et al (2021) Resurrection of wheat cultivar PBW343 using marker-assisted gene pyramiding for rust resistance. Front Plant Sci 12:570408
Shi L, Weng J, Liu C et al (2013) Identification of promoter motifs regulating ZmeIF4E expression level involved in maize rough dwarf disease resistance in maize (Zea Mays L.). Mol Genet Genomics 288(3–4):89–99
Tao Y, Liu Q, Wang H et al (2013) Identification and fine-mapping of a QTL, qMrdd1, that confers recessive resistance to maize rough dwarf disease. BMC Plant Biol 13:145
Tong L, Yan M, Zhu M et al (2022) ZmCCT haplotype H5 improves yield, stalk-rot resistance, and drought tolerance in maize. Front Plant Sci 13:984527
Wang C, Yang Q, Wang W et al (2017) A transposon-directed epigenetic change in ZmCCT underlies quantitative resistance to Gibberella stalk rot in maize. New Phytol 215(4):1503–1515
Wang X, Yang Q, Dai Z et al (2019) Identification of QTLs for resistance to maize rough dwarf disease using two connected RIL populations in maize. PLoS ONE 14(12):e0226700
Wang P, Liu J, Lyu Y et al (2022a) A review of vector-borne rice viruses. Viruses 14(10):2258
Wang R, Du K, Jiang T et al (2022b) Comparative proteomic analyses of susceptible and resistant maize inbred lines at the stage of enations forming following infection by rice black-streaked dwarf virus. Viruses 14(12):2604
Wang F, Zhang M, Hu Y et al (2023) Pyramiding of adult-plant resistance genes enhances all-stage resistance to wheat stripe rust. Plant Dis 107(3):879–885
Xu Z, Hua J, Wang F et al (2020) Marker-assisted selection of qMrdd8 to improve maize resistance to rough dwarf disease. Breed Sci 70(2):183–192
Xu Z, Wang F, Zhou Z et al (2022) Identification and fine-mapping of a novel QTL, qMrdd2, that confers resistance to maize rough dwarf disease. Plant Dis 106(1):65–72
Xu Z, Zhou Z, Cheng Z et al (2023) A transcription factor ZmGLK36 confers broad resistance to maize rough dwarf disease in cereal crops. Nat Plants 9(10):1720–1733
Yang Y, Wang A, Wang M et al (2022) ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCF2 and ABCG9 regulate rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection in its insect vector, Laodelphaxstriatellus (Fallén). B Entomol Res 112(3):327–334
Ye J, Zhong T, Zhang D et al (2019) The auxin-regulated protein ZmAuxRP1 coordinates the balance between root growth and stalk rot disease resistance in maize. Mol Plant 12(3):360–373
Yue R, Sun Q, Ding J et al (2022) Functional analysis revealed the involvement of ZmABCB15 in resistance to rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection. BMC Plant Biol 22(1):484
Zhang J, Dong Y, Wang M et al (2021a) MicroRNA-315-5p promotes rice black-streaked dwarf virus infection by targeting a melatonin receptor in the small brown planthopper. Pest Manag Sci 77(7):3561–3570
Zhang Y, Yang Z, Ma H et al (2021b) Pyramiding of Fusarium head blight resistance quantitative trait loci, Fhb1, Fhb4, and Fhb5, in modern Chinese wheat cultivars. Front Plant Sci 12:694023
Zhang N, Qi X, Li X et al (2022) Introgression of the RppQ gene from field corn improves southern rust resistance in sweet corn. Mol Breed 42(9):53
Zhao X, Tan G, Xing Y et al (2012) Marker-assisted introgression of qHSR1 to improve maize resistance to head smut. Mol Breed 30(2):1077–1088
Zhao M, Liu S, Pei Y et al (2022) Identification of genetic loci associated with rough dwarf disease resistance in maize by integrating GWAS and linkage mapping. Plant Sci 315:111100
Zhou C, Xiong H, Fu M et al (2023) Genetic mapping and identification of Rht8-B1 that regulates plant height in wheat. BMC Plant Biol 23(1):333
Zuo W, Chao Q, Zhang N et al (2015) A maize wall-associated kinase confers quantitative resistance to head smut. Nat Genet 47(2):151–157
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFD1201802), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32301799) and the Agricultural Science & Technology Innovation Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The experiment was designed and conceived by JW and JZ; GL and ZX were responsible for data analysis, manuscript writing, and artificial inoculation of RBSDV; ZZ and JH extracted the DNA; XL, ZH and ML provided the material; DZ, JW, CM and HY recorded and analyzed the agronomic traits and MRDD resistance. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Xu, Z., Wang, J. et al. Gene pyramiding of ZmGLK36 and ZmGDIα-hel for rough dwarf disease resistance in maize. Mol Breeding 44, 25 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-024-01466-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-024-01466-9