Abstract
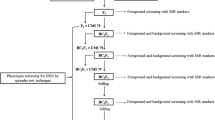
Head smut, one of the most devastating diseases in maize, causes severe yield losses worldwide. Resistance to head smut has been proven to be a quantitative inherited trait. In our previous study, a major resistance quantitative trait locus (named qHSR1) was detected on maize chromosome 2 (bin 2.09), and a number of molecular markers have been developed in the qHSR1 region. Here, we report the marker-assisted introgression of qHSR1 to improve maize resistance to head smut. The 10 maize inbred lines, namely Ji853, 444, 98107, 99094, Chang7-2, V022, V4, 982, 8903, and 8902, which have high yield potential but are susceptible to head smut, were selected for resistance improvement. Each of the 10 high-yielding lines was crossed with a donor parent Ji1037 that is completely resistant to head smut, followed by five generations of backcrossing to the respective recurrent parent. Marker-assisted foreground selection was conducted to identify qHSR1. Recombinant selection was carried out in the fourth backcross (BC4) generation by using the flanking markers to reduce the size of the Ji1037 donor segment carrying qHSR1. Background selection was performed in the BC5 generation with genome-wide SSR markers to select the line with the highest recovery rate of the recurrent parent genome. Self-pollination was conducted twice for the BC5 plant with both the shortest qHSR1 region and the highest recovery rate to obtain converted inbred lines harboring qHSR1. The 10 converted inbred lines all showed substantial improvement in resistance to head smut. Furthermore, the hybrids prepared from the converted lines also showed significant increase in resistance to head smut, while remaining mostly unchanged for other agronomic traits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchez A, Hospital F, Causse M, Gallais A, Charcosset A (2002) Marker-assisted introgression of favorable alleles at quantitative trait loci between maize elite lines. Genetics 162(4):1945–1959
Charcosset A, Moreau L (2004) Use of molecular markers for the development of new cultivars and the evaluation of genetic diversity. Euphytica 137(1):81–94
Chen S, Xu CG, Lin XH, Zhang Q (2001) Improving bacterial blight resistance of ‘6078’, an elite restorer line of hybrid rice, by molecular marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed 120(2):133–137
Chen YS, Chao Q, Tan GQ, Zhao J, Zhang MJ, Ji Q, Xu ML (2008) Identification and fine-mapping of a major QTL conferring resistance against head smut in maize. Theor Appl Genet 117(8):1241–1252. doi:10.1007/s00122-008-0858-4
Collard BCY, Jahufer MZZ, Brouwer JB, Pang ECK (2005) An introduction to markers, quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping and marker-assisted selection for crop improvement: The basic concepts. Euphytica 142(1–2):169–196. doi:10.1007/s10681-005-1681-5
Frederiksen RA (1977) Head smuts of corn and sorghum. Proc Corn Sorghum Res Conf 32:89–104
Frisch M, Bohn M, Melchinger A (1999) Minimum sample size and optimal positioning of flanking markers in marker-assisted backcrossing for transfer of a target gene. Crop Sci 39:967–975
Holland J (2001) Epistasis and plant breeding. Plant Breed Rev 21:27–92
Hospital F (2005) Selection in backcross programmes. Philos Trans R Soc B 360:1503–1511. doi:10.1098/rstb.2005.1670
Hospital F, Charcosset A (1997) Marker-assisted introgression of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 147(3):1469–1485
Liao CY, Wu P, Hu B, Yi KK (2001) Effects of genetic background and environment on QTLs and epistasis for rice (Oryza sativa L.) panicle number. Theor Appl Genet 103(1):104–111
Liu SP, Li X, Wang CY, Li XH, He YQ (2003) Improvement of resistance to rice blast in Zhenshan 97 by molecular marker-aided selection. Acta Bot Sin 45(11):1346–1350
Liu WG, Sun ZC, Jing SL, Zhou XD (2008) Discussion on prevention and control of maize head smut (in Chinese). J Maize Sci China 16(3):121–122, 125
Lu XW, Brewbaker JL (1999) Molecular mapping of QTLs conferring resistance to Sphacelotheca reiliana (Kühn) Clint. Maize Genet Coop Newsl 73:36
Lübberstedt T, Xia XC, Tan G, Liu X, Melchinger AE (1999) QTL mapping of resistance to Sporisorium reiliana in maize. Theor Appl Genet 99(3–4):593–598
Ma BY, Li YL, Duan SK (1983) Study on the resistance to head smut of corn varieties and its inheritance (in Chinese). Sci Agric Sin 4:12–17
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8(19):4321–4325
Ribaut JM, Hoisington D (1998) Marker-assisted selection: new tools and strategies. Trends Plant Sci 3(6):236–239
Ribaut JM, Morris M, Dreher K, Khairallah M (2003) Money matters (II): costs of maize inbred line conversion schemes at CIMMYT using conventional and marker-assisted selection. Mol Breed 11(3):235–247
Shi HL, Jiang YX, Wang ZH, Li XH, Li MS, Zhang SH (2005) QTL identification of resistance to head smut in maize (in Chinese, English abstract). Acta Agron Sin 31:1449–1454
Steele KA, Price AH, Shashidhar HE, Witcombe JR (2006) Marker-assisted selection to introgress rice QTLs controlling root traits into an Indian upland rice variety. Theor Appl Genet 112(2):208–221. doi:10.1007/s00122-005-0110-4
Tan GQ, Xing YX, Xu ML, Jin QM (2009) Discovery and verification about the phenomena of germ-carrying plant with head smut of maize (in Chinese). J Maize Sci China 17(3):120–123
Toojinda T, Baird E, Booth A, Broers L, Hayes P, Powell W, Thomas W, Vivar H, Young G (1998) Introgression of quantitative trait loci (QTLs) determining stripe rust resistance in barley: an example of marker-assisted line development. Theor Appl Genet 96(1):123–131
Willcox MC, Khairallah MM, Bergvinson D, Crossa J, Deutsch JA, Edmeades GO, Gonalez-de-Leon D, Jiang C, Jewell DC, Mihm JA, Williams WP, Hoisington D (2002) Selection for resistance to southwestern corn borer using marker-assisted and conventional backcrossing. Crop Sci 42(5):1516–1528
Xu ML, Melchinger AE, Lubberstedt T (1999) Species-specific detection of the maize pathogens Sporisorium reiliana and Ustilago maydis by dot blot hybridization and PCR-based assays. Plant Dis 83(4):390–395
Xu ML, Li BL, Fengler K, Chao Q, Chen YS, Zhao XR, Zhao J (2010) Genetic loci associated with head smut resistance in maize. International patent Pub. No.: US 2010/0050291 A1
Yu XY, Wang FG, Zhao JR (2007) Redesigning and optimizing SSR core primer pairs for establishing DNA fingerprinting profiles (in Chinese). Mol Plant Breed China 5(3):443–447
Zhou XG, Li X, Wang LF (2006) Research advance on head smut disease in maize (in Chinese). Chem Prev Cure Plant Dis China 5:35–39
Acknowledgments
The authors cordially thank Prof. Jiuran Zhao, Dr. Fengge Wang, and Mr. Hongmei Yi for their technical assistance in background selection. This study was financially supported by the national ‘863’ high-tech program of China; the national ‘973’ basic research program; and the Beijing agricultural innovative platform–Beijing natural science fund program, Grant No. D08070500690802.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Tan, G., Xing, Y. et al. Marker-assisted introgression of qHSR1 to improve maize resistance to head smut. Mol Breeding 30, 1077–1088 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9694-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9694-3