Abstract
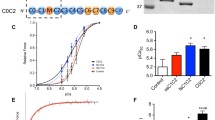
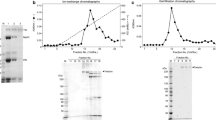
Molluscan muscle twitchin, a titin/connectin-related giant protein, regulates interactions between actin and myosin filaments at low Ca2+ concentrations. When it is dephosphorylated, actin filaments tightly bind to myosin filaments, resulting in the catch state known as the state of high passive tension with very low energy consumption. Yet when twitchin is phosphorylated actin filaments detach from the myosin filaments, resulting in relaxation of the catch. Here, steady-state Mg-ATPase activities of purified myosin were measured under various conditions: without twitchin, with dephosphorylated twitchin, or with phosphorylated twitchin; with or without phalloidin-stabilized F-actin; and at various Ca2+ concentrations. At low Ca2+ concentration, Mg-ATPase was activated by F-actin only in the presence of dephosphorylated twitchin (catch state). The activation was about two orders lower than that fully activated by Ca2+ and F-actin. In the absence of F-actin, twitchin and its phosphorylation state did not affect Mg-ATPase activities in any of the conditions we tested. Based on these results, we propose a molecular mechanism for the catch, where twitchin alone does not interact with the myosin catalytic motor domain but its complex with F-actin does, forming the bridge between actin and myosin filaments and the myosin slowly hydrolyzes Mg-ATP in the catch state.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann MA, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A (2011) Myosin binding protein-C: a regulator of actomyosin interaction in striated muscle. J Biomed Biotech 2011:636403
Andruchov O, Andruchova O, Galler S (2006) The catch state of mollusc catch muscle is established during activation: experiments on skinned fibre preparations of the anterior byssus retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis L. using the myosin inhibitors orthovanadate and blebbistatin. J Exp Biol 209:4319–4328
Andruchova O, Höpflinger MC, Andruchov O, Galler S (2005) No effect of twitchin phosphorylation on the rate of myosin head detachment in molluscan catch muscle: are myosin heads involved in the catch state? Pflügers Arch 450:326–334
Baguet F, Gillis JM (1968) Energy cost of tonic contraction in a lamellibranch catch muscle. J Physiol 198:127–143
Benian GM, Kiff JE, Neckelmann N, Moerman DG, Waterston RH (1989) Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity in C. elegans. Nature 342:45–50
Bers DM, Patton CW, Nuccitelli R (1994) A practical guide to the preparation of Ca2+ buffers. Methods Cell Biol 40:3–29
Butler TM, Mooers SU, Li C, Narayan S, Siegman MJ (1998) Regulation of catch muscle by twitchin phosphorylation: effects on force, ATPase, and shortening. Biophys J 75:1904–1914
Butler TM, Narayan SR, Mooers SU, Hartshorne DJ, Siegman MJ (2001) The myosin cross-bridge cycle and its control by twitchin phosphorylation in catch muscle. Biophys J 80:415–426
Butler TM, Mooers SU, Siegman MJ (2006) Catch force links and the low to high force transition of myosin. Biophys J 90:3193–3202
Butler TM, Mooers SU, Narayan SR, Siegman MJ (2010) The N-terminal region of twitchin binds thick and thin contractile filaments. J Biol Chem 285:40654–40665
Funabara D, Watabe S, Mooers SU, Narayan S, Dudas C, Hartshorne DJ, Siegman MJ, Butler TM (2003) Twitchin from molluscan catch muscle. J Biol Chem 278:29308–29316
Funabara D, Hamamoto C, Yamamoto K, Inoue A, Ueda M, Osawa R, Kanoh S, Hartshorne DJ, Suzuki S, Watabe S (2007) Unphosphorylated twitchin forms a complex with actin and myosin that may contribute to tension maintenance in catch. J Exp Biol 210:4399–4410
Funabara D, Osawa R, Ueda M, Kanoh S, Hartshorne DJ, Watabe S (2009) Myosin loop 2 is involved in the formation of a trimeric complex of twitchin, actin, and myosin. J Biol Chem 284:18015–18020
Galler S, Höpflinger MC, Andruchov O, Andruchova O, Grassberger H (2005) Effects of vanadate, phosphate and 2,3-butanedione monoxime (BDM) on skinned molluscan catch muscle. Pflügers Arch 449:372–383
Güth K, Gagelmann M, Rüegg JC (1984) Skinned smooth muscle: time course of force and ATPase activity during contraction cycle. Experientia 40:174–176
Höpflinger MC, Andruchova O, Andruchov O, Grassberger H, Galler S (2006) Effects of pH on the rate of myosin head detachment in molluscan catch muscle: are myosin heads involved in the catch state? J Exp Biol 209:668–676
Ishii N, Simpson AWM, Ashley CC (1989) Free calcium at rest during “catch” in single smooth muscle cells. Science 243:1367–1368
Ishii N, Mitsumori F, Takahashi K (1991) Changes in sarcoplasmic metabolite concentrations and pH associated with the catch contraction and relaxation of the anterior byssus retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis measured by phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 12:242–246
James J, Robbins J (2011) Signaling and myosin-binding protein C. J Biol Chem 286:9913–9919
Kendrick-Jones J, Lehman W, Szent-Györgyi AG (1970) Regulation in molluscan muscles. J Mol Biol 54:313–326
Maruyama K, Matsubara S, Natori R, Nonomura Y, Kimura S, Ohashi K, Murakami F, Handa S, Eguchi G (1977) Connectin, an elastic protein of muscle. J Biochem 82:317–337
Mukou M, Kishi H, Shirakawa I, Kobayashi T, Tominaga K, Imanishi H, Sugi H (2004) Marked load-bearing ability of Mytilus smooth muscle in both active and catch states as revealed by quick increases in load. J Exp Biol 207:1675–1681
Pfitzer G, Rüegg JC (1982) Molluscan catch muscle: regulation and mechanics in living and skinned anterior byssus retractor muscle of Mytilus edulis. J Comp Physiol B 147:137–142
Shelud’ko NS, Matusovskaya GG, Permyakova TV, Matusovsky OS (2004) Twitchin, a thick-filament protein from molluscan catch muscle, interacts with F-actin in a phosphorylation-dependent way. Arch Biochem Biophys 432:269–277
Siegman MJ, Mooers SU, Li C, Narayan S, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Watabe S, Hartshorne DJ, Butler TM (1997) Phosphorylation of a high molecular weight (~600 kDa) protein regulates catch in invertebrate smooth muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 18:655–670
Siegman MJ, Funabara D, Kinoshita S, Watabe S, Hartshorne DJ, Butler TM (1998) Phosphorylation of a twitchin-related protein controls catch and calcium sensitivity of force production in invertebrate smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5383–5388
Spudich JA, Watt S (1971) The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin–troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem 246:4866–4871
Sugi H, Iwamoto H, Shimo M, Shirakawa I (1999) Evidence for load-bearing structures specialized for the catch state in Mytilus smooth muscle. Comp Biochem Physiol A 122:347–353
Tsutsui Y, Yoshio M, Oiwa K, Yamada A (2005) Twitchin purified from molluscan catch muscles regulates interactions between actin and myosin filaments at rest in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 26:461–465
Tsutsui Y, Yoshio M, Oiwa K, Yamada A (2007) Striated muscle twitchin of bivalves has “catchability”, the ability to bind thick filaments tightly to thin filaments, representing the catch state. J Mol Biol 365:325–332
Twarog BM (1954) Responses of a molluscan smooth muscle to acetylcholine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Cell Comp Physiol 44:141–163
Vibert P, Edelstein SM, Castellani L, Elloitt BW Jr (1993) Mini-titins in striated and smooth molluscan muscles: structure, location and immunological crossreactivity. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 14:598–607
Wang K, McClure J, Tu A (1979) Titin: major myofibrillar components of striated muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:3698–3702
Yamada A, Yoshio M, Kojima H, Oiwa K (2001) An in vitro assay reveals essential protein components for the “catch” state of invertebrate smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6635–6640
Yamada A, Yoshio M, Nakamura A, Kohama K, Oiwa K (2004) Protein phosphatase 2B dephosphorylates twitchin, initiating the catch state of invertebrate smooth muscle. J Biol Chem 279:40762–40768
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science KAKENHI Grant No. 22570167 to A.Y.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, A., Yoshio, M. & Oiwa, K. Myosin Mg-ATPase of molluscan muscles is slightly activated by F-actin under catch state in vitro. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 34, 115–123 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-013-9339-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-013-9339-8