Summary
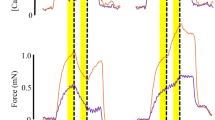
Immediate stiffness and static elastic modulus were estimated in skinned and living molluscan smooth muscle during active contraction and catch state. The stiffness to tension ratio was found to be greater in catch than in active contraction. In skinned preparations, a catch like state could be reproduced in a Ca2+ free solution (pCa>8) which was mechanically not different from catch in living muscle. Addition of cAMP or the catalytic subunit of the cAMP dependent protein kinase type II caused a rapid relaxation of this catch like state. The results are discussed in terms of a dual intracellular regulatory mechanism of catch and active contraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achazi RK (1979) Phosphorylation of molluscan paramyosin. Pflügers Arch 379:197–201
Achazi RK, Dölling B, Haakshorst R (1974) 5-HT-induzierte Erschlaffung und cyclisches AMP bei einem glatten Molluskenmuskel. Pflügers Arch 349:19–27
Cornelius F (1980) The regulation of tension in a chemically skinned molluscan smooth muscle. J Gen Physiol 75:709–725
Gordon AR (1978) Contraction of detergent-treated smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:3527–3530
Heinl P, Kuhn HJ, Rüegg JC (1974) Tension responses to quick length changes of glycerinated skeletal muscle fibres from the frog and tortoise. J Physiol (Lond) 237:243–258
Huxley AF, Simmons RM (1971) Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature (Lond) 233:533–538
Huxley AF, Simmons RM (1973) Mechanical transients and the origin of muscular force. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 37:669–680
Jewell BR (1959) The nature of the phasic and tonic responses of the anterior byssus retractor muscle of mytilus. J Physiol (Lond) 149:154–177
Jewell BR, Rüegg JC (1966) Oscillatory contraction of insect fibrillar muscle after glycerol extraction. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 164:428–459
Marchand-Dumont G, Baguet F (1975) The control mechanism of relaxation in molluscan catch muscle (ABRM). Pflügers Arch 354:87–100
Pfitzer G, Rüegg JC, Sparrow M (1981) c-AMP dependent protein kinase unlocks “catch” of a skinned molluscan smooth muscle. Pflügers Arch 389:R61
Rüegg JC (1971) Smooth muscle tone. Physiol Rev 51:201–248
Tameyasu T, Sugi H (1976) The series elastic component and the force-velocity relation in the anterior byssal retractor muscle ofMytilus edulis during active and catch contractions. J Exp Biol 64:497–510
Twarog BM (1954) Responses of a molluscan smooth muscle to acetylcholine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Cell Comp Physiol 44:141–163
Twarog BM (1976) Aspects of smooth muscle function in molluscan catch muscle. Physiol Revs 56:829–838
Twarog BM, Muneoka Y (1973) Calcium and the control of contraction and relaxation in a molluscan catch muscle. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 37:489–503
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfitzer, G., Rüegg, J.C. Molluscan catch muscle: Regulation and mechanics in living and skinned anterior byssus retractor muscle ofMytilus edulis . J Comp Physiol B 147, 137–142 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689302
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689302