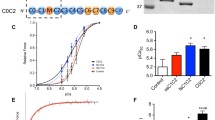
Abstract
Molluscan smooth muscle exhibits a unique muscle contraction, called catch, where the tension is maintained for long periods with little energy consumption. Catch contraction is regulated by twitchin, also called mini-titin, a member of the titin/connectin family. Twitchin is also found in molluscan non-catch striated muscle. We isolated twitchins from catch and striated muscles in the Yesso scallop Mizuhopecten yessoensis. Both twitchins are ~500 kDa in size. Western blotting using the anti-twitchin kinase domain antibody revealed that both twitchins have a kinase domain. Both twitchins were phosphorylated by the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in vitro. Stoichiometric analysis revealed that 0.6 and 1.7 mol Pi were incorporated into catch and striated muscle twitchins, respectively. Phosphopeptide mapping revealed that catch muscle twitchin has one phosphorylation site, whereas striated muscle twitchin has two. cDNA cloning gave partial sequences of two Yesso scallop twitchin isoforms. One had two putative phosphorylation sites and the other had one.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Funabara D, Kanoh S, Siegman MJ, Butler TM, Hartshorne DJ, Watabe S (2005) Twitchin as a regulator of catch contraction in molluscan smooth muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 26:455–460
Funabara D, Hamamoto C, Yamamoto K, Inoue A, Ueda M, Osawa R, Kanoh S, Hartshorne DJ, Suzuki S, Watabe S (2007) Unphosphorylated twitchin forms a complex with actin and myosin that may contribute to tension maintenance in catch. J Exp Biol 210:4399–4410
Funabara D, Osawa R, Ueda M, Kanoh S, Hartshorne DJ, Watabe S (2009) Myosin loop 2 is involved in the formation of a trimeric complex of twitchin, actin, and myosin. J Biol Chem 284:18015–18020
Siegman MJ, Funabara D, Kinoshita S, Watabe S, Hartshorne DJ, Butler TM (1998) Phosphorylation of a twitchin-related protein controls catch and calcium sensitivity of force production in invertebrate smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5383–5388
Waterston RH, Thomson JN, Brenner S (1980) Mutants with altered muscle structure in Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol 77:271–302
Benian GM, Kiff JE, Neckelmann N, Moerman DG, Waterston RH (1989) Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity in C. elegans. Nature 342:45–50
Benian GM, L’Hernault SW, Morris ME (1993) Additional sequence complexity in the muscle gene, unc-22, and its encoded protein, twitchin, of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 134:1097–1104
Funabara D, Watabe S, Mooers SU, Narayan S, Dudas C, Hartshorne DJ, Siegman MJ, Butler TM (2003) Twitchin from molluscan catch muscle: primary structure and relationship between site-specific phosphorylation and mechanical function. J Biol Chem 278:29308–29316
Funabara D, Kinoshita S, Watabe S, Siegman MJ, Butler TM, Hartshorne DJ (2001) Phosphorylation of molluscan twitchin by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry 40:2087–2095
Probst WC, Cropper EC, Heierhorst J, Hooper SL, Jaffe H, Vilim F, Beushausen S, Kupfermann I, Weiss KR (1994) cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of Aplysia twitchin may mediate modulation of muscle contractions by neuropeptide cotransmitters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8487–8491
Vibert P, Edelstein SM, Castellani L, Elliott BW (1993) Mini-titins in striated and smooth molluscan muscles: structure, location and immunological crossreactivity. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 14:598–607
Tsutsui Y, Yoshio M, Oiwa K, Yamada A (2007) Striated muscle twitchin of bivalves has “catchability”, the ability to bind thick filaments tightly to thin filaments, representing the catch state. J Mol Biol 365:325–332
Dinkel H, Van Roey K, Michael S, Davey NE, Weatheritt RJ, Born D, Speck T, Krüger D, Grebnev G, Kuban M, Strumillo M, Uyar B, Budd A, Altenberg B, Seiler M, Chemes LB, Glavina J, Sánchez IE, Diella F, Gibson TJ (2014) The eukaryotic linear motif resource ELM: 10 years and counting. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D259–266
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Kusaka M, Ikeda D, Funabara D, Hartshorne DJ, Watabe S (2008) The occurrence of tissue-specific twitchin isoforms in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. Fish Sci 1:677–686
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Funabara, D., Watabe, S. & Kanoh, S. Phosphorylation properties of twitchin from Yesso scallop catch and striated muscles. Fish Sci 81, 541–550 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-015-0866-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12562-015-0866-7