Abstract
The distribution of lotic fauna is widely acknowledged to be patchy reflecting the interaction between biotic and abiotic factors. In an in situ field study, the distribution of benthic and hyporheic invertebrates in the heads (downwelling) and tails (upwelling) of riffles were examined during stable baseflow conditions. Riffle heads were found to contain a greater proportion of interstitial fine sediment than riffle tails. Significant differences in the composition of benthic communities were associated with the amount of fine sediment. Riffle tail habitats supported a greater abundance and diversity of invertebrates sensitive to fine sediment such as EPT taxa. Shredder feeding taxa were more abundant in riffle heads suggesting greater availability of organic matter. In contrast, no significant differences in the hyporheic community were recorded between riffle heads and tails. We hypothesise that clogging of hyporheic interstices with fine sediments may have resulted in the homogenisation of the invertebrate community by limiting faunal movement into the hyporheic zone at both the riffle heads and tails. The results suggest that vertical hydrological exchange significantly influences the distribution of fine sediment and macroinvertebrate communities at the riffle scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The distribution of invertebrates in lotic ecosystems is typically patchy, often reflecting spatial patterns which are structured around physical, chemical and trophic processes (Silva et al., 2014; Gibbins et al., 2016; Verdonschot et al., 2016). Research examining lotic environments has typically focussed on longitudinal and lateral gradients (environmental and ecological) as exemplified through the river continuum (Vannote et al., 1980; Rosi-Marshall et al., 2016) and flood pulse concepts (Junk et al., 1989; Turić et al., 2015). However, the majority of historic research has focussed on benthic habitats and communities, with little consideration of surface–groundwater interactions (Dole-Oliver & Marmonier, 1992; Boulton & Foster, 1998; Krause et al., 2011a).
Although there is growing recognition of the role that interstitial flows play in structuring benthic and hyporheic invertebrate communities (e.g. Dole-Olivier, 1998; Davy-Bowker et al., 2006; Mathers & Wood, 2016), the consequences of flow dynamics at small spatial scales and the associated sedimentary characteristics upon benthic and hyporheic invertebrate assemblages remain poorly quantified (Marmonier et al., 2010, 2012; Descloux et al., 2014; Jones et al., 2015). Despite several seminal papers over multiple decades which identified the potential importance of vertical hydraulic connectivity (Orghidan, 1959; Tilzer, 1968; Hynes, 1983), linkages between surface and groundwater and its influence on instream communities remain poorly studied (Boulton et al., 1999; Krause et al., 2011a).
At the scale of riffle–pool sequences (bed-form driven), decreasing water depth at the end of a pool (riffle head) forces some water downwards into the sediments (downwelling). This water travels through the sediments in a downstream direction, where typically at the tail of a riffle, increasing water depth produces a zone of low pressure forcing upwelling water through the bed sediments and into the channel (Savant et al., 1987; Boulton et al., 1998; Franken et al., 2001). Consequently, well-defined riffle units are often considered to be areas within which hydrological exchange is high compared to the surrounding sediment matrix (Malard et al., 2002). However, flow paths are often more complex than conceptual models suggest, responding to a range of factors such as flooding (Wondzell & Swanson, 1996; Dudley-Southern & Binley, 2015), bed topography (Boano et al., 2013; Wildhaber et al., 2014), sediment composition and porosity (Packman & Bencala, 2003; Gomez-Velez et al., 2014) and other instream morphological units such as coarse wood accumulations (Sawyer & Cardenas, 2012; Krause et al., 2014).
The spatial and temporal heterogeneity of surface and subsurface flows in riffle–pool sequences (Käser et al., 2009) often leads to a mosaic of depositional and erosional areas which are characterised by differing grain size distributions (Boulton & Stanley, 1995; Swan & Palmer, 2000). This pattern of fine sediment deposition (typically sand- and silt-sized fractions of ≤2 mm; Wentworth, 1922; Jones et al., 2012) directly influences the structure and composition of invertebrate communities (Brunke & Gonser, 1999) but also the nature of vertical hydrological exchange (Leek et al., 2009; Hartwig & Borchardt, 2015; Datry et al., 2015). Consequently, the dynamic pattern of vertical hydraulic exchange exerts a strong influence on physical and chemical conditions such as temperature, oxygen concentrations and the residence time of water (Olsen & Townsend, 2003; Krause et al., 2011b). Surface water downwelling into subsurface sediments typically delivers oxygen and inputs of organic matter to hyporheic habitats, promoting aerobic microbial processes (Findlay et al., 1993; Pinay et al., 2015). In contrast, oxygen poor, nutrient-rich water often enters the stream at upwelling locations (Grimm et al., 2007).
Although the processes which structure invertebrate communities at varying spatial scales have been examined (Brussock & Brown, 1991; Newson, 2002; Chessman et al., 2006), knowledge regarding the sediment characteristics and patterns of vertical hydrological exchange at the habitat/geomorphic unit scale (small-scale morphological features) and their associated relationships with macroinvertebrates requires further examination through field investigations. It is widely acknowledged that geomorphic units and river bed sedimentary characteristics influence the structure and functioning of macroinvertebrates, but community variation across individual morphological units (e.g. riffles—from the head to the tail) has not been widely investigated (Harper & Everard, 1998; Thomson et al., 2004). Riffle-scale surface and subsurface flow heterogeneity almost certainly plays a role in determining the micro- distribution patterns of macroinvertebrates (e.g. Brown & Brown, 1984; Pepin & Hauer, 2002; Davy-Bowker et al., 2006) and therefore represents a potentially influential factor in stream ecology which has been poorly quantified to date.
The aim of this study was to examine the riffle-scale distribution of benthic and hyporheic invertebrates (riffle heads and tails) in association with patterns of vertical hydraulic exchange and fine sediment characteristics. Specifically, we addressed the following questions: (i) Do benthic and hyporheic invertebrate assemblages differ between riffle heads and tails under stable flow conditions?; (ii) Do patterns of fine sediment accumulation (deposition) and vertical hydrological exchange differ between the heads and tails of riffles?; (ii) Can the patterns of fine sediment and vertical hydrological exchange help explain the microdistribution of invertebrate populations?
Methods
Study site
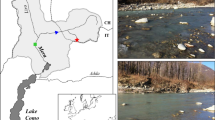
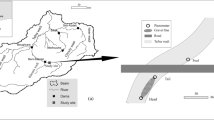
Blackbrook (52°76′N, −1°32′E) is a small regulated stream located to the west of Loughborough (Leicestershire, UK). The river rises at a height of 250 m and drains into the River Soar, a tributary of the River Trent (NRFA, 2016). The catchment is underlain by Pre-Cambrian volcanic and intrusive igneous rocks covered by Triassic Mercia Mudstones and boulder clay (Greenwood et al., 2001). The river predominantly drains pastoral agricultural land before flowing through the town of Loughborough (UK). The study sites were located 800 m downstream of a small headwater reservoir (Blackbrook reservoir). Sampling of five riffles within a 1,200 m reach was undertaken during spring (8th April–4th May 2013). Hydrological data from a local gauging station on the River Soar (Kegworth, 52°82′N, −1°27′E) indicated stable but gradually declining baseflow discharge values over the study period (average 6.5 m3/s, range 5.07–8.2 m3/s; see Mathers & Wood, 2016).
Experimental design and invertebrate sampling
Paired benthic and hyporheic macroinvertebrate samples were collected to examine differences between community composition in the heads and tails of five riffles. At each riffle, five sampling points in the head and tail were selected at random for hyporheic sampling (ten samples on each riffle). All sample points were at least 0.5 m from the transition of the habitat (pool or riffle) to ensure that the environmental conditions were representative of the habitat. For each sampling point, open ended PVC pipes (19 mm internal diameter) were driven into the substrate using a stainless steel T-bar to a depth of 200 mm (Boulton & Stanley, 1995; Wood et al., 2010). This depth was selected based on a number of previous studies which have investigated fine sedimentation and macroinvertebrate relationships (Pacioglu et al., 2012; Descloux et al., 2013; Mathers and Wood, 2016). These pipes functioned as permanent sampling wells and were positioned ≥0.5 m apart to minimise any influence from sampling in adjacent wells (Stubbington et al., 2011). Wells were installed and left in situ for 21 days to enable sufficient time for the streambed to recover after installation. Pipes were sealed between installation and sampling to prevent sediment deposition and colonisation by benthic invertebrates. A total of 6 L of water was extracted from the base of each well using a manual bilge pump which was then passed through a 125 µm sieve to retain macroinvertebrates and sediment (typically 125 µm to <4 mm). Two pipes were lost during the experimental period (one from a riffle head and tail respectively), reducing the total number of replicates to 48.
To examine spatial differences in benthic communities, ten Surber samples (five in the riffle head and five in the tail) were collected at each riffle site, providing a total of 50 samples. Samples were collected using a modified Surber sampler (150 × 200 mm frame fitted with a 250 µm mesh net) over a 1-min time period. The distance between sample points was ≥0.5 m to minimise the effect of disturbance from adjacent samples. All invertebrate samples (benthic and hyporheic) were preserved in the field with 10% formaldehyde and returned to the laboratory for processing and identification.
Environmental variables
Physical and chemical characteristics of the water were sampled from each of the hyporheic stand pipes (ten samples per site—five in the riffle head and five in the tail) for pH, conductivity and temperature using standard instruments (Hanna Instruments, Leighton Buzzard, UK). Measurements were taken in the final 2 L sample from the sampling wells to avoid possible surface water contamination. Dissolved oxygen concentrations (DO, mg l−1) were recorded at ten randomised locations in the open channel above the river bed at each riffle. All DO concentration readings were >90% saturation and did not vary significantly between sites. Flow velocity (m s−1) readings (Valeport Instrument, Totnes, UK) were recorded at five locations in each riffle head and tail. To quantify the potential influence of vertical hydraulic exchange, the direction of hydrologic exchange was estimated through the installation of a mini-piezometer (Lee & Cherry, 1978) in the head and tail at each of the five riffle sites. Pipes were inserted into the river bed to a depth of 200 mm using the same method as the sampling wells. The piezometer pipe comprises small (4.5 mm) perforations at the base of the pipe to enable communication with the saturated sediments. The second pipe (stage well) had solid walls and was held in the water column facilitating the measurement of the river stage level. The direction of vertical hydraulic exchange was obtained through comparison of the two water levels (see Mathers & Wood, 2016). The relative volume of interstitial sedimentation was examined by retaining fine sediment extracted in the bilge pump samples (Mauclaire et al., 1998).
Laboratory procedures
In the laboratory, benthic and hyporheic invertebrate samples were passed through a 90 µm sieve and processed. All fine sediments extracted from the hyporheic well samples were retained and oven dried at 60°C until a constant weight was recorded (Pacioglu et al., 2012). Samples were then gently disaggregated using a pestle and mortar, passed through a sieve nest (2 and 1 mm) and each fraction weighed to determine the grain size distribution (>2 mm, 2–1 mm and <1 mm; Gordon et al., 1994). All invertebrates were identified to the lowest taxonomic level possible, most to species or genus with the exception of Sphaeriidae, Zonitidae and Diptera (family), Hydracarina (order) and Oligochaeta, Cyclopidae and Hydra which were recorded as such.
Statistical analysis
Differences in the invertebrate community composition and environmental parameters between riffle heads and tails were examined via non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) in R (version 3.12; R Development Core Team, 2014) using the metaMDS function in the vegan package (Oksanen et al., 2015). Similarity matrices were calculated using Bray–Curtis coefficients for invertebrate communities and Euclidean distances were employed for environmental variables. Homogeneity of multivariate dispersions between aquatic macroinvertebrate assemblages (based on Bray–Curtis distance matrices), and the environmental data (based on Euclidian distance matrices) from benthic and hyporheic habitats were calculated using the betadisper function and compared using One-Way ANOVA. One-way Analysis of Similarities (ANOSIM) was employed to test for heterogeneity between riffle head and tail communities in PRIMER V6 (Clarke & Gorley, 2006). Taxa contributing to the divergence of the communities between riffle heads and tails were identified through the application of the similarity percentage procedure (SIMPER), and the top five taxa driving dissimilarity in benthic and hyporheic samples tested to determine if differences were statistically significant.
Community abundance and taxa richness metrics were derived from the raw data. Functional feeding traits based on Tachet et al. (2010) and abundances of taxa characterised as highly or moderately sensitive to sediment as defined by the Fine Sediment Sensitivity Ratings (FSSR; Extence et al., 2013) were calculated for each benthic sample. Feeding traits were assigned based on the dominant weighted group (fuzzy coded categories). Where a taxon had equal weightings for two categories, taxon abundance was assigned to both the groups. In addition, abundances of Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera and Trichoptera (EPT) groups, and individual taxon were examined. Abundances of feeding trait groups, sediment sensitive macroinvertebrates, EPT and individual taxa were log(x + 1) transformed prior to analysis to comply with the underlying assumptions of the statistical tests (McMullen & Lytle, 2012).
A linear mixed effects (LME) model was developed for each of the macroinvertebrate community descriptors and individual taxon abundances to test for differences between riffle head and tail communities. Models were fitted using the ‘nlme’ package in R Version 3.1.2. Location was specified as a fixed factor and riffle site as a random factor in recognition that replicates within a riffle are less independent than those at different riffle sites. The model was fitted using the restricted maximum likelihood (REML) estimation function. LMEs were also fitted to each of the environmental parameters (pH, conductivity, velocity, grains >2 mm, 2–1 mm and <1 mm) to test for any location differences (riffle heads versus tails).
Results
Variability in environmental parameters between riffle heads and tails
Vertical hydraulic exchange in riffle heads was downwelling at four out of the five sites examined, with riffle tails characterised by upwelling water (all sites). The magnitude of vertical hydraulic exchange varied, ranging from +2.5 cm (upwelling) to −1.2 cm (downwelling). Multivariate dispersion for environmental parameters were higher (Fig. 1a) for riffle heads (average distance: 48.73) than for riffle tails (average distance: 32.42), although this was not statistically significant (F 1,48 = 1.524, P = 0.22). When differences in fine sediment content between the riffle head and tail were considered, greater quantities were recorded in riffle heads for all grain sizes examined (Fig. 2), although this was only significant for the 2–1 mm fraction (F 1,41 = 5.316, P = 0.026). Significant differences in pH were recorded between riffle heads and tails (F 1,41 = 12.624, P = 0.001), with riffle heads having higher pH values than tails. No other significant differences in environmental parameters were observed between riffle head and tail locations. Mean values for environmental parameters recorded in the field by site and riffle location (head or tail) are presented in Table 1.
Variability in the benthic community between riffle heads and tails
A total of 4576 individuals and 41 taxa (32 in riffle heads and 35 in riffle tails) were recorded in 50 benthic Surber samples. A total of 6 taxa were unique to riffle heads, 9 to tail communities and 17 to the benthos (Table 2). The most abundant taxa were Chironomidae (68% of total benthic abundance), followed by Oligochaeta (7%), Baetis rhodani (Leach, 1815; 6%) and Chloroperla torrentium (Pictet, 1841; 6%). NMDS indicated significant differences between benthic invertebrate communities within riffle heads and tails (ANOSIM R = 0.206, P < 0.001; Fig. 1b). Riffle head communities demonstrated significantly greater heterogeneity (average distance: 0.3777) than tails (average distance: 0.3037; F 1,48 = 5.2112, P = 0.027). The top 5 taxa driving dissimilarity between riffle head and tail communities were: B. rhodani (13.3% dissimilarity), Oligochaeta (9.6%), C. torrentium (7.9%), Chironomidae (7.8%) and Gammarus pulex (Linnaeus, 1758; 7.3%). B. rhodani was the only taxon to demonstrate significant differences in abundances between riffle heads and tails, with significantly more individuals in riffle tails (F 1,30 = 14.050, P < 0.001).
Community abundance (F 1,44 = 5.101, P = 0.028) and taxa richness (F 1,44 = 6.429, P = 0.015) were significantly greater at riffle tails than heads (Fig. 3). Significant differences between the abundances of EPT (F 1,44 = 21.962, P < 0.001) and taxa sensitive to fine sediment (F 1,43 = 15.095, P < 0.001) were recorded between riffle heads and tails, with greater total abundances found in riffle tails. Greater abundances of scraper feeders were recorded in riffle tails (F 1,39 = 30.144, P < 0.001; Fig. 4). No other significant differences were determined in the abundances of benthic predators, filterers, deposit feeders or shredders, although the relative proportion of shredders was greater at riffle head sites (Fig. 4).
Relative abundance of functional feeding groups for benthic and hyporheic communities from the head and tail of riffles on Blackbrook. Note: meiofauna classified as deposit feeders based on the literature available (Henderson, 1990; Dussart & Defaye, 2001) and the order of groups in the bar chart corresponds directly to those presented in the key
Variability in the hyporheic community between riffle heads and tails
A total of 470 individuals comprising 27 taxa (21 in the riffle head and 19 in the riffle tail) were recorded from the 48 hyporheic samples. A total of 7 taxa were unique to heads and 6 to the riffle tails, and 3 taxa were unique to hyporheic samples (Table 2). The most abundant taxa were Cyclopidae (24% of total abundance), Chironomidae (23%) and Candona sp. (21%). NMDS indicated no distinct differences between hyporheic communities recorded from riffle heads or tails, with communities from both locations displaying considerable overlap (ANOSIM R = 0.001, P = 0.401; Fig. 1c). Multivariate dispersion was not significantly different for riffle heads (average distance: 0.4944) or tails (average distance: 0.4890; F 1,48 = 0.0199 P = 0.8885). The top 5 taxa driving dissimilarity between riffle head and tail communities were as follows: Cyclopidae (18.5% dissimilarity), Chironomidae (17.7%), Oligochaeta (16.1%), Candona sp. (Baird, 1854; 15.5%) and Hydra (12.4%). No significant differences between riffle heads or tails were recorded for any of the hyporheic community metrics or individual taxon tested (LME P > 0.05; Figs. 3, 4).
Discussion
Riffle-scale variability in benthic communities
The results from this study indicate that benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages differed between the head and tail of riffles during the period of stable base flow examined, illustrating the presence of clear microdistribution patterns of fauna. Comparable patterns have been reported for benthic communities in a limited number of studies conducted on riffle-scale variability (Brown & Brown, 1984; Pepin & Hauer, 2002; Davy-Bowker et al., 2006). The dynamic nature of stream habitats, in particular substratum composition, flow velocity and trophic resources, typically results in patchy microdistribution of invertebrates (Fonseca & Hart, 2001; Brosse et al., 2003). Environmental parameters in this study varied more within riffle heads and correspond with the greater community heterogeneity (beta-diversity) recorded at these localities.
The fine sediment content of hyporheic substrates (subsurface sediments) was found to be significantly greater at the riffle heads in this study, reflecting the widely reported characteristics of vertical hydraulic exchange (VHE). Downwelling water is typically associated with the transport of sediment into the river bed at the head of riffles, whilst upwelling water, often at the riffle tail, has the potential to flush fine sediments from interstitial spaces (Huettel et al., 1996; Ren & Packman, 2007; Datry et al., 2015). A number of other studies have also reported greater quantities of fines in the riffle head associated with downwelling water and flows during high discharge events (Brown & Brussock, 1991; Dole-Olivier & Marmonier, 1992; Dole-Olivier et al., 1997; Saenger et al., 2005). Although the strength of VHE varied between riffle heads and tails, the significant difference in pH indicates the occurrence of vertical exchange within the substrates. This difference also probably reflects microbial activity in the hyporheic zone which can result in a different physio-chemical signature when water re-enters the stream channel (Boulton et al., 1999; Fowler & Scarsbrook, 2002).
The quantities of fine sediment in benthic sediments within this study stream are unlikely to have been great enough to limit or prevent movement of organisms within the interstices of the benthic zone (Mathers & Wood, 2016), although it was clearly strong enough to have influenced the observed riffle-scale faunal distribution patterns. Lotic invertebrate communities typically constitute highly dynamic rather than sessile assemblages (Downes et al., 1993), and as a consequence, in response to abiotic and biotic cues, the varying dispersal abilities of taxa can lead to small-scale spatial variations in macroinvertebrate communities (Wilson & McTammany, 2016). These abiotic and biotic parameters are most stable under baseflow conditions (Poff et al., 1997; Suren & Jowett, 2006). A number of EPT taxa have been documented to avoid colonisation of habitats containing large amounts of fine sediment (Larson & Ormerod, 2010), and this characteristic is reflected in tail communities supporting significantly more EPT taxa. In this study, B. rhodani abundance was significantly higher in the riffle tail where fine sediment deposition was observed to be lower. Previous research has found that B. rhodani is highly sensitive to fine sediment (Wood et al., 2005). Similarly, taxa which are characterised as being particularly sensitive to the presence of fine sediments (Extence et al., 2013) were found in greater abundances in riffle tails where fine sediment accumulation was lower.
Feeding traits associated with the physical habitat template and resource availability may also influence micro-scale spatial variability. Substrates containing less fine sediment at the tail of riffles in this study supported significantly greater abundances of scrapers (Relyea et al., 2000; Bo et al., 2007). The presence of fine sediments can inhibit access to trophic resources, with some species in other studies reported to be confined to areas of clean gravel (Wood & Armitage, 1999; Rabeni et al., 2005). The distribution of organic matter is also frequently patchy (Maridet et al., 1997; Wipfli et al., 2007), but typically higher volumes are recorded at riffle heads due to their proximity to upstream pools which are often a store of organic material (Mermillod-Blondin et al., 2000). Some of this material will be transported as suspended particulate organic matter and carried into the interstitial spaces of the sediments at the head of riffles (Pusch, 1996; Brunke & Gosner, 1999), and may explain the higher abundances of shredders recorded in these areas in this study.
The riffle-scale distribution patterns in this study are almost certainly linked to sampling taking place during a period of stable low-flow conditions (Schmid, 1993; Buendia et al., 2014; Campbell et al., 2015). It is also likely that these patterns will not always be as clear and will breakdown during periods of elevated discharge (spates). Disturbances play an important role in patch dynamics and the microdistribution of invertebrates, as they often reset community trajectories through the alteration of physical templates and resource partitioning (Winterbottom et al., 1997; Death, 2010). Consequently, studies which examine the distribution of invertebrates should do so whilst acknowledging local disturbance history and its potential effect on biotic and abiotic parameters (Effenberger et al., 2006; Mathers & Wood, 2016).
Riffle-scale variability in hyporheic communities
In marked contrast to benthic samples, no significant differences in hyporheic communities were evident between head and tail communities. NMDS indicated that the hyporheic communities from riffle heads and tails were comparable. However, in contrast to the findings in this study, previous studies examining the distribution of the hyporheos in relation to hydrological exchange and sediment structure report that diversity is often greatest in downwelling zones (Fowler & Scarsbrook, 2002; Olsen & Townsend, 2003). These findings however, are typically a function of the physio-chemical properties of the water which influences the dominance of hypogean and epigean fauna. Downwelling water is often characterised by high DO levels, which supports both epigean and hypogean fauna. In contrast, upwelling water is characterised by a dominance of hypogean fauna which display adaptations to low dissolved oxygen levels (Dole-Oliver & Marmonier, 1992; Franken et al., 2001).
The lack of differences between hyporheic communities in the two zones in this study may reflect the homogenous nature of the hyporheic zone with clogging of subsurface interstitial spaces (colmation) by fine sediment reducing the amount of available pore space between substrates (Strommer & Smock, 1989; Descloux et al., 2013). It is hypothesised that colmation limited faunal movement and utilisation of the subsurface sediments to the extent that the community was largely comprised (92%) of five ubiquitous taxa (Cyclopidae, Chironomidae, Candona sp., Oligochaeta and Hydra). Blackbrook is regulated via a small reservoir upstream of the study location and it is widely recognised that impoundment often reduces the magnitude and frequency of high flow events that naturally flush fines (Petts, 1984; Wood & Armitage, 1997; Milan & Large, 2014). In the absence of high flows, sedimentation of benthic and hyporheic sediments may occur, with river beds characterised by a finer gravel matrix than comparable unregulated rivers (Armitage, 1987; Sear, 1993; Jones et al., 2015).
Colmation of hyporheic sediments is widely acknowledged to lead to reductions in the diversity and density of invertebrates within the hyporheic zone (Richards & Bacon, 1994; Strayer et al., 1997; Weigelhofer & Waringer, 2003; Bo et al., 2007). Increasing interstitial fine sediment concentrations have been documented to increase divergence of benthic and hyporheic communities (Descloux et al., 2013); a feature which was evident in this study with 17 taxa being unique to the benthic community. Clogging of the interstitial pore spaces restricts the movement of individuals between benthic and hyporheic sediments (Sarriquet et al., 2007; Descloux et al., 2013; Mathers et al., 2014), with only burrowing taxa or those characterised by a smaller body size able to penetrate deeper into the substratum (Gayraud & Phillipe, 2001; Duan et al., 2009; Xu et al., 2012).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that small-scale differences in sediment composition within the heads and tails of riffle influences the distribution of benthic invertebrates under stable baseflow conditions. This pattern reflects the direction of vertical hydrological exchange and illustrates the influence that interstitial flows can play on the distribution of both macroinvertebrate communities and fine sediments at the riffle scale. These results also highlight the importance of micro-scale habitats in maintaining stream diversity. High volumes of interstitial fine sediment were present in the hyporheic sediments, and this could account for the limited faunal abundances and richness of hyporheic communities. It may also help explain the homogeneous hyporheic community composition recorded in both riffle heads and tails in this study. It is important to recognise that this study was undertaken during stable baseflow flow conditions and seasonal shifts in the riffle-scale distribution of macroinvertebrates will occur reflecting the dynamic hydrological conditions within the stream. Few studies have attempted to address the effect of local hydraulic exchange and sedimentation patterns on benthic and hyporheic faunal distribution, and there is a need for further in situ studies to build upon the observations reported in this study.
References
Armitage, P. D., 1987. The classification of tailwater sites receiving residual flows from upland reservoirs in Great Britain, using macroinvertebrates. In Craig, J. F. & J. B. Kemper (eds), Regulated streams: Advances in Ecology. Plenum Press, New York.
Bo, T., S. Fenoglio, G. Malacarna, M. Pessino & F. Sgariboldi, 2007. Effects of clogging on stream macroinvertebrates: an experimental approach. Limnologica 37: 186–192.
Boano, F., R. Revelli & L. Ridolfi, 2013. Modelling hyporheic exchange with unsteady stream discharge and bedform dynamics. Water Resources Research. doi:10.1002/wrcr.20322.
Boulton, A. J. & E. H. Stanley, 1995. Hyporheic processes during flooding and drying in a Sonoran Desert stream II. Faunal dynamics. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 134: 27–52.
Boulton, A. J. & J. G. Foster, 1998. Effects of buried leaf litter and vertical hydrologic exchange on hyporheic water chemistry and fauna in a gravel-bed river in northern New South Wales, Australia. Freshwater Biology 40: 229–243.
Boulton, A. J., S. Findlay, P. Marmonier, E. H. Stanley & H. M. Valett, 1998. The functional significance of the hyporheic zone in streams and rivers. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 29: 59–81.
Boulton, A. J., P. Marmonier & J. A. Davis, 1999. Hydrological exchange and subsurface water chemistry in stream varying in salinity in south-western Australia. International Journal of Salt Lake Research 8: 36–382.
Brosse, S., C. J. Arbuckle & C. R. Townsend, 2003. Habitat scale and biodiversity: influence of catchment, stream reach and bedform scales on local invertebrate diversity. Biodiversity and Conservation 12: 2057–2075.
Brown, A. V. & K. B. Brown, 1984. Distribution of insects within riffles of streams. Freshwater Invertebrate Biology 3: 2–11.
Brown, A. V. & P. P. Brussock, 1991. Comparisons of benthic invertebrates between riffles and pools. Hydrobiologia 220: 99–108.
Brunke, M. & T. Gonser, 1999. Hyporheic invertebrates – the clinal nature of interstitial communities structure by hydrological exchange and environmental gradients. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 18: 344–363.
Brussock, P. P. & A. V. Brown, 1991. Riffle-pool geomorphology disrupts longitudinal patterns of stream benthos. Hydrobiologia 220: 109–117.
Buendia, C., C. N. Gibbins, D. Vericat & R. J. Batalla, 2014. Effects of flow and fine sediment dynamics on the turnover of stream invertebrate assemblages. Ecohydrology 7: 105–1123.
Campbell, R. E., M. J. Winterbourn, T. A. Cochrane & A. R. McIntosh, 2015. Flow-related disturbance creates a gradient of metacommunity types within stream networks. Landscape Ecology 3: 667–680.
Chessman, B. C., K. A. Fryirs & G. J. Brierley, 2006. Linking geomorphic character, behaviour and condition to fluvial biodiversity: implications for river management. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 16: 267–288.
Clarke, K. R. & R. N. Gorley, 2006. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial. PRIMER E-Ltd, Plymouth.
Datry, T., N. Lamouroux, G. Thivin, S. Descloux & J. M. Baudoin, 2015. Estimation of sediment hydraulic conductivity in river reaches and its potential use to evaluate streambed clogging. River Research and Applications 31: 880–891.
Davy-Bowker, J., W. Sweeting, N. Wright, R. T. Clarke & S. Arnott, 2006. The distribution of benthic and hyporheic macroinvertebrates from the head and tails of riffles. Hydrobiologia 563: 109–123.
Death, R. G., 2010. Disturbance and riverine benthic communities: what has it contributed to general ecological theory? River Research and Applications 26: 15–25.
Descloux, S., T. Datry & P. Marmonier, 2013. Benthic and hyporheic invertebrate assemblages along a gradient of increasing streambed colmation by fine sediment. Aquatic Sciences 75: 493–507.
Descloux, S., T. Datry & P. Usseglio-Polatera, 2014. Trait-based structure of invertebrates along a gradient of sediment colmation: benthos versus hyporheos responses. Science of the Total Environment 466: 265–276.
Dole-Olivier, M. J., 1998. Surface water–groundwater exchanges in three dimensions on a backwater of the Rhône River. Freshwater Biology 40: 93–109.
Dole-Oliver, M. J. & P. Marmonier, 1992. Patch distribution of interstitial communities: prevailing factors. Freshwater Biology 27: 177–191.
Dole-Olivier, M. J., P. Marmonier & J. L. Beffy, 1997. Response of in invertebrates to lotic disturbance: is the hyporheic zone a patchy refugium?. Freshwater Biology 37: 257–276.
Downes, B. J., P. S. Lake & S. G. Schreiber, 1993. Spatial variation in the distribution of stream in-vertebrates: implications of patchiness for models of community organization. Freshwater Biology 30: 119–132.
Duan, X., Z. Wang, M. Xu & K. Zhang, 2009. Effect of streambed sediment on benthic ecology. International Journal of Sediment Research 24: 325–338.
Dudley-Southern, M. & A. Binley, 2015. Temporal responses of groundwater-surface water exchange to successive storm events. Water Resources Research 51: 112–1126.
Dussart, B. H. & D. Defaye, 2001. Introduction to the Copepoda. (2nd Edition). Guides to the Identification of the Macroinvertebrate of the Continental Water of the World. Volume 16. Backhuys Publishers, Leiden. 344 pp.
Effenberger, M., G. Sailer, C. R. Townsend & C. D. Matthaei, 2006. Local disturbance history and habitat parameters influence the microdistribution of stream invertebrates. Freshwater Biology 51: 31–332.
Extence, C. A., R. P. Chadd, J. England, M. J. Dunbar, P. J. Wood & E. D. Taylor, 2013. The assessment of fine sediment accumulation in rivers using macro-invertebrate community response. River Research and Applications 29: 17–55.
Findlay, S., D. Strayer, C. Goumbla & K. Gould, 1993. Metabolism of streamwater dissolved organic carbon in the shallow hyporheic zone. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 1493–1499.
Fonseca, D. M. & D. D. Hart, 2001. Colonization history masks habitat preferences in local distributions of stream insects. Ecology 82: 2897–2910.
Fowler, R. T. & M. R. Scarsbrook, 2002. Influence of hydrologic exchange patterns on water chemistry and hyporheic invertebrate communities in three gravel-bed rivers. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 36: 471–482.
Franken, R. J. M., R. G. Storey & D. D. Williams, 2001. Biological, chemical and physical characteristics of downwelling and upwelling zones in the hyporheic zone of a north temperate stream. Hydrobiologia 444: 183–195.
Gayraud, S. & M. Philippe, 2001. Does subsurface interstitial space influence general characteristics and features and morphological traits of benthic macroinvertebrate communities in streams. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 151: 667–686.
Gibbins, C. N., J. Grant, I. A. Malcom & C. Soulsby, 2016. Influence of groundwater chemistry on hyporheic invertebrate assemblages is revelead by fine-scale sampling. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 187: 207–221.
Gomez-Velez, J., S. Krause & J. L. Wilson, 2014. Effect of low-permeability layers on spatial patterns of hyporheic exchange and groundwater upwelling. Water Resources Research 50: 5196–5215.
Gordon, N. D., T. A. McMahon & B. L. Finlayson, 1994. Stream Hydrology: An Introduction for Ecologists. Wiley, Chichester.
Greenwood, M. T., M. A. Bickerton & G. E. Petts, 2001. Assessing adult Trichoptera communities of small streams: a case study from Charnwood Forest, Leicestershire, UK. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 11: 93–107.
Grimm, N. B., C. V. Baxter & C. L. Crenshaw, 2007. Surface- subsurface interactions in streams. In Haeur, F. R. & G. A. Lamberti (eds), Methods in Stream Ecology, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego.
Harper, D. & M. Everard, 1998. Why should the habitat-level approach underpin holistic river survey and management?. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 8: 395–413.
Hartwig, M. & D. Borchardt, 2015. Alteration of key hyporheic functions through biological and physical clogging along a nutrient and fine-sediment gradient. Ecohydrology 8: 961–975.
Henderson, P. A. 1990. Freshwater Ostracods. Synopses of the British Fauna (New Series). The Linnean Society of London and the Estuarine and Coastal Sciences Association. 228 pp.
Huettel, M., W. Ziebis & S. Forster, 1996. Flow-induced uptake of particulate matter in permeable sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 4: 309–322.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1983. Groundwater and stream ecology. Hydrobiologia 100: 93–99.
Jones, J. I., J. F. Murphy, A. L. Collins, D. A. Sear, P. S. Naden & P. D. Armitage, 2012. The impact of fine sediment on macroinvertebrates. River Research and Applications 28: 1055–1071.
Jones, I., I. Growns, A. Arnold, S. McCall & M. Bowes, 2015. The effects of increased flow and fine sediment on hyporheic invertebrates and nutrients in stream mesocosms. Freshwater Biology 60: 813–826.
Junk, W. J., P. B. Bayley & R. E. Sparks, 1989. The flood pulse concept in river-floodplain systems, In Dodge, D. P. (eds), Proceedings of the International Large River Symposium. Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 106: 110–127.
Käser, D. H., A. Binley, A. L. Heathwaite & S. Kruase, 2009. Spatio-temporal variations of hyporheic flow in a riffle-step-pool sequence. Hydrological Processes 23: 2138–2149.
Krause, S., D. M. Hannah, J. H. Fleckenstein, C. M. Heppell, D. Kaeser, R. Pickup, G. Pinay, A. L. Robertson & P. J. Wood, 2011a. Inter-disciplinary perspectives on processes in the hyporheic zone. Ecohydrology 4: 481–499.
Krause, S., D. M. Hannah & T. Blume, 2011b. Interstitial pore-water temperature dynamics across a pool-riffle-pool sequence. Ecohydrology 4: 549–563.
Krause, S., M. J. Klaar, D. M. Hannah, J. Mant, J. Bridgeman, M. Trimmer & S. Manning-Jones, 2014. The potential of large woody debris to alter biogeochemical processes and ecosystem services in lowland rivers. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Water 1: 263–275.
Larson, S. & S. J. Ormerod, 2010. Low-level effects of inert sediments on temperate stream invertebrates. Freshwater Biology 55: 476–486.
Lee, D. R. & J. A. Cherry, 1978. A field exercise on groundwater flow using seepage meters and min-piezometers. Journal of Geological Education 27: 6–10.
Leek, R., J. Q. Wu, L. Wang, T. P. Hanrahan, M. E. Barber & H. Qiu, 2009. Heterogeneous characteristics of streambed saturated hydraulic conductivity of the Touchet River, south eastern Washington, USA. Hydrological Processes 23: 1236–1246.
Malard, F., K. Tockner, M. Dole-Oliver & J. V. Ward, 2002. A landscape perspective of surface-subsurface hydrological exchanges in river corridors. Freshwater Biology 47: 621–640.
Maridet, L., M. Philippe, J. G. Wasson & J. Mathieu, 1997. Seasonal dynamics and storage of particulate organic matter within bed sediment of three streams with contrasted riparian vegetation and morphology. In Gibert, J., J. Mathieu & F. Fournier (eds), Groundwater/Surface Water Ecotones: Biological and Hydrological Interactions and Management Options. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Marmonier, P., H. Luczyszyn, M. Creuze des Chatelliers, N. Landon, C. Claret & M.-J. Dole-Olivier, 2010. Hyporheic flowpaths and interstitial invertebrates associated with stable and eroded river sections: interactions between micro and meso-scales. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 176: 303–317.
Marmonier, P., G. Archambaud, N. Belaidi, N. Bougon, P. Breil, E. Chauvet, C. Claret, J. Cornut, T. Datry, M.-J. Dole-Olivier, B. Dumont, N. Flipo, A. Foulquier, M. Gerino, A. Guilpart, F. Julien, C. Maazouzi, D. Martin, F. Mermillod-Blondin, B. Montuelle, Ph Namour, S. Navel, D. Ombredane, T. Pelte, C. Piscart, M. Pusch, S. Stroffek, A. Robertson, M.-J. Sanchez-Perez, S. Sauvage, A. Taleb, M. Wantzen & Ph Vervier, 2012. The role of organism in hyporheic processes: gaps in current knowledge, needs for future research and applications. Annales de Limnologie: International Journal of Limnology 48: 253–266.
Mathers, K. L., J. Millett, A. L. Robertson, R. Stubbington & P. J. Wood, 2014. Faunal response to benthic and hyporheic sedimentation varies with direction of vertical hydrological exchange. Freshwater Biology 59: 2278–2289.
Mathers, K. L. & P. J. Wood, 2016. Fine sediment deposition and interstitial flow effects on macroinvertebrate community composition within riffle heads and tails. Hydrobiologia 776: 147–160.
Mauclaire, L., P. Marmonier & J. Gibert, 1998. Sampling water and sediment in interstitial habitats: a comparison of coring and pumping techniques. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 142: 111–123.
McMullen, L. E. & D. A. Lytle, 2012. Quantifying invertebrate resistance to flood: a global-scale meta-analysis. Ecological Applications 22: 2164–2175.
Mermillod-Blondin, F., M. Creuzé des Châtelliers, P. Marmonier & M.-J. Dole‐Olivier, 2000. Distribution of solutes, microbes and invertebrates in river sediments along a riffle-pool-riffle sequence. Freshwater Biology 44: 255–269.
Milan, D. J. & A. R. Large, 2014. Magnetic tracing of fine-sediment over pool-riffle morphology. Catena 115: 134–149.
National River Flow Archive, 2016. Black Brook at One Barrow Data Webpage. Available at: http://www.ceh.ac.uk/data/nrfa/data/station.html?28030. [Access Date: 12th April 2016].
Newson, M. D., 2002. Geomorphologic concepts and tools for sustainable river ecosystem management. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 12: 365–379.
Oksanen, J., F. G. Blanchet, M. Friendly, R. Kindt, P. Legendre, D. McGlinn, P. R. Minchin, R. B. O’Hara, G. L. Simpson, P. Solymos, H. H. Stevens, E. Szoecs, & H. Wagner, 2015. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package Version 2.3-1. [Accessible at http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan].
Olsen, D. A. & C. R. Townsend, 2003. Hyporheic community composition in a gravel-bed stream: influence of vertical hydrological exchange, sediment structure and physicochemistry. Freshwater Biology 48: 1363–1378.
Orghidan, T., 1959. Ein neuer Lebensraum des unterirdischen Wassers: der hyporheische Biotop. Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 55: 392–414.
Pacioglu, O., P. Shaw & A. Robertson, 2012. Patch scale response of hyporheic invertebrates to fine sediment removal in two chalk rivers. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 18: 283–288.
Packman, A. I. & K. E. Bencala, 2003. Relative roles of stream flow and sedimentary conditions in controlling hyporheic exchange. Hydrobiologia 494: 291–297.
Pepin, D. M. & F. R. Hauer, 2002. Benthic response to groundwater-surface water exchange in 2 alluvial rivers in north-western Montana. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 21: 370–383.
Petts, G. E., 1984. Sedimentation within a regulated river. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 9: 125–134.
Pinay, G., S. Peiffer, J. R. De Dreuzy, S. Krause, D. M. Hannah, J. H. Fleckenstein, M. Sebilo, K. Bishop & L. Hubert-Moy, 2015. Upscaling nitrogen removal capacity from local hotspots to low stream orders’ drainage basins. Ecosystems 18: 1101–1120.
Poff, N. L., J. D. Allan, M. B. Bain, J. R. Karr, K. L. Prestegaard, B. D. Richter, R. E. Sparks & J. C. Stromberg, 1997. The natural flow regime. BioScience 47: 769–784.
Pusch, M., 1996. The metabolism of organic matter in the hyporheic zone of a mountain stream, and its spatial distribution. Hydrobiologia 323: 107–118.
R Development Core Team, 2014. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0.
Rabeni, C., K. Doisy & L. D. Zweig, 2005. Stream Invertebrate community functional responses to deposited sediment. Aquatic Sciences 65: 395–402.
Relyea, C. D., G. W. Minshall & R. J. Danehy, 2000. Stream insects as bioindicators of fine sediment. Proceedings of the water Environment Federation 6: 663–686.
Ren, J. & A. I. Packman, 2007. Changes in fine sediment size distributions due to interactions with streambed sediments. Sediment Geology 3: 529–537.
Richards, C. & K. L. Bacon, 1994. Influence of fine sediment on macroinvertebrate colonisation of surface and hyporheic stream substrates. Great Basin Naturalist 54: 106–113.
Rosi-Marshall, E. J., K. L. Vallis, C. V. Baxter & J. M. Davis, 2016. Retesting a prediction of the River Continuum Concept: autochthonous versus allochthonous resources in the diets of invertebrates. Freshwater Science 35: 534–543.
Saenger, N., P. K. Kitandis & R. L. Street, 2005. A numerical study of surface-subsurface exchange processes at a riffle-pool pair in the Lahn River. Germany. Water Resources Research 41: W12424.
Sarriquet, P. E., P. Bordenave & P. Marmonier, 2007. Effects of bottom sediment restoration on interstitial habitat characteristics and benthic macroinvertebrate assemblages in a headwater stream. River Research and Applications 23: 815–828.
Savant, S. A., D. D. Reible & L. J. Thibodeaux, 1987. Convective transport within stable river sediments. Water Research 23: 1763–1768.
Sawyer, A. H. & M. B. Cardenas, 2012. Effect of experimental wood addition on hyporheic exchange and thermal dynamics in a losing meadow stream. Water Resources Research 48: W10537.
Schmid, P. E., 1993. Random patch dynamics of larval chironomidae (Diptera) in the bed sediments of a gravel stream. Freshwater Biology 30: 239–255.
Sear, D. A., 1993. Fine sediment infiltration into gravel spawning beds within a regulated river experiencing floods: ecological implications for salmonids. Regulated Rivers: Research and Management 8: 373–390.
Silva, D. R. O., R. Ligeiro, R. M. Hughes & M. Callisto, 2014. Visually determined stream mesohabitats influence benthic macroinvertebrate assessments in headwater streams. Environmental Monitoring for Assessment 186: 5479–5488.
Strayer, D. L., S. E. May, P. Nielsen, W. Wollheim & S. Hausam, 1997. Oxygen, organic matter, and sediment granulometry as controls on hyporheic animal communities. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 140: 131–144.
Strommer, J. L. & L. A. Smock, 1989. Vertical distribution and abundance of invertebrates within the sandy substrate of a low gradient headwater stream. Freshwater Biology 22: 263–274.
Stubbington, R., P. J. Wood & I. Reid, 2011. Spatial variability in the hyporheic zone refugium of temporary streams. Aquatic Sciences 73: 499–511.
Suren, A. M. & I. G. Jowett, 2006. Effects of floods versus low flows on invertebrates in a New Zealand gravel-bed river. Freshwater Biology 51: 2207–2227.
Swan, C. M. & M. A. Palmer, 2000. What drives small scale spatial patterns in lotic meiofauna communities? Freshwater Biology 44: 109–121.
Tachet, H., M. Bournaud, P. Richoux & P. Usseglio-Polatera, 2010. Invertébrés d’eau douce: systématique, biologie, écologie. CNRS Editions, Paris.
Thomson, J. R., M. P. Taylor & G. J. Brierley, 2004. Are River Styles ecologically meaningful? A test of the ecological significance of a geomorphic river characterization scheme. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 14: 24–48.
Tilzer, M., 1968. Zur Okologie und Besiedlung des hochalpinen hyporheischen Interstitials im Arlberggebiet (Osterreich). Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 140: 131–144.
Turić, N., M. Temunović, A. Radović, G. Vignjević, M. Sudarić Bogojević & E. Merdić, 2015. Flood pulses drive the temporal dynamics of assemblages of aquatic insects (Heteroptera and Coleoptera) in a temperate floodplain. Freshwater Biology 60: 2051–2065.
Vannote, R. L., G. W. Minshall, K. W. Cummins, J. R. Sedell & C. E. Cushing, 1980. The river continuum concept. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 37: 130–137.
Verdonschot, R. C. M., J. Kail, B. G. McKie & P. R. M. Verdonschot, 2016. The role of benthic microhabitats in determining the effects of hydromorphological river restoration on macroinvertebrates. Hydrobiologia 769: 55–66.
Weigelhofer, G. & J. Waringer, 2003. Vertical distribution of benthic macroinvertebrates in riffles versus deep runs with differing contents of fine sediments (Weidlingbach, Austria). International Review of Hydrobiology 88: 304–313.
Wentworth, C. K., 1922. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. The Journal of Geology 30: 377–392.
Wildhaber, Y. S., C. Michel, J. Epting, R. A. Wildhaber, E. Huber, P. Huggenberger, P. Burkhardt-Holm & C. Alewell, 2014. Effects of river morphology, hydraulic gradients, and sediment deposition on water exchange and oxygen dynamics in salmonid redds. Science of the Total Environment 470: 488–500.
Wilson, M. J. & M. E. McTammany, 2016. Spatial scale and dispersal influence metacommunity dynamics of benthic invertebrates in a large river. Freshwater Science 35: 738–747.
Winterbottom, J. H., S. E. Orton, A. G. Hildrew & J. Lancaster, 1997. Field experiments on flow refugia in streams. Freshwater Biology 37: 569–580.
Wipfli, M. S., J. S. Richardson & R. J. Naiman, 2007. Ecological linkages between headwaters and downstream ecosystems: transport of organic matter, invertebrates, and wood down headwater channels. Journal of the American Water Resources Association 43: 72–85.
Wondzell, S. M. & F. J. Swanson, 1996. Seasonal and storm dynamics of the hyporheic zone of a 4th order mountain stream: hydrological Processes. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 15: 3–19.
Wood, P. J. & P. D. Armitage, 1997. Biological effects of fine sediment in the lotic environment. Environmental Management 21: 203–217.
Wood, P. J. & P. D. Armitage, 1999. Sediment deposition in a small lowland stream – management implications. Regulated Rivers: Research and Management 15: 199–210.
Wood, P. J., J. Toone, M. T. Greenwood & P. D. Armitage, 2005. The response of four lotic macroinvertebrate taxa to burial by sediments. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 163: 145–162.
Wood, P. J., A. J. Boulton, S. Little & R. Stubbington, 2010. Is the hyporheic zone a refugium for macroinvertebrates during severe low flow conditions? Fundamental and Applied Limnology 176: 377–390.
Xu, M. Z., Z. Y. Wang, B. Z. Pan & N. Zhao, 2012. Distribution and species composition of macroinvertebrates in the hyporheic zone of bed sediment. International Journal of Sediment Research 27: 129–140.
Acknowledgements
KLM acknowledges the Department of Geography Laboratory staff, Stuart Ashby and Barry Kenny, for technical and laboratory support. The authors would like to thank Joni Cook who provided assistance with fieldwork. The authors would also like to thank two anonymous reviewers for their comments on the manuscript which helped improve the clarity of the text.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Marcelo S. Moretti
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Mathers, K.L., Hill, M.J. & Wood, P.J. Benthic and hyporheic macroinvertebrate distribution within the heads and tails of riffles during baseflow conditions. Hydrobiologia 794, 17–30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3092-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3092-8