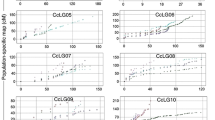
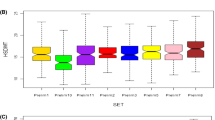
Abstract
High prices of fish oil make linseed attractive for aquaculture and animal feed. To ensure a constant supply of linseed, the development of stable cultivars is of strategic importance. In this study, 35 linseed genotypes were evaluated in five Chilean environments (E) from 2009 to 2012. The additive main effect and multiplicative interaction analysis (AMMI), genotype (G) plus genotype by environment (GE) interaction (GGE) biplot analysis and three stability parameters were tested with the aim of identifying adapted genotypes for the development of linseed cultivars. An association mapping (AM) analysis was also conducted for four agronomic traits and the stability of the associated markers was evaluated using the QQE (QTL main effect and QTL by environment interaction) approach. Combined analysis of variance for yield, seeds per boll (SPB), plant height (PH) and days to flowering (DTF) were significant for G, E and GE (P < 0.001). The combined stability analysis identified some Canadian, Argentinean and Chilean accessions to be the best adapted and highest yielding genotypes. Coancestry analysis indicated that crossing Canadian and Chilean genotypes could maximize transgressive segregation for yield. Significant associations for DTF, PH and SPB explained up to 59 % of the phenotypic variation for these traits. The QQE and AM analyses were consistent in identifying marker LGM27B as the most stable and significant across all environments with the largest effect in reducing DTF. The combined application of the stability, AM and QQE analyses could accelerate the development of marketable linseed cultivars adapted to Southern Chile.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adugna W, Labuschagne MT (2003) Association of linseed characters and its variability in different environments. J Agric Sci 140:285–296
Annicchiarico P (1997) Joint regression versus AMMI analysis of genotype–environment interactions for cereals in Italy. Euphytica 94:53–62
Balcázar-Muñoz BR, Martínez-Abundis E, González-Ortiz M (2003) Efecto de la administración oral de inulina sobre el perfil de lípidos y la sensibilidad a la insulina en individuos con obesidad y dislipidemia. Rev Med Chile 131:597–604
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B 57:289–300
Berti M, Fischer S, Wilckens R, Hevia F (2009) Flaxseed response to N, P, and K fertilization in South Central Chile. Chil J Agric Res 69:145–153
Berti M, Fisher S, Wilckens R, Hevia F, Johnson B (2010) Adaptation and genotype x environment interaction of flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) genotypes in South Central Chile. Chil J Agric Res 70:345–356
Brachi B, Faure N, Horton M, Flahauw E, Vazquez A, Nordborg M, Bergelson J, Cuguen J, Roux F (2010) Linkage and association mapping of Arabidopsis thaliana flowering time in nature. PLoS Genet 6:e1000940
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Breseghello F, Sorrells M (2006) Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 172:1165–1177
Caballero A, Toro MA (2002) Analysis of genetic diversity for the management of conserved subdivided populations. Conserv Genet 3:289–299
Casa R, Russell G, Lo Cascio B, Rossini F (1999) Environmental effects on linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) yield and growth of flax at different stand densities. Eur J Agron 11:267–278
CIREN (2002) Descripciones de suelos, materiales y símbolos. Estudio agrológico IX Región. Publicación No 122. Centro de Información de Recursos Naturales (CIREN), Santiago, p 360
Cloutier S, Niu Z, Datla R, Duguid S (2009) Development and analysis of EST-SSRs for flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). Theor Appl Genet 119:53–63
Cloutier S, Ragupathy R, Niu Z, Duguid S (2011) SSR-based linkage map of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) and mapping of QTLs underlying fatty acid composition traits. Mol Breed 28:437–451
Cloutier S, Miranda E, Ward K, Radovanovic N, Reimer E, Walichnowski A, Datla R, Rowland G, Duguid S, Ragupathy R (2012a) Simple sequence repeat marker development from bacterial artificial chromosome end sequences and expressed sequence tags of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). Theor Appl Genet 125:685–694
Cloutier S, Ragupathy R, Miranda E, Radovanovic N, Reimer E, Walichnowski A, Ward K, Rowland G, Duguid S, Banik M (2012b) Integrated consensus genetic and physical maps of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). Theor Appl Genet 125:1783–1795
Delhaize E, Ma JF, Ryan PR (2012) Transcriptional regulation of aluminium tolerance genes. Trends Plant Sci 17:341–348
Deng X, Long S, He D, Li X, Wang Y, Liu J, Chen X (2010) Development and characterization of polymorphic microsatellite markers in Linum usitatissimum. J Plant Res 123:119–123
Diederichsen A (2007) Ex situ collections of cultivated flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) and other species of the genus Linum L. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:661–678
Diederichsen A, Raney JP, Duguid SD (2006) Variation of mucilage in flax seed and its relationship with other seed characters. Crop Sci 46:365–371
Diederichsen A, Kusters PM, Kessler D, Bainas Z, Gugel RK (2013) Assembling a core collection from the flax world collection maintained by plant gene resources of Canada. Genet Resour Crop Evol 60:1479–1485
Ersoz ES, Yu J, Buckler ES (2009) Applications of linkage disequilibrium and association mapping in maize. In: Kriz AL, Larkins BA (eds) Molecular genetic approaches to maize improvement. Springer, Berlin, pp 173–195
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
FAOSTAT (2013) Production of crops: linseed: area harvested/yield and production (tonnes). Available at http://faostat3.fao.org/home/index.html. Accessed March 2013
Fu YB, Rowland GG, Duguid SD, Richards K (2003) RAPD analysis of 54 North American flax cultivars. Crop Sci 43:1510–1515
Gallardo F, Borie F, Alvear L, Baer EV (1999) Evaluation of aluminium tolerance of three barley cultivars by two short-term screening methods and field experiments. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 45:713–719
Gauch HG (1992) AMMI analysis of yield trials. In: Kang MS, Gauch HG (eds) Genotype-by-environment interaction. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 1–40
Gauch HG, Zobel RW (1997) Identifying mega-environment and targeting genotypes. Crop Sci 37:311–326
Gauch HG, Piepho HP, Annicchiarico P (2008) Statistical analysis of yield trials by AMMI and GGE: further considerations. Crop Sci 48:866–889
Grossniklaus U, Kelly B, Ferguson-Smith AC, Pembrey M, Lindquist S (2013) Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: How important is it? Nat Rev Genet 14:228–235
Gutiérrez JP, Royo LJ, Álvarez I, Goyache F (2005) MolKin v2.0: a computer program for genetic analysis of populations using molecular coancestry information. J Hered 96:718–721
Hardy OJ, Vekemans X (2002) SPAGeDi: a versatile computer program to analyse spatial genetic structure at the individual or population levels. Mol Ecol Notes 2:618–620
Harris, DR (1997) The spread of neolithic agriculture from the Levant to Western-Central Asia. In: Damania AB,Valkoun J, Willcox G, Qualset CO (eds) The origin of agriculture and crop domestication. In: Proceedings of Harlan Symposium, ICARDA, Aleppo, Syria, May 10–14, pp 65–82
Hubisz MJ, Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2009) Inferring weak population structure with the assistance of sample group information. Mol Ecol Resour 9:1322–1332
Jarillo JA, Piñeiro M (2011) Timing is everything in plant development. The central role of floral repressors. Plant Sci 181:364–378
Kim DH, Doyle MR, Sung S, Amasino RM (2009) Vernalization: winter and the timing of flowering in plants. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25:277–299
King GJ, Amoah S, Kurup S (2010) Exploring and exploiting epigenetic variation in crops. Genome 53:856–868
Kozlowska J, Muñoz GA, Kolodziejczyk PP (2008) Food and feed application for flaxseed components. In: Proceedings of the 2008 international conference on flax and other bast plants, Saskatoon, SK, pp 299
Kumar S, You FM, Cloutier S (2012) Genome wide SNP discovery in flax through next generation sequencing of reduced representation libraries. BMC Genomics 13:684
Lukens LN, Zhan S (2007) The plant genomes methylation status and response to stress: implications for plant improvement. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:317–322
Mohammadi R, Amri A (2013) Genotype × environment interaction and genetic improvement for yield and yield stability of rainfed durum wheat in Iran. Euphytica 192:227–249
Myles S, Peiffer J, Brown PJ, Ersoz ES, Zhang Z, Costich DE, Bukler ES (2009) Association mapping: critical considerations shift from genotyping to experimental design. Plant Cell 21:2194–2202
Oh TJ, Gorman M, Cullis CA (2000) RFLP and RAPD mapping in flax (L. usitatissimum). Theor Appl Genet 101:590–593
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GENALEX 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Rosenberg NA, Donnelly P (2000) Association mapping in structured populations. Am J Hum Genet 67:170–181
Purchase JL (1997) Parametric analysis to describe G × E interaction and yield stability in winter wheat. Dissertation, University of the Orange Free State
Ragupathy R, Rathinavelu R, Cloutier S (2011) Physical mapping and BAC-end sequence analysis provide initial insights into the flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) genome. BMC Genomics 12:217
Rahimi MM, Zarei MA, Arminian A (2011) Selection criteria of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) for seed yield, yield components and biochemical compositions under various planting dates and nitrogen. Afr J Agric Res 6:3167–3175
Roose-Amsaleg C, Cariou-Pham E, Vautrin D, Tavernier R, Solignac M (2006) Polymorphic microsatellite loci in Linum usitatissimum. Mol Ecol Notes 6:796–799
Rowland GG, Hormis YA, Rashid KY (2002) CDC Bethune flax. Can J Plant Sci 82:101–102
Shi J, Li R, Qiu D, Jiang C, Long Y, Morgan C, Bancroft I, Zhao J, Meng J (2009) Unraveling the complex trait of crop yield with quantitative trait loci mapping in Brassica napus. Genetics 182:851–861
Smýkal P, Bačová-Kerteszová N, Kalendar R, Corander J, Schulman AH, Pavelek M (2011) Genetic diversity of cultivated flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) germplasm assessed by retrotrasnsposon-based markers. Theor Appl Genet 122:1385–1397
Soto-Cerda BJ, Cloutier S (2012) Association mapping in plant genomes. In: Caliskan M (ed) Genetic diversity in plants. InTech, Rijeka, pp 29–54
Soto-Cerda BJ, Carrasco RA, Aravena GA, Urbina HA, Navarro CS (2011a) Identifying novel polymorphic microsatellites from cultivated flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) following data mining. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:753–759
Soto-Cerda BJ, Urbina Saavedra H, Navarro Navarro C, Mora Ortega P (2011b) Characterization of novel genic SSR markers in Linum usitatissimum (L.) and their transferability across eleven Linum species. Electron J Biotechnol. doi:10.2225/vol14-issue2-fulltext-6
Soto-Cerda BJ, Maureira-Butler I, Muñoz G, Rupayan A, Cloutier S (2012) SSR-based population structure, molecular diversity and linkage disequilibrium analysis of a collection of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) varying for mucilage seed-coat content. Mol Breed 30:875–888
Soto-Cerda BJ, Diederichsen A, Ragupathy R, Cloutier S (2013) Genetic characterization of a core collection of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) suitable for association mapping studies and evidence of divergent selection between fiber and linseed types. BMC Plant Biol 13:78
Spielmeyer W, Green AG, Bittisnich D, Mendham N, Lagudah ES (1998) Identification of quantitative trait loci contributing to Fusarium wilt resistance on an AFLP linkage map of flax (Linum usitatissimum). Theor Appl Genet 97:633–641
Springer NM (2012) Epigenetics and crop improvement. Trends Genet. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2012.10.009
StatSoft, Inc (2007) Electronic statistics textbook [online]. StatSoft, Tulsa, Okla. Available from www.statsoft.com/textbook/stathome.html. Accessed June 2013
Storey JD, Tibshirani R (2003) Statistical significance for genomewide studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9440–9445
St-Pierre CA, Klinck HR, Gauthier FM (1967) Early generation selection under different environments as it influences adaptation of barley. Can J Plant Sci 47:507–517
Tester M, Langridge P (2010) Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 327:818–822
The EPIC Planning Committee (2012) Reading the second code: mapping epigenomes to understand plant growth, development, and adaptation to the environment. Plant Cell 24:2257–2261
van der Merwe R, Labuschagne MT, Herselman L, Hugo A (2013) Stability of seed oil quality traits in high and mid-oleic acid sunflower hybrids. Euphytica. doi:10.1007/s10681-013-0888-0
VSN International (2011) GenStat for windows 14th edn. VSN International, Hemel Hempstead. http://www.GenStat.co.uk
Wang Z, Hobson N, Galindo L, Zhu S, Shi D, McDill J, Yang L, Hawkins S, Neutelings G, Datla R, Lambert G, Galbraith DW, Grassa CJ, Geraldes A, Cronk QC, Cullis C, Dash PK, Kumar PA, Cloutier S, Sharpe AG, Wong GK, Wang J, Deyholos MK (2012) The genome of flax (Linum usitatissimum) assembled de novo from short shotgun sequence reads. Plant J 72:461–473
Xiao-Jun L, Xin X, Wei-Hua L, Xiu-Quan L, Xin-Ming Y, Li-Hui L (2009) Genetic contribution of introduced varieties to wheat breeding in China evaluated using microsatellite markers. Acta Agron Sin 35:778–785
Yan W (2001) GGEbiplot—a windows application for graphical analysis of multi-environment trial data and other types of two-way data. Agron J 93:1111–1118
Yan W, Kang MS (2003) GGE biplot analysis: a graphical tool for breeders, geneticists, and agronomists. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Yan W, Tinker NA (2005) A biplot approach for investigating QTL-by-environment patterns. Mol Breed 15:31–43
Yan W, Hunt LA, Sheng Q, Szlavnics Z (2000) Cultivar evaluation and mega-environment investigation based on the GGE biplot. Crop Sci 40:597–605
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs W, Vroh Bi I, Yamasaki M, Doebley J, McMullen M, Gaut B, Nielsen D, Holland J, Kresovich S, Buckler E (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208
Yu J, Holland JB, McMullen MD, Buckler ES (2008) Genetic design and statistical power of nested association mapping in maize. Genetics 178:539–551
Zhang X, Wang J, Huang J, Lan H, Wang C, Yin C, Wu Y, Tang H, Qian Q, Li J, Zhang H (2012) Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:21534–21539
Zobel RW, Wright MJ, Gauch HG (1988) Statistical analysis of a yield trial. Agron J 80:388–393
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Héctor Pauchard for supplying the meteorological data and Dana Kowal for the help in the preparation of figures. We acknowledge INIA and Monica Gebert for their support providing experimental fields. This work was supported by the Agriaquaculture Nutritional Genomic Center (CGNA). Braulio Soto-Cerda was supported by Becas Chile—Comisión Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (CONICYT).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soto-Cerda, B.J., Westermeyer, F., Iñiguez-Luy, F. et al. Assessing the agronomic potential of linseed genotypes by multivariate analyses and association mapping of agronomic traits. Euphytica 196, 35–49 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-1012-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-013-1012-1