Abstract
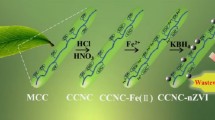
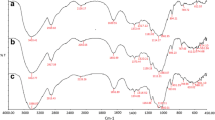
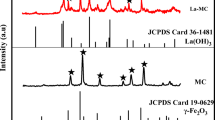
Microcrystalline cellulose immobilized zerovalent iron nanoparticles (CI-1-3) with different loading of 6, 12 and 24% w/w Fe0 were synthesized by NaBH4 reduction under simultaneous co-precipitation of cellulose from ionic liquid ([BMIM]Cl)-water binary mixture. SEM, TEM, FTIR, VSM, XRD and XPS analysis were carried out to characterize the material. The electron microscopy studies revealed the immobilization of iron nanoparticle in the bulk and surface of microcrystalline cellulose with a size range of 20–100 nm. CI-1-3 showed strong interaction between cellulose hydroxyl moiety and nZVI, immobilized on the polymer and saturation magnetization of 3 emu/g for CI-2. The materials were studied for Cr(VI) adsorption which revealed the qmax value of 28.57, 58.82 and 38.48 mg Cr(VI)/g of CI-1-3, respectively.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alidokht L, Khataee AR, Reyhanitabar A, Oustan S (2011) Reductive removal of Cr(VI) by starch-stabilized Fe0 nanoparticles in aqueous solution. Desalination 270:105–110
Anirudhan TS, Jalajamony S, Suchithra PS (2009) Improved performance of a cellulose-based anion exchanger with tertiary amine functionality for the adsorption of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions. Colloids Surf A 335:107–113
APHA (2005) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 21st ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC, pp 3-67–3-68
Bezbaruah AN, Krajangpan S, Chisholm BJ, Khan E, Bermudez JJE (2009) Entrapment of iron nanoparticles in calcium alginate beads for ground water remediation application. J Hazard Mater 166:1339–1343
Cai J, Kimura S, Wada M, Kuga S (2008) Nanoporous cellulose as metal nanoparticles support. Biomacromol 10:87–94
Choi K, Lee S, Park JO, Park JA, Cho SH, Lee SY, Lee JH, Choi JW (2018) Chromium removal from aqueous solution by a PEI-silica nanocomposite. Sci Rep 8:1438
Crane RA, Scott TB (2012) Nanoscale zero-valent iron: future prospects for an emerging water treatment technology. J Hazard Mater 211:112–125
Crowhurst L, Mawdsley PR, Perez JM (2003) Solvent-solute interaction in ionic liquid. Phys Chem Chem Phys 5:2790–2794
Dafader NC, Rahman N, Majumdar SK, Khan MM, Rahman MM (2018) Preparation and characterization of iminodiacetate group containing nonwoven polyethylene fabrics and its application in chromium adsorption. J Polym Environ 26:740–748
Dalla Vecchia E, Coisson M, Appino C, Vinai F, Sethi R (2009) Magnetic characterization and interaction modeling of zerovalent iron nanoparticles for the remediation of contaminated aquifers. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 9:3210–3218
Datta KKR, Petala E, Datta KJ, Perman JA, Tucek J, Bartak P, Zboril R (2014) NZVI modified magnetic filter paper with high redox and catalytic activities for advanced water treatment technologies. Chem Commun 50:15673–15676
de Morais Teixeira E, Corrêa AC, Manzoli A, de Lima Leite F, de Oliveira CR, Mattoso LHC (2010) Cellulose nanofibers from white and naturally colored cotton fibers. Cellulose 17(3):595–606
Devan RS, Ho WD, Chen CH, Shiu HW, Ho CH, Cheng CL, Wu SY, Liou Y, Ma YR (2009) High room-temperature photoluminescence of one-dimensional Ta2O5 nanorod arrays. Nanotechnology 20:445708
Devan RS, Lin JH, Ho WD, Wu SY, Liou Y, Ma YR (2010) Investigation of high-temperature phase transformation in one-dimensional Ta2O5 nanorods. J Appl Crystallogr 43:1062–1067
Devan RS, Lin CL, Gao SY, Cheng CL, Liou Y, Ma YR (2011) Enhancement of green-light photoluminescence of Ta2O5 nanoblock stacks. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:13441–13446
Devan RS, Ma YR, More MA, Khare RT, Antad VV, Patil RA, Thakare VP, Dhayal RS, Schmidt-Mende L (2016) Promising field electron emission performance of vertically aligned one dimensional (1D) brookite (β) TiO2 nanorods. RSC Adv 6:98722–98729
Devan RS, Thakare VP, Antad VV, Chikate PR, Khare RT, More MA, Dhayal RS, Patil SI, Ma YR, Schmidt-Mende L (2017) Nano-heteroarchitectures of two-dimensional MoS2@ one-dimensional brookite TiO2 nanorods: prominent electron emitters for displays. ACS Omega 2:2925–2934
Duan J, He X, Zhang L (2015) Magnetic cellulose–TiO2 nanocomposite microspheres for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem Commun 51:338–341
Eliodorio KP, Andolfatto VS, Martins MR, de Sá BP, Umeki ER, de Araújo Morandim-GiannettiA (2017) Treatment of chromium effluent by adsorption on chitosan activated with ionic liquids. Cellulose 24:2559–2570
Fitz-Patrick M, Champagne P, Cunningham MF, Whitney RA (2010) A biorefinery processing perspective: treatment of lignocellulosic materials for the production of value-added products. Bioresour Technol 101:8915–8922
Fu F, Wang Q (2011) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: a review. J Environ Manag 92:407–418
Fu F, Ma J, Xie L, Tang B, Han W, Lin S (2013) Chromium removal using resin supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. J Environ Manag 128:822–827
Fu R, Yang Y, Xu Z, Zhang X, Guo X, Bi D (2015) The removal of chromium(VI) and lead(II) from groundwater using sepiolite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (S-NZVI). Chemosphere 138:726–734
Galan B, Castañeda D, Ortiz I (2005) Removal and recovery of Cr(VI) from polluted ground waters: a comparative study of ion-exchange technologies. Water Res 39:4317–4324
Gelesky MA, Scheeren CW, Foppa L, Pavan FA, Dias SL, Dupont J (2009) Metal nanoparticle/ionic liquid/cellulose: new catalytically active membrane materials for hydrogenation reactions. Biomacromol 10:1888–1893
Geng B, Jin Z, Li T, Qi X (2009) Kinetics of hexavalent chromium removal from water by chitosan-Fe0 nanoparticles. Chemosphere 75:825–830
Gheju M (2011) Hexavalent chromium reduction with zero-valent iron (ZVI) in aquatic system. Water Air Soil Pollut 222:103–148
Golder AK, Samanta AN, Ray S (2007) Removal of trivalent chromium by electrocoagulation. Sep Purif Technol 53:33–41
Guo ZR, Zhang G, Fang J, Dou X (2006) Enhanced chromium recovery from tanning wastewater. J Clean Prod 14:75–79
Gurgel LVA, de Melo JCP, de Lena JC, Gil LF (2009) Adsorption of chromium(VI) ion from aqueous solution by succinylated-mercerized cellulose functionalized with quaternary ammonium groups. Bioresour Technol 100:3214–3220
Hafez A, El-Mariharawy S (2004) Design and performance of the two-stage/two-pass RO membrane system for chromium removal from tannery wastewater. Desalination 165:141–151
Halada GP, Clayton CR (1991) Photoreduction of hexavalent chromium during X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of electrochemical and thermal films. J Electrochem Soc 138:2921–2927
Harvey AE Jr, Smart JA, Amis ES (1955) Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of iron(II) and total iron with 1,10-phenanthroline. Anal Chem 27:26–29
He F, Zhao D, Liu J, Roberts CB (2007) Stabilization of Fe–Pd nanoparticles with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for enhanced transport and dechlorination of trichloroethylene in soil and groundwater. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:29–34
Hines JH, Wanigasekara E, Rudkevich DM, Rogers RD (2008) Calix[4]arenes immobilized in a cellulose-based platform for entrapment and detection of NO x gases. J Mater Chem 18:4050–4055
Horzum N, Demir MM, Nairat M, Shahwan T (2013) Chitosan fiber-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles as a novel sorbent for sequestration of inorganic arsenic. RSC Adv 3:7828–7837
Hu XJ, Wang JS, Liua YG, Li X, Zenga GM, Bao ZL, Zeng XX, Chen AW, Long F (2011) Adsorption of chromium(VI) by ethylenediamine-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan resin: isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 185:306–314
Jabeen H, Chandra V, Jung S, Lee JW, Kim KS, Kim SB (2011) Enhanced Cr(VI) removal using iron nanoparticle decorated graphene. Nanoscale 3:3583–3585
Jones F, Farrow JB, Van Bronswijk W (1998) An infrared study of a polyacrylate flocculant adsorbed on hematite. Langmuir 14:6512–6517
Kim UJ, Kuga S (2001) Thermal decomposition of dialdehyde cellulose and its nitrogen-containing derivatives. Thermochim Acta 369:79–85
Kim UJ, Wada M, Kuga S (2004) Solubilization of dialdehyde cellulose by hot water. Carbohydr Polym 56:7–10
Kim JH, Kim JH, Bokare V, Kim EJ, Chang YY, Chang YS (2012) Enhanced removal of chromate from aqueous solution by sequential adsorption-reduction on mesoporous iron–iron oxide nanocomposite. J Nanopart Res 14:1010
Klein-Marcuschamer D, Simmons BA, Blanch HW (2011) Techno-economic analysis of a lignocellulosic ethanol biorefinery with ionic liquid pre-treatment. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 5:562–569
Kotelnikova N, Vainio U, Pirkkalainen K, Serimaa R (2007) Novel approaches to metallization of cellulose by reduction of cellulose-incorporated copper and nickel Ions. Macromol Symp 254:74–79
Koujalagi PS, Divekar SV, Kulkarni RM, Nagarale RK (2013) Kinetics, thermodynamic, and adsorption studies on removal of chromium(VI) using Tulsion A-27(MP) resin. Desalin Water Treat 51:3273–3283
Kumar AS, Jiang SJ, Tseng WL (2015) Effective adsorption of chromium(VI)/Cr(III) from aqueous solution using ionic liquid functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a super sorbent. J Mater Chem A 3:7044–7057
Kwak HW, Kim MK, Lee JY, Yun H, Kim MH, Park YH, Lee KH (2015) Preparation of bead-type biosorbent from water-soluble Spirulina platensis extracts for chromium(VI) removal. Algal Res 7:92–99
Li XQ, Zhang WX (2007) Sequestration of metal cations with zerovalent iron nanoparticles a study with high resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS). J Phys Chem C 111:6939–6946
Li XQ, Cao J, Zhang WX (2008) Stoichiometry of Cr(VI) immobilization using nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI): a study with high-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HR-XPS). Ind Eng Chem Res 47:2131–2139
Li L, Li Y, Cao L, Yang C (2015) Enhanced chromium(VI) adsorption using nanosized chitosan fibers tailored by electrospinning. Carbohydr Polym 125:206–213
Li Q, Xu B, Zhuang L, Xu X, Wang G, Zhang X, Chen J, Tang Y (2018) Preparation, characterization, adsorption kinetics and thermodynamics of chitosan adsorbent grafted with a hyperbranched polymer designed for Cr(VI) removal. Cellulose 25:3471–3486
Liu Z, Wang H, Liu C, Jiang Y, Yu G, Mu X, Wang X (2012) Magnetic cellulose–chitosan hydrogels prepared from ionic liquids as reusable adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions. Chem Commun 48:7350–7352
Liu X, Zhou W, Qian X, Shen J, An X (2013) Polyaniline/cellulose fiber composite prepared using persulfate as oxidant for Cr(VI)-detoxification. Carbohydr Polym 92:659–661
Lu P, Hsieh YL (2010) Preparation and properties of cellulose nanocrystals: rods, spheres, and network. Carbohydr Polym 82:329–336
Manning BA, Kiser JR, Kwon H, Kanel SR (2007) Spectroscopic investigation of Cr(III)-and Cr(VI)-treated nanoscale zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 41:586–592
Matuana LM, Balatinecz JJ, Sodhi RNS, Park CB (2001) Surface characterization of esterified cellulosic fibers by XPS and FTIR spectroscopy. Wood Sci Technol 35:191–201
Miao Q, Yan J (2013) Comparison of three ornamental plants for phytoextraction potential of chromium removal from tannery sludge. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 15:98–105
Moulder J (1992) Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: a reference book of standard spectra for identification and interpretation of XPS data. Chastain J, King RC (eds) Eden Prairie, Physical Electronics Division, Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Minnesota
Mukherjee R, Kumar R, Sinha A, Lama Y, Saha AK (2015) A review on synthesis, characterization and applications of nano-zero valent iron (nZVI) for environmental remediation. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46:443–466
Narayani M, Vidya SK (2012) Chromium-resistant bacteria and their environmental condition for hexavalent chromium removal: a review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 43:955–1009
National Toxicology Program, Department of Health and Human Services (NIEHS) (2011) Report on Carcinogens, 12th ed. http://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/ntp/roc/twelfth/roc12.pdf
Owlad M, Aroua MK, Daud WAW, Baroutian S (2009) Removal of hexavalent chromium-contaminated water and wastewater: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 200:59–77
Parlayici S, Pehlivan E (2015) Natural biosorbents (garlic stem and horse chesnut shell) for removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions. Environ Monit Assess 187:763
Patterson JW, Passino R (1987) Metals separation and recovery. In: Patterson JW (ed) Metal speciation separation and recovery. Lewis, USA, pp 63–96
Perez-González A, Urtiaga AM, Ibáñez R, Ortiz I (2012) State of the art and review on the treatment technologies of water reverse osmosis concentrates. Water Res 46:267–283
Ponder SM, Darab JG, Mallouk TE (2000) Remediation of Cr(VI) and Pb(II) aqueous solutions using supported nanoscale zerovalent iron. Environ Sci Technol 34:2564–2569
Powell RM, Plus RW, Hightower SK, Sabatini DA (1995) Coupled iron corrosion and chromate reduction: mechanisms for subsurface remediation. Environ Sci Technol 29:1913–1922
Qiu B, Xu C, Sun D, Wang Q, Gu H, Zhang X, Weeks BL, Hopper J, Ho T, Guo Z, Wei S (2015) Polyaniline coating with various substrates for hexavalent chromium removal. Appl Surf Sci 334:7–14
Raychoudhury T, Tufenkji N, Ghoshal S (2012) Aggregation and deposition kinetics of carboxymethyl cellulose-modified zero-valent iron nanoparticles in porous media. Water Res 46:1735–1744
Sajana TK, Ghangrekar MM, Mitra A (2014) Effect of presence of cellulose in the freshwater sediment on the performance of sediment microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 155:84–90
Saliba R, Gauthier H, Gauthier R, Petit-Ramel M (2000) Adsorption of copper(II) and chromium(III) ions onto amidoximated cellulose. J Appl Polym Sci 75:1624–1631
Seid KA, Badot JC, Dubrunfaut O, Levasseur S, Guyomard D, Lestriez B (2012) Influence of the carboxymethyl cellulose binder on the multiscale electronic transport in carbon–LiFePO4 nanocomposites. J Mater Chem 22:24057–24066
Sharma YC, Srivastava V, Weng CH, Upadhyay SN (2009) Removal of Cr(VI) from wastewater by adsorption on iron nanoparticles. Can J Chem Eng 87:921–929
Sharma P, Bihari V, Agarwal SK, Verma V, Kesavachandran CN, Pangtey BS, Mathur N, Singh PK, Shrivastava M, Goel SK (2012) Groundwater contaminated with hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)]: a health survey and clinical examination of community inhabitants (Kanpur, India). PLoS ONE 7:e47877
Sharma AK, Kumar R, Mittal S, Hussain S, Arora M, Sharma RC, Babu JN (2015) In-situ reductive regeneration of zerovalent iron nanoparticles immobilized on cellulose for atom efficient Cr(VI) adsorption. RSC Adv 5:89441–89446
Shi LN, Zhang X, Chen ZL (2011) Removal of chromium(VI) from wastewater using bentonite-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron. Water Res 45:886–892
Singh R, Misra V, Singh RP (2011) Synthesis, characterization and role of zero-valent iron nanoparticle in removal of hexavalent chromium from chromium-spiked soil. J Nanopart Res 13:4063–4073
Singha AS, Guleria A (2014) Use of low cost cellulosic biopolymer based adsorbent for the removal of toxic metal ions from the aqueous solution. Sep Sci Technol 49:2557–2567
Stefaniuk M, Oleszczuk P, Ok YS (2016) Review on nanozerovalent iron (nZVI): from synthesis to environmental applications. Chem Eng J 287:618–632
Swatloski RP, Spear SK, Holbery JD, Rogers RD (2002) Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 124:4974–4975
Trujillo-Reyes J, Peralta-Videa JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2014) Supported and unsupported nanomaterials for water and soil remediation: Are they a useful solution for worldwide pollution? J Hazard Mater 280:487–503
USEPA (2011) http://www.rpi.edu/dept/chem-eng/Biotech-Environ/Adsorb/bet.htm. Accessed 06/01/2018
USEPA (2013) http://www.rpi.edu/dept/chem-eng/Biotech-Environ/Adsorb/bet.htm. Accessed 06/01/2018
Uzum C, Shahwan T, Eroğlu AE, Hallam KR, Scott TB, Lieberwirth I (2009) Synthesis and characterization of kaolinite-supported zero-valent iron nanoparticles and their application for the removal of aqueous Cu2+ and Co2+ ions. Appl Clay Sci 43:172–181
Vaid U, Mittal S, Babu JN (2013) Removal of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using biomass derived fly ash from waste-to-energy power plant. Desalin Water Treat 52:7845–7855
Wen Z, Zhang Y, Dai C (2014) Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution using nanoscale zerovalent iron (nZVI). Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 457:433–440
Xiao S, Shen M, Guo R, Wang S, Shi X (2009) Immobilization of zerovalent iron nanoparticles into electrospun polymer nanofibers: synthesis, characterization, and potential environmental applications. J Phys Chem C 113:18062–18068
Xie P, Hao X, Mohamad OA, Liang J, Wei G (2013) Comparative study of chromium biosorption by mesorhizobiumamorphae strain CCNWGS0123 in single and binary mixtures. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:570–587
Yadav R, Sharma AK, Babu JN (2016) Sorptive removal of arsenite [As(III)] and arsenate [As(V)] by fuller’s earth immobilized nanoscale zero-valent iron nanoparticles (F-nZVI): effect of Fe0 loading on adsorption activity. J Environ Chem Eng 4:681–694
Yu X, Tong S, Ge M, Zuo J, Cao C, Song W (2013) One-step synthesis of magnetic composites of cellulose@ iron oxide nanoparticles for arsenic removal. J Mater Chem A 1:959–965
Zhang Y, Xu L, Zhao L, Peng J, Li C, Li J, Zhai M (2012) Radiation synthesis and Cr(VI) removal of cellulose microsphere adsorbent. Carbohydr Polym 88:931–938
Zhu S, Wu Y, Chen Q, Yu Z, Wang C, Jin S, Ding Y, Wu G (2006) Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids and its application: a mini-review. Green Chem 8:325–327
Acknowledgments
Archana Kumari Sharma is thankful to CUPB for providing university fellowship for carrying out the proposed research. We are all thankful to CSMCRI, CIL-CUPB for the analytical services provided. J. N. Babu is thankful to CUPB for research seed money grant and to DST, New Delhi, India for providing funds through DST Fast Track Young Scientist as Project Ref. No. 240/2010 for research support. The authors’ acknowledge Electron Microscope Division, AIIMS, New Delhi for TEM facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A.K., Devan, R.S., Arora, M. et al. Reductive-co-precipitated cellulose immobilized zerovalent iron nanoparticles in ionic liquid/water for Cr(VI) adsorption. Cellulose 25, 5259–5275 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1932-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1932-y