Abstract
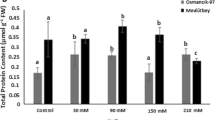
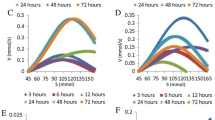
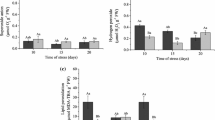
The objective of this study was to relate the activation of enzymatic antioxidant system to the production of reactive oxygen species induced by salt stress. Rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes BRS Bojuru and BRS Pampa, tolerant and sensitive to salinity, respectively, were subjected to 150 mM NaCl for 0, 6, 24, 48, and 72 h. A significant increase of superoxide anion and H2O2 and a decrease in malondialdehyde (MDA) content were observed in the tolerant genotype, whereas in the sensitive genotype, there was no change in superoxide anion content, reduced H2O2 content, and increased MDA content. The superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity increased significantly in both genotypes, and increases in amounts of transcript were observed for OsSOD3Cu/Zn and OsSODA1-Mn in the tolerant genotype and for OsSOD4-Cu/Zn, OsSOD3-Cu/Zn, OsSODCc1-Cu/Zn, OsSOD-Fe, and OsSODA1-Mn in the sensitive genotype. The activities of catalase (CAT), ascorbate peroxidase (APX), and glutathione reductase (GR) were not significantly and consistently changed, but OsCATA, OsAPX2 and OsGR1 were induced in both genotypes. OsCATB transcription was increased in the tolerant genotype and OsCATC and OsAPX3 in the sensitive genotype under salinity. It is concluded that OsAPX3, OsGR2, OsGR3, and OsSOD3-Cu/Zn genes are the most suitable to distinguish tolerant from sensitive genotypes under salt stress.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APX:
-
ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
catalase
- GR:
-
glutathione reductase
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- TBA:
-
thiobarbituric acid
- TCA:
-
trichloroacetic acid
References
Ahmad, P., Sarwat, M., Sharma, S.: Reactive oxygen species, antioxidants and signaling in plants. — J. Plant Biol. 51: 167–173, 2008.
Ahmad, P., Jaleel, C.A., Salem, M.A., Nabi, G., Sharma, S.: Roles of enzymatic and nonenzymatic antioxidants in plants during abiotic stress. — Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 30: 161–175, 2010.
Asada, K.: The water-water cycle in chloroplasts: scavenging of active oxygens and dissipation of excess photons. — Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant. mol. Biol. 50: 601–639, 1999.
Asada, K.: Production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in chloroplasts and their functions. — Plant Physiol. 141: 391–396, 2006.
Ashraf, M.: Biotechnological approach of improving plant salt tolerance using antioxidants as markers. — Biotechnol. Adv. 27: 84–93, 2009.
Azevedo, R.A., Alas, R.M., Smith R.J., Lea, P.J.: Response of antioxidant enzymes to transfer from elevated carbon dioxide to air and ozone fumigation, in the leaves and roots of wild-type and a catalase-deficient mutant of barley. — Physiol. Plant. 104: 280–29, 1998.
Aydin, S.S., Büyük, I., Aras, S.: Relationships among lipid peroxidation, SOD enzyme activity, and SOD gene expression profile in Lycopersicum esculentum L. exposed to cold stress. — Genet. mol. Res. 12: 3220–3229, 2013.
Bhatnagar-Mathur, P., Valdez, V., Sharma K.K.: Transgenic approaches for abiotic stress tolerance in plants: retrospect and prospects. — Plant Cell Rep. 27: 411–424, 2008.
Bradford, M.: A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. — Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254, 1976.
Cakmak, I., Strbac, D., Marschner, H.: Activities of hydrogen peroxide-scavenging enzymes in germination wheat seeds. — J. exp. Bot. 44: 127–132, 1993.
Courtney, A.J., Xu, J., Xu, Y.: Responses of growth, antioxidants and gene expression in smooth cordgrass (Spartina alterniflora) to various levels of salinity. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 99: 162–170, 2016.
Dajic Z.: Salt stress. In: Madhava, R.K.V., Raghavendra, A.S., Janardhan, R.K. (ed.): Physiology and Molecular Biology of Stress Tolerance in Plants. Vol. 1. Pp. 41–100. Springer, Dordrecht 2006.
Demiral, T, Turkan, I.: Comparative lipid peroxidation, antioxidant defense systems and proline content in roots of two rice cultivars differing in salt tolerance. — Environ. exp. Bot. 53: 247–257, 2005.
Foyer, C.H., Noctor, G.: Redox sensing and signaling associated with reactive oxygen in chloroplast, peroxisomes and mitochondria. — Physiol. Plant. 119: 355–364, 2003.
Foyer, C.H., Noctor, G.: Oxidant and antioxidant signaling in plants: a re-evaluation of the concept of oxidative stress in a physiological context. — Plant Cell Environ. 28: 1056–1071, 2005.
Gao, J.P., Chao, D.Y., Lin, H.X.: Understanding abiotic stress tolerance mechanisms: recent studies on stress response in rice. — J. integr. Plant Biol. 49: 742–750, 2007.
Giannopolitis, C.N., Ries, S.K.: Superoxide dismutase. I. Occurrence in higher plants. — Plant Physiol. 59: 309–314, 1977.
Gill, S.S., Tuteja, N.: Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 48: 909–930, 2010.
Guo, Z., Ou, W., Lu, S., Zhong, Q.: Differential responses of antioxidative system to chilling and drought in four rice cultivars differing in sensitivity. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 44: 828–836, 2006.
Hakeem, K.R., Khan, F., Chandna, R., Siddiqui, T.O., Iqbal, M.: Genotypic variability among soybean genotypes under NaCl stress and proteome analysis of salt-tolerant genotype. — Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 168: 2309–2329, 2012.
Heath, R.L., Packer, L.: Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplast. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. — Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 125: 189–198, 1968.
Hong, C.Y., Chao, Y.Y., Yang, M.Y., Cheng, S.Y., Cho, S.C., Kao, C.H.: NaCl-induced expression of glutathione reductase in roots of rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings is mediated through hydrogen peroxide but not abscisic acid. — Plant Soil 320: 103–115, 2009.
Jaleel, C.A., Riadh, K., Gopi, R., Manivannan, P., Inès, J., Al-Juburi, H.J., Zhao, C.-X., Shao, H.-B., Panneerselvam, R.: Antioxidant defense responses: physiological plasticity in higher plants under abiotic constraints. — Acta Physiol. Plant. 31: 427–436, 2009.
Kaminaka, H., Morita, S., Tokumoto, M., Tanaka, K.: Differential gene expression of rice superoxide dismutase isoforms to oxidative and environmental stresses. — Free Radicals Res. 31: 219–225, 1999.
Khare, T., Kumar, V., Kishor, K.P.B.: Na+ and Cl− ions show additive effects under NaCl stress on induction of oxidative stress and the responsive antioxidative defense in rice. — Protoplasma. 252: 1149–65, 2014.
Kim, J.K., Lee, S.Y., Chu, S.M., Lim, S.H., Suh, S.-C., Lee, Y.T., Cho, H.S., Ha, S.H.: Variation and correlation analysis of flavonoids and carotenoids in Korean pigmented rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. — J. Agr. Food Chem. 58: 12804–12809, 2010.
Lee, T., Rinaldi, N.J., Robert, F., Odom, D.T., Bar-Joseph, Z., Gerber, G.K., Hannett, N.M., Harbison, C.T., Thompson, C.M., Simon, I.: Transcriptional regulatory networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. — Science 298: 799–804, 2002.
Li, C., Bai, T., Maa, F., Hana, M.: Hypoxia tolerance and adaptation of anaerobic respiration to hypoxia stress in two Malus species. — Sci. Hort. 124: 274–279, 2010.
Livak K.J., Schmittgen, T.D.: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. — Methods 25: 402–408, 2001.
Menezes-Benavente, L., Teixeira, F.K., Kamei C.L.A., Margis-Pinheiro, M.: Salt stress induces altered expression of genes encoding antioxidant enzymes in seedlings of a Brazilian indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). — Plant Sci. 166: 323–331, 2004.
Miller, G., Suzuki, N., Ciftci-Yilmaz, S., Mittler, R.: Reactive oxygen species homeostasis and signalling during drought and salinity stresses. — Plant Cell Environ. 33: 453–467, 2010.
Mishra, P., Bhoomika, K., Dubey, R.S.: Differential responses of antioxidative defense system to prolonged salinity stress in salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. — Protoplasma 250: 3–19, 2013.
Mittler, R., Vanderauwera, S., Gollery, M., Van-Breusegem, F.: Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. — Trends Plant Sci. 9: 490–498, 2004.
Moradi, F., Ismail, A.M.: Responses of photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence and ROS-scavenging systems to salt stress during seedling and reproductive stages in rice. — Ann. Bot. 99: 1161–1173, 2007.
Moraes, G.P., Benitez, L.C., Amaral Do, M.N., Vighi, I.L., Auler, P.A., Maia Da, L.C., Bianchi, V.J., Braga, E.J.B.: Evaluation of reference genes for RT-qPCR studies in the leaves of rice seedlings under salt stress. — Genet. mol. Res. 14: 2384–2398, 2015.
Morison, J.I.L., Baker, N.R., Mullineaux, P.M., Davies, W.J.: Improving water use in crop production. — Phil. Trans. roy. Soc. London B. Biol. Sci. 363: 639–658, 2007.
Morita, S., Nakatani, S., Koshiba, T., Masumura, T., Ogihara, Y., Tanaka, K.: Differential expressions of two cytosolic ascorbate peroxidase and two superoxide dismutase genes in response to abiotic stress in rice. — Rice Sci. 18: 157–166, 2011.
Nakano, Y., Asada, K.: Hydrogen peroxide is scavenged by ascorbate specific peroxidase in spinach chloroplasts. — Plant Cell Physiol. 22: 867–880, 1981.
Neill, S.J., Desikan, R., Clarke, A., Hurst, R.D., Hancock, J.T.: Hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide as signaling molecules in plants. — J. exp. Bot. 53: 1237–1247, 2002.
Paiva, A.L.C., Teixeira, R.B., Yamaki, M., Menezes, G.R.O., Leite, C.D.S., Torres, R. A.: Principal component analysis in laying hen production traits. — Roy. Bras. Zootech. 39: 285–288, 2010.
Sharma, P., Jai, A.B., Dubey, R.S., Pessarakli, M.: Reactive oxygen species, oxidative damage, and antioxidative defense mechanism in plants under stressful conditions. — J. Bot. 1: 1–26, 2012.
Shikanai, T., Takeda, T., Yamauchi, H., Sano, S., Tomizawa, K., Yokota, A., Shigeoka, S.: Inhibition of ascorbate peroxidase under oxidative stress in tobacco having bacterial catalase in chloroplasts. — FEBS Lett. 428: 47–51, 1998.
Simova-Stoilova, L., Vaseva, I., Grigorova, B., Demirevska, K., Feller, U.: Proteolytic activity and cysteine protease expression in wheat leaves under severe soil drought and recovery. — Plant Physiol. Biochem. 48: 200–206, 2010.
Singh, R.K., Redoña, E., Refuerzo, L.: Varietal improvement for abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants: special reference to salinity in rice. - In: Pareek, A., Sopory, S.K., Bohnert, H., Govindjee (ed.): Abiotic Stress Adaptation in Plants: Physiological, Molecular and Genomics Foundation. Vol. 1. Pp. 387–415. Springer, New York 2010.
Tan, W., Brestic, M., Olsovska, K., Yang, X.: Photosynthesis is improved by exogenous calcium in heat-stressed tobacco plants. — J. Plant Physiol. 168: 2063–2071, 2011.
Tang, B., Xu, S-Z., Zou, X-L., Zheng, Y-L., Qiu, F-Z.: Changes of antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in leaves and roots of waterlogging-tolerant and waterloggingsensitive maize genotypes at seedling stage. — Agr. Sci. China 9: 651–661, 2010a.
Tang, K., Zhan, J-C., Yang, H-R., Huan G, W-D.: Changes of resveratrol and antioxidant enzymes during UV-induced plant defense response in peanut seedlings. — J. mol. Evol. 167: 95–102, 2010b.
Teixeira, F.K., Menezes-Benavente, L., Galvão, V.C., Margis, R., Margis-Pinheiro, M.: Rice ascorbate peroxidase gene family encodes functionally diverse isoforms localized in different subcellular compartments. — Planta 224: 300–314, 2006.
Teixeira, F.K., Menezes-Benavente, L., Margis, R., Margispinheiro, M.: Analysis of the molecular evolutionary history of the ascorbate peroxidase gene family: inferences from the rice genome. — J. mol. Evol. 59: 761–770, 2004.
Turan, S., Tripathy, B.C.: Salt and genotype impact on antioxidative enzymes and lipid peroxidation in two rice cultivars during de-etiolation. — Protoplasma 250: 209–222, 2013.
Velikova, V., Yordanov, I., Edreva, A.: Oxidative stress and some antioxidant systems in acid rain-treated bean plants. — Plant Sci. 151: 59–66, 2000.
Witcombe, J.R., Hollington, P.A., Howarth, C.J., Reader, S., Steele, K.A.: Breeding for abiotic stresses for sustainable agriculture. — Trans. roy. Soc. London B. Biol. Sci. 363: 703–716, 2008.
Wu, T.M., Lin, W.R., Kao, Y.T., Hsu, Y.T., Yeh, C.H., Hong, C.Y., Kao, C.H.: Identification and characterization of a novel chloroplast/mitochondria co-localized glutathione reductase 3 involved in salt stress response in rice. — Plant mol. Biol. 83: 379–390, 2013.
Yamane, K., Mitsuya, S., Taniguchi, M., Miyake, H.: Transcription profiles of genes encoding catalase and ascorbate peroxidase in the rice leaf tissues under salinity. — Plant Prod. Sci. 13: 164–168, 2010.
Yoshida, S., Forno, D.A., Cock, J.H., Gomez, K.A. (ed.): Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. - International Rice Research Institute, Manila 1976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Acknowledgements: Research supported by the following Brazilian funding agencies: Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS).
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vighi, I.L., Benitez, L.C., Amaral, M.N. et al. Functional characterization of the antioxidant enzymes in rice plants exposed to salinity stress. Biol Plant 61, 540–550 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-017-0727-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-017-0727-6