Abstract
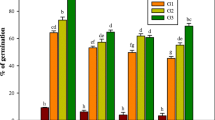
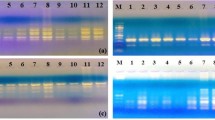
The aim of the present study was to determine the effect of nickel on shoot regeneration in tissue culture as well as to identify polymorphisms induced in leaf explants exposed to nickel through random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD). In vitro leaf explants of Jatropha curcas were grown in nickel amended Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium at four different concentrations (0, 0.01, 0.1, 1 mM) for 3 weeks. Percent regeneration, number of shoots produced and genotoxic effects were evaluated by RAPD using leaf explants obtained from the first three treatments following 5 weeks of their subsequent subculture in metal free MS medium. Percent regeneration decreased with increase in addition of nickel to the medium up to 14 days from 42.31% in control to zero in 1.0 mM. The number of shoot buds scored after 5 weeks was higher in control as compared to all other treatments except in one of the metal free subculture medium wherein the shoot number was higher in 0.01 mM treatment (mean = 7.80) than control (mean = 7.60). RAPD analysis produced only 5 polymorphic bands (3.225%) out of a total of 155 bands from 18 selected primers. Only three primers OPK-19, OPP-2, OPN-08 produced polymorphic bands. The dendrogram showed three groups A, B, and C. Group A samples showed 100% genetic similarity within them. Samples between groups B and C were more genetically distant from each other as compared to samples between groups A and B as well as groups A and C. Cluster analysis based on RAPD data correlated with treatments.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog medium
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
- BAP:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- IAA:
-
Indole 3-acetic acid
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- AFLP:
-
Amplification fragment length polymorphism
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- AP-PCR:
-
Arbitrarily primed PCR
- JSC:
-
Jaccard’s similarity coefficients
- CTAB:
-
Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
References
Al-Zahim MA, Ford-Lloyd BV, Newbury HJ (1999) Detection of somaclonal variation in garlic (Allium sativum L.) using RAPD and cytological analysis. Plant Cell Rep 18:473–477
Anand KGV, Prakash CR, Reddy MP (2008) Effect of nickel on growth and mineral composition in callus culture of Jatropha curcas L. In: Paper presented in National symposium on plant biotechnology for conservation, characterization and crop improvement, Udaipur, India 8–10 February 2008, p 172
Atienzar FA, Conradi M, Evenden AJ, Jha AN, Depledge MH (1999) Qualitative assessment of genotoxicity using random amplified polymorphic DNA: comparison of genomic template stability with key fitness parameters in Daphnia magna exposed to benzo[a]pyrene. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:2275–2282
Atienzar FA, Cheung VV, Jha AN, Depledge MH (2001) Fitness parameters and DNA effects are sensitive indicators of copper-induced toxicity in Daphnia magna. Toxicol Sci 59:241–250
Atienzar FA, Venier P, Jha AN, Depledge MH (2002) Evaluation of the random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) assay for the detection of DNA damage and mutations. Mutat Res 521:151–163
Boominathan R, Doran PM (2002) Ni-induced oxidative stress in roots of the Ni hyperaccumulator, Alyssum bertolonii. New Phytol 156:205–215
Boyd RS (2004) Ecology of metal hyperaccumulation. New Phytol 162:563–567
Boyd RS (2007) The defense hypothesis of elemental hyperaccumulation: status, challenges and new directions. Plant Soil 293:153–176
Cenkci S, Yıldız M, Cigerci IH, Konuk M, Bozdag A (2009) Toxic chemicals-induced genotoxicity detected by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 76:900–906
Chen C, Huang D, Liu J (2009) Functions and toxicity of nickel in plants: recent advances and future prospects. Clean 37:304–313
Devaux P, Kilian A, Kleinhofs A (1993) Anther culture and Hordeum bulbosum-derived barley doubled haploids—mutations and methylation. Mol Gen Genet 241:674–679
Enan MR (2006) Application of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) to detect the genotoxic effect of heavy metals. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 43:147–154
Enan MR (2007) Assessment of genotoxic activity of para-nitrophenol in higher plant using arbitrarily primed- Polymerase Chain Reaction (AP-PCR). Am J Biotechnol Biochem 3(2):103–109
Fornazier RF, Ferreira RR, Pereira GJG, Molina SMG, Smith JR, Lea PJ, Azevedo RA (2002) Cadmium stress in sugar cane callus cultures: effect on antioxidant enzymes. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 71:125–131
Gerendas J, Polacco JC, Freyermuth SK, Sattelmacher B (1999) Significance of nickel for plant growth and metabolism. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 162:241–256
Gesteira AS, Otoni WC, Barros EG, Moreira MA (2002) RAPD-based detection of genomic instability in soybean plants derived from somatic embryogenesis. Plant Breed 121:269–271
Hao F, Wang X, Chen J (2006) Involvement of plasma-membrane NADPH oxidase in nickel-induced oxidative stress in roots of wheat seedlings. Plant Sci 170:151–158
Hartwig A, Kruger I, Beyersmann D (1994) Mechanisms in nickel genotoxicity: the significance of interactions with DNA repair. Toxicol Lett 72:353–358
Heller R (1953) Recherces sur la nutrition minérale des tissues végétaux cultivés in vitro. Ann Sci Nat 14:1–223
Isabel N, Tremblay L, Michand M, Tremblay FM, Bousquet J (1993) RAPD as aids to evaluate the genetic integrity of somatic embryogenesis-derived populations of Picea mariana (Mill.). Theor Appl Genet 86:81–87
Joshi A, Kothari SL (2007) High copper levels in the medium improves shoot bud differentiation and elongation from the cultured cotyledons of Capsicum annuum L. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 88:127–133
Kim K, Lee SH, Seo YR, Perkins SN, Kasprzak KS (2002) Nickel(II)-induced apoptosis in murine T cell hybridoma cells is associated with increased fas ligand expression. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 185:41–47
Kumar GP, Yadav SK, Thawale PR, Singh SK, Juwarkar AA (2008) Growth of Jatropha curcas on heavy metal contaminated soil amended with industrial wastes and Azotobacter—a greenhouse study. Bioresource Technol 99:2078–2082
Labra M, Fabio TD, Grassi F (2003) AFLP analysis as biomarker of exposure to organic and inorganic genotoxic substances in plants. Chemosphere 52:1183–1188
Liu W, Yang YS, Li PJ, Zhou QX, Xie LJ, Han YP (2009) Risk assessment of cadmium-contaminated soil on plant DNA damage using RAPD and physiological indices. J Hazard Mater 161:878–883
Lu H, Shi X, Costa M, Huang C (2005) Carcinogenic effect of nickel compounds. Mol Cell Biochem 279:45–67
Lu G, Zhang X, Zou Y, Zou O, Xiang X, Cao J (2007) Effect of radiation on regeneration of Chinese narcissus and analysis of genetic variation with AFLP and RAPD markers. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 88:319–327
Lynn S, Yew FH, Chen KS, Jan KY (1997) Reactive oxygen species are involved in nickel inhibition of DNA repair. Environ Mol Mutagen 29:208–216
Mangkoedihardjo S, Surahmaida (2008) Jatropha curcas L. for Phytoremediation of lead and cadmium polluted soil. World App Sci J 4:519–522
Monteiro M, Santos C, Mann RM, Soares AMVM, Lopes T (2007) Evaluation of cadmium genotoxicity in Lactuca sativa L. using nuclear microsatellites. Environ Exp Bot 60:421–427
Munthali MT, Newbury HJ, Ford-Lloyd BV (1996) The detection of somaclonal variants of beet using RAPD. Plant Cell Rep 15:474–478
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Palomino M, Kennedy PG, Simms EL (2007) Nickel hyperaccumulation as an anti-herbivore trait: considering the role of tolerance to damage. Plant Soil 293:189–195
Pietrasan LI, Smith BL, MacLeod MC (2000) A novel approach for analyzing the structure of DNA modified by benzo[a]pyrine diol epoxide at single-molecule resolution. Chem Res Toxicol 13:351–355
Rancelis V, Cesniene T, Zvingila D, Barysas D, Balciuniene L, Dapkuniene S (2006) Polymorphism of response to cobalt excess in individual Vicia faba plants. Environ Exp Bot 55:221–234
Reeves RD, Baker AJM (2000) Metal-accumulating plants. In: Raskin I, Ensley BD (eds) Phytoremediation of toxic metals: using plants to clean up the environment. Wiley, New York, pp 193–229
Sharma NK (2008) Studies on regeneration and genetic transformation in Jatropha curcas. PhD thesis, Bhavnagar University, India
Sharma SS, Dietz KJ (2009) The relationship between metal toxicity and cellular redox imbalance. Trends Plant Sci 14:43–50
Sokal RR, Sneath PHA (1963) Principles of numeric taxonomy. Freeman, San Francisco, p 359
Sudheer PDVN, Pandya N, Reddy MP, Radhakrishnan T (2009a) Comparative study of interspecific genetic divergence and phylogenic analysis of genus Jatropha by RAPD and AFLP. Mol Biol Rep 36:901–907
Sudheer PDVN, Sarkar R, Meenakshi K, Boricha G, Reddy MP (2009b) A simple protocol for isolation of high quality genomic DNA from Jatropha curcas for genetic diversity and molecular marker studies. Indian J Biotechnol 8:187–192
Swaileh KM, Hussein R, Ezzughayyar A (2008) Evaluating wastewater-induced plant genotoxicity using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA. Environ Toxicol 23:117–122
Valles MP, Wang ZY, Montavon P, Potrykus I, Spangenberg G (1993) Analysis of genetic stability of plants regenerated from suspension cultures and protoplasts of meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis Huds.). Plant Cell Rep 12:101–106
Vinterhalter B, Vinterhalter D (2005) Nickel hyperaccumulation in shoot cultures of Alyssum markgrafii. Biol Plantarum 49:121–124
Williams JG, Kubelik AR, Livak J, Rafalski J, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphism amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Witte CP, Tiller SA, Taylor MA, Davies HV (2002) Addition of nickel to Murashige and Skoog medium in plant tissue culture activates urease and may reduce metabolic stress. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 68:103–104
Acknowledgements
TS and KGV wish to thank Dr. D. V. N. Sudheer Pamidimarri for his valuable suggestions during manuscript preparation. The authors are also thankful to Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, T., Vijay Anand, K.G. & Reddy, M.P. Effect of nickel on regeneration in Jatropha curcas L. and assessment of genotoxicity using RAPD markers. Biometals 23, 1149–1158 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9364-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-010-9364-7