Abstract
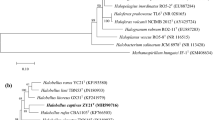
Two halophilic archaeal strains, YC21T and YC77, were isolated from an inland salt lake of China. Both have pleomorphic rod-shaped cells that lyse in distilled water, stain Gram-negative and form red-pigmented colonies. They are neutrophilic, require at least 2.1 M NaCl for growth under the optimum growth temperature of 37 °C. The major polar lipids of the two strains were phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylglycerol phosphate methyl ester (PGP-Me), phosphatidylglycerol sulfate (PGS), two major glycolipids (GL1 and GL2) chromatographically identical to sulfated mannosyl glucosyl diether (S-DGD-1) and mannosyl glucosyl diether (DGD-1), respectively. Trace amounts of two unidentified lipids (GL0-1 and GL0-2) were also detected. The 16S rRNA gene sequences of the two strains are 99.9 % identical, show 94.0–98.9 % similarity to the closest relative members of Halobellus of the family Halobacteriaceae. The rpoB′ gene similarity between strains YC21T and YC77 is 99.8 % and show 90.3–95.3 % similarity to the closest relative members of Halobellus. The DNA G+C content of strains YC21T and YC77 were 66.1 and 66.2 mol%, respectively. The DNA–DNA hybridization value between strain YC20T and strain YC77 was 89 %, and the two strains showed low DNA–DNA relatedness with Halobellus limi TBN53T, the most related member of Halobellus. The phenotypic, chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic properties suggest that strains YC21T and YC77 represent a novel species of the genus Halobellus, for which the name Halobellus rarus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is YC21T (=CGMCC 1.12121T = JCM 18362T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castillo AM, Gutiérrez MC, Kamekura M, Ma YH, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2006a) Halovivax asiaticus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:765–770
Castillo AM, Gutiérrez MC, Kamekura M, Xue YF, Ma YH, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2006b) Halostagnicola larsenii gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a saline lake in Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1519–1524
Castillo AM, Gutiérrez MC, Kamekura M, Xue Y-F, Ma Y-H, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2006c) Halorubrum orientale sp. nov., a novel halophilic archaeon isolated from Lake Ejinor, Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2559–2563
Castillo AM, Gutiérrez MC, Kamekura M, Xue Y-F, Ma Y-H, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2006d) Natrinema ejinorense sp. nov., isolated from a saline lake in Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2683–2687
Castillo AM, Gutiérrez MC, Kamekura M, Xue Y-F, Ma Y-H, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2007a) Halovivax ruber sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from Lake Xilinhot, Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1024–1027
Castillo AM, Gutiérrez MC, Kamekura M, Xue Y-F, Ma Y-H, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2007b) Halorubrum ejinorense sp. nov., isolated from Lake Ejinor, Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2538–2542
Cui H-L, Tohty D, Feng J, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J (2006a) Natronorubrum aibiense sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from Aibi salt lake in Xin-Jiang, China, and emended description of the genus Natronorubrum. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1515–1517
Cui H-L, Tohty D, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J (2006b) Halorubrum lipolyticum sp. nov. and Halorubrum aidingense sp. nov., isolated from two salt lakes in Xin-Jiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1631–1634
Cui H-L, Tohty D, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J (2006c) Haloterrigena longa sp. nov. and Haloterrigena limicola sp. nov., two extremely halophilic archaea isolated from salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1837–1840
Cui H-L, Tohty D, Liu H-C, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J (2007a) Natronorubrum sulfidifaciens sp. nov., an extremely haloalkaliphilic archaeon isolated from Aiding salt lake in Xin-Jiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:738–740
Cui H-L, Lin Z-Y, Dong Y, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J (2007b) Halorubrum litoreum sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from a solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2204–2206
Cui H-L, Zhou P-J, Oren A, Liu S-J (2009) Intraspecific polymorphism of 16S rRNA genes in two halophilic archaeal genera, Haloarcula and Halomicrobium. Extremophiles 13:31–37
Cui H-L, Gao X, Yang X, Xu X-W (2010) Halorussus rarus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from a marine solar saltern. Extremophiles 14:493–499
Cui H-L, Yang X, Gao X, Xu X-W (2011a) Halobellus clavatus gen. nov., sp. nov. and Halorientalis regularis gen. nov., sp. nov., two new members of the family Halobacteriaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2682–2689
Cui H-L, Yang X, Mou YZ (2011b) Salinarchaeum laminariae gen. nov., sp. nov.: a new member of the family Halobacteriaceae isolated from salted brown alga Laminaria. Extremophiles 15:625–631
Cui H-L, Yang X, Zhou YG, Liu HC, Zhou YG, Dyall-Smith ML (2012) Halobellus limi sp. nov. and Halobellus salinus sp. nov., isolated from two marine solar salterns in Australia and China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1307–1313
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Dussault HP (1955) An improved technique for staining red halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol 70:484–485
Fan H-P, Xue Y-F, Ma Y-H, Ventosa A, Grant WD (2004) Halorubrum tibetense sp. nov., a novel haloalkaliphilic archaeon from Lake Zabuye in Tibet, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1213–1216
Feng J, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J (2004) Halorubrum xinjiangense sp. nov., a novel halophile isolated from saline lakes in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1789–1791
Feng J, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J, Warren-Rhodes K (2005) Halorubrum alkaliphilum sp. nov., a novel haloalkaliphile isolated from a soda lake in Xinjiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:149–152
Gonzalez C, Gutierrez C, Ramirez C (1978) Halobacterium vallismortis sp. nov. an amylolytic and carbohydrate-metabolizing, extremely halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol 24:710–715
Gutiérrez C, González C (1972) Method for simultaneous detection of proteinase and esterase activities in extremely halophilic bacteria. Appl Microbiol 24:516–517
Gutiérrez MC, Castillo AM, Kamekura M, Xue YF, Ma YH, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2007) Halopiger xanaduensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from the saline lake Shangmatala in Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1402–1407
Gutiérrez MC, Castillo AM, Kamekura M, Ventosa A (2008a) Haloterrigena salina sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2880–2884
Gutiérrez MC, Castillo AM, Pagaling E, Heaphy S, Kamekura M, Xue Y, Ma Y, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ventosa A (2008b) Halorubrum kocurii sp. nov., an archaeon isolated from a saline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2031–2035
Gutiérrez C, Castillo AM, Corral P, Minegishi H, Ventosa A (2010) Natronorubrum sediminis sp. nov., an archaeon isolated from a saline lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1802–1806
Gutiérrez MC, Castillo AM, Corral P, Kamekura M, Ventosa A (2011) Halorubrum aquaticum sp. nov., an archaeon isolated from hypersaline lakes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1144–1148
Hezayen FF, Tindall BJ, Steinbuchel A, Rehm BHA (2002) Characterization of a novel halophilic archaeon, Halobiforma haloterrestris gen. nov., sp. nov., and transfer of Natronobacterium nitratireducens to Halobiforma nitratireducens comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:2271–2280
Hu L, Pan H, Xue Y, Ventosa A, Cowan DA, Jones BE, Grant WD, Ma Y (2008) Halorubrum luteum sp. nov., isolated from Lake Chagannur, Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1705–1708
Huss VAR, Festl H, Schleifer KH (1983) Studies on the spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:184–192
Itoh T, Yamaguchi T, Zhou PJ, Takashina T (2005) Natronolimnobius baerhuensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and Natronolimnobius innermongolicus sp. nov., novel haloalkaliphilic archaea isolated from soda lakes in Inner Mongolia, China. Extremophiles 9:111–116
Liu H, Zhou Y, Liu R, Zhang K-Y, Lai R (2009) Bacillus solisalsi sp. nov., a halotolerant, alkaliphilic bacterium isolated from soil around a salt lake. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1460–1464
Liu B–B, Tang S-K, Zhang Y-G, Lu X-H, Li L, Cheng J, Zhang Y-M, Zhang L–L, Li W-J (2013) Halalkalicoccus paucihalophilus sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon from Lop Nur region in Xinjiang, northwest of China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:1007–1014
Marmur J, Doty P (1962) Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol 5:109–118
McDade JJ, Weaver RH (1959) Rapid methods for the detection of gelatin hydrolysis. J Bacteriol 77:60–64
Minegishi H, Kamekura M, Itoh T, Echigo A, Usami R, Hashimoto T (2010) Further refinement of Halobacteriaceae phylogeny based on the full-length RNA polymerase subunit B’ (rpoB ’) gene. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2398–2408
Oren A, Ventosa A, Grant WD (1997) Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:233–238
Owen RJ, Pitcher D (1985) Current methods for estimating DNA base composition and levels of DNA–DNA hybridization. In: Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (eds) Chemical methods in bacterial systematics. Academic Press, London, pp 67–93
Qiu X-X, Mou Y-Z, Zhao M-L, Zhang W-J, Han D, Ren M, Cui H-L (2013) Halobellus inordinatus sp. nov., from a marine solar saltern and an inland salt lake of China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.053066-0
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Sun Y, Song W, Zhong Y, Zhang R, Abatzopoulos TJ, Chen R (1999) Diversity of genetic differentiation in Artemia species and populations detected by AFLP markers. Int J Salt Lake Res 8:341–350
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Xin H-W, Itoh T, Zhou P-J, Suzuki K, Kamekura M, Nakase T (2000) Natrinema versiforme sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from Aibi salt lake, Xinjiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1297–1303
Xin H-W, Itoh T, Zhou P-J, Suzuki K, Kamekura M, Nakase T (2001) Natronobacterium nitratireducens sp. nov., a haloalkaliphilic archaeon isolated from a soda lake in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1825–1829
Xu Y, Zhou PJ, Tian XY (1999) Characterization of two novel haloalkaliphilic archaea Natronorubrum bangense gen. nov., sp. nov. and Natronorubrum tibetense gen. nov., sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:261–266
Xu Y, Wang Z-X, Xue Y, Zhou P-J, Ma Y-H, Ventosa A, Grant WD (2001) Natrialba hulunbeirensis sp. nov. and Natrialba chahannaoensis sp. nov., novel haloalkaliphilic archaea from soda lakes in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1693–1698
Xu X-W, Liu S-J, Tohty D, Oren A, Wu M, Zhou P-J (2005a) Haloterrigena saccharevitans sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon from Xin-Jiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2539–2542
Xu X-W, Ren P-G, Liu S-J, Wu M, Zhou P-J (2005b) Natrinema altunense sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a salt lake in Altun Mountain in Xinjiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1311–1314
Xu X-W, Wu M, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J (2005c) Halobiforma lacisalsi sp. nov., isolated from a salt lake in China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1949–1952
Xu X-W, Wu Y-H, Zhang H-B, Wu M (2007) Halorubrum arcis sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a saline lake on the Qinghai-Tibet plateau, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1069–1072
Xue YF, Fan HP, Ventosa A, Grant WD, Jones BE, Cowan DA, Ma YH (2005) Halalkalicoccus tibetensis gen. nov., sp. nov., representing a novel genus of haloalkaliphilic archaea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2501–2505
Yang Y, Cui H-L, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J (2006) Halobacterium jilantaiense sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon isolated from a saline lake in Inner Mongolia, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2353–2355
Yang Y, Cui H-L, Zhou P-J, Liu S-J (2007) Haloarcula amylolytica sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from Aibi salt lake in Xin-Jiang, China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:103–106
Zheng X-Y, Zhang M-G, Xu C, Li B-X (2002) An overview of salt lakes in China. Science, Beijing (In Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Qinglan project of Jiangsu Province, the opening project of Xinjiang Production & Construction Corps Key Laboratory of Protection and Utilization of Biological Resources in Tarim Basin (BRZD1206) and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the 16S rRNA gene sequences of strains YC21T and YC77 are JQ237123 and KF193579, respectively. Those for the rpoB′ gene sequences of strains YC21T and YC77 are KF193580 and KF193581, respectively. Phase-contrast micrographs of strains YC21T and YC77, thin-layer chromatograms of strains YC21T, YC77 and some other haloarchaea, are available as supplementary materials.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, WJ., Han, D., Qiu, XX. et al. Halobellus rarus sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon from an inland salt lake of China. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 104, 377–384 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9960-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-013-9960-y