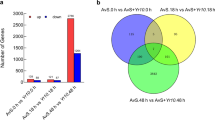
Abstract
Stripe rust (Sr), caused by Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici (Pst), is the most devastating disease that poses serious threat to the wheat-growing nations across the globe. Developing resistant cultivars is the most challenging aspect in wheat breeding. The function of resistance genes (R genes) and the mechanisms by which they influence plant-host interactions are poorly understood. In the present investigation, comparative transcriptome analysis was carried out by involving two near-isogenic lines (NILs) PBW343 and FLW29. The seedlings of both the genotypes were inoculated with Pst pathotype 46S119. In total, 1106 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified at early stage of infection (12 hpi), whereas expressions of 877 and 1737 DEGs were observed at later stages (48 and 72 hpi) in FLW29. The identified DEGs were comprised of defense-related genes including putative R genes, 7 WRKY transcriptional factors, calcium, and hormonal signaling associated genes. Moreover, pathways involved in signaling of receptor kinases, G protein, and light showed higher expression in resistant cultivar and were common across different time points. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to further confirm the transcriptional expression of eight critical genes involved in plant defense mechanism against stripe rust. The information about genes are likely to improve our knowledge of the genetic mechanism that controls the stripe rust resistance in wheat, and data on resistance response–linked genes and pathways will be a significant resource for future research.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data used and analyzed during this investigation may be obtained from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Agenbag GM, Pretorius ZA, Boyd LA et al (2012) Identification of adult plant resistance to stripe rust in the wheat cultivar Cappelle-Desprez. Theor Appl Genet 125:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1819-5
Anders S, Huber W (2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Nat Preced 2010:1–1. https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4282.2
Axtell MJ, Chisholm ST, Dahlbeck D, Staskawicz BJ (2003) Genetic and molecular evidence that the Pseudomonas syringae type III effector protein AvrRpt2 is a cysteine protease. Mol Microbiol 49:1537–1546. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03666.x
Bittner-Eddy PD, Crute IR, Holub EB, Beynon JL (2000) RPP13 is a simple locus in Arabidopsis thaliana for alleles that specify downy mildew resistance to different avirulence determinants in Peronospora parasitica. Plant J 21:177–188. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2000.00664.x
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Boudsocq M, Willmann MR, McCormack M et al (2010) Differential innate immune signalling via Ca 2+ sensor protein kinases. Nature 464:418–422. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08794
Chandra S, Kazmi AZ, Ahmed Z, Roychowdhury G, Kumari V, Kumar M, Mukhopadhyay K (2017) Genome-wide identification and characterization of NB-ARC resistant genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and their expression during leaf rust infection. Plant Cell Rep 36:1097–1112
Chen XM (2005) Epidemiology and control of stripe rust [Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici] on wheat. Can J Plant Pathol 27:314–337. https://doi.org/10.1080/07060660509507230
Chen Q, Han Z, Jiang H et al (2010) Strong positive selection drives rapid diversification of R-genes in arabidopsis relatives. J Mol Evol 70:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-009-9316-4
Chen X, Coram T, Huang X et al (2013) Understanding molecular mechanisms of durable and non-durable resistance to stripe rust in wheat using a transcriptomics approach. Curr Genom 14:111–126. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202911314020004
Chen F, Hu Y, Vannozzi A et al (2017) The WRKY transcription factor family in model plants and crops. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 36:311–335
Chinchilla D, Bauer Z, Regenass M et al (2006) The Arabidopsis receptor kinase FLS2 binds flg22 and determines the specificity of flagellin perception. Plant Cell 18:465–476. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.036574
Coram TE, Settles ML, Chen X (2008a) Transcriptome analysis of high-temperature adult-plant resistance conditioned by Yr39 during the wheat-Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici interaction. Mol Plant Pathol 9:479–493. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2008.00476.x
Coram TE, Wang M, Chen X (2008b) Transcriptome analysis of the wheat-Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici interaction. Mol Plant Pathol 9:157–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2007.00453.x
Datta D, Bhardwaj SC, Prashar M (2008) Development of bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) lines with specific rust resistance genes and their authentication through molecular markers. Indian J Genet Plant Breed 68:113–123
David P, Chen NW, Pedrosa-Harand A, Thareau V, Sévignac M, Cannon SB, Debouck D, Langin T, Geffroy V (2009) A nomadic subtelomeric disease resistance gene cluster in common bean. Plant physiology 151(3):1048–1065
Dixon RA, Achnine L, Kota P et al (2002) The phenylpropanoid pathway and plant defence - a genomics perspective. Mol Plant Pathol 3:371–390
Eddy SR (2011) Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput Biol 7:1002195. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195
Eulgem T, Somssich IE (2007) Networks of WRKY transcription factors in defense signaling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:366–371
Feng J, Wang M, See DR et al (2018) Characterization of novel gene Yr79 and four additional quantitative trait loci for all-stage and high-temperature adult-plant resistance to stripe rust in spring wheat PI 182103. Phytopathology 108:737–747. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-11-17-0375-R
Feuillet C, Travella S, Stein N et al (2003) Map-based isolation of the leaf rust disease resistance gene Lr10 from the hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:15253–15258. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2435133100
Freymark G, Diehl T, Miklis M et al (2007) Antagonistic control of powdery mildew host cell entry by barley calcium-dependent protein kinases (CDPKs). Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 20:1213–1221. https://doi.org/10.1094/MPMI-20-10-1213
Gangwar OP, Kumar S, Bhardwaj SC et al (2019) Characterization of three new Yr9-virulences and identification of sources of resistance among recently developed Indian bread wheat germplasm. J Plant Pathol 101:955–963. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-019-00302-w
Gao X, Cox KL, He P (2014) Functions of calcium-dependent protein kinases in plant innate immunity. Plants 3:160–176
Gessese M, Bariana H, Wong D et al (2019) Molecular mapping of stripe rust resistance gene Yr81 in a Common wheat landrace Aus27430. Plant Dis 103:1166–1171. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-06-18-1055-RE
Gómez-Gómez L, Boller T (2000) FLS2: An LRR receptor-like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 5:1003–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80265-8
Gong X, Liu X, Pan Q et al (2020) Combined physiological, transcriptome, and genetic analysis reveals a molecular network of nitrogen remobilization in maize. J Exp Bot 71:5061–5073. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa229
Grabherr MG, Haas BJ, Yassour M et al (2011) Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat Biotechnol 29:644–652. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1883
Hao W, Collier SM, Moffett P, Chai J (2013) Structural basis for the interaction between the potato virus X resistance protein (Rx) and its cofactor ran GTPase-activating protein 2 (RanGAP2). J Biol Chem 288:35868–35876. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.517417
Hao Y, Wang T, Wang K et al (2016) Transcriptome analysis provides insights into the mechanisms underlying wheat plant resistance to stripe rust at the adult plant stage. PLoS One 11:e0150717. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150717
He ZH, Cheeseman I, He D, Kohorn BD (1999) A cluster of five cell wall-associated receptor kinase genes, Wak1-5, are expressed in specific organs of Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 39:1189–1196. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006197318246
Hepler JR, Gilman AG (1992) G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 17:383–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/0968-0004(92)90005-T
Howe E, Holton K, Nair S et al (2010) MeV: MultiExperiment viewer. In: Biomedical Informatics for Cancer Research. Springer, US, pp 267–277
Hu Y, Dong Q, Yu D (2012) Arabidopsis WRKY46 coordinates with WRKY70 and WRKY53 in basal resistance against pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Sci 185–186:288–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2011.12.003
Huang L, Brooks SA, Li W et al (2003) Map-based cloning of leaf rust resistance gene Lr21 From the Large and Polyploid Genome of Bread Wheat. Genetics 164:655
Hulbert SH, Bai J, Fellers JP et al (2007) Gene expression patterns in near isogenic lines for wheat rust resistance gene Lr34/Yr18. Phytopathology 97:1083–1093. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-97-9-1083
Idänheimo N, Gauthier A, Salojärvi J et al (2014) The Arabidopsis thaliana cysteine-rich receptor-like kinases CRK6 and CRK7 protect against apoplastic oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 445:457–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.013
Johnson R (1984) A critical analysis of durable resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 22:309–330. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.py.22.090184.001521
Kazan K, Manners JM (2009) Linking development to defense: auxin in plant-pathogen interactions. Trends Plant Sci 14:373–382
Khong GN, Richaud F, Coudert Y et al (2008) Modulating rice stress tolerance by transcription factors. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 25:381–404. https://doi.org/10.5661/bger-25-381
Klymiuk V, Yaniv E, Huang L et al (2018) Cloning of the wheat Yr15 resistance gene sheds light on the plant tandem kinase-pseudokinase family. Nat Commun 9:3735. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06138-9
Kobayashi M, Ohura I, Kawakita K et al (2007) Calcium-dependent protein kinases regulate the production of reactive oxygen species by potato NADPH oxidase. Plant Cell 19:1065–1080. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.048884
Krattinger SG, Lagudah ES, Spielmeyer W et al (2009) A putative ABC transporter confers durable resistance to multiple fungal pathogens in wheat. Science 80:1360–1363. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1166453
Kumar S, Phogat BS, Vikas VK et al (2019) Mining of Indian wheat germplasm collection for adult plant resistance to leaf rust. PLoS One 14:e0213468. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213468
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Li W, Godzik A (2006) Cd-hit: a fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 22:1658–1659. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btl158
Li J, Brader G, Palva ET (2004) The WRKY70 transcription factor: a node of convergence for jasmonate-mediated and salicylate-mediated signals in plant defense. Plant Cell 16:319–331. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.016980
Li J, Brader G, Kariola T, Tapio Palva E (2006) WRKY70 modulates the selection of signaling pathways in plant defense. Plant J 46:477–491. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02712.x
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A et al (2009) The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Li B, Meng X, Shan L, He P (2016) Transcriptional regulation of pattern-triggered immunity in plants. Cell Host Microbe 19:641–650
Li N, Han X, Feng D et al (2019) Signaling crosstalk between salicylic acid and ethylene/Jasmonate in plant defense: do we understand what they are whispering? Int J Mol Sci 20(3):671
Li H, Bariana H, Singh D et al (2020) A durum wheat adult plant stripe rust resistance QTL and its relationship with the bread wheat Yr80 locus. Theor Appl Genet 133:3049–3066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03654-5
Liu W, Frick M, Huel R et al (2014) The stripe rust resistance gene Yr10 encodes an evolutionary-conserved and unique CC-NBS-LRR sequence in wheat. Mol Plant 7:1740–1755. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssu112
Liu Y, Gu H-Y, Zhu J et al (2019) Identification of hub genes and key pathways associated with bipolar disorder based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Front Physiol 10:1081. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.01081
Lu K, Liang S, Wu Z et al (2016) Overexpression of an Arabidopsis cysteine-rich receptor-like protein kinase, CRK5, enhances abscisic acid sensitivity and confers drought tolerance. J Exp Bot 67:5009–5027. https://doi.org/10.1093/JXB/ERW266
Lu L, Rong W, Zhou R et al (2019) TaCML36, a wheat calmodulin-like protein, positively participates in an immune response to Rhizoctonia cerealis. Crop J 7:608–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2019.02.001
Marchal C, Zhang J, Zhang P et al (2018) BED-domain-containing immune receptors confer diverse resistance spectra to yellow rust. Nat. Plants 4:662–668
McDowell JM, Dhandaydham M, Long TA et al (1998) Intragenic recombination and diversifying selection contribute to the evolution of downy mildew resistance at the RPP8 locus of arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1861–1874. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.10.11.1861
McHale L, Tan X, Koehl P, Michelmore RW (2006) Plant NBS-LRR proteins: adaptable guards. Genome Biol 7:212
Mierziak J, Kostyn K, Kulma A (2014) Flavonoids as important molecules of plant interactions with the environment. Molecules 19:16240–16265
Mondragon-Palomino M, Gaut BS (2005) Gene conversion and the evolution of three leucine-rich repeat gene families in arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Biol Evol 22:2444–2456. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msi241
Moore JW, Herrera-Foessel S, Lan C et al (2015) A recently evolved hexose transporter variant confers resistance to multiple pathogens in wheat. Nat Genet 47:1494–1498. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3439
Nakagami H, Maeda K, Morishita R et al (2005) Novel autologous cell therapy in ischemic limb disease through growth factor secretion by cultured adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:2542–2547. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000190701.92007.6d
Nakashima KK, Bastos EL (2019) Rationale on the high radical scavenging capacity of betalains. Antioxidants 8:222. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8070222
Nowack MK, Harashima H, Dissmeyer N et al (2012) Genetic framework of cyclin-dependent kinase function in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 22:1030–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.02.015
Nürnberger T, Scheel D (2001) Signal transmission in the plant immune response. Trends Plant Sci. 6:372–379
Pakeerathan K, Bariana H, Qureshi N et al (2019) Identification of a new source of stripe rust resistance Yr82 in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 132:3169–3176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03416-y
Pan Q, Liu YS, Budai-Hadrian O et al (2000) Comparative genetics of nucleotide binding site-leucine rich repeat resistance gene homologues in the genomes of two dicotyledons: tomato and arabidopsis. Genetics 155:309–322
Qi M, Wang H, Jing B et al (2015) Occurrence and molecular identification of Cryptosporidium spp. in dairy calves in Xinjiang Northwestern China. Vet Parasitol 212:404–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.07.002
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ, Smyth GK (2009) edgeR: a bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 26:139–140. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616
Rojas CM, Senthil-Kumar M, Tzin V, Mysore KS (2014) Regulation of primary plant metabolism during plant-pathogen interactions and its contribution to plant defense. Front. Plant Sci. 5:17
Shanmugam V (2005) Role of extracytoplasmic leucine rich repeat proteins in plant defence mechanisms. Microbiol Res 160:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2004.09.014
Sharmin RA, Bhuiyan MR, Lv W et al (2020) RNA-Seq based transcriptomic analysis revealed genes associated with seed-flooding tolerance in wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. & Zucc.). Environ Exp Bot 171:103906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.103906
Singh S, Chand S, Singh NK, Sharma TR (2015) Genome-wide distribution, organisation and functional characterization of disease resistance and defence response genes across rice species. PLoS One 10:e0125964. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125964
Smita S, Katiyar A, Lenka SK et al (2020) Gene network modules associated with abiotic stress response in tolerant rice genotypes identified by transcriptome meta-analysis. Funct Integr Genomics 20:29–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-019-00697-w
Strugnell L (2018) New publications: the importance of wheat in the global food supply to a growing population. CIMMYT
Sui XX, Wang MN, Chen XM (2009) Molecular mapping of a stripe rust resistance gene in spring wheat cultivar zak. Phytopathology 99:1209–1215. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-99-10-1209
Sun XL, Yu QY, Tang LL et al (2013) GsSRK, a G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine protein kinase, is a positive regulator of plant tolerance to salt stress. J Plant Physiol 170:505–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.11.017
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H et al (2017) The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res 45:D362–D368. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw937
Takahashi Y, Soyano T, Kosetsu K et al (2010) HINKEL kinesin, ANP MAPKKKs and MKK6/ANQ MAPKK, which phosphorylates and activates MPK4 MAPK, constitute a pathway that is required for cytokinesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1766–1776. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcq135
Tang P, Zhang Y, Sun X et al (2010) Disease resistance signature of the leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase genes in four plant species. Plant Sci 179:399–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.06.017
Thimm O, Bläsing O, Gibon Y et al (2004) MAPMAN: a user-driven tool to display genomics data sets onto diagrams of metabolic pathways and other biological processes. Plant J 37:914–939. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02016.x
Van Loon LC (1997) Induced resistance in plants and the role of pathogenesis-related proteins. Eur J Plant Pathol. 103:753–765
Van Loon LC, Rep M, Pieterse CMJ (2006) Significance of inducible defense-related proteins in infected plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol 44:135–162
Wang M, Chen X (2017) Stripe rust resistance. In: Stripe Rust. Springer, Netherlands, pp 353–558
Wang D, Pajerowska-Mukhtar K, Culler AH, Dong X (2007) Salicylic acid inhibits pathogen growth in plants through repression of the auxin signaling pathway. Curr Biol 17:1784–1790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.09.025
Wang J, Tao F, An F et al (2017) Wheat transcription factor TaWRKY70 is positively involved in high-temperature seedling plant resistance to Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici. Mol Plant Pathol 18:649–661. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12425
Worland AJ, Law CN (1986) Genetic analysis of chromosome 2 d of wheat i. the location of genes affecting height day length insensitivity hybrid dwarfism and yellow rust resistance. Zeitschrift fuer Pflanzenzuechtung 96:331–345
Yokotani N, Sato Y, Tanabe S et al (2013) WRKY76 is a rice transcriptional repressor playing opposite roles in blast disease resistance and cold stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 64:5085–5097. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert298
Zhang ZJ, Yang GH, Li GH et al (2001) Transgressive segregation, heritability, and number of genes controlling durable resistance to stripe rust in one Chinese and two Italian wheat cultivars. Phytopathology 91:680–686. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO.2001.91.7.680
Zhang H, Yang Y, Wang C et al (2014) Large-scale transcriptome comparison reveals distinct gene activations in wheat responding to stripe rust and powdery mildew. BMC Genomics 15:898. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-898
Zhang K, Yue D, Wei W et al (2016) Characterization and functional analysis of calmodulin and calmodulin-like genes in Fragaria vesca. Front Plant Sci 7:1820. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01820
Zhu X, Perez M, Aldon D, Galaud JP (2017) Respective contribution of CML8 and CML9, two arabidopsis calmodulin-like proteins, to plant stress responses. Plant Signal Behav 12:e1322246. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592324.2017.1322246
Zou C, Jiang W, Yu D (2010) Male gametophyte-specific WRKY34 transcription factor mediates cold sensitivity of mature pollen in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 61:3901–3914. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erq204
Andersen EJ, Nepal MP, Purintun JM et al (2020) Wheat disease resistance genes and their diversification through integrated domain fusions. Front Genet 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00898
Kuykendall D, Shao J, Trimmer K (2009) A nest of LTR retrotransposons adjacent the disease resistance-priming gene NPR1 in Beta vulgaris L. U.S. Hybrid H20. Int J Plant Genomics 2009. https://doi.org/10.1155/2009/576742
Negi P, Rai AN, Suprasanna P (2016) Moving through the stressed genome: Emerging regulatory roles for transposons in plant stress response. Front Plant Sci 7
New publications: The importance of wheat in the global food supply to a growing population – CIMMYT.2018 https://www.cimmyt.org/publications/new-publications-the-importance-of-wheat-in-the-global-food-supply-to-a-growing-population/. Accessed 23 Oct 2020
Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt RY et al (2012) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 40. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr1065
Singh RP, William HM, Huerta-Espino J, Rosewarne G (2004) Wheat rust in Asia: meeting the challenges with old and new technologies. Proc 4th Int Crop Sci Congr 1–13
Tzin V, Galili G, Aharoni A (2012) Shikimate pathway and aromatic amino acid biosynthesis. In: eLS. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Chichester, UK
Funding
This research was financially supported by Indian Council of Agriculture Research under (ICAR-CABin) Project Scheme
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZAM, DC, NB, and SK: conceptualization; ZAM, DC, and SK conceived the idea; ZAM, DC, AKP, VS, DS, NB, DCM, VJ, TKS, MG, OPG, SK, SCB, JCP, AKS, AR, GPS. and SK: experimentation and data analysis. ZAM, DC, NB, and SK wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Human and animal ethics
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
Supplementary Table 1: Summary of data output quality generated by RNA-seq library (DOCX 17 kb)
ESM 2
Supplementary Table 2: Result of mapping statistics from trinity software using BWA (DOCX 14 kb)
ESM 3
Supplementary Table 3a: Number of DEGs uniquely expressed after Pst treatment. Supplementary Table 3b: List of DEGs obtained from blast results in Triticum aestivum and Puccinia striiformis genome. (ZIP 6355 kb)
ESM 4
Supplementary Table 4: Gene Ontology Details and Summary (XLSX 14 kb)
ESM 5
Supplementary Table 5: KEGG pathway statistics, enrichment and distribution of differentially regulated pathways and pathway network (XLSX 46 kb)
ESM 6
Supplementary Table 6: Functional annotation of DEGs involved in calcium ion signaling (XLSX 14 kb)
ESM 7
Supplementary Table 7: List of WRKY transcription factors (XLSX 11 kb)
ESM 8
Supplementary Table 8: List of R genes in expression heatmap, statistics of putative R gene (XLSX 76 kb)
ESM 9
Supplementary Table 9: Protein-protein network degree file (XLSX 13 kb)
ESM 10
Supplementary Table 10: Mapman Annotation (XLSX 134 kb)
ESM 11
Supplementary Table 11: list of putative genes conferring resistance to Pst (XLSX 11 kb)
ESM 12
Supplementary Figure 1 Venn diagram illustrating comparison of expression levels across 3 time points (1-12, 2-48 and 3-72 hpi) between Pst treated and non-uninoculated varieties. a) non-uninoculated DEGs b) treated DEGs c) unique DEGs after treatment (Purple colour indicates DEGs at 12 hpi, Pink colour indicates DEGs at 48 hpi and green colour indicates DEGs at 72 hpi). In addition, A-PBW343, B-FLW29, C-Control, T-treatment. Supplementary Figure 2-Venn daigram depicting the list of DEGs obtained from the blast results of Triticum aestivum and Puccinia striiformis genome. DEGs unique to both the genomes were identified. Supplementary Figure 3- Bar graph representation of gene ontology (GO) for genes differentially expressed in transcriptome analyses at different time points. Supplementary Figure 4-Transcription factors (TFs) belonging to 5 TF family along with number of genes across different time periods at a) 12 hpi b) 48 hpi and c) 72 hpi. Supplementary Figure 5- The Protein-Protein interactions obtained from string database based on analysis are represented by dots such that peach color dots indicate hub proteins and the cyan colour dots represent the interacting partners. The network is layout by degree value of the nodes. The interactions were determined by using T. aestivum as model organism and visualization was done using cytoscape. Supplementary Figure 6- Alignment of TRINITY_DN128400_c0_g3_i2 with MN334950.1 (DOCX 1741 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mir, Z.A., Chauhan, D., Pradhan, A.K. et al. Comparative transcriptome profiling of near isogenic lines PBW343 and FLW29 to unravel defense related genes and pathways contributing to stripe rust resistance in wheat. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 169 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01104-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01104-1