Abstract
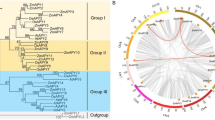
The Hsf gene family, one of the most important transcription factor families, plays crucial roles in regulating heat resistance. However, a systematic and comprehensive analysis of this gene family has not been reported in Chinese cabbage. Therefore, systematic analysis of the Hsf gene family in Chinese cabbage has profound significance. In this study, 35 BrHsf genes were identified from Chinese cabbage, which could be classified into three groups according to their structural characteristics and phylogenetic comparisons with Arabidopsis and rice. Thirty-three BrHsf genes mapped on chromosomes were further assigned to three subgenomes and eight ancestral karyotypes. Distribution mapping showed that BrHsf genes were non-randomly localized on chromosomes. Chinese cabbage and Arabidopsis shared 22 orthologous gene pairs. The expansion of BrHsf genes mainly resulted from genome triplication. Comparative analysis showed that the most Hsf genes were in Chinese cabbage among the five species analyzed. Interestingly, the number of Hsf genes of heat-resistant plants (Theobroma cacao and Musa acuminata) was fewer than that in Chinese cabbage. The expression patterns of BrHsf genes were different in six tissues, based on RNA-seq. Quantitative real-time-PCR analysis showed that the expression level of BrHsf genes varied under various abiotic stresses. In conclusion, this comprehensive analysis of BrHsf genes will provide rich resources, aiding the determination of Hsfs functions in plant heat resistance. Furthermore, the comparative genomics analysis deepened our understanding of Hsf genes’ evolution accompanied by the polyploidy event of Chinese cabbage.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey TL, Boden M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L, Ren J, Li WW, Noble WS (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W202–W208
Baniwal SK, Bharti K, Chan KY, Fauth M, Ganguli A, Kotak S, Mishra SK, Nover L, Port M, Scharf KD, Tripp J, Weber C, Zielinski D, von Koskull-Doring P (2004) Heat stress response in plants: a complex game with chaperones and more than twenty heat stress transcription factors. J Biosci. 29:471–487
Chawade A, Brautigam M, Lindlof A, Olsson O, Olsson B (2007) Putative cold acclimation pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana identified by a combined analysis of mRNA co-expression patterns, promoter motifs and transcription factors. BMC Genomics 8:304
Cheng F, Liu S, Wu J, Fang L, Sun S, Liu B, Li P, Hua W, Wang X (2011) BRAD, the genetics and genomics database for Brassica plants. BMC Plant Biol 11:136
Cheng F, Mandakova T, Wu J, Xie Q, Lysak MA, Wang X (2013) Deciphering the diploid ancestral genome of the mesohexaploid Brassica rapa. Plant Cell 25:1541–1554
Chung E, Kim KM, Lee JH (2013) Genome-wide analysis and molecular characterization of heat shock transcription factor family in Glycine max. J Genet Genomics 40:127–135
D′Hont A, Denoeud F, Aury JM, Baurens FC, Carreel F, Garsmeur O (2012) The banana (Musa acuminata) genome and the evolution of monocotyledonous plants. Nature 488:213–217
Damberger FF, Pelton JG, Harrison CJ, Nelson HC, Wemmer DE (1994) Solution structure of the DNA-binding domain of the heat shock transcription factor determined by multidimensional heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Protein Sci 3:1806–1821
Giorno F, Guerriero G, Baric S, Mariani C (2012) Heat shock transcriptional factors in Malus domestica: identification, classification and expression analysis. BMC Genomics 13:639
Glazebrook J (2001) Genes controlling expression of defense responses in Arabidopsis–2001 status. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:301–308
Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J, Mitros T, Dirks W, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Rokhsar DS (2012) Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1178–D1186
Guo J, Wu J, Ji Q, Wang C, Luo L, Yuan Y, Wang Y, Wang J (2008) Genome-wide analysis of heat shock transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. J Genet Genomics 35:105–118
Kotak S, Port M, Ganguli A, Bicker F, von Koskull-Doring P (2004) Characterization of C-terminal domains of Arabidopsis heat stress transcription factors (Hsfs) and identification of a new signature combination of plant class A Hsfs with AHA and NES motifs essential for activator function and intracellular localization. Plant J 39:98–112
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA (2009) Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res 19:1639–1645
la Cour T, Kiemer L, Molgaard A, Gupta R, Skriver K, Brunak S (2004) Analysis and prediction of leucine-rich nuclear export signals. Protein Eng Des Sel 17:527–536
Lee T, Tang H, Wang X, Paterson A (2013) PGDD: a database of gene and genome duplication in plants. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D1152–D1158
Letunic I, Doerks T, Bork P (2012) SMART 7: recent updates to the protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D302–D305
Li L, Stoeckert CJ Jr, Roos DS (2003) OrthoMCL: identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res 13:2178–2189
Li J, Gao G, Zhang T, Wu X (2013) The putative phytocyanin genes in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L.): genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis. Mol Genet Genomics 288:1–20
Lin YX, Jiang HY, Chu ZX, Tang XL, Zhu SW, Cheng BJ (2011) Genome-wide identification, classification and analysis of heat shock transcription factor family in maize. BMC Genomics 12:76
Mittal D, Chakrabarti S, Sarkar A, Singh A, Grover A (2009) Heat shock factor gene family in rice: genomic organization and transcript expression profiling in response to high temperature, low temperature and oxidative stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:785–795
Morimoto RI (1998) Regulation of the heat shock transcriptional response: cross talk between a family of heat shock factors, molecular chaperones, and negative regulators. Gene Dev 12:3788–3796
Morimoto RI (2002) Dynamic remodeling of transcription complexes by molecular chaperones. Cell 110:281–284
Mun JH, Yu HJ, Shin JY, Oh M, Hwang HJ, Chung H (2012) Auxin response factor gene family in Brassica rapa: genomic organization, divergence, expression, and evolution. Mol Genet Genomics 287:765–784
Nguyen Ba AN, Pogoutse A, Provart N, Moses AM (2009) NLStradamus: a simple Hidden Markov Model for nuclear localization signal prediction. BMC Bioinforma 10:202
Nover L, Scharf KD, Gagliardi D, Vergne P, Czarnecka-Verner E, Gurley WB (1996) The Hsf world: classification and properties of plant heat stress transcription factors. Cell Stress Chaperones 1:215–223
Nover L, Bharti K, Doring P, Mishra SK, Ganguli A, Scharf KD (2001) Arabidopsis and the heat stress transcription factor world: how many heat stress transcription factors do we need? Cell Stress Chaperons 6:177–189
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Pirkkala L, Nykanen P, Sistonen L (2001) Roles of the heat shock transcription factors in regulation of the heat shock response and beyond. FASEB J 15:1118–1131
Punta M, Coggill PC, Eberhardt RY, Mistry J, Tate J, Boursnell C, Pang N, Forslund K, Ceric G, Clements J, Heger A, Holm L, Sonnhammer EL, Eddy SR, Bateman A, Finn RD (2012) The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D290–D301
Renak D, Gibalova A, Solcova K, Honys D (2014) A new link between stress response and nucleolar function during pollen development in Arabidopsis mediated by AtREN1 protein. Plant Cell Environ 37(3):670–683
Santoro N, Johansson N, Thiele DJ (1998) Heat shock element architecture is an important determinant in the temperature and transactivation domain requirements for heat shock transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol 18:6340–6352
Scharf KD, Berberich T, Ebersberger I, Nover L (2012) The plant heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) family: structure, function and evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta 1819:104–119
Schranz ME, Lysak MA, Mitchell-Olds T (2006) The ABC’s of comparative genomics in the Brassicaceae: building blocks of crucifer genomes. Trends Plant Sci 11:535–542
Singh K, Foley RC, Onate-Sanchez L (2002) Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:430–436
Song X, Li Y, Hou X (2013a) Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factor superfamily in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). BMC Genomics 14:573
Song X, Liu T, Duan W, Ma Q, Ren J, Wang Z, Li Y, Hou X (2013b) Genome-wide analysis of the GRAS gene family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Genomics
Song X, Huang Z, Duan W, Ren J, Liu T, Li Y, Hou X (2014) Genome-wide analysis of the bHLH transcription factor family in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). Mol Genet Genomics 289(1):77–91
Sorger PK, Pelham HRB (1988) Yeast heat-shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell 54:855–864
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Tong C, Wang X, Yu J, Wu J, Li W, Huang J, Dong C, Hua W, Liu S (2013) Comprehensive analysis of RNA-seq data reveals the complexity of the transcriptome in Brassica rapa. BMC Genomics 14:689
Tunc-Ozdemir M, Tang C, Ishka MR, Brown E, Groves NR, Myers CT, Rato C, Poulsen LR, McDowell S, Miller G, Mittler R, Harper JF (2013) A cyclic nucleotide-gated channel (CNGC16) in pollen is critical for stress tolerance in pollen reproductive development. Plant Physiol 161:1010–1020
von Koskull-Doring P, Scharf KD, Nover L (2007) The diversity of plant heat stress transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 12:452–457
Wang X, Wang H, Wang J, Sun R, Wu J, Liu S, Bai Y, Mun JH, Bancroft I, Cheng F (2011) The genome of the mesopolyploid crop species Brassica rapa. Nat Genet 43:1035–1039
Wang F, Dong Q, Jiang H, Zhu S, Chen B, Xiang Y (2012a) Genome-wide analysis of the heat shock transcription factors in Populus trichocarpa and Medicago truncatula. Mol Biol Rep 39:1877–1886
Wang Y, Tang H, Debarry JD, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, Lee TH, Jin H, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger JC, Paterson AH (2012b) MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e49
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez JC, Williams KL, Appel RD, Hochstrasser DF (1999) Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol Biol 112:531–552
Zhang L, Wu B, Zhao D, Li C, Shao F, Lu S (2013) Genome-wide analysis and molecular dissection of the SPL gene family in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J Integr Plant Biol 56(1):38–50
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Key Program, No. 31330067), National Program on Key Basic Research Projects (The 973 Program: 2012CB113900), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2012AA100101), and Shanghai ‘2011’ program (No. ZF12051301).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
X. Song and G. Liu contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Liu, G., Duan, W. et al. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of the heat shock transcription factor family in Chinese cabbage. Mol Genet Genomics 289, 541–551 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0833-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-014-0833-5