Abstract
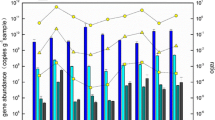
Community structures of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms were investigated using PCR primers designed to specifically target the ammonia monooxygenase α-subunit (amoA) gene in the sediment of Jinshan Lake. Relationships between the abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB), and physicochemical parameters were also explored. The AOA abundance decreased sharply from west to east; however, the AOB abundance changed slightly with AOB outnumbering AOA in two of the four sediment samples (JS), JS3 and JS4. The AOA abundance was significantly correlated with the NH4–N, NO3–N, and TP. No significant correlations were observed between the AOB abundance and environmental variables. AOB had a higher diversity and richness of amoA genes than AOA. Among the 76 archaeal amoA sequences retrieved, 57.89, 38.16, and 3.95 % fell within the Nitrosopumilus, Nitrososphaera, and Nitrososphaera sister clusters, respectively. The 130 bacterial amoA gene sequences obtained in this study were grouped with known AOB sequences in the Nitrosomonas and Nitrosospira genera, which occupied 72.31 % and 27.69 % of the AOB group, respectively. Compared to the other three sample sites, the AOA and AOB community compositions at JS4 showed a large difference. This work could enhance our understanding of the roles of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in freshwater lake environment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brochier-Armanet C, Boussau B, Gribaldo S, Forterre P (2008) Mesophilic crenarchaeota: proposal for a third archaeal phylum, the Thaumarchaeota. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:245–252
Cao H, Li M, Hong Y, Gu JD (2011) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in polluted mangrove sediment. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:513–523
Cao H, Hong Y, Li M, Gu JD (2011) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in sediments from the coastal Pearl River estuary to the South China Sea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100:545–556
Chen GY, Qiu SL, Zhou YY (2009) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in eutrophic and oligotrophic basins of a shallow Chinese lake (Lake Donghu). Res Microbiol 160:173–178
Erguder TH, Boon N, Wittebolle L, Marzorati M, Verstraete W (2009) Environmental factors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:855–869
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:14683–14688
French E, Kozlowski JA, Mukherjee M, Bullerjahn G, Bollmann A (2012) Ecophysiological characterization of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria from freshwater. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:5773–5780
Hou J, Song C, Cao X, Zhou Y (2013) Shifts between ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in relation to nitrification potential across trophic gradients in two large Chinese lakes (Lake Taihu and Lake Chaohu). Water Res 47:2285–2296
Hugoni M, Etien S, Bourges A et al (2013) Dynamics of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in contrasted freshwater ecosystems. Res Microbiol 164:360–370
Jin T, Zhang T, Ye L et al (2011) Diversity and quantity of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1137–1145
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9:299–306
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M et al (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442:806–809
Li M, Cao H, Hong Y, Gu JD (2011) Spatial distribution and abundances of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in mangrove sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1243–1254
Li X, Xiao Y, Ren W et al (2012) Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in different types of soil in the Yangtze River estuary. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 13:769–782
Li Z, Jin W, Liang Z, Yue Y, Lv J (2013) Abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in response to various habitats in Pearl River Delta of China, a subtropical maritime zone. J Environ Sci 25:1195–1205
Liu Y, Zhang JX, Zhang XL, Xie SG (2014) Depth-related changes of sediment ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in a high-altitude freshwater wetland. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s00253-014-5651-5
Lu RK (1999) Chemical Analysis Method Of Soil Agriculture. Agricultural Science and Technology, China
Pester M, Rattei T, Flechl S et al (2012) amoA-based consensus phylogeny of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and deep sequencing of amoA genes from soils of four different geographic regions. Environ Microbiol 14:525–539
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1501–1506
Sims A, Horton J, Gajaraj S et al (2012) Temporal and spatial distributions of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria and their ratio as an indicator of oligotrophic conditions in natural wetlands. Water Res 46:4121–4129
Tourna M, Freitag TE, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2008) Growth, activity and temperature responses of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in soil microcosms. Environ Microbiol 10:1357–1364
Wang XY, Wang C, Bao LL, Xie SG (2014) Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in reservoir sediment and adjacent soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:1883–1892
Wang Y, Gu J (2013) Higher diversity of ammonia/ammonium-oxidizing prokaryotes in constructed freshwater wetland than natural coastal marine wetland. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7015–7033
Wu Y, Xiang Y, Wang J et al (2010) Heterogeneity of archaeal and bacterial ammonia-oxidizing communities in Lake Taihu, China. Environ Microbiol Rep 2:569–576
Wuchter C, Abbas B, Coolen MJ et al (2006) Archaeal nitrification in the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12317–12322
Yao H, Gao Y, Nicol GW et al (2011) Links between ammonia oxidizer community structure, abundance, and nitrification potential in acidic soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4618–4625
Zhao D, Zeng J, Wan W et al (2013) Vertical distribution of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in sediments of a Eutrophic Lake. Curr Microbiol 67:327–332
Zheng Y, Hou L, Liu M et al (2013) Diversity, abundance, and activity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in Chongming eastern intertidal sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:8351–8363
Zheng Y, Hou L, Newell S et al (2014) Community dynamics and activity of ammonia-oxidizing Prokaryotes in intertidal sediments of the Yangtze Estuary. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:408–419
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 51109097; the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China under Grant BK2011520; the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project under Grant 2012T50464; and the Research and Innovation Project for College Graduate of Jiangsu Province under Grant 1223000281.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Li, Y., Zhang, J. et al. Abundance and Diversity of Ammonia-Oxidizing Microorganisms in the Sediments of Jinshan Lake. Curr Microbiol 69, 751–757 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0646-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0646-0