Abstract
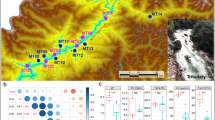
Ammonia oxidation plays a pivotal role in the cycling and removal of nitrogen in aquatic sediments. Certain bacterial groups and a novel group of archaea, which is affiliated with the novel phylum Thaumarchaeota, can perform this initial nitrification step. We examined the diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing β-Proteobacteria (β-AOB) and ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) in the sediments of Chongming eastern tidal flat using the ammonia monooxygenase-α subunit (amoA) gene as functional markers. Clone library analysis showed that AOA had a higher diversity of amoA gene than β-AOB. The β-Proteobacterial amoA community composition correlated significantly with water soluble salts in the sediments, whereas the archaeal amoA community composition was correlated more with nitrate concentrations. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) results indicated that the abundance of β-AOB amoA gene (9.11 × 104–6.47 × 105 copies g−1 sediment) was always greater than that of AOA amoA gene (7.98 × 103–3.51 × 105 copies g−1 sediment) in all the samples analyzed in this study. The β-Proteobacterial amoA gene abundance was closely related to organic carbon, while no significant correlations were observed between archaeal amoA gene abundance and the environmental factors. Potential nitrification rates were significantly greater in summer than in winter and correlated strongly with the abundance of amoA genes. Additionally, a greater contribution of single amoA gene to potential nitrification occurred in summer (1.03–5.39 pmol N copy−1 day−1) compared with winter (0.16–0.38 pmol N copy−1 day−1), suggesting a higher activity of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in warm seasons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antje K, Heinz H (1982) Effect of organic matter on growth and cell yield of ammonia oxidizing bacteria. Arch Microbiol 133:50–54
Bayer K, Schmitt S, Hentschel U (2008) Physiology, phylogeny and in sit evidence for bacterial and archaeal nitrifiers in the marine sponge Aplysina aerophoba. Environ Microbiol 10:2942–2955
Beman JM, Francis CA (2006) Diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the sediments of a hyper-nitrified subtropical estuary: Bahia del Tobari, Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7767–7777
Beman JM, Popp BN, Francis CA (2008) Molecular and biogeochemical evidence for ammonia oxidation by marine Crenarchaeota in the Gulf of California. ISME J 2:429–441
Bernhard AE, Donn T, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2005) Loss of diversity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria correlates with increasing salinity in an estuary system. Environ Microbiol 7:1289–1297
Bernhard AE, Tucker J, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2007) Functionally distinct communities of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria along an estuarine salinity gradient. Environ Microbiol 9:1439–1447
Bernhard AE, Landry ZC, Blevins A, de la Torre JR, Giblin AE, Stahl DA (2010) Abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria along an estuarine salinity gradient in relation to potential nitrification rates. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2026–2034
Caffrey JM, Bano N, Kalanetra K, Hollibaugh JT (2007) Ammonia oxidation and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea from estuaries with differing histories of hypoxia. ISME J 1:660–662
Cébron A, Coci M, Garnier J, Laanbroek HJ (2004) Denaturin gradient gel electrophoretic analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacterial community structure in the lower Seine River: impact of Paris wastewater effluent. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6726–6737
Chai C, Yu ZM, Song XX, Gao XH (2006) The status and characteristics of eutrophication in the Yangtze River (Changjiang) Estuary and the adjacent East China Sea, China. Hydrobiologia 563:313–328
Chen X, Zhang LM, Shen JP, Wei WX, He JZ (2011) Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in an acid paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 47:323–331
Christman GD, Cottrell MT, Popp BN, Gier E, Kirchman DL (2011) Abundance, diversity, and activity of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in the coastal arctic ocean in summer and winter. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2026–2034
Dang H, Zhang X, Sun J, Li T, Zhang Z, Yang G (2008) Diversity and spatial distribution of sediment ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeota in response to estuarine and environmental gradients in the Changjiang Estuary and East China Sea. Microbiology 154:2084–2095
Dang H, Li J, Chen R, Wang L, Guo L, Zhang Z, Klotz MG (2010) Diversity, abundance, and spatial distribution of sediment ammonia-oxidizing Betaproteobacteria in response to environmental gradients and coastal eutrophication in Jiaozhou Bay, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4691–4702
Fan GN, Zhu GB, Wang Y, Wang SY, Wang CX, Yin CQ (2010) New functional microorganisms in nitrogen cycle restoration of river riparian ecosystems. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 30:1558–1563
Francis CA, O’Mullan GD, Ward BB (2003) Diversity of ammonia monooxygenase (amoA) genes across environmental gradients in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Geobiology 1:129–140
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:14683–14688
Francis CA, Beman JM, Kuypers MMM (2007) New processes and players in the nitrogen cycle: the microbial ecology of anaerobic and archaeal ammonia oxidation. ISME J 1:19–27
Glaser K, Hackl E, Inselsbacher E, Strauss J, Wanek W, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Sessitsch A (2010) Dynamics of ammonia-oxidizing communities in barley-planted bulk soil and rhizosphere following nitrate and ammonium fertilizer amendment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:575–591
Graham DW, Trippett C, Dodds WK, O’Brien JM, Banner EBK, Head IM, Smith MS, Yang RK, Knapp CW (2010) Correlations between in situ denitrification activity and nir-gene abundances in pristine and impacted prairie streams. Environ Pollut 158:3225–3229
Gruber N, Galloway JN (2008) An Earth-system perspective of the global nitrogen cycle. Nature 451:293–296
Hatzenpichler R, Lebedeva EV, Spieck E, Stoecher K, Richter A, Daims H, Wagner M (2008) A moderately thermophilic ammonia-oxidizing crenarchaeote from a hot spring. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:134–2139
Henriksen K (1980) Measurement of in situ rates of nitrification in sediment. Microb Ecol 6:329–337
Henriksen K, Kemp WM (1986) Nitrification in estuarine and coastal marine sediments: Methods, patterns and regulating factors, p 207–250. In: Blackburn TH, Sørensen J (eds) Nitrogen cycling in coastal marine environments. Wiley, New York
Hou LJ, Liu M, Xu SY, Ou DN, Yu J, Cheng SB, Lin X, Yang Y (2007) The effects of semi-lunar spring and neap tidal change on nitrification, denitrification, and N2O vertical distribution in the intertidal sediments of the Yangtze estuary, China. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 73:607–616
Hou LJ, Liu M, Carini SA, Gardner WS (2012) Transformation and fate of nitrate near the sediment-water interface of Copano Bay. Cont Shelf Res 35:86–94
Jensen K, Sloth NP, Risgaard-Petersen N, Rysgaard S, Revsbech NP (1994) Estimation of nitrification and denitrification from microprofiles of oxygen and nitrate in model sediment systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2094–2100
Jin T, Zhang T, Ye L, Lee OO, Wong YH, Qian PY (2011) Diversity and quantity of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria in sediment of the Pearl River Estuary, China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:1137–1145
Kalanetra KM, Bano N, Hollibaugh JT (2009) Ammonia-oxidizing Archaea in the Arctic Ocean and Antarctic coastal waters. Environ Microbiol 11:2434–2445
Konneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437:543–546
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Lam P, Jensen MM, Lavik G, McGinnis DF, Muller B, Schubert CJ, Amann R, Thamdrup B, Kuypers MMM (2007) Linking crenarchaeal and bacterial nitrification to anammox in the Black Sea. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:7104–7109
Li M, Cao H, Hong Y, Gu JD (2011) Spatial distribution and abundances of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in mangrove sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1243–1254
Liu SM, Zhang J, Chen HT, Wu Y, Xiong H, Zhang EF (2003) Nutrients in the Changjiang and its tributaries. Biogeochemistry 62:1–18
Maidak BL, Cole JR, Parker CT Jr, Garrity GM, Larsen N, Li B, Lilburn TG, McCaughey MJ, Olsen MJ, Overbeek R, Pramanik S, Schmidt TM, Tiedje JM, Woese CR (1999) A new version of the RDP (Ribosomal Database Project). Nucleic Acids Res 27:171–173
Martens-Habbena W, Berube PM, Urakawa H, de la Torre JR, Stahl DA (2009) Ammonia oxidation kinetics determine niche separation of nitrifying Archaea and Bacteria. Nature 461:976–979
Mincer TJ, Church MJ, Taylor LT, Preston C, Karl DM, DeLong EF (2007) Quantitative distribution of presumptive archaeal and bacterial nitrifiers in Monterey Bay and the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Environ Microbiol 9:1162–1175
Mosier AC, Francis CA (2008) Relative abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the San Francisco Bay estuary. Environ Microbiol 10:3002–3016
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural water. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Mußmann M, Brito I, Pitcher A, Sinninghe Damsté JS, Hatzenpichler R, Richter A, Nielsen JL, Halkjær Nielsen P, Müller A, Daims H, Wagner M, Head IM (2011) Thaumarchaeotes abundant in refinery nitrifying sludges express amoA but are not obligate autotrophic ammonia oxidizers. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:16771–16776
Norton JM, Alzerreca JJ, Suwa Y, Klotz MG (2002) Diversity of ammonia monooxygenase operon in autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Arch Microbiol 177:139–149
Purkhold U, Pommerening-Röser A, Juretschko S, Schmid MC, Koops HP, Wagner M (2000) Phylogeny of all recognized species of ammonia oxidizers based on comparative 16S rRNA and amoA sequence analysis: implications for molecular diversity surveys. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5368–5382
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Rysgaard S, Thastum P, Dalsgaard T, Christensen PB, Sloth NP (1999) Effects of salinity on NH4 + adsorption capacity, nitrification, and denitrification in Danish estuarine sediments. Estuaries 22:21–30
Santoro AE, Francis CA, de Sieyes NR, Boehm AB (2008) Shifts in the relative abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea across physicochemical gradients in a subterranean estuary. Environ Microbiol 10:1068–1079
Seitzinger S (1988) Denitrification in fresh water and coastal marine ecosystems: ecological and geochemical significance. Limnol Oceanogr 33:702–724
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Vitousek PM, Aber JD, Howarth RW, Likens GE, Matson PA, Schindler DW (1997) Technical report: human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle: sources and consequences. Ecol Appl 7:737–750
Wang SY, Wang Y, Feng XJ, Zhai LM, Zhu GB (2011) Quantitative analyses of ammonia-oxidizing Archaea and bacteria in the sediments of four nitrogen-rich wetlands in China. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:779–787
Wuchter C, Abbas B, Coolen MJL, Herfort L, van Bleijswijk J, Timmers P, Strous M, Teira E, Herndl GJ, Middelburg JJ, Schouten S, Sinninghe Damste JS (2006) Archaeal nitrification in the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:12317–12322
Yao HY, Gao YM, Nicol GW, Campbell CD, Prosser J, Zhang LM, Han WY, Singh BK (2011) Links between ammonia oxidizer community structure, abundance, and nitrification potential in acidic soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4618–4625
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundations (Nos. 41130525, 40721004, 41021064, and 41071135) and the State Key Laboratory of Estuarine and Coastal Research (No. 2010RCDW07). It was also supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the Marine Scientific Research Project for Public Interest (No. 200905007). We thank Drs. Xiaoli Zhang, Jun Gong and Bing Xie for sharing their analytical expertise on measurements of ammonia-oxidizers. Professor Wayne S. Gardner and the anonymous reviewers are thanked for their constructive comments on a preliminary draft of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 127 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Hou, L., Liu, M. et al. Diversity, abundance, and activity of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in Chongming eastern intertidal sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97, 8351–8363 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4512-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4512-3