Abstract
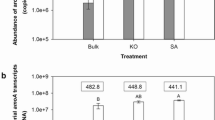
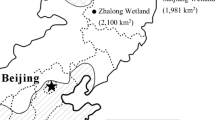
Ammonia oxidation is an important process for global nitrogen cycling. Both ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) and archaea (AOA) can be the important players in nitrification process. However, their relative contribution to nitrification remains controversial. This study investigated the abundance and community structure of AOA and AOB in sediment of Miyun Reservoir and adjacent soils. Quantitative PCR assays indicated that the highest AOA abundance occurred in unplanted riparian soil, followed by reservoir sediment, reed-planted riparian soil and agricultural soil. The AOB community size in agricultural soil was much larger than that in the other habitats. Large variations in the structures of AOA and AOB were also observed among the different habitats. The abundance of Nitrosospira-like AOB species were detected in the agricultural soil and reservoir sediment. Pearson’s correlation analysis showed the AOB diversity had positive significant correlations with pH and total nitrogen, while the AOA diversity might be negatively affected by nitrate nitrogen and ammonia nitrogen. This work could add new insights towards nitrification in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auguet JC, Casamayor EO (2013) Partitioning of Thaumarchaeota populations along environmental gradients in high mountain lakes. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 84:154–164
Beman JM, Francis CA (2006) Diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the sediments of a hypernutrified subtropical estuary: Bahia del Tobari, Mexico. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:7767–7777
Cao HL, Hong YG, Li M, Gu JD (2011a) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in sediments from the coastal Pearl River estuary to the South China Sea. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100:545–556
Cao HL, Li M, Hong YG, Gu JD (2011b) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in polluted mangrove sediment. Syst Appl Microbiol 34:513–523
Cao HL, Hong YG, Li M, Gu JD (2012) Lower abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria detected in the subsurface sediments of the Northern South China Sea. Geomicrobiol J 29:332–339
Chen X, Zhang LM, Shen JP, Wei WX, He JZ (2011) Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in an acid paddy soil. Biol Fertil Soils 47:323–331
DaebelerA AGC, Bodelier PL, Bodrossy L, Frampton DM, Hefting MM, Laanbroek HJ (2012) Archaeal dominated ammonia-oxidizing communities in Icelandic grassland soils are moderately affected by long-term N fertilization and geothermal heating. Front Microbiol 3:352
de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Ingalls AE, Konneke M, Stahl DA (2008) Cultivation of a thermophilic ammonia oxidizing archaeon synthesizing crenarchaeol. Environ Microbiol 10:810–818
Erguder TH, Boon N, Wittebolle L, Marzorati M, Verstraete W (2009) Environmental actors shaping the ecological niches of ammonia-oxidizing archaea. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:855–869
Feng S, Zhang XJ, Wang QF, Wan R, Chen C, Xie SG (2012) Heterogeneity of ammonia-oxidizing community structures in a pilot-scale drinking water biofilter. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 70:148–152
Francis CA, Roberts KJ, Beman JM, Santoro AE, Oakley BB (2005) Ubiquity and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in water columns and sediments of the ocean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:14683–14688
Glaser K, Hackl E, Inselsbacher E, Strauss J, Wanek W, Zechmeister-Boltenstern S, Sessitsch A (2010) Dynamics of ammonia-oxidizing communities in barley-planted bulk soil and rhizosphere following nitrate and ammonium fertilizer amendment. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:575–591
Gubry-Rangin C, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2010) Archaea rather than bacteria control nitrification in two agricultural acidic soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:566–574
Hayden HL, Drake J, Imhof M, Oxley APA, Norng S, Mele PM (2010) The abundance of nitrogen cycle genes amoA and nifH depends on land-uses and soil types in South-Eastern Australia. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1774–1783
He J, Shen J, Zhang L, Zhu Y, Zheng Y, Xu M, Di HJ (2007) Quantitative analyses of the abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea of a Chinese upland red soil under long-term fertilization practices. Environ Microbiol 9:2364–2374
He JZ, Hu HW, Zhang LM (2012) Current insights into the autotrophic thaumarchaeal ammonia oxidation in acidic soils. Soil Biol Biochem 55:146–154
Herrmann M, Saunders AM, Schramm A (2008) Archaea dominate the ammonia-oxidizing community in the rhizosphere of the freshwater macrophyte Littorella uniflora. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:3279–3283
Hu BL, Liu SA, Shen LD, Zheng P, Xu XY, Lou LP (2012) Effect of different ammonia concentrations on community succession of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in a simulated paddy soil column. PLOS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044122
Huang R, Wu YC, Zhang JB, Zhong WH, Jia ZJ, Cai ZC (2012) Nitrification activity and putative ammonia-oxidizing archaea in acidic red soils. J Soils Sediments 12:420–428
Jia ZJ, Conrad R (2009) Bacteria rather than Archaea dominate microbial ammonia oxidation in an agricultural soil. Environ Microbiol 11:1658–1671
Kasuga I, Nakagaki H, Kurisu F, Furumai H, Kasuga I, Nakagaki H, Kurisu F, Furumai H (2010) Predominance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea on granular activated carbon used in a full-scale advanced drinking water treatment plant. Water Res 44(SI):5039–5049
Könneke M, Bernhard AE, de la Torre JR, Walker CB, Waterbury JB, Stahl DA (2005) Isolation of an autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing marine archaeon. Nature 437:543–546
Lehtovirta-Morley LE, Stoecker K, Vilcinskas A, Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2011) Cultivation of an obligate acidophilic ammonia oxidizer from a nitrifying acid soil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:15892–15897
Leininger S, Urich T, Schloter M, Schwark L, Qi J, Nicol GW, Prosser JI, Schuster SC, Schleper C (2006) Archaea predominate among ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in soils. Nature 442:806–809
Li M, Cao HL, Hong YG, Gu JD (2011) Spatial distribution and abundances of ammonia-oxidizing archaea (AOA) and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) in mangrove sediments. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1243–1254
Li XR, Xiao YP, Ren WW, Liu ZF, Shi JH, Quan ZX (2012) Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in different types of soil in the Yangtze River estuary. J Zhejiang Univ-SCI B 13:769–782
Liu YR, Zheng YM, Shen JP, Zhang LM, He JZ (2010a) Effects of mercury on the activity and community composition of soil ammonia oxidizers. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17:1237–1244
Liu G, Cheng L, Wang B, Zhao Q, Qu D (2010b) Changes of soil ammonia-oxidizing bacterial diversity in response to long-term fertilization in dry highland of Loess Plateau. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 43:2706–2714
Liu ZH, Huang SB, Sun GP, Xu ZC, Xu MY (2011) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in the Dongjiang River, China. Microbiol Res 166:337–345
Liu S, Shen L, Lou L, Tian G, Zheng P, Hu B (2013) Spatial distribution and factors shaping the niche segregation of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in the qiantang river, china. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4065–4071
Long X, Chen CR, Xu ZH, Linder S, He JZ (2012a) Abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizing bacteria and archaea in a Sweden boreal forest soil under 19-year fertilization and 12-year warming. J Soils Sediments 12:1124–1133
Long X, Chen CR, Xu ZH, Oren R, He JZ (2012b) Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in a temperate forest ecosystem under ten-years elevated CO2. Soil Biol Biochem 46:163–171
Malchair S, De Boeck HJ, Lemmens CMHM, Ceulemans R, Merckx R, Nijs I, Carnol M (2010) Diversity-function relationship of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in soils among functional groups of grassland species under climate warming. Appl Soil Ecol 44:15–23
Mertens J, Broos K, Wakelin SA, Kowalchuk GA, Springael D, Smolders E (2009) Bacteria, not archaea, restore nitrification in a zinc-contaminated soil. ISME J 3:916–923
Moin NS, Nelson KA, Bush A, Bernhard AE (2009) Distribution and diversity of archaeal and bacterial ammonia oxidizers in salt marsh sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7461–7468
Nicol GW, Leininger S, Schleper C, Prosser JI (2008) The influence of soil pH on the diversity, abundance and transcriptional activity of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria. Environ Microbiol 10:2966–2978
Offre P, Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2009) Growth of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in soil microcosms is inhibited by acetylene. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 70:99–108
Ollivier J, Wanat N, Austruy A, Hitmi A, Joussein E, Welzl G, Munch JC, Schloter M (2012) Abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in the root-rhizosphere complex of Miscanthus x giganteus grown in heavy metal-contaminated soils. Microb Ecol 64:1038–1046
Park SJ, Park BJ, Rhee SK (2008) Comparative analysis of archaeal 16S rRNA and amoA genes to estimate the abundance and diversity of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in marine sediments. Extremophiles 12:605–615
Park BJ, Park SJ, Yoon DN, Schouten S, Damste JSS, Rhee SK (2010) Cultivation of autotrophic ammonia-oxidizing archaea from marine sediments in coculture with sulfur-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:7575–7587
Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2012) Archaeal and bacterial ammonia-oxidisers in soil: the quest for niche specialisation and differentiation. Trends Microbiol 20:523–531
Rotthauwe JH, Witzel KP, Liesack W (1997) The ammonia monooxygenase structural gene amoA as a functional marker: molecular fine-scale analysis of natural ammonia-oxidizing populations. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4704–4712
Sakami T (2012) Distribution of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in the surface sediments of matsushima bay in relation to environmental variables. Microbes Environ 27:61–66
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1501–1506
Shen JP, Zhang LM, Zhu YG, Zhang JB, He JZ (2008) Abundance and composition of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea communities of an alkaline sandy loam. Environ Microbiol 10:1601–1611
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4, molecular evolutionary genetics analysis, MEGA software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tourna M, Stieglmeier M, Spang A, Könneke M, Schintlmeister A, Urich T, Engel M, Schloter M, Wagner M, Richter A (2011) Nitrososphaera viennensis, an ammonia oxidizing archaeon from soil. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:8420–8425
Verhamme DT, Prosser JI, Nicol GW (2011) Ammonia concentration determines differential growth of ammonia-oxidising archaea and bacteria in soil microcosms. ISME J 5:1067–1071
Wang X, Li T, Xu Q, He W (2001) Study of the distribution of non-point source pollution in the watershed of the Miyun Reservoir, Beijing, China. Water Sci Technol 44:35–40
Wankel SD, Mosier AC, Hansel CM, Paytan A, Francis CA (2011) Spatial variability in nitrification rates and ammonia-oxidizing microbial communities in the agriculturally impacted Elkhorn Slough Estuary, California. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:269–280
Xu YG, Yu WT, Ma Q, Zhou H (2012) Responses of bacterial and archaeal ammonia oxidisers of an acidic luvisols soil to different nitrogen fertilization rates after 9 years. Biol Fertil Soils 48:827–837
Yao H, Gao Y, Nicol GW, Campbell CD, Prosser JI, Zhang L, Han W, Singh BK (2011) Links between ammonia oxidizer community structure, abundance, and nitrification potential in acidic soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:4618–4625
Zeng J, Zhao DY, Huang R, Wu QL (2012) Abundance and community composition of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in two different zones of Lake Taihu. Can J Microbiol 58:1018–1026
Zhang LM, Offre PR, He JZ, Verhamme DT, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2010) Autotrophic ammonia oxidation by soil thaumarchaea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:17240–17245
Zhang LM, Hu HW, Shen JP, He JZ (2012) Ammonia-oxidizing archaea have more important role than ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in ammonia oxidation of strongly acidic soils. ISME J 6:1032–1045
Zhao P, Xia BC, Hu YF, Yang YJ (2013) A spatial multi-criteria planning scheme for evaluating riparian buffer restoration priorities. Ecol Eng 54:155–164
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.40971258, 41271495) and Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (No. 20121108110006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, C., Bao, L. et al. Abundance and community structure of ammonia-oxidizing microorganisms in reservoir sediment and adjacent soils. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 1883–1892 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5174-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5174-5