Abstract
Anaerobic fungi found in the guts of large herbivores are prolific biomass degraders whose genomes harbor a wealth of carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes), of which only a handful are structurally or biochemically characterized. Here, we report the structure and kinetic rate parameters for a glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 5 subfamily 4 enzyme (CelD) from Piromyces finnis, a modular, cellulosome-incorporated endoglucanase that possesses three GH5 domains followed by two C-terminal fungal dockerin domains (double dockerin). We present the crystal structures of an apo wild-type CelD GH5 catalytic domain and its inactive E154A mutant in complex with cellotriose at 2.5 and 1.8 Å resolution, respectively, finding the CelD GH5 catalytic domain adopts the (β/α)8-barrel fold common to many GH5 enzymes. Structural superimposition of the apo wild-type structure with the E154A mutant-cellotriose complex supports a catalytic mechanism in which the E154 carboxylate side chain acts as an acid/base and E278 acts as a complementary nucleophile. Further analysis of the cellotriose binding pocket highlights a binding groove lined with conserved aromatic amino acids that when docked with larger cellulose oligomers is capable of binding seven glucose units and accommodating branched glucan substrates. Activity analyses confirm P. finnis CelD can hydrolyze mixed linkage glucan and xyloglucan, as well as carboxymethylcellulose (CMC). Measured kinetic parameters show the P. finnis CelD GH5 catalytic domain has CMC endoglucanase activity comparable to other fungal endoglucanases with kcat = 6.0 ± 0.6 s−1 and Km = 7.6 ± 2.1 g/L CMC. Enzyme kinetics were unperturbed by the addition or removal of the native C-terminal dockerin domains as well as the addition of a non-native N-terminal dockerin, suggesting strict modularity among the domains of CelD.
Key points
• Anaerobic fungi host a wealth of industrially useful enzymes but are understudied.
• P. finnis CelD has endoglucanase activity and structure common to GH5_4 enzymes.
• CelD’s kinetics do not change with domain fusion, exhibiting high modularity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Microbial degradation of lignocellulose is a fundamental biological process that is crucial to nutrient cycling in nature, a process that turns over ~ 1015 pounds of plant biomass and releases the equivalent amount of energy in 640 billion barrels of oil per year (Boudet et al. 2003; Ragauskas et al. 2006). Microbes achieve such efficient degradation of lignocellulose by employing a synergistic consortium of enzymes that attack the different biopolymers present in plant cell walls—hemicellulose, lignin, and most abundantly, cellulose. The core synergism promoting cellulose saccharification occurs among various carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZymes) of the glycoside hydrolase (GH) family, including endo-cleaving enzymes, which randomly cleave internal β-1,4 linkages, cellobiohydrolases that progressively remove cellobiose units from chain ends, and β-glucosidases which hydrolyze the freed cellobiose into glucose (Woodward 1991; Wilson and Wood 1992). The complete depolymerization of hemicellulose is achieved in a similar manner, though a greater diversity of GH family enzymes, as well as enzymes from other families including carbohydrate esterases (CE), are required to break the diverse sugar linkages and branched chains present in hemicellulose (Lowe et al. 1987; Mountfort and Asher 1989; Moreira and Filho 2008, 2016). More recently, the importance of auxiliary, non-hydrolytic enzymes, such as lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs), to synergistic lignocellulose degradation has also been emphasized (Hemsworth et al. 2015; Forsberg et al. 2019).
While this enzyme consortium consists exclusively of freely diffusing enzymes in aerobic microorganisms, anaerobic bacteria and fungi have evolved multi-enzyme complexes called cellulosomes that colocalize lignocellulolytic enzymes to greatly enhance their degradative activity (Dijkerman et al. 1997b; Artzi et al. 2017). As such, cellulosomes make attractive potential components of enzyme cocktails for industrial waste biomass valorization. In both bacterial and fungal systems, noncatalytic dockerin domains on the C- and/or N-termini of proteins mediate complex formation via interaction with cohesin repeat domains on a central scaffolding protein, though these domains share no sequence homology between the two systems (Fontes and Gilbert 2010; Haitjema et al. 2017). Bacterial cellulosomes from several different species of anaerobic bacteria have been studied extensively for over three decades and the structures and mechanisms of the dockerin-cohesin interaction are well understood, enabling the construction of engineered cellulosomes optimized for lignocellulose saccharification (Carvalho et al. 2003; Adams et al. 2006). Despite knowledge that fungal cellulosomes harbor greater enzyme diversity to degrade more recalcitrant biomass (Lankiewicz et al. 2023) and produce glucose rather than cellobiose as the major degradation product (Trinci et al. 1994; Solomon et al. 2016), a mechanistic understanding of fungal cellulosome assembly remains incomplete. The fungal dockerin, originally annotated as a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) family 10 due to its sequence homology to the CBM10 protein family (InterPro family IPR002883), was first identified as a modular protein binding domain in the 1990s (Fanutti et al. 1995). Only two structures of fungal dockerin domains exist (Raghothama et al. 2001; Nagy et al. 2007) and the identity and structure of the companion cohesin domain to which they bind remain unknown, with many potential candidates suggested over the last several decades (Steenbakkers et al. 2001; Gilmore et al. 2015; Haitjema et al. 2017).
A rich catalog of past literature on anaerobic fungi supports their potential for exploitation in industrial bioprocessing (Akin et al. 1990; Dijkerman et al. 1997a; Solomon et al. 2016). Anaerobic fungi are prolific producers of CAZymes, encoding on average over four-fold more CAZymes than Trichoderma reesei and Aspergillus niger, the sources of the most popular cellulolytic cocktails (www.mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov; Seppälä et al. 2017). In addition to encoding many cellulosome-incorporating CAZymes, anaerobic fungal genomes encode many modular proteins with multiple enzymatic activities, which is rare among lignocellulolytic organism genomes sequenced to date (Brunecky et al. 2013; Cragg et al. 2015; Jia and Han 2019). Furthermore, the secreted proteome has been shown to rival and even exceed the cellulolytic activity of T. reesei and significantly exceed the hemicellulose degrading power of traditional enzyme cocktails (Wood et al. 1986; Solomon et al. 2016). Thus, mining anaerobic fungal genomes for better lignocellulolytic enzymes may yield higher performing enzymes for industrial biomass valorization applications.
However, only seven unique enzymes from anaerobic fungi have crystal structures (PDB IDs: 6IDW, 5YN3, 5U22, 5CXU, 3WP4, 3AYR, 2C1F), presenting a challenge to understanding what structural characteristics impart high lignocellulolytic activity to these organisms. Fungal cellulosomes are particularly interesting due to their robust hydrolytic activity, but previous works measuring positive or negative contributions to enzyme activity by dockerin domains have produced conflicting results, obfuscating whether dockerin fusion and cellulosome incorporation alter the kinetics of individual enzymes (Fanutti et al. 1995; Huang et al. 2005; Gilmore et al. 2020). These knowledge gaps in the biochemistry of individual anaerobic fungal CAZymes themselves, and of fungal cellulosomes comprising many CAZymes, present a challenge towards designing lignocellulolytic enzyme cocktails that leverage the degradative machinery of anaerobic fungi.
In this study, we characterized, at the structural and functional levels, the CelD enzyme from the anaerobic fungus Piromyces finnis. This fungal enzyme belongs to the glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 5 subfamily 4 of cellulases and acts strictly as an endo-β-1,4-glucanase (EC 3.2.1.4) with confirmed activity against carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), mixed linkage glucan (MLG), and xyloglucan. The full-length CelD is a 136 kDa multi-domain enzyme containing three GH5 domains and two C-terminal dockerin domains, also termed a “double dockerin” (GenBank ORX48147.1). To facilitate bacterial protein expression and to study the contribution of fungal dockerins to enzyme catalytic activity, we characterized a single GH5 catalytic domain in isolation (ORX48147.1 residues 748–1105), as well as a GH5 with the native C-terminal double dockerin (ORX48147.1 residues 748–1192) and a GH5 with native C-terminal double dockerin and a non-native N-terminal dockerin domain. We present the crystal structure of a CelD GH5 catalytic domain in its apo wild-type form and complementary structure of an inactive E154A mutant in complex with cellotriose solved at a resolution of 2.5 Å and 1.8 Å, respectively (for convenience, in this work, we used 1–362 numbering for the catalytic domain which corresponds to 91–452 residue numbering of the “1–536” in Supplemental Table S1). We also measure kinetic parameters for CMC hydrolysis of three CelD constructs with and without dockerin domains. CelD possesses kinetic parameters comparable to other fungal endoglucanases in rate constant and catalytic efficiency. We observe no change in these parameters upon the addition of natural and unnatural dockerin domain fusions, indicating CelD’s catalytic and dockerin domains are highly modular and that this enzyme’s performance does not change when incorporated into a fungal cellulosome. Overall, the presented atomic-resolution structure and detailed biochemical characterization of CelD add to our growing understanding of how anaerobic fungal cellulosomes rapidly degrade biomass and provide additional insight towards leveraging anaerobic fungal enzymes for industrial biomass valorization applications.
Methods
Enzyme cloning, expression, and purification
The cDNA fragment corresponding to the cellulase catalytic domain CelD (residues 748–1105, GenBank accession number: ORX48147.1) was cloned from the anaerobic fungus P. finnis isolated from horse feces (Solomon et al. 2016; Haitjema et al. 2017). The PCR amplified construct (denoted 91–452) was cloned into pMCSG68 expression vector with the sequence for an N-terminal His-tag of MHHHHHHSSGVDLWSHPQFEKGTENLYFQSNA (Kim et al. 2011). cDNA for construct 91–536, containing the third CelD GH5 domain with native C-terminal double dockerin (residues 748–1192, GenBank accession number: ORX48147.1), was obtained as described above. Construct 1–536 was obtained by cloning a non-native, N-terminal dockerin domain from P. finnis upstream of construct 91–536 in the pMCSG68 backbone. The E154A point mutation within construct 91–452 was introduced using a QuickChange kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol using the following primers: 5′-GGTCAAAACGCACCAAGAAAGAACGGTACTCCAGTTGA-3′ as a forward primer and 5′-CTTTCTTGGTGCGTTTTGACCTTCGAAGATTAAACGTTCA-3′ as a reverse primer. Both wild-type and mutated amino acid sequences were verified by nucleotide sequencing of the cloned constructs.
Recombinant catalytic domains of wild-type CelD with and without dockerin domain fusions as well as the inactive E154A mutant were expressed in Escherichia coli BL21-gold (DE3) (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) cells by induction with 0.5 mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside at 18 °C for 12 h. Following induction, cells were lysed and the 6 × His-tagged proteins purified from soluble cell lysate using a nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid HisTrap column (Cytiva Life Sciences, Marlborough, MA, USA) on an AKTA express system (Cytiva Life Sciences, Marlborough, MA, USA). Protein purity was confirmed by routine SDS-PAGE analysis. Native PAGE analysis revealed the presence of multimers for dockerin-containing constructs (data not shown).
After routine immobilized metal affinity chromatography, protein for crystallization then underwent proteolytic cleavage by a TEV protease at 4 °C for 12 h. Uncleaved protein and His-tagged TEV protease were removed by AKTA express using a HisTrap column (Cytiva Life Sciences, Marlborough, MA, USA) to remove uncleaved product and His-tagged TEV protease. Cleaved CelD catalytic domain or the E154A mutant was then isolated by size exclusion chromatography on a Superdex 200 column (Cytiva Life Sciences, Marlborough, MA, USA) in 15 mM Tris–HCl buffer, pH 7.5, supplemented with 150 mM NaCl.
Complex formation, crystallization, and structure determination
The best crystals of apo wild-type of the catalytic domain were obtained at 16 °C from sitting drops containing 0.4 µL of the protein sample at concentration of 21 mg/mL and 0.4 µL of reservoir solution consisting of 0.1 M Tris–HCl buffer, pH 8.7, 0.5 M LiCl2, and 28% PEG 6000. The complex between the E154A mutant protein and cellotriose was formed by adding the ligand stock solution (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) to the protein solution at 10 mM final concentration. The complex crystals were produced using a similar crystallization approach to that described above except the reservoir solution contained 0.1 M sodium acetate, 1.2 M LiCl2, and 24% PEG 6000, and the protein concentration was 16 mg/mL. Several cycles of microseeding under similar crystallization conditions were carried out to obtain crystals suitable for X-ray analysis for both structures. For data collection, crystals were harvested with 20% (v/v) ethylene glycol in the reservoir solution. Diffraction data were collected from a single flash-frozen crystal on the Structural Biology Center beamlines, 19-ID for the apo form and 19-BM for the E154A mutant-cellotriose complex (Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, IL, USA). Data were indexed and processed with HKL-3000 software suite (Otwinowski and Minor 1997).
The structure of the apo form of the catalytic domain was solved by molecular replacement using the molrep program (Vagin and Teplyakov 1997) from the HKL3000 software suite, with the structure of the catalytic domain of EglA GH5 endoglucanase from Piromyces rhizinflata (PDB code 3AYR) as a search model (McCoy et al. 2007). The refined model of the apo form structure was used as a search model to solve the structure of the complex between the E154A mutant and cellotriose. The final refined models of both structures were obtained by carrying out several iterative alternative cycles consisting of manual model building using COOT (Emsley and Cowtan 2004) and phenix.refine (Adams et al. 2010) until the model converged to the stereochemically good models with Rwork/Rfree of 0.188/0.230 for the apo form and 0.176/0.205 for the E154A mutant-cellotriose complex as indicated in Table 1. Both structures were validated by Ramachandran plot and MolProbity (Laskowski et al. 1993; Chen et al. 2010) and RCSB validation before the coordinates were deposited in the Protein Data Bank (PDB codes 8GHX and 8GHY for the apo and the E154A mutant complex, respectively).
Enzymatic activity assays
Cellulolytic activity of P. finnis CelD on CMC, beechwood xylan, MLG, xyloglucan, phosphoric acid swollen cellulose (PASC), and arabinogalactan was assessed using the dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) reducing sugar assay essentially as described elsewhere (King et al. 2009). CMC was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA); xyloglucan, MLG, and arabinogalactan were purchased from Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA); and beechwood xylan was purchased from Megazyme (Bray, Ireland). PASC was prepared as described previously (Morag (Morgenstern) et al. 1992). For specific activity measurements on CMC, MLG, PASC, and xyloglucan, 200-µL reactions in 0.1 M sodium acetate pH 5.5 containing CelD at 0.70 µM and substrate at 1% w/v final concentration were statically incubated at 39 °C. The same mixture substituting enzyme for acetate buffer was used as a negative control. Three 60-µL samples were taken after 1, 2, and 24 h of incubation time and their reducing sugar composition was measured using the DNS assay (King et al. 2009). Briefly, 100 µL of DNS was added to each reaction sample and the mixture is incubated at 95 °C for 5 min. One hundred microliters of this mixture was added to 100 µL of water and the absorbance at 540 nm was measured using a Tecan Infinite® M1000 plate reader (Tecan Group, Männedorf, Switzerland). A540nm was converted to g/L glucose equivalents with a standard curve of glucose in 0.1 M sodium acetate buffer pH 5.5. Specific activities were calculated using protein concentrations measured by A280nm with appropriate parameters and reducing sugar concentrations measured by DNS assay using standard curves of glucose. Absorbance measurements were blank subtracted by a negative control of substrate without enzyme.
For specific activity measurements on xylan and arabinogalactan, 30 µL of protein in 0.1 M sodium acetate pH 5.5 (0.1 mg total protein) was added to 30 µL of 2% (w/v) freshly prepared, unautoclaved polysaccharide solution in 0.1 M sodium acetate (pH 5.5). Reactions were performed at 39 °C unless otherwise stated and in triplicate, with reaction times of 45 min for xylan and 14 h for arabinogalactan.
Kinetic parameters for CelD on CMC were obtained by adding 5 µL enzyme in 0.1 M sodium acetate pH 5.5 to 195 µL of pre-warmed CMC substrate at concentrations of 0–30 g/L CMC to a final enzyme concentration of 0.05 µM. Enzyme–substrate mixtures were incubated at 39 °C with shaking at 188 RPM. Three 60-µL samples were taken after 5–35 min of incubation time, and their reducing sugar composition was measured as described above. Initial rates were extracted by linear regression of the A540nm vs time curve and converted to the appropriate units using a glucose standard curve after subtraction of A540nm signal from a substrate only control. Initial rate vs substrate concentration data were then fit to a Michaelis–Menten model by nonlinear regression using the SciPy Python package (https://scipy.org/) to determine kcat and Km parameters for each GH5 variant.β-Glucosidase and β-galactosidase activities were assessed by adding 30 µL of protein (0.1 mg total protein) to 970 µL of 5 mM 4-nitrophenyl β-D-glucopyranoside (pNPG) or 4-nitrophenyl β-D-galactopyranoside (pNPGal) in 50 mM sodium phosphate (dibasic) buffer (pH 7.0) with 2% (w/v) bovine serum albumin. Absorbance at 405 nm as measured by a Tecan Infinite® M1000 plate reader tracked reaction progression over 24 h.
Results
Overall structure of the CelD catalytic domain
The unliganded structures of the wild-type catalytic domain and its inactive E154A mutant in complex with cellotriose were determined by molecular replacement and refined to 2.5 Å and 1.8 Å resolution, respectively (Table 1 and Fig. 1). The crystals of the apo form and the complex belonged to orthorhombic P212121 space group and contained two domain molecules per asymmetric unit. Almost all amino acid residues of the CelD catalytic domain, with the exception of a few side chains and three C-terminal residues, were traceable in the final electron density map. The overall root mean square deviation (RMSD) between apo wild form and inactive E154A-ligand complex protein models was 0.26 Å for 359/362 Cα pairs, demonstrating high overall similarity and illustrating that substrate binding results in little to no conformational change (Fig. 1). The CelD catalytic domain displays strong structural similarity to GH clan A, a group of 28 unique GH families exhibiting a (β/α)8–barrel fold in structure, with the highest sequence similarity to proteins from GH5 subfamily 4 (GH5_4), a family of enzymes that predominantly display endoglucanase activity (EC 3.2.1.4) (Fig. 1a) (Jenkins et al. 1995; Pickersgill et al. 1998; Drula et al. 2022). In addition to the eight core β/α elements, CelD has another three small helixes located between α4/βV, βV/α5, and βVI/α6 secondary structure elements and two short β-strands located on the loop between C-terminal βVIII/α8 elements (Supplemental Fig. S1).
The overall structure of the CelD catalytic domain. a Ribbon diagram of the apo-CelD structure with the secondary structural elements indicated. The α-helixes (α1–α8, cyan) flanking the β-strands (βI–βVIII, magenta) are labeled. Arrows indicate the N- and C-termini of the protein. b The structure of the E154A CelD variant in complex with the cellotriose (gray sticks). One disulfide bond and the catalytic residues are indicated and are shown as a yellow stick model. The reducing (RE) and non-reducing (NRE) ends of the oligosaccharide are indicated. c Superposition of the apo wild-type (magenta) and the E154A-ligand (cyan) crystal structures. The catalytic domains are superimposed by aligning the Cα atoms and are presented as ribbon diagrams. The cellotriose ligand is shown as a gray stick. d The substrate binding area in the ligand-bound complex. The protein moiety is presented as a cyan ribbon. The cellotriose molecule (green) bound to the − 3, − 2, and − 1 glucose-binding subsites and the residues of the active site (yellow) are shown as sticks. The electron density map (gray mash) around the bound ligand is countered at the 1.4σ level
The sequences most homologous to P. finnis CelD that have solved experimental structures were all GH5_4 enzymes from P. rhizinflata (PDB: 3AYR, 82% identity), Ruminococcus champanellensis (PDB: 6WQP, 43.1% identity), Acetivibrio cellulolyticus (PDB: 6MQ4, 39.4% identity), and Clostridium cellulovorans (PDB: 3NDY, 40% identity) (Tseng et al. 2011; Glasgow et al. 2020) (Supplemental Fig. S1). These structures align to P. finnis CelD with Cα RMSDs of 0.45 Å, 1.37 Å, 1.44 Å, and 1.82 Å for 3AYR, 6WQP, 6MQ4, and 3NDZ respectively. All enzymes conserve the catalytic glutamic acid residues at positions 154 and 278 characteristic of GH5 enzymes (Jenkins et al. 1995) and many of the strictly conserved sites in the multiple sequence alignment (MSA) encode aromatic amino acids, suggesting their role in substrate binding. The primary structural feature differentiating the apo structures is the loop connecting the β1-strand with the α1-helix (Fig. 1a and Supplemental Fig. S1). CelD and 3AYR both have 13 residue loops pinned by a disulfide bond between Cys27 and Cys43. 6WQP maintains a long loop of 12 residues, while 6MQ4 and 3NDY contain shorter loops of 9 and 2 residues respectively. Other loops exhibiting structural diversity among the enzymes connect the β6-strand with the α6-helix and the β8-strand with the β9-strand (Supplemental Fig. S2). The proximity of these loops to the substrate binding site (Fig. 1b) suggests their structure, and amino acid composition plays an important role in substrate binding specificity.
As only nine GH5 structures from the fungal kingdom have been solved to date, we sought to compare P. finnis CelD to other fungal GH5 structures. Based on a sequence alignment of CelD with three fungal GH5 members studied at the structural level (Piromyces rhizinflata EglA (PDB 3AYR), a GH5_4; Trichoderma reesei EgII (PDB 3QR3), a GH5_5; and Thermoascus aurantiacus EngI (PDB 1GZJ), a GH5_5), EglA from P. rhizinflata is unsurprisingly the closest structural homolog from the fungal kingdom to CelD with sequence identity to CelD of 82% (Supplemental Fig. S3) (Lo Leggio and Larsen 2002; Lee et al. 2011; Tseng et al. 2011). Optimal superposition of the CelD catalytic domain structure with corresponding EglA, EgII, and EngI homologous domains results in 356, 242,, and 254 equivalent Cα atoms with the RMSD values of 0.43 Å, 1.91 Å, and 2.22 Å, respectively (Supplemental Fig. S4). Although these enzymes all share the same basic (β/α)8–barrel topology, they exhibit significant sequence diversity in the loop areas connecting the major structural elements. There are several extra residue insertions observed for CelD and EglA in the loops between βI/α1, βIV/α4, α5/βVI, and βVIII/α8 compared to very compact loop structures of EgII and EngI. As previously mentioned for the N-terminal loop, these loops could contribute differently to substrate binding and enzyme specificity as well as to thermal stability of the enzyme. It is also interesting to note that the T. reesei EgII cellulase contains 8 cysteine residues, which form four disulfide bonds, and one of these bridges (Cys222–Cys249), pinning the α6/βVI loop to the N-terminus of the α7-helix, corresponds to that observed in Thermoascus aurantiacus EngI (Supplemental Fig. S3 and S4). T. aurantiacus EngI is a hyperthermophilic enzyme with a Tm of about 81 °C; meanwhile, the reported Tm value for T. reesei EgII is 69.5 °C (Lee et al. 2002). CelD and EglA also exhibit one disulfide bridge located in the N-terminal loop, but there is no thermal stability data yet available for these enzymes.
Structure of the CelD-cellotriose complex
Attempts to crystallize the CelD active catalytic domain with cellobiose or cellotriose substrates were unsuccessful using both soaking and co-crystallization approaches. We additionally attempted to crystallize CelD with its natural dockerin domains, which would have represented the first full structure of a fungal dockerin-fused enzyme but failed to get high-quality crystals. After introducing the inactivating E154A mutation to the active site of a single CelD catalytic domain, we were able to obtain high-quality crystals of the E154A-cellotriose complex. As described above, we did not observe substantial conformational changes between the apo-enzyme structure and the mutant structure with the bound ligand. Thus, the catalytic residues in the apo-CelD structure are likely to be in a catalytically competent position and superposition of the active enzyme structure and the mutant structure with the bound ligand provides sound structural information about the substrate binding and mechanism of the enzyme catalysis. Like other GH5 enzymes, CelD contains two invariant catalytic glutamate residues, the acid/base Glu154 and the nucleophile Glu278. Superposition of two structures solved in this work confirms that the carboxylate OE1 and OE2 oxygens of the catalytic acid/base glutamate point towards the O1 atom of the − 1 glucopyranose unit at 1.5 Å and 1.7 Å, respectively, and the carboxylate oxygen of the complementary nucleophile glutamate forms a hydrogen bond with the anomeric C1 carbon of the same saccharide unit at 3.1 Å (Fig. 2a). Meanwhile, the nucleophile Glu278 is sandwiched between two conserved Arg66 and Tyr231 residues which form hydrogen bonds to the carboxylate oxygens and appear to serve a supportive role to stabilize this Glu residue throughout catalysis as observed for other GH5 enzymes (Fig. 2c) (Dominguez et al. 1995; Tseng et al. 2011).
Substrate binding area of the CelD cellulase. a Zoomed in view of the active site with bound cellotriose molecule (gray stick) surrounded by 8 water molecules (red spheres) and several catalytic residues (yellow stick). The hydrogen bonds are shown as black dotted lines, and the locations of the substrate binding sites (the − 3, − 2, and − 1) are labeled. b Ribbon representation of the CelD-ligand complex (cyan). The positions of the conserved aromatic residues involved in substrate binding are shown in yellow stick; the cellotriose ligand is shown as gray spheres. c The same as in b except that the positions of the conserved and spatially conserved residues associated with cellulolytic activity are shown in yellow stick. d Total view of the protein surface (in the same color as in b and c) showing the wide CelD active side cleft with the modeled hepta-oligosaccharide substrate is presented. The hepta-oligosaccharide is shown as spheres. The modeled saccharide units from the − 1 subsite to the + 4 subsite are shown as green spheres, and experimentally observed carbohydrate units at the − 3 and − 2 subsites are shown as gray spheres. The scissile glycoside bond is between the − 1 and + 1 sites. The positions of conserved aromatic residues served to mediate carbohydrate binding in the encounter complex are indicated in yellow color
We found 8 ordered water molecules making multiple hydrogen bonds with both the protein moiety and the cellotriose molecule in the ligand-bound structure; two of them are located near the anomeric carbon of the − 1 saccharide moiety (Fig. 2a). One of these water molecules may participate in the catalytic mechanism of the CelD as a nucleophilic attack on the glycosyl-enzyme intermediate (Davies et al. 1998).
Holo CelD E154A-Cellotriose structure reveals key substrate recognition sites
Structural comparison of the CelD cellulase with other known GH5_4 family enzymes suggests that a cleft containing the enzyme active site may provide a favorable platform for binding oligomers up to seven sugar units within the − 3 to + 4 subsites. This cleft presents a flat platform for interacting with negative sugar subsites and a U-shaped groove that appears to orient the substrate for catalysis and provide interaction sites for positive sugar subsites. The CelD active site groove is lined with aromatic residues, Trp44, Trp164, Tyr231, Tyr234, Trp258, and Trp311, and all these positions except Trp258 are strictly conserved among the GH5_4 enzymes we analyzed (Supplemental Fig. S1). Trp164 and Tyr234 are proximal to the + 2 and + 3 subsites and Trp44 and Tyr231 are close to the − 3 and − 1 binding sites, respectively (Fig. 2b, d). Trp258 is positioned to interact with a linear polysaccharide chain at the + 4 position.
The overall shape of the CelD polysaccharide binding site appears optimal for strictly linear polysaccharides, but an indent in the enzyme surface into which the C6 atom of the − 2 backbone glucose points (Fig. 2c) suggests this enzyme may accommodate a substrate like xyloglucan, which contains a glucose backbone with branched xylose and galactose sugars. Structural and biochemical analysis of several GH5_4 enzymes suggests some structural and sequence signatures indicative of enzyme activity on branched polysaccharide substrates include aromatic and polar side chains within the loops between β3 and α4, β4 and α5, and β8 and β9 (Glasgow et al. 2020). Aligning the CelD structure to the xyloglucan oligosaccharide-bound structures 2JEQ (Gloster et al. 2007) and 4W88 (dos Santos et al. 2015) suggests CelD can spatially accommodate xyloglucan, with potential favorable hydrogen bonding interactions with the − 3 xylose branch at E317 or E319; the − 2 xylose and galactose involving H111, R156, and E26; the + 2 galactose at E163; and the + 2 xylose at E321 (Fig. 3). However, CelD does not appear to have any aromatic side chains poised to interact with branched sugars that would suggest this enzyme is specific for branched polysaccharides.
Potential contacts between xyloglucan branched sugars and CelD modeled by alignment with 4W88 and 2JEQ with annotated CelD residues interacting with negative substrate subsites (a) and positive substrate subsites (b). CelD is shown both as a gray surface and green cartoon representation to visualize both atomic contacts and the fit of xyloglucan to the active site
Characterization CelD substrate specificity and enzyme kinetics
We tested the P. finnis CelD catalytic domain against several soluble and insoluble substrates to determine the catalytic domain’s specificity for cellulose vs hemicellulose polysaccharides, its endoglucanase vs β-glucosidase activity, and its preference for β-1,4 vs other α linkages. As indicated by structural analysis, CelD hydrolyzes the linear cellulose analog carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and the branched polysaccharides β-D-glucan (mixed linkage glucan or MLG) and xyloglucan, but displays very poor activity against insoluble, phosphoric acid swollen cellulose (PASC) (Table 2), supporting CelD’s characterization as a broad-spectrum endoglucanase. Time course measurements are provided in Supplemental Fig. S5.
The enzyme showed no activity against xylan or arabinogalactan or β-glucosidase activity (data not shown). Relative positions of key pyranose binding residue W44, which interacts with the substrate at the − 3 position, and the catalytic E154 position corroborate the lack of β-glucosidase activity (Fig. 2a, b).
We measured kinetic rate parameters for the CelD catalytic domain acting on the soluble cellulase substrate carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) at 39 °C and pH 5.5, the physiological temperature for anaerobic fungi and acidic pH typical of endoglucanase enzymes. Our measured kcat and Km for P. finnis CelD are comparable to those of other fungal endoglucanases but well below those of thermophilic bacterial cellulose degraders like Thermotoga maritima and Clostridium thermocellum (Table 3).
CelD cellulase kinetics are unperturbed by the addition of N- and C-Terminal dockerins
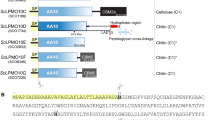
A key question we sought to answer was whether CelD’s natural C-terminal dockerin domains conferred any catalytic benefit and whether this enzyme could tolerate non-natural dockerin domain fusions, such as one on its N-terminus. True modularity in the construction of catalytic domain–dockerin domain chimeras is highly desirable in building synthetic enzyme systems for applications like lignocellulose valorization. Our results show that CelD’s intrinsic kinetics are unchanged when dockerin domains are fused to the N- or C-terminus of this protein, indicating the natural CelD protein is highly modular and suggesting that the CelD catalytic domain can accommodate other fusion partners (Fig. 4).
Addition of N- and C-terminal fungal dockerin domains does not affect enzyme kinetics. (a) Kinetic parameters for hydrolysis of carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) were fit from initial rate data for the GH5 catalytic domain alone (91–452, red circles) as well as the GH5 with two C-terminal dockerins (91–536, green crosses) and the GH5 with N- and C-terminal dockerins (1–536, blue stars). (b) Initial rates for each enzyme at each substrate concentration were taken from time course measurements of released reducing sugar vs time, as quantified by the DNS assay. Fit parameter uncertainties are reported ± one standard deviation from nonlinear least squares fit. (c) A diagram showing the relative position of dockerins (abbreviated “doc” for short) relative to the GH5 for tested variants
Discussion
This crystal structure represents one of only a few solved structures of anaerobic fungal enzymes and is the second GH5 from Neocallimastigomycota to be solved (Tseng et al. 2011), presenting a reference by which to compare other GH5 endoglucanases from Neocallimastigomycetes (of which there are 637 unique, annotated sequences, www.mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov), towards identifying GH5 enzymes with desirable properties for industrial bioprocessing. CelD displayed endoglucanase activity against β-1,4-glycosidic bonds in CMC, xyloglucan, and β-D-glucan, and measured kinetic parameters on CMC enabled direct comparison of CelD to other endoglucanases.
Structural features that differentiated the P. finnis catalytic domain from other GH5 enzymes were longer loops around the substrate binding site (between βI/α1, βIV/α4, α5/βVI, and βVIII/α8) and possessing only one disulfide bridge instead of four present in GH5’s from other fungi (Lee et al. 2002, 2011). Further biochemical studies are needed to investigate the contribution of these loop regions and missing disulfide bonds to enzyme–substrate specificity and thermal stability.
The effect of fungal dockerin domains on the activity of gut fungal enzymes has previously been evaluated in only a few cases with conflicting results. While no change in activity was observed upon removal of the native C-terminal dockerin from a Piromyces mannanase at 39 °C (Fanutti et al. 1995), Huang and co-authors (2005) found removal of the native C-terminal double dockerin from Neocallimastix frontalis Xyn11A and Xyn11B to increase specific xylanase activity at all temperatures (39–70 °C). We have also found the addition of the C-terminal double dockerin from P. finnis CelD to T. maritima enzymes Cel5A and XynA to cause insignificant changes to specific enzyme activity at 80 °C (Gilmore et al. 2020).
This lack of consistency suggests the effect of fungal dockerin fusions on catalytic domain activity is context dependent, at least when evaluating enzymes recombinantly produced in E. coli. Unfortunately, our attempts to crystallize a construct containing both the catalytic and dockerin domains were unsuccessful, and a structure of a complete, dockerin-containing enzyme from an anaerobic fungus with which to definitively address these questions remains unsolved. Negative effects of dockerin domains on enzymatic activity have previously been tied to a reduction in protein thermostability and melting temperature (Huang et al. 2005). However, it is difficult to decouple potential intrinsic instability of the dockerin domain from the possibility that these domains, which are known to possess several disulfide bonds (Raghothama et al. 2001; Nagy et al. 2007), are misfolded when produced recombinantly in E. coli. More efficient disulfide bond formation was shown to have a dramatic impact on the measured enzymatic activity of a non-dockerin-containing Neocallimastix patriciarum xylanase, which the authors evaluated by producing the same enzyme in E. coli and Pichia pastoris (Cheng et al. 2014). Ongoing work investigating dockerin-containing enzymes from their native system will build on these previous results to address this outstanding question of how dockerin domains contribute to enzyme activity and stability.
Anaerobic fungi deploy an array of CAZymes that act in solution and as members of multi-enzyme cellulosomes to rapidly hydrolyze lignocellulose. However, very few enzymes in the vast CAZyme repertoire encoded by anaerobic fungal genomes have been functionally characterized, and as a result, we have little biochemical understanding of how anaerobic fungi excel at degrading biomass, which presents a challenge towards converting anaerobic fungal enzyme systems into useful biotechnologies. By characterizing the atomic-resolution structure and kinetic properties of the P. finnis CelD GH5 endoglucanase, we provide additional insight towards gaining biochemical understanding of anaerobic fungal enzyme systems. The kinetic data indicate the domains of CelD are highly modular and can likely be augmented to functionalize this GH5 enzyme with other domains, while the structure presents a platform for rational engineering of this enzyme for higher thermostability or activity criteria.
Data availability
Crystallographic data for structures reported in this article were deposited to the Protein Data Bank (PDB codes 8GHX and 8GHY for the apo and the E154A-mutant complex, respectively). All other relevant data generated and analyzed in this study are included in this article or the supplementary information. Plasmids encoding the enzyme constructs studied in this work are available upon reasonable request.
References
Adams JJ, Pal G, Jia Z, Smith SP (2006) Mechanism of bacterial cell-surface attachment revealed by the structure of cellulosomal type II cohesin-dockerin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:305–310. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507109103
Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung L-W, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH (2010) PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66:213–221. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444909052925
Akin DE, Borneman WS, Lyon CE (1990) Degradation of leaf blades and stems by monocentric and polycentric isolates of ruminal fungi. Anim Feed Sci Technol 31:205–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-8401(90)90125-R
Artzi L, Bayer EA, Moraïs S (2017) Cellulosomes: bacterial nanomachines for dismantling plant polysaccharides. Nat Rev Microbiol 15:83–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.164
Boudet AM, Kajita S, Grima-Pettenati J, Goffner D (2003) Lignins and lignocellulosics: a better control of synthesis for new and improved uses. Trends Plant Sci 8:576–581. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2003.10.001
Brunecky R, Alahuhta M, Xu Q, Donohoe BS, Crowley MF, Kataeva IA, Yang S-J, Resch MG, Adams MWW, Lunin VV, Himmel ME, Bomble YJ (2013) Revealing Nature’s cellulase diversity: the digestion mechanism of Caldicellulosiruptor bescii CelA. Science 342:1513–1516. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1244273
Carvalho AL, Dias FMV, Prates JAM, Nagy T, Gilbert HJ, Davies GJ, Ferreira LMA, Romão MJ, Fontes CMGA (2003) Cellulosome assembly revealed by the crystal structure of the cohesin–dockerin complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:13809–13814. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1936124100
Chen VB, Arendall WB III, Headd JJ, Keedy DA, Immormino RM, Kapral GJ, Murray LW, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (2010) MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallografica D66:12–21
Cheng Y-S, Ko T-P, Huang J-W, Wu T-H, Lin C-Y, Lua W, Li Q, Ma Y, Huang C-H, Wang AH-J, Liu J-R, Guo R-T (2012) Enhanced activity of Thermotoga maritima cellulase 12A by mutating a unique surface loop. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 95:661–669
Cheng Y-S, Chen C-C, Huang C-H, Ko T-P, Luo W, Huang J-W, Liu J-R, Guo R-T (2014) Structural analysis of a glycoside hydrolase family 11 xylanase from Neocallimastix patriciarum: insights into the molecular basis of a thermophilic enzyme. J Biol Chem 289:11020–11028. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.550905
Cragg SM, Beckham GT, Bruce NC, Bugg TD, Distel DL, Dupree P, Etxabe AG, Goodell BS, Jellison J, McGeehan JE, McQueen-Mason SJ, Schnorr K, Walton PH, Watts JE, Zimmer M (2015) Lignocellulose degradation mechanisms across the Tree of Life. Curr Opin Chem Biol 29:108–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.10.018
Davies GJ, Mackenzie L, Varrot A, Dauter M, Brzozowski AM, Schülein M, Withers SG (1998) Snapshots along an enzymatic reaction coordinate: analysis of a retaining β-glycoside hydrolase. Biochemistry 37:11707–11713. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi981315i
Dijkerman R, Bhansing DCP, Op den Camp HJM, van der Drift C, Vogels GD (1997a) Degradation of structural polysaccharides by the plant cell-wall degrading enzyme system from anaerobic fungi: an application study. Enzyme Microb Technol 21:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-0229(96)00251-7
Dijkerman R, Op den Camp HJM, Van der Drift C, Vogels GD (1997b) The role of the cellulolytic high molecular mass (HMM) complex of the anaerobic fungus Piromyces sp. strain E2 in the hydrolysis of microcrystalline cellulose. Arch Microbiol 167:137–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002030050426
Dominguez R, Souchonl H, Spinelli S, Dauter Z, Wilson KS, Chauvaux S, Beguin P, Alzari PM (1995) A common protein fold and similar active site in two distinct families of β-glucanases. Nat Struct Biol 2(7):569–576. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0795-569
Dong J, Hong Y, Shao Z, Liu Z (2010) Molecular cloning, purification, and characterization of a novel, acidic, pH-stable endoglucanase from Martelella mediterranea. J Microbiol 48:393–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-010-9361-0
dos Santos CR, Cordeiro RL, Wong DWS, Murakami MT (2015) Structural basis for xyloglucan specificity and α-d-Xylp(1 → 6)-d-Glcp recognition at the −1 subsite within the GH5 family. Biochemistry 54:1930–1942. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.5b00011
Drula E, Garron M-L, Dogan S, Lombard V, Henrissat B, Terrapon N (2022) The carbohydrate-active enzyme database: functions and literature. Nucleic Acids Res 50:D571–D577. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab1045
Emsley P, Cowtan KD (2004) Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallografica D60:2126–2132
Fanutti C, Ponyi T, Black GW, Hazlewood GP, Gilbert HJ (1995) The conserved noncatalytic 40-residue sequence in cellulases and hemicellulases from anaerobic fungi functions as a protein docking domain. J Biol Chem 270:29314–29322. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.49.29314
Fontes CMGA, Gilbert HJ (2010) Cellulosomes: highly efficient nanomachines designed to deconstruct plant cell wall complex carbohydrates. Annu Rev Biochem 79:655–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-091208-085603
Forsberg Z, Sørlie M, Petrović D, Courtade G, Aachmann FL, Vaaje-Kolstad G, Bissaro B, Røhr ÅK, Eijsink VG (2019) Polysaccharide degradation by lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases. Curr Opin Struct Biol 59:54–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.02.015
Gilmore SP, Henske JK, O’Malley MA (2015) Driving biomass breakdown through engineered cellulosomes. Bioengineered 6:204–208
Gilmore SP, Lillington SP, Haitjema CH, de Groot R, O’Malley MA (2020) Designing chimeric enzymes inspired by fungal cellulosomes. Synth Syst Biotechnol 5:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2020.01.003
Glasgow EM, Kemna EI, Bingman CA, Ing N, Deng K, Bianchetti CM, Takasuka TE, Northen TR, Fox BG (2020) A structural and kinetic survey of GH5_4 endoglucanases reveals determinants of broad substrate specificity and opportunities for biomass hydrolysis. J Biol Chem 295:17752–17769. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.015328
Gloster TM, Ibatullin FM, Macauley K, Eklöf JM, Roberts S, Turkenburg JP, Bjørnvad ME, Jørgensen PL, Danielsen S, Johansen KS, Borchert TV, Wilson KS, Brumer H, Davies GJ (2007) Characterization and three-dimensional structures of two distinct bacterial xyloglucanases from families GH5 and GH12. J Biol Chem 282:19177–19189. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M700224200
Haitjema CH, Gilmore SP, Henske JK, Solomon KV, de Groot R, Kuo A, Mondo SJ, Salamov AA, LaButti K, Zhao Z, Chiniquy J, Barry K, Brewer HM, Purvine SO, Wright AT, Hainaut M, Boxma B, van Alen T, Hackstein JHP, Henrissat B, Baker SE, Grigoriev IV, O’Malley MA (2017) A parts list for fungal cellulosomes revealed by comparative genomics. Nat Microbiol 2:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.87
Hemsworth GR, Johnston EM, Davies GJ, Walton PH (2015) Lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases in biomass conversion. Trends Biotechnol 33:747–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2015.09.006
Huang Y-H, Huang C-T, Hseu R-S (2005) Effects of dockerin domains on Neocallimastix frontalis xylanases. FEMS Microbiol Lett 243:455–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsle.2005.01.008
Jenkins J, Lo Leggio L, Harris G, Pickersgill R (1995) β-glucosidase, β-galactosidase, family A cellulases, family F xylanases, and two barley glycanases form a superfamily of enzymes with 8-fold β/α architecture and with two conserved glutamates near the carboxy-terminal ends of B-strands four and seven. FEBS Lett 362:281–285
Jia X, Han Y (2019) The extracellular endo-β-1,4-xylanase with multidomain from the extreme thermophile Caldicellulosiruptor lactoaceticus is specific for insoluble xylan degradation. Biotechnol Biofuels 12:143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-019-1480-1
Kim Y, Babnigg G, Jedrzejczak R, Eschenfeldt WH, Li H, Maltseva N, Hatzos-Skintges C, Gu M, Makowska-Grzyska M, Wu R, An H, Chhor G, Joachimiak A (2011) High-throughput protein purification and quality assessment for crystallization. Methods 55:12–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2011.07.010
King BC, Donnelly MK, Bergstrom GC, Walker LP, Gibson DM (2009) An optimized microplate assay system for quantitative evaluation of plant cell wall-degrading enzyme activity of fungal culture extracts. Biotechnol Bioeng 102:1033–1044
Lankiewicz TS, Choudhary H, Gao Y, Amer B, Lillington SP, Leggieri PA, Brown JL, Swift CL, Lipzen A, Na H, Amirebrahimi M, Theodorou MK, Baidoo EEK, Barry K, Grigoriev IV, Timokhin VI, Gladden J, Singh S, Mortimer JC, Ralph J, Simmons BA, Singer SW, O’Malley MA (2023) Lignin deconstruction by anaerobic fungi. Nat Microbiol 8:596–610. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-023-01336-8
Laskowski RA, MacArthur MW, Moss DS, Thornton JM (1993) PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J Appl Crystallogr 26:283–291
Lee TM, Farrow MF, Arnold FH, Mayo SL (2002) Biochemical characterization and mode of action of a thermostable endoglucanase purified from Thermoascus aurantiacus. Arch Biochem Biophys 404:243–253
Lee TM, Farrow MF, Arnold FH, Mayo SL (2011) A structural study of Hyprocrea jecorina Cel5A. Protein Sci 20:1935–1940
Liang C, Xue Y, Fioroni M, Rodríguez-Ropero F, Zhou C, Schwaneberg U, Ma Y (2011) Cloning and characterization of a thermostable and halo-tolerant endoglucanase from Thermoanaerobacter tengcongensis MB4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:315–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2842-6
Lo Leggio L, Larsen S (2002) The 1.62 Å structure of Thermoascus aurantiacus endoglucanase: completing the structural picture of subfamilies in glycoside hydrolase family 5. FEBS Lett 523:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02954-X
Lowe SE, Theodorou MK, Trinci AP (1987) Cellulases and xylanase of an anaerobic rumen fungus grown on wheat straw, wheat straw holocellulose, cellulose, and xylan. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1216–1223. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.53.6.1216-1223.1987
McCoy A, Grosse-Kunstleve R, Adams P, Winn M, Storoni L, Read R (2007) Phaser crystallographic software. J Appl Crystallogr 40:658–674
Merzlov DA, Zorov IN, Dotsenko GS, Denisenko YuA, Rozhkova AM, Satrutdinov AD, Rubtsova EA, Kondratieva EG, Sinitsyn AP (2015) Properties of enzyme preparations and homogeneous enzymes — endoglucanases EG2 Penicillium verruculosum and LAM Myceliophthora thermophila. Biochem Mosc 80:473–482. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915040112
Morag (Morgenstern) E, Bayer EA, Lamed R (1992) Affinity digestion for the near-total recovery of purified cellulosome from Clostridium thermocellum. Enzyme Microb Technol 14:289–292
Moreira LRS, Filho EXF (2008) An overview of mannan structure and mannan-degrading enzyme systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:165–178
Moreira LRS, Filho EXF (2016) Insights into the mechanism of enzymatic hydrolysis of xylan. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:5205–5214
Mountfort DO, Asher RA (1989) Production of xylanase by the ruminal anaerobic fungus Neocallimastix frontalis. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1016–1022
Nagy T, Tunnicliffe RB, Higgins LD, Walters C, Gilbert HJ, Williamson MP (2007) Characterization of a double dockerin from the cellulosome of the anaerobic fungus Piromyces equi. J Mol Biol 373:612–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.007
Otwinowski Z, Minor W (1997) Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol 276:307–326
Pickersgill R, Harris G, Leggio LL, Mayans O, Jenkins J (1998) Superfamilies: the 4/7 superfamily of βα-barrel glycosidases and the right-handed parallel β-helix superfamily. Biochem Soc Trans 26:190–197. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0260190
Qin Y, Wei X, Song X, Qu Y (2008) Engineering endoglucanase II from Trichoderma reesei to improve the catalytic efficiency at a higher pH optimum. J Biotechnol 135:190–195
Ragauskas AJ, Williams CK, Davison BH, Britovsek G, Cairney J, Eckert CA, Frederick WJ, Hallett JP, Leak DJ, Liotta CL, Mielenz JR, Murphy R, Templer R, Tschaplinski T (2006) The path forward for biofuels and biomaterials. Science 311:484–489. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1114736
Raghothama S, Eberhardt RY, Simpson P, Wigelsworth D, White P, Hazlewood GP, Nagy T, Gilbert HJ, Williamson MP (2001) Characterization of a cellulosome dockerin domain from the anaerobic fungus Piromyces equi. Nat Struct Biol 8:775–778. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0901-775
Ren HN (2009) Cloning. Expression and Characterization of Novel Fungal Endoglucanases, Concordia University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Seppälä S, StE W, Knop D, Solomon KV, O’Malley MA (2017) The importance of sourcing enzymes from non-conventional fungi for metabolic engineering and biomass breakdown. Metab Eng 44:45–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2017.09.008
Solomon KV, Haitjema CH, Henske JK, Gilmore SP, Borges-Rivera D, Lipzen A, Brewer HM, Purvine SO, Wright AT, Theodorou MK, Grigoriev IV, Regev A, Thompson DA, O’Malley MA (2016) Early-branching gut fungi possess a large, comprehensive array of biomass-degrading enzymes. Science 351:1192–1195. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad1431
Steenbakkers PJM, Li X-L, Ximenes EA, Arts JG, Chen H, Ljungdahl LG, Op den Camp HJM (2001) Noncatalytic docking domains of cellulosomes of anaerobic fungi. J Bacteriol 183:5325–5333. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.183.18.5325-5333.2001
Trinci APJ, Davies DR, Gull K, Lawrence MI, Bonde Nielsen B, Rickers A, Theodorou MK (1994) Anaerobic fungi in herbivorous animals. Mycol Res 98:129–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(09)80178-0
Tseng C-W, Ko T-P, Guo R-T, Huang J-W, Wang H-C, Huang C-H, Cheng Y-S, Wang AH-J, Liu J-R (2011) Substrate binding of a GH5 endoglucanase from the ruminal fungus Piromyces rhizinflata. Acta Crystallogr Sect F 67:1189–1194. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309111032428
Vagin A, Teplyakov A (1997) MOLREP: an automated program for molecular replacement. J Appl Crystallogr 30:1022–1025
Wilson CA, Wood TM (1992) Studies on the cellulase of the rumen anaerobic fungus Neocallimastix frontalis, with special reference to the capacity of the enzyme to degrade crystalline cellulose. Enzyme Microb Technol 14:258–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(92)90148-H
Wood TM, Wilson CA, McCrae SI, Joblin KN (1986) A highly active extracellular cellulase from the anaerobic rumen fungus Neocallimastix frontalis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 34:37–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.1986.tb01344.x
Woodward J (1991) Synergism in cellulase systems. Bioresour Technol 36:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/0960-8524(91)90100-X
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the staff at the SBC-CAT BM-beamline of the Advanced Proton Source, Argonne National Laboratory, IL, where crystallographic data were collected. We thank Lucas Welk for help with protein purification.
Funding
The authors acknowledge funding support from the Office of Science (BER), U.S. Department of Energy (DE-SC0010352, DE-SC0020420, and DE-SC0022142), the Institute for Collaborative Biotechnologies through grants W911NF-09-D-0001 and W911NF-19-D-0001 from the U.S. Army Research Office, and the Office of Biological and Environmental Research of the U.S. Department of Energy Joint BioEnergy Institute (JBEI, http://www.jbei.org) through contract DE-AC02–05CH11231 (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory). The Structural Biology Center 19BM beamline is supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Biological and Environmental Research, under contract DE-AC02-06CH11357.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. D. designed and conducted crystallization experiments, S. P. L. and S. J. conducted activity assays of all enzyme variants and analyzed structures, J. R. cloned the protein constructs, Y. K. set up the AKTA purification system and oversaw protein purification, Y. K. and K. M. analyzed structures; A. J. and M. A. O. were responsible for oversight of the project. A. D., S. P. L., S. J., A. J., and M. A. O. wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal participants performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Alexey Dementiev and Stephen P. Lillington contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Dementiev, A., Lillington, S.P., Jin, S. et al. Structure and enzymatic characterization of CelD endoglucanase from the anaerobic fungus Piromyces finnis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 107, 5999–6011 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12684-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-023-12684-0