Abstract
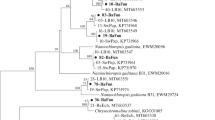
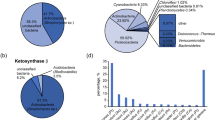
Compared with sponge-associated bacteria, the phylogenetic diversity of fungi in sponge and the association of sponge fungi remain largely unknown. Meanwhile, no detection of polyketide synthase (PKS) or non-ribosomal peptide synthase (NRPS) genes in sponge-associated fungi has been attempted. In this study, diverse and novel cultivable fungi including 10 genera (Aspergillus, Ascomycete, Fusarium, Isaria, Penicillium, Plectosphaerella, Pseudonectria, Simplicillium, Trichoderma, and Volutella) in four orders (Eurotiales, Hypocreales, Microascales, and Phyllachorales) of phylum Ascomycota were isolated from 10 species marine sponges in the South China Sea. Eurotiales and Hypocreales fungi were suggested as sponge generalists. The predominant isolates were Penicillium and Aspergillus in Eurotiales followed by Volutella in Hypocreales. Based on the conserved Beta-ketosynthase of PKS and A domain of NRPS, 15 polyketide synthases, and four non-ribosomal peptides synthesis genes, including non-reducing and reducing PKSs and hybrid PKS–NRPS, were detected in these fungal isolates. A lateral gene transfer event was indicated in the comparison between the phylogenetic diversity of 18S rRNA genes and β-ketoacyl synthase domain sequences. Some fungi, especially those with PKS or NRPS genes, showed antimicrobial activity against P. fluorescens, S. aureus and B. subtilis. It was the first time to investigate PKS and NRPS genes in sponge-associated fungi. Based on the detected antibiotics biosynthesis-related PKS and NRPS genes and antimicrobial activity, the potential ecological role of sponge-associated fungi in the chemical defense for sponge host was suggested. This study extended our knowledge of sponge-associated fungal phylogenetic diversity and their potential roles in the chemical defense.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amagata T, Morinaka BI, Amagata A, Tenney K, Valeriote FA, Lobkovsky E, Clardy J, Crews PA (2006) Chemical study of cyclic depsipeptides produced by a sponge-derived fungus. J Nat Prod 69:1560–1565
Amnuaykanjanasin A, Punya J, Paungmoung P, Rungrod A, Tachaleat A, Pongpattanakitshote S, Cheevadhanarak S, Tanticharoen M (2005) Diversity of type I polyketide synthase genes in the wood-decay fungus Xylaria sp. BCC 1067. FEMS Microbiol Lett 251:125–136
Baker P, Kennedy J, Dobson A, Marchesi J (2009) Phylogenetic diversity and antimicrobial activities of fungi associated with Haliclona simulans isolated from Irish coastal waters. Mar Biotechnol 11:540–547
Blunt JW, Copp BR, Hu WP, Munro MHG, Northcote PT, Prinsep MR (2009) Marine natural products. Nat Prod Rep 26:170–244
Borneman J, Hartin RJ (2000) PCR primers that amplify fungal rRNA genes from environmental samples. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4356–4360
Bugni TS, Ireland CM (2004) Marine-derived fungi: a chemically and biologically diverse group of microorganisms. Nat Prod Rep 21:143–163
Ding B, Yin Y, Zhang FL, Li Z (2010) Recovery and phylogenetic diversity of culturable fungi associated with marine sponges Clathrina luteoculcitella and Holoxea sp. in the South China Sea. Mar Biotechnol. doi:10.1007/s10126-010-9333-8
Gao Z, Li B, Zheng C, Wang G (2008) Molecular detection of fungal communities in the Hawaiian marine sponges Suberites zeteki and Mycale armata. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6091–6101
Gesner S, Cohen N, Ilan M, Yarden O, Carmeli S (2005) Pandangolide 1a, a metabolite of the sponge-associated fungus Cladosporium sp., and the absolute stereochemistry of pandangolide 1 and iso-Cladospolide B. J Nat Prod 68:1350–1353
Grunig C, Brunner P, Du A, Sieber T (2007) Suitability of methods for species recognition in the Phialocephala fortinii-Acephala applanata species complex using DNA analysis. Fungal Genet Biol 44:773–788
Hentschel U, Usher KM, Taylor MW (2006) Marine sponges as microbial fermenters. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 55:167–77
Hochmuth T, Piel J (2009) Polyketide synthases of bacterial symbionts in sponges-Evolution-based applications in natural products research. Phytochemistry 70:1841–1849
Höller U, Wright AD, Matthee GF, Konig GM, Draeger S, Aust H, Schulz B (2000) Fungi from marine sponges: diversity, biological activity and secondary metabolites. Mycologia 104:1354–1365
Hyde KD, Sarma VV, Jones EBG (2000) Morphology and taxonomy of higher marine fungi. In: Hyde KD, Pointing SB (eds) Marine mycology: a practical approach. Fungal Diversity Press, Hong Kong, pp 172–204
Jebaraj CS, Raghukumar C, Behnke A, Stoeck T (2010) Fungal diversity in oxygen-depleted regions of the Arabian Sea revealed by targeted environmental sequencing combined with cultivation. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 71:399–412
Jiang S, Sun W, Chen M, Dai S, Zhang L, Liu Y, Lee K, Li X (2007) Diversity of culturable actinobacteria isolated from marine sponge Haliclona sp. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 92:405–416
Kennedy J, Codling CE, Jones BV, Dobson ADW, Marchesi JR (2008) Diversity of microbes associated with the marine sponge, Haliclona simulans, isolated from Irish waters and identification of polyketide synthase genes from the sponge metagenome. Environ Microbiol 10:1888–1902
Kim T, Fuerst J (2006) Diversity of polyketide synthase genes from bacteria associated with the marine sponge Pseudoceratina clavata: culture-dependent and culture-independent approaches. Environ Microbiol 8:1460–1470
Kohlmeyer J, Kohlmeyer E (1979) Marine Mycology: The Higher Fungi. Academic, London
König G, Kehraus S, Seibert S, Abdel-Lateff A, Müller D (2006) Natural products from marine organisms and their associated microbes. Chembiochem 7:229–238
Li Q, Wang G (2009) Diversity of fungal isolates from three Hawaiian marine sponges. Microbiol Res 164:233–241
Li ZY, Liu Y (2006) Marine sponge Craniella austrialiensis-associated bacterial diversity revelation based on 16S rDNA library and biologically active actinomycetes screening, phylogenetic analysis. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:410–416
Liu WC, Li CQ, Zhu P, Yan JL, Cehng KD (2010) Phylogenetic diversity of culturable fungi associated with two marine sponges: Haliclona simulans and Gelliodes carnosa, collected from the Hainan Island coastal waters of the South China Sea. Fungal Divers 42:1–15
Lopez JV (2003) Naturally mosaic operons for secondary metabolite biosynthesis: variability and putative horizontal transfer of discrete catalytic domains of the epothilone polyketide synthase locus. Mol Gen Genomics 270:420–431
Maldonado M, Cortadellas N, Trillas MI, Ruetzler K (2005) Endosymbiotic yeast maternally transmitted in a marine sponge. Biol Bull 209:94–106
Müler WEG, Brümmer F, Batel R, Müler IM, Schröder HC (2003) Molecular biodiversity. Case study: Porifera (sponges). Naturwissenschaften 90:103–120
Nicholson T, Rudd B, Dawson M, Lazarus C, Simpson T, Cox R (2001) Design and utility of oligonucleotide gene probes for fungal polyketide synthases. Chem Biol 8:157–178
Nierman WC, Pain A, Anderson MJ, Wortman JR, Kim HS, Arroyo J, Berriman M, Abe K, Archer DB, Bermejo C et al (2005) Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 438:1151–1156
Piel J (2004) Metabolites from symbiotic bacteria. Nat Prod Rep 21:519–538
Piel J, Hui D, Fusetani N, Matsunaga S (2004) Targeting modular polyketide synthases with iteratively acting acyltransferases from metagenomes of uncultured bacterial consortia. Environ Microbiol 6:921–927
Pivkin M, Aleshko S, Krasokhin V, Khudyakova Y (2006) Fungal assemblages associated with sponges of the southern coast of Sakhalin Island. Russ J Mar Biol 32:207–213
Pruesse E, Quast C, Knittel K, Fuchs B, Ludwig W, Peplies J, Glockner F (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucleic Acids Res 35:7188–7196
Raghukumar C (2008) Marine fungal biotechnology: an ecological perspective. Fungal Divers 31:19–35
Rot C, Goldfarb I, Ilan M, Huchon D (2006) Putative cross-kingdom horizontal gene transfer in sponge (Porifera) mitochondria. BMC Evol Biol 6:71
Saleem M, Ali SM, Hussain S, Jabbar A, Ashraf M, Lee YS (2007) Marine natural products of fungal origin. Nat Prod Rep 24:1142–1152
Schirmer A, Gadkari R, Reeves C, Ibrahim F, Delong E, Hutchinson C (2005) Metagenomic analysis reveals diverse polyketide synthase gene clusters in microorganisms associated with the marine sponge Discodermia dissoluta. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4840–4849
Schmitt I, Lumbsch HT (2009) Ancient horizontal gene transfer from bacteria enhances biosynthetic capabilities of fungi. PLoS ONE 4:e4437
Siegl A, Hentschel U (2010) PKS and NRPS gene clusters from microbial symbiont cells of marine sponges by whole genome amplification. Environ Microbiol Rep 2:507–513
Slightom JL, Metzger BP, Luu HT, Elhammer AP (2009) Cloning and molecular characterization of the gene encoding the aureobasidin A biosynthesis complex in Aureobasidium pullulans BP-1938. Gene 431:67–79
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Taylor J, Jacobson D, Kroken S, Kasuga T, Geiser D, Hibbet D, Fisher M (2000) Phylogenetic species recognition and species concepts in fungi. Fungal Genet Biol 31:21–32
Taylor MW, Hill RT, Piel J, Thacker RW, Hentschel U (2007) Soaking it up: the complex lives of marine sponges and their microbial associates. ISME J 1:187–190
Taylor MW, Radax R, Steger D, Wagner M (2007) Sponge-associated microorganisms: evolution, ecology, and biotechnological potential. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 71:295–347
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL-X windows interface:flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Van Den Berg M, Albang R, Albermann K, Badger JH, Daran J, Driessen AJM, Garcia-Estrada C, Fedorova ND, Harris DM, Heijne WHM et al (2008) Genome sequencing and analysis of the filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. Nat Biotechnol 26:1161–1168
Wang G, Li Q, Zhu P (2008) Phylogenetic diversity of culturable fungi associated with the Hawaiian sponges Suberites zeteki and Gelliodes fibrosa. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 93:163–174
Wu Z, Tsumura Y, Blomquist G, Wang X (2003) 18S rRNA gene variation among common airborne fungi, and development of specific oligonucleotide probes for the detection of fungal isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:5389–5397
Zhang W, Li Z, Miao X, Zhang F (2009) The screening of antimicrobial bacteria with diverse novel non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) genes from South China Sea sponges. Mar Biotechnol 11:346–355
Zhang W, Zhang FL, Li ZY, Miao XL, Meng QP, Zhang XS (2009) Investigation of sponge-associated cultivable bacteria with polyketide synthase genes and antimicrobial activity in the South China Sea. J Appl Microbiol 107:567–575
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the High-Tech Research and Development Program of China (2011AA09070203), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (41076077, 30821005). The authors are grateful for the supply of sponges by Prof. Houwen Lin at Second Military Medical University, P. R. China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, K., Zhang, X., Zhang, F. et al. Phylogenetically Diverse Cultivable Fungal Community and Polyketide Synthase (PKS), Non-ribosomal Peptide Synthase (NRPS) Genes Associated with the South China Sea Sponges. Microb Ecol 62, 644–654 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9859-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-011-9859-y