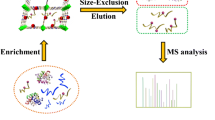
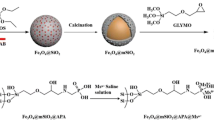
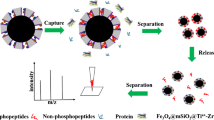
Abstract
Saliva contains various proteins, particularly abundant are phosphoproteins, that may be related to disease occurrences and that play significant roles in a biological system. Thus, medical diagnostics will benefit tremendously if disease-related protein biomarkers are discovered from saliva. In this paper, we propose and demonstrate an approach using functional zinc oxide coated iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4@ZnO MNPs) as affinity probes to selectively enrich phosphoproteins from complex saliva samples and as microwave absorbers to assist the enrichment and subsequent tryptic digestion of trapped proteins under microwave heating. The target species trapped by MNPs were characterized by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI MS) combined with protein database search. Entire analysis time was shortened to less than 20 min. The detection limit of this approach for a monophosphopeptide was as low as 250 pM (10 μL).

Fe3O4@ZnO MNPs are successfully used to assist enrichment and enzymatic digestion of phosphoproteins from saliva, allowing analysis of the phosphoproteins by MALDI MS






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huq NL, Cross KJ, Ung M, Myroforidis H, Veith PD, Chen D, Stanton D, He H, Ward BR, Reynolds EC (2007) Int J Pept Res Ther 13:547–564
Opiteck GJ, Scheffler JE (2004) Expert Rev Proteomics 1:57–66
Yu LR, Issaq HJ, Veenstra TD (2007) Proteom Clin Appl 1:1042–1057
Millea KM, Krull IS, Chakraborty AB, Gebler JC, Berger SJ (2007) Proteomics 1774:97–906
Espina V, Mueller C, Edmiston K, Sciro M, Petricoin EF, Liotta LA (2009) Proteom Clin Appl 3:874–882
Lee HJ, Kang MJ, Lee EY, Cho SY, Kim H, Paik YK (2008) Proteomics 8:3371–3381
Riener MO, Stenner F, Liewen H, Soll C, Breitenstein S, Pestalozzi BC, Samaras P, Probst-Hensch N, Hellerbrand C, Mullhaupt B, Clavien PA, Bahra M, Neuhaus P, Wild P, Fritzsche F, Moch H, Jochum W, Kristiansen G (2009) Hepatology 49:1602–1609
Helmerhorst EJ, Oppenheim FG (2007) J Dent Res 86:680–693
Pinkse MWH, Uitto PM, Hilhorst MJ, Ooms B, Heck AJR (2004) Anal Chem 76:3935–3943
Kokubu M, Ishihama Y, Sato T, Nagasu T, Oda Y (2005) Anal Chem 77:5144–5154
Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2005) Anal Chem 77:5912–5919
Liang S-S, Makamba H, Huang S-Y, Chen S-H (2006) J Chromatogr A 1116:38–45
Rinalducci S, Larsen MR, Mohammed S, Zolla L (2006) J Proteome Res 5:973–982
Larsen MR, Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P, Jorgensen TJD (2005) Proteomics 4:873–886
Sano A, Nakamura H (2004) Anal Sci 20:565–566
Lo C-Y, Chen W-Y, Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2007) J Proteome Res 6:887–893
Kweon HK, Hakansson K (2006) Anal Chem 78:1743–1749
Chen C-T, Chen W-Y, Tsai P-J, Chien K-Y, Yu J-S, Chen Y-C (2007) J Proteome Res 6:316–325
Lin H-Y, Chen W-Y, Chen Y-C (2009) J Biomed Nanotechnol 5:215–223
Ficarro SB, Parikh JR, Blank NC, Marto JA (2008) Anal Chem 80:4606–4613
Lin H-Y, Chen W-Y, Chen Y-C (2009) Anal Bioanal Chem 394:2129–2136
Ojida A, Inoue M, Mito-oka Y, Hamachi I (2003) J Am Chem Soc 125:10184–10185
Ojida A, Inoue M, Tsutsumi H, Sada K, Hamachi I (2006) J Am Chem Soc 128:2052–2058
Chen W-Y, Chen Y-C (2007) Anal Chem 79:8061–8066
Chen W-Y, Chen Y-C (2007) Anal Chem 79:2394–2401
Xia H-L, Tang F-Q (2003) J Phys Chem B 107:9175–9178
Zhong Q, Matijević E (1996) J Mater Chem 6:443–447
Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2008) J Mass Spectrom 43:538–7541
Bieber AL, Tubbs KA, Nelson RW (2004) Mol Cell Proteomics 3:266–272
Acknowledgements
We thank the National Science Council (NSC) of Taiwan for supporting this work financially. We also thank Tsung-Yi Chen and Ju-Yu Lin for their assistance in preparing the scheme and figures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 6828 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, WY., Chen, YC. Functional Fe3O4@ZnO magnetic nanoparticle-assisted enrichment and enzymatic digestion of phosphoproteins from saliva. Anal Bioanal Chem 398, 2049–2057 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4174-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-4174-x