Abstract
A zirconium-organic framework was modified with titanium(IV) ions to obtain a modified framework that is shown to be a viable sorbent for selective capture of phosphopeptides. This dual-metal affinity probe exhibits 0.1 fM limits of detection and excellent size-exclusion effect (the mass ratio of β-casein digests/BSA/intact β-casein is 1:1000:1000). This is attributed to abundant Ti(IV) and Zr(IV) coordination sites and high porosity. The performance of the sorbent for extracting endogenous phosphopeptides from human serum and saliva was investigated. Especially, 105 endogenous phosphopeptides from saliva were captured specifically. In addition, the amino acid frequency of the enriched phosphopeptides was analyzed. Conservation of sequence around the identified phosphorylated sites from saliva confirmed that phosphorylation took place in the proline-directed motifs.

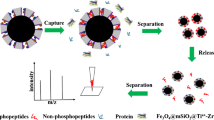
Schematic representation of a method for the specific enrichment of phosphopeptides by a modified metal-organic framework. Following size-exclusion elution, the phosphopeptides are quantified by mass spectrometry.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Humphrey SJ, Azimifar SB, Mann M (2015) High-throughput phosphoproteomics reveals in vivo insulin signaling dynamics. Nat Biotechnol 33(9):990–995. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3327
Liu SQ, Cai X, Wu JX, Cong Q, Chen X, Li T, Du FH, Ren JY, Wu YT, Grishin NV, Chen ZJJ (2015) Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science 347(6227):aaa2630. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa2630
Olsen JV, Mann M (2013) Status of large-scale analysis of post-translational modifications by mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 12(12):3444–3452. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.O113.034181
Zhou HJ, Ye ML, Dong J, Corradini E, Cristobal A, Heck AJR, Zou HF, Mohammed S (2013) Robust phosphoproteome enrichment using monodisperse microsphere-based immobilized titanium (IV) ion affinity chromatography. Nat Protoc 8(3):461–480. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2013.010
Hong YY, Zhan QL, Zheng Y, Pu CL, Zhao HL, Lan MB (2019) Hydrophilic phytic acid-functionalized magnetic dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres with immobilized Ti4+: a dual-purpose affinity material for highly efficient enrichment of glycopeptides/phosphopeptides. Talanta 197:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.01.005
Yao YT, Wang Y, Wang SJ, Liu XY, Liu Z, Li YA, Fang Z, Mao JW, Zheng Y, Ye ML (2019) One-step SH2 superbinder-based approach for sensitive analysis of tyrosine phosphoproteome. J Proteome Res 18(4):1870–1879. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.9b00045
Tan SY, Wang JD, Han Q, Liang QL, Ding MY (2018) A porous graphene sorbent coated with titanium(IV)-functionalized polydopamine for selective lab-in-syringe extraction of phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185(7):316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2846-y
Jiang DD, Li XQ, Lv XJ, Jia Q (2018) A magnetic hydrazine-functionalized dendrimer embedded with TiO2 as a novel affinity probe for the selective enrichment of low-abundance phosphopeptides from biological samples. Talanta 185:461–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.04.006
Tseng HC, Ovaa H, Wei NJC, Ploegh H, Tsai LH (2005) Phosphoproteomic analysis with a solid-phase capture-release-tag approach. Chem Biol 12(7):769–777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2005.05.012
Dong MM, Ye ML, Cheng K, Song CX, Pan YB, Wang CL, Bian YY, Zou HF (2012) Depletion of acidic phosphopeptides by SAX to improve the coverage for the detection of basophilic kinase substrates. J Proteome Res 11(9):4673–4681. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr300503z
Peng JX, Niu H, Zhang HY, Yao YT, Zhao XY, Zhou XY, Wan LH, Kang XH, Wu RA (2018) Highly specific enrichment of multi-phosphopeptides by the diphosphorylated fructose-modified dual-metal-centered zirconium-organic framework. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(38):32613–32621. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b11138
Chen YJ, Xiong ZC, Peng L, Gan YY, Zhao YM, Shen J, Qian JH, Zhang LY, Zhang WB (2015) Facile preparation of core-shell magnetic metal organic framework nanoparticles for the selective capture of phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(30):16338–16347. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03335
Gao CH, Bai J, He YT, Zheng Q, Ma WD, Lei ZX, Zhang MY, Wu J, Fu FF, Lin Z (2019) Postsynthetic functionalization of Zr4+-immobilized core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic frameworks for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(14):13735–13741. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b03330
Jayasunder KB, Iliuk AB, Nguyen A, Higgins R, Geahlen RL, Tao WA (2014) Global phosphoproteomics of activated B cells using complementary metal ion functionalized soluble nanopolymers. Anal Chem 86(13):6363–6371. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac500599r
Jiang JB, Sun XN, She XJ, Li JJ, Li Y, Deng CH, Duan GL (2018) Magnetic microspheres modified with Ti(IV) and Nb(V) for enrichment of phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185(6):309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2837-z
Liu QJ, Sun NR, Gao MX, Deng CH (2018) Magnetic binary metal-organic framework as a novel affinity probe for highly selective capture of endogenous phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(3):4382–4389. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00023
Luo B, Yang MG, Jiang PP, Lan F, Wu Y (2018) Multi-affinity sites of magnetic guanidyl-functionalized metal-organic framework nanospheres for efficient enrichment of global phosphopeptides. Nanoscale 10(18):8391–8396. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr01914b
Peng JX, Zhang HY, Li X, Liu SJ, Zhao XY, Wu J, Kang XH, Qin HQ, Pan ZF, Wu RA (2016) Dual-metal centered zirconium-organic framework: a metal-affinity probe for highly specific interaction with phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(51):35012–35020. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12630
Liu GP, Chernikova V, Liu Y, Zhang K, Belmabkhout Y, Shekhah O, Zhang C, Yi SL, Eddaoudi M, Koros WJ (2018) Mixed matrix formulations with MOF molecular sieving for key energy-intensive separations. Nat Mater 17(3):283–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-017-0013-1
Islamoglu T, Ortuno MA, Proussaloglou E, Howarth AJ, Vermeulen NA, Atilgan A, Asiri AM, Cramer CJ, Farha OK (2018) Presence versus proximity: the role of pendant amines in the catalytic hydrolysis of a nerve agent simulant. Angew Chem Int Ed 57(7):1949–1953. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201712645
Xu XY, Lian X, Hao JN, Zhang C, Yan B (2017) A double-stimuli-responsive fluorescent center for monitoring of food spoilage based on dye covalently modified eumofs: from sensory hydrogels to logic devices. Adv Mater 29(37):1702298. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201702298
Anik Ü, Timur S, Dursun Z (2019) Metal organic frameworks in electrochemical and optical sensing platforms: a review. Microchim Acta 186(3):196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3321-0
Feng L, Yuan S, Zhang LL, Tan K, Li JL, Kirchon A, Liu LM, Zhang P, Han Y, Chabal YJ, Zhou HC (2018) Creating hierarchical pores by controlled linker thermolysis in multivariate metal-organic frameworks. J Am Chem Soc 140(6):2363–2372. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b12916
Yang XQ, Xia Y (2016) Urea-modified metal-organic framework of type MIL-101(Cr) for the preconcentration of phosphorylated peptides. Microchim Acta 183(7):2235–2240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1860-1
Li LJ, Tang SF, Wang C, Lv XX, Jiang M, Wu HZ, Zhao XB (2014) High gas storage capacities and stepwise adsorption in a UiO type metal-organic framework incorporating Lewis basic bipyridyl sites. Chem Commun 50(18):2304–2307. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc48275h
Dan-Hardi M, Serre C, Frot T, Rozes L, Maurin G, Sanchez C, Ferey G (2009) A new photoactive crystalline highly porous titanium(IV) dicarboxylate. J Am Chem Soc 131(31):10857–10859. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja903726m
Zhou Y, Yan B (2015) Lanthanides post-functionalized nanocrystalline metal–organic frameworks for tunable white-light emission and orthogonal multi-readout thermometry. Nanoscale 7(9):4063–4069. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr06873d
Wang JX, Wang YA, Gao MX, Zhang XM, Yang PY (2016) Facile synthesis of hydrophilic polyamidoxime polymers as a novel solid-phase extraction matrix for sequential characterization of glyco- and phosphoproteomes. Anal Chim Acta 907:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.12.015
Crooks GE, Hon G, Chandonia JM, Brenner SE (2004) WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome Res 14(6):1188–1190. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.849004
Stone MD, Chen XB, McGowan T, Bandhakavi S, Cheng B, Rhodus NL, Griffin TJ (2011) Large-scale phosphoproteomics analysis of whole saliva reveals a distinct phosphorylation pattern. J Proteome Res 10(4):1728–1736. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr1010247
Wang JW, Wang ZD, Sun NR, Deng CH (2019) Immobilization of titanium dioxide/ions on magnetic microspheres for enhanced recognition and extraction of mono-and multi-phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 186(4):236–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3346-4
Zhang KN, Hu DH, Deng SM, Han M, Wang XF, Liu HL, Liu Y, Xie MX (2019) Phytic acid functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles loaded with Ti(IV) ions for phosphopeptide enrichment in mass spectrometric analysis. Microchim Acta 186(2):68–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3177-8
Lin HZ, Chen HM, Shao X, Deng CH (2018) A capillary column packed with azirconium(IV)-basedorganic framework for enrichment of endogenous phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185(12):562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3109-7
Sun NR, Wang JW, Yao JZ, Chen HM, Deng CH (2019) Magnetite nanoparticles coated with mercaptosuccinic acid-modified mesoporous titania as a hydrophilic sorbent for glycopeptides and phosphopeptides prior to their quantitation by LC-MS/MS. Microchim Acta 186(3):159–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3274-3
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Project 2016YFA0501401, 2016YFA0501402 and 2017YFA0505003) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project:21974023 and 21475027).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the experiments in this work were carried out in compliance with the ethical standards, and conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Fudan University.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2442 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Wang, J., Gao, M. et al. Titanium(IV)-functionalized zirconium-organic frameworks as dual-metal affinity probe for recognition of endogenous phosphopeptides prior to mass spectrometric quantification. Microchim Acta 186, 829 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3962-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3962-z