Abstract
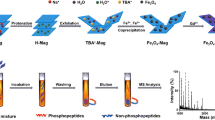
A new type of metal-oxide-coated magnetic nanoparticles (NPs)—tantalum-oxide-coated magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4@Ta2O5) NPs—which are used as affinity probes for selectively trapping phosphopeptides from complex samples, is demonstrated in this study. In this approach, phosphopeptide enrichment was achieved by incubating the NPs with sample solutions under microwave heating within 1 min. The NP–target species conjugates were readily isolated from samples by magnetic separation followed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometric analysis. When using human serum as the sample, phosphorylated fibrinopeptide-A-derived ions are the only ions observed in the MALDI mass spectra after enrichment by the Fe3O4@Ta2O5 NPs. Furthermore, only phosphopeptides appear in the MALDI mass spectra after using the affinity probes to selectively trap target species from the tryptic digest of a cell lysate and milk sample. The results demonstrated that the Fe3O4@Ta2O5 NPs have the capability of selectively trapping phosphorylated peptides from complex samples. The detection limit of this approach for a phosphopeptide (FQpSEEQQQTEDELQDK) was ~10 fmol.

For the first time, tantalum oxide-coated magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4@Ta2O5) NPs were demonstrated as suitable affinity-probes for selectively trapping phosphopeptides from complex samples. To shorten the analysis time, phosphopeptide enrichment was achieved by incubating the NPs with sample solutions under microwave-heating within 1 min. MALDI MS was employed for characterization of the species trapped by the NPs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao W, Dickinson L, Grozinger C, Morin FG, Reven L (1996) Langmuir 12:6429–6435
Bram C, Jung C, Stratmann M (1997) Fresenius’ J Anal Chem 358:108–111
Brovelli D, Hähner G, Ruiz L, Hofer R, Kraus G, Waldner A, Schlösser J, Oroszlan P, Ehrat M, Spencer ND (1999) Langmuir 15:4324–4327
Hofer R, Textor M, Spencer ND (2001) Langmuir 17:4014–4020
Pawsey S, Yach K, Reven L (2002) Langmuir 18:5205–5212
Tosatti S, Michel R, Textor M, Spencer ND (2002) Langmuir 18:3537–3548
Pinkse MWH, Uitto PM, Hilhorst MJ, Ooms B, Heck AJR (2004) Anal Chem 76:3935–3943
Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2005) Anal. Chem 77:5912–5919
Liang S-S, Makamba H, Huang S-Y, Chen S-H (2006) J Chromatogr A 1116:38–45
Rinalducci S, Larsen MR, Mohammed S, Zolla L (2006) J Proteome Res 5:973–982
Larsen MR, Thingholm TE, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P, Jorgensen TJD (2005) Mol Cell Proteomics 4:873–886
Sano A, Nakamura H (2004) Anal Sci 20:565–566
Lo C-Y, Chen W-Y, Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2007) J Proteome Res 6:887–893
Kweon HK, Hakansson K (2006) Anal Chem 78:1743–1749
Chen C-T, Chen W-Y, Tsai P-J, Chien K-Y, Yu J-S, Chen Y-C (2007) J Proteome Res 6:316–325
Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2008) J Biomed Nanotechnol 4:73–79
Chen C-T, Chen Y-C (2008) J Mass Spectrom 43:538–541
Ficarro SB, Parikh JR, Blank NC, Marto JA (2008) Anal Chem 80:4606–4613
Li Y, Wu JS, Qi DW, Xu XQ, Deng CH, Yang PY, Zhang XM (2008) Chem Commun 5:564–566
Kweon HK, Hakansson K (2008) J Proteome Res 7:749–755
Liang XQ, Fonnum G, Hajivandi M, Stene T, Kjus NH, Ragnhildstveit E, Arnshey JW, Predki P, Pope RM (2007) J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 18:1932–1944
Sturm M, Leitner A, Smatt JH, Linden M, Lindner W (2008) Adv Fun Mater 18:2381–2389
Sugiyama N, Masuda T, Shinoda K, Nakamura A, Tomita M, Ishihama Y (2007) Mol Cell Proteomics 6:1103–1109
Han L, Shan Z, Chen DH, Yu XJ, Yang PY, Tu B, Zhao DY (2008) J. Colloid Interface Sci 318:315–321
Wolschin F, Wienkoop S, Weckwerth W (2005) Proteomics 5:4389–4397
Lin HY, Chen WY, Chen YC (2009) J Biomed Nanotechnol 5:215–223
Chen W-Y, Chen Y-C (2007) Anal Chem 79:8061–8066
Yildirim S, Ulutas K, Deger D, Zayim EO, Turhan I (2005) Vacuum 77:329–335
Li Y-C, Lin Y-S, Tsai P-J, Chen C-T, Chen W-Y, Chen Y-C (2007) Anal Chem 79:7519–7525
Acknowledgment
We thank the National Science Council of Taiwan and MOE-ATU (96W821G021 and 96W801H109) for supporting this research financially.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, HY., Chen, WY. & Chen, YC. Iron oxide/tantalum oxide core–shell magnetic nanoparticle-based microwave-assisted extraction for phosphopeptide enrichment from complex samples for MALDI MS analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 394, 2129–2136 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2890-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2890-x