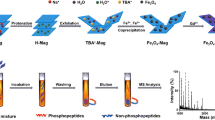
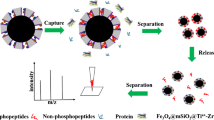
Abstract
A strategy for effectively enriching global phosphopeptides was successfully developed by using ammonia methyl phosphate (APA) as a novel chelating ligand and Ti4+ and Nb5+ as double functional ions (referred to as Fe3O4@mSiO2@APA@Ti4+/Nb5+). With the advantage of large specific surface area (151.1 m2/g), preeminent immobilized ability for metal ions (about 8% of total atoms), and unbiased enrichment towards phosphopeptides, Fe3O4@mSiO2@APA@Ti4+/Nb5+ displays high selectivity (maximum mass ratio β-casein to BSA is 1:1500), low limit of detection (LOD, as low as 0.05 fmol), good relative standard deviation (RSD, lower than 7%), recovery rate of 87% (18O isotope labeling method), outstanding phosphopeptide loading capacity (330 μg/mg), and at least five times re-use abilities. In the examination of the actual sample, 24 phosphopeptides were successfully detected in saliva and 4 phosphopeptides were also selectively extracted from human serum. All experiments have shown that Fe3O4@mSiO2@APA@Ti4+/Nb5+ exhibits exciting potential in view of the challenge of low abundance of phosphopeptides.

Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu YL, Liu QJ, Deng CH (2019) L-Cysteine-modified metal-organic frameworks as multifunctional probes for efficient identification of N-linked glycopeptides and phosphopeptides in human crystalline lens. Anal Chim Acta 1061:110–121
Wang ZD, Wang JW, Sun NR, Deng CH (2019) A promising nanoprobe based on hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and immobilized metal affinity chromatography for capture of glycopeptides and phosphopeptides. Anal Chim Acta 1067:1–10
Wang JW, Wang ZD, Sun NR, Deng CH (2019) Immobilization of titanium dioxide/ions on magnetic microspheres for enhanced recognition and extraction of mono- and multi-phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 186:236
Sun NR, Wang ZD, Wang JW, Chen HM, Wu H, Shen S, Deng CH (2019) Hydrophilic tripeptide combined with magnetic titania as a multipurpose platform for universal enrichment of phospho- and glycopeptides. J Chromatogr A 1595:1–10
Sun NR, Wang JW, Yao JZ, Chen HM, Deng CH (2019) Magnetite nanoparticles coated with mercaptosuccinic acid-modified mesoporous titania as a hydrophilic sorbent for glycopeptides and phosphopeptides prior to their quantitation by LC-MS/MS. Microchim Acta 186:159
Li YL, Liu LL, Wu H, Deng CH (2019) Magnetic mesoporous silica nanocomposites with binary metal oxides core-shell structure for the selective enrichment of endogenous phosphopeptides from human saliva. Anal Chim Acta 1079:111–119
Wu YL, Liu QJ, Xie YQ, Deng CH (2018) Core-shell structured magnetic metal-organic framework composites for highly selective enrichment of endogenous N-linked glycopeptides and phosphopeptides. Talanta 190:298–312
Zheng HY, Hu P, Quinn DF, Wang YK (2005) Phosphotyrosine proteomic study of interferon alpha signaling pathway using a combination of immunoprecipitation and immobilized metal affinity chromatography. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:721–730
Faserl K, Kremser L, Muller M, Teis D, Lindner HH (2015) Quantitative proteomics using ultralow flow capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 87:4633–4640
Hennrich ML, Groenewold V, Kops GJ, Heck AJ, Mohammed S (2011) Improving depth in phosphoproteomics by using a strong cation exchange-weak anion exchange-reversed phase multidimensional separation approach. Anal Chem 83:7137–7143
Atakay M, Celikbicak O, Salih B (2012) Amine-functionalized sol-gel-based lab-in-a-pipet-tip approach for the fast enrichment and specific purification of phosphopeptides in MALDI-MS applications. Anal Chem 84:2713–2720
Cao LC, Zhao YM, Chu ZY, Zhang XM, Zhang WB (2020) Core-shell magnetic bimetallic MOF material for synergistic enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta 206:120165
Xiao RL, Pan YN, Li J, Zhang LY, Zhang WB (2019) Layer-by-layer assembled magnetic bimetallic metal-organic framework composite for global phosphopeptide enrichment. J Chromatogr A 1601:45–52
Jiang DD, Li XQ, Jia Q (2018) Design of two-dimensional layered double hydroxide nanosheets embedded with Fe3O4 for highly selective enrichment and isotope labeling of phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:421–429
Xiao J, Yang SH, Wu JX, Wang H, Yu X, Shang WB, Chen GQ, Gu ZY Highly selective capture of monophosphopeptides by two-dimensional metal-organic framework nanosheets. Anal Chem 91:9093–9101
Jiang DD, Li Z, Jia QA (2019) Sensitive and selective phosphopeptide enrichment strategy by combining polyoxometalates and cysteamine hydrochloride-modified chitosan through layer-by-layer assembly. Anal Chim Acta 1066:58–68
Ma WF, Zhang Y, Li LL, You LJ, Zhang P, Zhang YT, Li JM, Yu M, Guo J, Lu HJ, Wang CC (2012) Tailor-made magnetic Fe3O4@mTiO2 microspheres with a tunable mesoporous anatase shell for highly selective and effective enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Nano 6:3179–3188
Lin HZ, Chen HM, Shao X, Deng CH (2018) A capillary column packed with a zirconium (IV)-based organic framework for enrichment of endogenous phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185:562
Lu J, Qi DW, Deng CH, Zhang XM, Yang PY (2010) Hydrothermal synthesis of alpha-Fe2O3@SnO2 core-shell nanotubes for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides for mass spectrometry analysis. Nanoscale 2:1892–1900
Liu QJ, Sun NR, Gao MX, Deng CH (2018) Magnetic binary metal–organic framework as a novel affinity probe for highly selective capture of endogenous phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:4382–4389
Jiang JB, Sun XN, Li Y, Deng CH, Duan GL (2018) Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@PDA core-shell microspheres functionalized with various metal ions: a systematic comparison of commonly-used metal ions for IMAC enrichment. Talanta 178:600–607
Cho KY, Chen LJ, Hu YW, Schnaubelt M, Zhang H (2019) Developing workflow for simultaneous analyses of phosphopeptides and glycopeptides. ACS Chem Biol 14:58–66
Gao CH, Bai J, He YT, Zheng Q, Ma WD, Lei ZX, Zhang MY, Wu J, Fu FF, Lin Z (2019) Postsynthetic functionalization of Zr4+-immobilized core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic frameworks for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:13735–13741
Bae SW, Kim JI, Cuot I, Sung J, Hong JI, Yeo WS (2017) Zinc ion-immobilized magnetic microspheres for enrichment and identification of multi-phosphorylated peptides by mass spectrometry. Anal Sci 33:1381–1386
Lai AC, Tsai CF, Hsu CC, Sun YN, Chen YJ (2012) Complementary Fe3+ and Ti4+-immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography for purification of acidic and basic phosphopeptides. Rapid Commun Mass Sp 26:2186–2194
Matthew C, Paul T (2012) Immobilized gallium (III) affinity chromatography of phosphopeptides. Anal Chem 71:2883–2892
Alexander L, Martin S, Wolfgang L (2011) Tools for analyzing the phosphoproteome and other phosphorylated biomolecules: a review. Anal Chim Acta 703:19–30
Zhai R, Tian F, Xue RQ, Jiao FL, Hao FR, Zhang YJ, Qian XH (2016) Metal ion-immobilized magnetic nanoparticles for global enrichment and identification of phosphopeptides by mass spectrometry. RSC Adv 6:1670–1677
Ma WF, Zhang Y, Li LL, Zhang YT, Yu M, Guo J, L HJ, Wang C (2013) Ti4+-immobilized magnetic composite microspheres for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Adv Funct Mater 23:107–115
Porath J, Carlsson J, Olsson I, Belfrage G (1975) Metal chelate affinity chromatography, a new approach to protein fractionation. Nature 258:598–599
Andersson L, Porath J (1986) Isolation of phosphoproteins by immobilized metal (Fe3+) affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem 154:250–254
Ficarro SB, Adeimant G, Tomar MN, Zhang Y, Cheng VJ, Marto JA (2009) Magnetic bead processor for rapid evaluation and optimization of parameters for phosphopeptide enrichment. Anal Chem 81:4566–4575
Yan YH, Zheng ZF, Deng CH, Zhan XM, Yang PY (2013) Facile synthesis Ti4+-immobilized Fe3O4@polydopamine core-shell microspheres for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Chem Commun 49:5055–5057
Su J, He XW, Chen LX, Zhang YK (2018) Adenosine phosphate functionalized magnetic mesoporous graphene oxide nanocomposite for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:2188–2196
Jiang JB, Sun XN, She XJ, Li JJ, Li Y, Deng CH, Duan G (2018) Magnetic microspheres modified with Ti(IV) and Nb(V) for enrichment of phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185:309–316
Wang HP, Jiao FL, Gao FY, Lv YY, Wu Q, Zhao Y, Shen YH, Zhang YJ, Qian XH (2017) Titanium (IV) ion-modified covalent organic frameworks for specific enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta 166:133–140
Zhou HJ, Ye ML, Dong J, Han GH, Jiang XN, Wu RN, Zou HF (2008) Specific phosphopeptide enrichment with immobilized titanium ion affinity chromatography adsorbent for phosphoproteome. Analysis 7:3957–3967
Salimi K, Usta DD, Celikbicak O, Pinar A, Salih B, Tuncel A (2017) Ti (IV) carrying polydopamine-coated, monodisperse-porous SiO2 microspheres with stable magnetic properties for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 153:280–290
Zheng HY, Wang JX, Gao MX, Zhang XM (2019) Titanium (IV)-functionalized zirconium-organic frameworks as dual-metal affinity probe for recognition of endogenous phosphopeptides prior to mass spectrometric quantification. Microchim Acta 186:829–839
Wang BC, Liu B, Yan YH, Tang KQ, Ding CF (2019) Binary magnetic metal-organic frameworks composites: a promising affinity probe for highly selective and rapid enrichment of mono- and multi-phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 186:832–841
Funding
This work is supported by Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation (LQ19C050002), State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science (SKLACLS1901), National Natural Science Foundation of China (511903050), and the K. C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 2083 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, B., Wang, B., Yan, Y. et al. Efficient separation of phosphopeptides employing a Ti/Nb-functionalized core-shell structure solid-phase extraction nanosphere. Microchim Acta 188, 32 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04652-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04652-6