Abstract
Background
The purpose of this study was to compare restoration of mechanical limb alignment and three-dimensional component-positioning between conventional and patient-specific instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty.
Methods
Radiographic data of patients undergoing mobile-bearing total knee arthroplasty (n = 1257), using either conventional (n = 442) or patient-specific instrumentation (n = 812), were analyzed. To evaluate accuracy of axis restoration and 3D-component-positioning between conventional and patient-specific instrumentation, absolute deviations from the targeted neutral mechanical limb alignment and planned implant positions were determined. Measurements were performed on standardized coronal long-leg and sagittal knee radiographs. CT-scans were evaluated for accuracy of axial femoral implant rotation. Outliers were defined as deviations from the targeted neutral mechanical axis of > ± 3° or from the intraoperative component-positioning goals of > ± 2°. Deviations greater than ± 5° from set targets were considered to be severe outliers.
Results
Deviations from a neutral mechanical axis (conventional instrumentation: 2.3°± 1.7° vs. patient-specific instrumentation: 1.7°± 1.2°; p < 0.001) and numbers of outliers (conventional instrumentation: 25.8% vs. patient-specific instrumentation: 10.1%; p < 0.001) were significantly lower in the patient-specific instrumentation group. Significantly lower mean deviations and less outliers were detected regarding 3D-component-positioning in the patient-specific instrumentation compared to the conventional instrumentation group (all p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Patient-specific instrumentation prevented from severe limb malalignment and component-positioning outliers (> ± 5° deviation). Use of patient-specific instrumentation proved to be superior to conventional instrumentation in achieving more accurate limb alignment and 3D-component positioning, particularly regarding femoral component rotation. Furthermore, the use of patient-specific instrumentation successfully prevented severe (> 5° deviation) outliers.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Restoration of neutral mechanical limb alignment and exact component positioning have been reported to be essential for satisfactory long-term outcome after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) [1, 2]. Various studies showed that coronal limb alignment is an important factor in implant durability, as outliers in the frontal plane had a significantly higher risk for early loosening and polyethylene wear with decreased overall implant survival [1, 2]. Mechanical malalignment and component malpositioning have also been implicated as causative for unsatisfactory clinical outcome [3,4,5]. Although the clinical importance of a neutral mechanical alignment on implant longevity has recently become a matter of discussion, there is currently no better parameter to aim for when performing TKA [1, 5, 6].
Despite correct surgical techniques, expanding knowledge and experience with manual instrumentation systems, imprecise alignment, and component positioning remain common issues in conventional TKA [7]. Consequentially, various efforts have been made to introduce technology to aid the surgeon in reliably improving accuracy of implantation in TKA over the last years with computer-assisted surgery leading the way [8]. Although computer-assisted surgery could improve surgical accuracy, it came with the disadvantages of complex instrumentation and longer surgery times.
As a contemporary alternative, patient-specific instrumentation (PSI) has been introduced to joint reconstruction in recent years. In short, for the purpose of PSI, computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance images (MRI) are used for preoperative three-dimensional (3D) planning and subsequent production of patient-specific cutting guides providing a unique fit on femur and tibia for exact bone resection and component positioning.
As the potential benefits of these systems, such as reduced surgical time and superior accuracy of knee replacement, come at the cost of increased economic and logistic expenses, PSI came under scrutiny quickly [9,10,11]. Although expectations were high, there is no clear consensus in literature regarding accuracy, reliability, and actual value of PSI in knee replacement surgery [12,13,14,15].
Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to compare radiological limb alignment and 3D-component positioning between conventional instrumentation (CVI) and a CT-based PSI system in primary, mobile-bearing TKA in the setting of a single-center over a period of multiple years. We hypothesized that PSI would be superior regarding mechanical alignment restoration and 3D-component positioning compared with CVI.
Methods
The current study had Institutional Review Board approval (#EK201305). The present retrospective cohort study (Levels of Evidence III) was based on analyses of prospectively collected radiographic data of patients, who underwent surgery with a mobile-bearing TKA system (GMK® Primary, Medacta International S.A., Castel San Pietro, Switzerland) regardless of preoperative varus or valgus deformity in a single center during the period 2007 to 2013. From 2007 to 2010, the GMK Primary system was only available with conventional instrumentation, whereas the MyKnee PSI technology was available starting from 2010. Since then, the included conventionally performed TKA group consisted of patients, who were scheduled on short notice without a minimum lead time of 2 weeks to procure the PSI and refused to wait for a later surgical date, refused performance of a preoperative CT, or opposed surgery with by then fairly new PSI technology.
Of initially available 1315 postoperative radiographs, 58 cases were excluded due to previous hip arthroplasty (n = 33), previous fractures of the femur or tibia (n = 5), implants around the knee (n = 7), or insufficient quality of radiographs (n = 13). Complete radiographic data of 1257 knee arthroplasties were evaluated including 442 cases performed with CVI and 815 cases with PSI. Additionally, 138 (CVI: n = 44, PSI: n = 94) available postoperative CT-scans were analyzed.
Preoperative CT-scans including sections of the femoral head, knee, and ankle, with the patient supine and the leg in complete extension according to a standardized protocol (MyKnee®, Medacta International S.A., Castel San Pietro, Switzerland), were made prior to surgery. Generated images were then uploaded to the company website for further processing. 3D-bone-models of the knee and cutting blocks were created and planned by an engineer according to the preferences of the surgeons. The planning targets for all patients were a neutral mechanical axis, a physiological joint line, a tibial slope between 0° and 6° to restore an anatomic situation, a flush fit of the femoral component on the anterior cortex to avoid notching (0° to 4° flexion), a femoral component rotation parallel to the transepicondylar axis, and a tibial component rotation oriented according to the tibial tuberosity. These intraoperative goals were the same for the CVI group, whereas planning of lower limb axis, coronal, and sagittal component position was done manually on standard long-leg and knee radiographs (mediCAD, Hectec GmbH, Altdorf, Germany).
All included patients underwent implantation using cemented mobile-bearing total knee prosthesis (GMK® Primary, Medacta International S.A., Castel San Pietro, Switzerland) without patellar resurfacing. After a midline skin incision, a medial or, in case of more than 5° valgus alignment, lateral parapatellar arthrotomy was performed. In the CVI group, the standard GMK® instrumentation system including an extra-medullary guidance rod for tibial- and an intra-medullary guidance rod for femoral alignment was used. For use of PSI, the tibial and femoral footprint areas were carefully cleaned of the remaining cartilage using the electro-cautery for an exact fit of the cutting blocks, and after pinning, bone cuts were performed in accordance to the preoperative planning. Suggested resections and femoral rotation were checked for accordance to the preoperative plan. Although the PSI system provided the possibility for intraoperative control, tibial component rotation was determined manually with the goal of orienting the tibial plateau according to the medial third of the tibial tuberosity. Therefore, an analysis of tibial component positioning was not included in the present study. Necessary removal of osteophytes and soft tissue balancing were carefully performed in both groups. All surgeries were performed by three senior surgeons trained in total joint reconstruction, whereas all operated on patients with CVI as well as with PSI. Mobilization and physiotherapy started on the first postoperative day in both groups. Continuous passive motion was used complementarily until a minimum flexion of 90° was possible.
Standardized coronal long-leg, sagittal knee joint, and tangential patella radiographs, which were taken prior to surgery and on the day of hospital discharge, were analyzed. CT-scans were used to compare femoral component rotation (FCR) of patients receiving PSI with the standard technique.
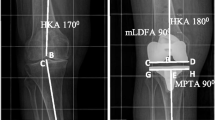
To evaluate overall limb alignment, the hip-knee-ankle angle (HKA) was measured on weight-bearing long-leg radiographs, whereas an HKA of over 180° was defined as valgus and a HKA under 180° was defined as varus alignment. Frontal femoral component (FFC) position was defined as the angle between the femoral mechanical axis and the line formed by the distal femoral condyles. Frontal tibial component (FTC) position was measured as the angle between the mechanical axis and the tibial plateau. For both measurements, an angle above or below 90° was considered a valgus or varus position. Lateral femoral (LFC) and tibial (LTC) component positions were defined as the angle between the femoral or tibial axis and the respective implant surfaces. FCR was assessed on axial CT scans by measuring the angle between the posterior component margins and the transepicondylar line (Fig. 1).
Postoperative radiographs (a, b) and CT-scan (c) of a right leg and knee, depicting the methods of angle measurements. The hip-knee-ankle angle (HKA), frontal femoral (FFC), and frontal tibial (FTC) component angle were measured on long-leg weight-bearing radiographs (a). Lateral femoral (LFC) and lateral tibial (LTC) component angles were evaluated on sagittal short view radiographs (b). Axial femoral component rotation (FCR) was analyzed on postoperative CT-scans of the knee (c)
Radiographic measurements were performed by two independent examiners, who were not involved in the surgical procedures and blinded regarding the used instrumentation. A random subset of 30 patients of each instrumentation group was measured twice by each examiner at two different time points to assess inter- and intra-rater reliability using interclass correlation coefficient (ICC). This analysis revealed intra- and inter-rater measurement agreement for all examined parameters (HKA, FFC, FTC, LFC, LTC, and FCR) ranging from 0.932 to 0.996 and from 0.931 to 0.996, respectively.
To analyze accuracy of mechanical axis restoration and 3D-component positioning between the CVI and PSI group, deviations from the targeted neutral mechanical limb alignment and 3D-component positioning in degrees were calculated. Outliers were defined as deviations from the targeted neutral mechanical axis of more than ± 3° (HKA) or from the intra-operative component positioning goals of more than ± 2° (FFC, FTC, LFC, LTC, and FCR). Deviations greater than ± 5° from set targets were considered to be severe outliers [16].
Descriptive statistic was used to present patients demographics. Distribution of data was assessed by a visual inspection of histograms and the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The independent or paired t test for normally distributed variables or the nonparametric Mann–Whitney U test or Wilcoxon signed rank test was performed to compare continuous variables. Fisher’s exact or Χ2 test were used to analyze categorical variables. With the current sample size, there was a 95% power to detect an effect size of > 0.21 for the deviation from a targeted neutral mechanical axis. Statistical significance was reported at a p value of < 0.05 level (two-sided). All statistical analyses were performed in SPSS21® (IBM® Corporation, Armonk, USA).
Results
Baseline patient characteristics were comparable between the instrumentation groups with significant differences only in the ratio of female to male patients and distribution of preoperative osteoarthritic degeneration according to the Kellgren–Lawrence classification (Table 1).
Significant HKA improvements from pre- to postoperative were detected in both groups (p < 0.001; Tables 1 and 2). Analysis of mean limb alignment and component positioning showed statistically significant differences (with the exception of LTC) between the two groups (Table 2).
Significantly less patients in the PSI compared to the CVI group experienced postoperative outliers regarding HKA (10.1% vs. 25.8%, p < 0.001), FFC (13.9% vs. 30.3%, p < 0.001), FTC (12.9% vs. 22.4%, p < 0.001), LFC (12.2% vs. 17.2%, p = 0.017), LTC (6.3% vs. 10.2%, p = 0.014), and FCR (3.2% vs. 39.2%, p < 0.001). Furthermore, there were significantly more severe outliers detected in the CVI compared to the PSI group regarding HKA (0% vs. 6.3%, p < 0.001), FTC (0% vs. 1.4%, p = 0.002), LFC (0% vs. 2.7%, p < 0.001), and LTC (0% vs. 1.1%, p = 0.005). Only 0.2% FFC and 3.9% FCR were found to be severe outliers in the CVI group, which was not significantly different to the PSI group. The numbers of all outliers are presented in Fig. 2.
Accuracy of mechanical axis restoration and 3D-component positioning of the conventional instrumentation (CVI) and the patient-specific instrumentation (PSI) group. Outliers (dark grey bars) were defined as deviations from the targeted neutral mechanical axis of more than ± 3° (hip-knee-ankle angle, HKA) or from the intra-operative component positioning goals of more than ± 2° (frontal femoral component angle, FFC; frontal tibial component angle, FTC; lateral femoral component angle, LFC; lateral tibial component angle, LTC; femoral component rotation, FCR; dark grey bars). Deviations greater than ± 5° from set targets were considered to be severe outliers (black bars). CT scans for the evaluation of rotational component alignment were available for 44 cases of the CVI group, and for 94 case of the PSI group. Values are presented as percentages and numbers of cases in parentheses
PSI also significantly reduced the mean absolute deviation from the targeted neutral mechanical alignment and planned component position in all planes (Table 3).
Discussion
This comparative study between conventional and patient-specific instrumentation in TKA presents results of a high number of cases (n = 1257) including standardized radiographic evaluation and CT scan data. The most important findings of the present study were that CT-based PSI significantly reduced the number of limb alignment (> 3°) and component positioning outliers (> 2°) in all planes, while protecting against the risk of severe outliers (> 5°). Furthermore, significantly more accurate mechanical alignment restoration and 3D-component positioning could be detected in the PSI compared to the CVI group.
The impetus for development of PSI was to aid the surgeon in achieving reproducible accuracy in TKA to eventually improve outcome and implant longevity. Considerable deviations from a targeted neutral mechanical axis have traditionally been implicated as cause for inferior clinical outcome and decreased implant survival [1, 2, 4, 5, 17, 18]. Although this longstanding concept has been challenged recently [19,20,21,22], it is today’s gold standard for intraoperative limb alignment. Less literature is available on the impact of individual component positioning on clinical outcome and implant survival. Incorrect tibiofemoral coronal implant placement has been implicated as reason for revision surgery [2]. Specifically, if an overall malalignment is based on certain biomechanically disadvantageous component position combinations, long-term failure rates have been shown to dramatically increase to over 10%, with an up to 54 times higher risk for failure than correctly placed implants [2]. Recent clinical studies showed that there is no relevant correlation between posterior tibial slope and kinematics after TKA [23,24,25]. However, tibial slopes below 0° and over 7° have been associated with increased risk of failure [25]. Inadequate femoral component rotation can negatively affect patellar tracking and knee kinematics [26]. An isolated internal rotation of the femoral component has been associated with anterior knee pain, instability, stiffness, and early revision [27,28,29,30,31].
Various meta-analyses comparing the number of outliers (> 3°) from a neutral mechanical axis of PSI and CVI found results between the instrumentation techniques to be comparable at best [12, 13, 15]. Similar disappointing outcomes have been reported for multi-planar component positioning [12, 13, 15]. Contrary to these inconsistent results, the present study suggests that PSI, if used deliberately, has the potential to significantly increase precision of intended 3D-component positioning and mechanical axis restoration, while at the same time significantly reducing the number of outliers in all planes.
Reasons for the often inconsistent results with PSI may originate in part in the different used PSI systems, nature of performed studies, varying surgical techniques, and disparity of measurements: There is considerable heterogeneity in accuracy between the available PSI systems. For example, one recent meta-analysis [13] found no difference in the overall number of HKA outliers between CVI (22.7%) and PSI (23.2%), whereas a subgroup analysis showed that there were substantial differences between various PSI systems. While three systems (Visionaire, Smith and Nephew, Memphis, TN; PSI, Zimmer, Warsaw, IN; TruMatch, DePuy, Warsaw, IN) provided comparable rates of outliers to CVI, one PSI system (Signature®, Biomet, Warsaw, IN) actually showed a 54% increased risk of producing an HKA outlier.
Another reason for inconsistency with PSI may originate in part from the nature of performed studies beyond issues of study design, PSI systems, varying surgical techniques, and disparity of measurements. Although being formally of high quality, studies might lack the sample size or length of study period necessary to account for learning curves for implementing needed logistics, optimizing the preoperative planning process, and adapting the surgical strategy for successful implementation of PSI.
In contrast to the variable results for limb alignment restoration and component positioning in the coronal and sagittal plane, there is predominant consensus about the superiority of PSI to achieve accurate femoral implant rotation with simultaneous reduction of outliers [12, 13, 15, 16, 29, 32]. Our results agree with the literature, proving femoral component rotation as benefiting the most from the use of PSI. Not only was there a significant improvement in accuracy (1.4° less deviation from target per case) but also a distinct reduction of outliers in the PSI group (CVI: 39.2% vs. PSI: 3.2%).
Ultimately, PSI has to be treated as a tool to aid the surgeon in potentially improving accuracy of TKA. Although promising, PSI is still in a relatively early phase of development and cannot yet completely mitigate against all pitfalls of TKA surgery. It is absolutely necessary for surgeons to be actively involved in the preoperative planning process [33,34,35,36,37]. Intraoperative PSI-specific details have to be considered and surgical techniques adjusted where necessary. Double-checking alignment and bony resections at relevant surgical steps according to traditional concepts is mandatory, because, for now, successful outcome of TKA is still the responsibility of the performing surgeon.
The present study has certain limitations. The results pertain only to the used MyKnee® PSI system and, thus, generalization of results to other PSI systems should be done with caution. The number of available CT-scans for axial component analysis was limited. In order to minimize costs and extensive radiation exposure, no additional CT scans were performed for the purpose of this study. Surgeries were performed by three different surgeons. Although this adds variability, it reflects clinical reality of multiple surgeons performing TKA at an institution. The number of knees with severest osteoarthritic changes was higher in the PSI group. However, if anything, this underlines the ability of PSI to reliably aid surgeons in achieving their desired radiological results independent of disease severity. Lastly, the present study was a radiographic evaluation in order to assess the accuracy of PSI compared to CVI. Future investigations are needed for the assessment of according clinical outcome.
Conclusions
In the current comparative study, we investigated the accuracy of conventional and patient-specific instrumentation in TKA (n = 1257) using standardized radiographic evaluation and CT scan data. The used CT-based PSI system significantly reduced the number of limb alignment (> 3°) and component positioning outliers (> 2°) in all planes, while protecting against the risk of severe outliers (> 5°). Furthermore, significantly more accurate restoration of mechanical alignment and 3D-component positioning could be achieved in the PSI group.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CVI:
-
Conventional instrumentation
- FCR:
-
Femoral component rotation
- FFC:
-
Frontal femoral component
- FTC:
-
Frontal tibial component
- HKA:
-
Hip-knee-ankle angle
- LFC:
-
Lateral femoral component
- LTC:
-
Lateral tibial component
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance images
- PSI:
-
Patient-specific instrumentation
- TKA:
-
Total knee arthroplasty
References
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(6 Suppl):39–43.
Ritter MA, Davis KE, Meding JB, Pierson JL, Berend ME, Malinzak RA. The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement, J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(17):1588–96.
Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MA. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Correlated biomechanical and clinical observations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;173:178–83.
Longstaff LM, Sloan K, Stamp N, Scaddan M, Beaver R. Good alignment after total knee arthroplasty leads to faster rehabilitation and better function. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(4):570–8.
Lotke PA, Ecker ML. Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;59(1):77–9.
Bonner TJ, Eardley WG, Patterson P, Gregg PJ. The effect of post-operative mechanical axis alignment on the survival of primary total knee replacements after a follow-up of 15 years. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(9):1217–22.
Daniilidis K, Tibesku CO. A comparison of conventional and patient-specific instruments in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2014;38(3):503–8.
Hetaimish BM, Khan MM, Simunovic N, Al-Harbi HH, Bhandari M, Zalzal PK. Meta-analysis of navigation vs conventional total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27(6):1177–82.
Nunley RM, Ellison BS, Ruh EL, Williams BM, Foreman K, Ford AD, Barrack RL. Are patient-specific cutting blocks cost-effective for total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(3):889–94.
Thienpont E, Bellemans J, Delport H, Van Overschelde P, Stuyts B, Brabants K, Victor J. Patient-specific instruments: industry's innovation with a surgeon's interest. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10):2227–33.
Thienpont E, Fennema P, Price A. Can technology improve alignment during knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2013;20(Suppl 1):S21–8.
Cavaignac E, Pailhe R, Laumond G, Murgier J, Reina N, Laffosse JM, Berard E, Chiron P. Evaluation of the accuracy of patient-specific cutting blocks for total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Int Orthop. 2015;39(8):1541–52.
Huijbregts HJ, Khan RJ, Sorensen E, Fick DP, Haebich S. Patient-specific instrumentation does not improve radiographic alignment or clinical outcomes after total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2016;87(4):386–94.
Thienpont E, Paternostre F, Van Wymeersch C. The indirect cost of Patient-Specific Instruments. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015;81(3):462–70.
Zhang QM, Chen JY, Li H, Chai W, Ni M, Zhang ZD, Yang F. No evidence of superiority in reducing outliers of component alignment for patient-specific instrumentation for total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Orthop Surg. 2015;7(1):19–25.
Anderl W, Pauzenberger L, Kolblinger R, Kiesselbach G, Brandl G, Laky B, Kriegleder B, Heuberer P, Schwameis E. Patient-specific instrumentation improved mechanical alignment, while early clinical outcome was comparable to conventional instrumentation in TKA, Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(1):102–11.
Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD. Does accurate anatomical alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(4):560–9.
Kamat YD, Aurakzai KM, Adhikari AR, Matthews D, Kalairajah Y, Field RE. Does computer navigation in total knee arthroplasty improve patient outcome at midterm follow-up? Int Orthop. 2009;33(6):1567–70.
Magnussen RA, Weppe F, Demey G, Servien E, Lustig S. Residual varus alignment does not compromise results of TKAs in patients with preoperative varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(12):3443–50.
Matziolis G, Adam J, Perka C. Varus malalignment has no influence on clinical outcome in midterm follow-up after total knee replacement. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(12):1487–91.
Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, Berry DJ. Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(12):2143–9.
Vanlommel L, Vanlommel J, Claes S, Bellemans J. Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10):2325–30.
Antony J, Tetsworth K, Hohmann E. Influence of sagittal plane component alignment on kinematics after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;25(6):1686–91.
Bauer T, Biau D, Colmar M, Poux X, Hardy P, Lortat-Jacob A. Influence of posterior condylar offset on knee flexion after cruciate-sacrificing mobile-bearing total knee replacement: a prospective analysis of 410 consecutive cases. Knee. 2010;17(6):375–80.
Kim KH, Bin SI, Kim JM. The Correlation between Posterior Tibial Slope and Maximal Angle of Flexion after Total Knee Arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2012;24(3):158–63.
Keshmiri A, Maderbacher G, Baier C, Zeman F, Grifka J, Springorum HR. Significant influence of rotational limb alignment parameters on patellar kinematics: an in vitro study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(8):2407–14.
Akagi M, Matsusue Y, Mata T, Asada Y, Horiguchi M, Iida H, Nakamura T. Effect of rotational alignment on patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1999;366:155–63.
Berger RA, Crossett LS, Jacobs JJ, Rubash HE. Malrotation causing patellofemoral complications after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1998;356:144–53.
Mannan A, Smith TO. Favourable rotational alignment outcomes in PSI knee arthroplasty: A Level 1 systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee. 2016;23(2):186–90.
Pietsch M, Hofmann S. Early revision for isolated internal malrotation of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2012;20(6):1057–63.
Rhoads DD, Noble PC, Reuben JD, Mahoney OM, Tullos HS. The effect of femoral component position on patellar tracking after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;260:43–51.
Thienpont E, Schwab PE, Fennema P. A systematic review and meta-analysis of patient-specific instrumentation for improving alignment of the components in total knee replacement. Bone Joint J. 2014;96(B-8):1052–61.
Boonen B, Schotanus MG, Kerens B, van der Weegen W, van Drumpt RA, Kort NP. Intra-operative results and radiological outcome of conventional and patient-specific surgery in total knee arthroplasty: a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10):2206–12.
Boonen B, Schotanus MG, Kort NP. Preliminary experience with the patient-specific templating total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(4):387–93.
Schotanus MG, Schoenmakers DA, Sollie R, Kort NP. Patient-specific instruments for total knee arthroplasty can accurately predict the component size as used peroperative. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016.
Issa K, Rifai A, McGrath MS, Callaghan JJ, Wright C, Malkani AL, Mont MA, McInerney VK. Reliability of templating with patient-specific instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2013;26(6):429–33.
Pietsch M, Djahani O, Hochegger M, Plattner F, Hofmann S. Patient-specific total knee arthroplasty: the importance of planning by the surgeon. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(10):2220–6.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LP and WA designed the study. LP, PRH, BL, and ES analysed and interpreted the data. MM, GB, and JKF performed data acquisition and critically revised the paper. All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The current study had Institutional Review Board of the St. Vincent Hospital Vienna, Austria approval (#EK201305).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
WA and PH receive consultant fees from Arthrex. WA receives royalties from Arthrex and Medacta. None of the companies had any influence on study design, data collection, interpretation of the results, or the final manuscript. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Pauzenberger, L., Munz, M., Brandl, G. et al. Patient-specific instrumentation improved three-dimensional accuracy in total knee arthroplasty: a comparative radiographic analysis of 1257 total knee arthroplasties. J Orthop Surg Res 14, 437 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1465-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-019-1465-6