Abstract
Background
Genetic counselling and testing for Lynch syndrome (LS) have recently been introduced in several Latin America countries. We aimed to characterize the clinical, molecular and mismatch repair (MMR) variants spectrum of patients with suspected LS in Latin America.
Methods
Eleven LS hereditary cancer registries and 34 published LS databases were used to identify unrelated families that fulfilled the Amsterdam II (AMSII) criteria and/or the Bethesda guidelines or suggestive of a dominant colorectal (CRC) inheritance syndrome.
Results
We performed a thorough investigation of 15 countries and identified 6 countries where germline genetic testing for LS is available and 3 countries where tumor testing is used in the LS diagnosis. The spectrum of pathogenic MMR variants included MLH1 up to 54%, MSH2 up to 43%, MSH6 up to 10%, PMS2 up to 3% and EPCAM up to 0.8%. The Latin America MMR spectrum is broad with a total of 220 different variants which 80% were private and 20% were recurrent. Frequent regions included exons 11 of MLH1 (15%), exon 3 and 7 of MSH2 (17 and 15%, respectively), exon 4 of MSH6 (65%), exons 11 and 13 of PMS2 (31% and 23%, respectively). Sixteen international founder variants in MLH1, MSH2 and MSH6 were identified and 41 (19%) variants have not previously been reported, thus representing novel genetic variants in the MMR genes. The AMSII criteria was the most used clinical criteria to identify pathogenic MMR carriers although microsatellite instability, immunohistochemistry and family history are still the primary methods in several countries where no genetic testing for LS is available yet.
Conclusion
The Latin America LS pathogenic MMR variants spectrum included new variants, frequently altered genetic regions and potential founder effects, emphasizing the relevance implementing Lynch syndrome genetic testing and counseling in all of Latin America countries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
LS is caused by a defective mismatch repair (MMR) system, due to the presence of germline defects in at least one of the MMR genes, MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2, or to deletions of the 3′ portion of the EPCAM gene [1]. Such variants are here referred to as path_MMR and, when specifying one of the genes, as path_MLH1, path_MSH2, path_MSH6, path_PMS2 or path_EPCAM [2, 3]. LS is clinically classified according to the Amsterdam (AMS) criteria and/or the Bethesda guidelines, both relying in clinical information and family history. The Bethesda guidelines also takes into account the microsatellite instability (MSI) tumor marker, which is a signature characteristic of MMR-deficient tumors [4,5,6,7]. MSI or immuno-histochemical (IHC) testing of tumors are strategies to select patients for subsequent germline diagnostic testing in blood [8].
LS patients have an increased lifetime risk of colorectal cancer (CRC) (70–80%), endometrial cancer (50–60%), stomach cancer (13–19%), ovarian cancer (9–14%), cancer of the small intestine, the biliary tract, brain as well as carcinoma of the ureters and renal pelvis [9]. The cumulative incidence of any cancer at 70 years of age is 72% for path_MLH1 and path_MSH2 carriers but lower in path_MSH6 (52%) and path_PMS2 (18%) carriers. Path_MSH6 and path_PMS2 carriers do not have an increased risk for cancer before 40 years of age [2, 3]. The identification of LS patients is a goal because an early diagnosis and intensive screening may predict the disease and/or improve the disease prognosis [2].
The path_MMR variant spectrum of LS has been widely studied in CRC patients from North America, Europe, Australia and Asia. In the past decade, significant advances have been made in molecular testing and genetic counseling for LS in several Latin America countries [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51].
A broad definition of Latin America is that all countries of the Americas south of the United States are included, with Mexico, Cuba, Puerto Rico and all the countries located in South America as well as the Caribbean Islands. Latin America presents with genetically somewhat different populations, where European and African immigrants have a concentration of the Caucasian population in the southern regions of the continent, whereas in the northern region, the population is predominantly Mestizo (a mixture of European and Amerindian) [52].
Among LS patients, the prevalence of path_MLH1 is 42%, path_MSH2 is 33%, path_MSH6 is 18% and path_PMS2 is 8% [53]. However, recent studies in Latin America LS families described the predominance of path_MSH2 (46%- 66%), followed by path_MLH1 (25%–43%), path_MSH6 (7%–8%), path_PMS2 (2%) and path_EPCAM (2%) [32, 36, 47]. Some Latin America LS variant spectrum included variants that have not previously been reported and potential founder effects which are useful for future development of genetic testing in these populations. It enables the comparison of LS characteristics and MMR variants across genetic ancestry background differences among these populations [12, 20, 23, 26, 32, 36, 40].
The clinical, molecular and MMR variant spectrum of LS has not been fully studied in all Latin America countries. Our study aims to combine both unpublished register data and published data in order to better describe the LS molecular profile and to update the previously described South American path_MMR variant spectrum study [32].
Methods
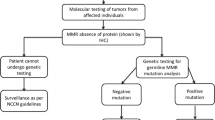
Unpublished data from hereditary cancer registries and published data from patients with suspected LS from Latin America have been included in this work. Through research collaborations, data from the Latin America hereditary cancer registers are available following direct contact with the register. The data include results from germline DNA testing, tumor testing (based on MSI analysis and/or IHC) and family history (Fig. 1).
Hereditary cancer registries
Families that fulfilled the AMSII criteria [4, 5], the Bethesda guidelines [6] and/or other criteria i.e. families suggestive of a dominant CRC inheritance syndrome were selected from 11 hereditary cancer registries from 8 countries: Hospital Italiano (Buenos Aires, Argentina), Hospital Español de Rosario (Rosario, Argentina), Hospital Privado Universitario de Cordoba (Cordoba, Argentina), Centro de Enfermedades Neoplasicas Oncovida (La Paz, Bolivia), Barretos Cancer Hospital (Barretos, Brazil), Hospital de Clinicas de Porto Alegre (Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil), Clinica Las Condes (Santiago, Chile), Clinica del Country (Bogota, Colombia), Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia (Mexico City, Mexico), Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplasicas (Lima, Peru) and Hospital de las Fuerzas Armadas (Montevideo, Uruguay).
Patients were informed about their inclusion into the registries, which generally contained data on family history, clinical information, age at onset and results of DNA testing or tumor screening in the diagnosis of LS. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants during genetic counseling sessions.
LS databases
A systematic review was performed in order to identify published reports on MMR variants in LS or hereditary CRC by querying the PubMed, SciELO and Google databases using specific key words (focusing on clinical, tumor or genetic testing information associated with the MMR genes) and taking into account publications in three languages, namely Spanish, English and Portuguese, up to July 2016. The search terms were “Lynch syndrome”, “hereditary colorectal cancer”, “hereditary colorectal cancer and Latin America” and “Lynch syndrome and Latin America”. We also used keywords in association with the names of Latin America countries (e.g., “Lynch syndrome and Colombia”). The results of the search were subsequently screened for the presence of path_MMR variants or tumor screening, clinical diagnosis and family history.
We found 34 LS reports from 12 countries including Argentina [10, 14, 17, 18], Brazil [11, 15, 19, 22, 25, 28, 29, 37, 38, 43], Chile [20, 31], Colombia [12, 16, 23, 48], Mexico [27, 44, 49, 51], El Salvador and Guatemala [51], Paraguay [50], Peru [24, 33, 35, 45], Puerto Rico and Dominican Republic [21, 36], South America [26, 32, 47] and Uruguay [13].
Germline DNA testing
Genetic testing was generally based on Sanger sequencing of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and/or PMS2 and/or EPCAM in 7 participating centers from Argentina (Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires and Hospital Español de Rosario), Brazil (Barretos Cancer Hospital and Hospital de Clinicas de Porto Alegre), Chile (Clinica Las Condes), Colombia (Clinica del Country) and Uruguay (Hospital de Las Fuerzas Armadas). Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) was used to analyze genomic rearrangements in MMR and EPCAM genes (SALSA kit P003, MRC-Holland, Amsterdam, Netherland). For PMS2 analysis, especially for exons 12 to 15, to ensure the correct analysis of PMS2 and to avoid pseudogene co-amplification, a long-range PCR followed by a nested PCRs strategy was adopted. After amplification, sequencing was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
In addition, we took into consideration the results of germline DNA testing described in 15 previously published LS reports [10, 13, 17, 18, 20, 23, 26, 31, 32, 36, 37, 44, 47, 48, 51].
Tumor testing
Methods to assess tumor MMR status, e.g. MSI analysis and/or MMR protein staining are being currently used in Cordoba (Argentina), Lima (Peru), La Paz (Bolivia) and Mexico City (Mexico) as an approach to identify potential carriers of germline path_MMR variants. Germline MMR testing is then mandatory to confirm LS cases.
Families from Peru (Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplasicas) were evaluated for MSI using a 5-mononucleotide marker panel (BAT-25, BAT-26, D2S123, D17S250 and D5S346). Tumors were classified into three categories and defined as MSI high (MSI-H) when ≥2 markers were unstable, MSI low (MSI-L) when one marker was unstable and microsatellite stable (MSS) when none of the markers were unstable. In Bolivia (Centro de Enfermedades Neoplasicas Oncovida), MSI analysis was evaluated by 1-mononucleotide marker panel (BAT-26).
IHC analysis for MMR protein expression was performed on paraffin-embedded tumor tissue sections, as previously described [32]. In Argentina (Hospital Privado Universitario de Cordoba), Mexico (Instituto Nacional de Cancerologia) and Peru, IHC was evaluated using 4-MMR proteins (MLH1, PMS2, MSH2 and MSH6).
Besides the information directly retrieved from these participating centers, we also collected MSI and/or IHC data from 15 LS published reports [14,15,16, 18, 21, 22, 24, 25, 27, 28, 31, 35, 38, 43, 45].
Family history
Available data of family history of patients with CRC included 4 published reports from Brazil [19], Mexico [49], Paraguay [50] and Peru [33].
MMR variants nomenclature and classification
The nomenclature guidelines of the Human Genome Variation Society (HGVS) were used to describe the detected MMR variants [54]. Variants were described by taking into account the following reference sequences: NM_000249.2 (MLH1), NM_000251.2 (MSH2), NM_000179.2 (MSH6), and NM_001322014.1 (PMS2). The recurrence or novelty of the identified variants was established by interrogating four databases (in their latest releases as of August 2016): the International Society of Gastrointestinal Hereditary Tumors (InSIGHT) database (accessed via the Leiden Open Variation Database/LOVD), the Universal Mutation Database (UMD), ClinVar, and the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD).
The MMR variants were classified according to the 5-tier classification system into the following categories: class 5 (pathogenic), class 4 (likely pathogenic), class 3 (uncertain variants), class 2 (likely not pathogenic) and class 1 (not pathogenic) [55]. Novel MMR variants were considered class 5 if they: a) introduced a premature stop codon in the protein sequence (nonsense or frameshift); b) occurred at the most conserved positions of donor or acceptor splice sites (i.e. IVS ± 1, IVS ± 2); or c) represented whole-exon deletions or duplications.
Well established polymorphisms, Class 1 variants and Class 2 variants were considered normal variants and not included in this study, except for the MSH6 c.733A > T, which has conflicting interpretations of pathogenicity. We focused on Class 3, Class 4 and Class 5 variants in this study.
In addition, we updated our previous South American LS study [32] according to the 5-tier classification system, with InSiGHT updates [55].
Splicing-dedicated bioinformatics analysis
The potential impact on RNA splicing induced by the MMR variants was evaluated by focusing on alterations of donor and acceptor splice sites. We took into consideration both the potential impairment of reference splice sites and the possibility of creation of de novo splice sites. The analysis was performed by using the MaxEntScan algorithm [56] interrogated by using the Alamut software (Interactive Biosoftware, France) [57, 58]. For stratification purposes, negative alterations of reference splice sites were deemed important when MaxEntScan scores showed ≥15% decrease relative to corresponding wild-type splice sites [57]. The possibility of variant-induced de novo splice sites was assessed by annotating all increments in local MaxEntScan scores and comparing their values with those of reference splice sites as well as of nearby cryptic splice sites. In this case and for exonic variants, only scores equal or higher to those of the corresponding reference splice site within the same exon (as well as of local cryptic sites) were considered worth noting. In the case of intronic variants, only scores equal or higher to those of the weakest corresponding reference splice site within the same gene (as well as of local cryptic splice sites) were considered as potentially creating de novo splice sites.
Statistical analysis
Clinical characteristics were described using frequency distributions for categorical variables and summary measures for quantitative variables. To assess comparability of study groups, chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test was used for categorical variables and Student’s t test or Mann-Whitney to compare quantitative variables.
The statistical analyses were performed using the statistical software package IBM SPSS Statistics 20 (SPSS©, Chicago, IL, USA) and STATA 12© (StataCorp. 2011. Stata Statistical Software: Release 12. College Station, TX: StataCorp LP).
Results
Path_MMR variants
By combining data provided by 7 participating centers, we identified suspected LS in a total of 881 Latin America individuals belonging to 344 unrelated families (Table 1, Fig. 1). Path_MMR genes were identified in 47% (range 39–64% depending on the participating countries/registries) of the families that fulfilled the AMSII criteria and/or the Bethesda guidelines and/or other criteria (Table 1). When the AMSII criteria were considered, the path_MMR genes detection raised to 64% (91/142), whereas 32% (54/170) and 23% (11/47) fulfilled the Bethesda guidelines and other criteria, respectively. The range of the mean age at diagnosis was 32–45 years for CRC and 43–51 years for endometrial cancer depending on the countries/registries (Table 1). Of the 410 path_MMR carriers, MLH1 was affected in 53.9% (221/410) of the cases, MSH2 in 32.4% (133/410), MSH6 in 9.5% (39/410), PMS2 in 3.4% (14/410) and EPCAM in 0.8% (3/410) (Table 1).
Fifteen published data from Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Dominican Republic, El Salvador, Guatemala, Mexico, Puerto Rico, South America and Uruguay contained information about 962 tested individuals belonging to 1514 suspected LS families (Table 2, Fig. 1). Path_MMR variants were identified in 40% (389/962) (range 25–100% in the different databases/countries) of the families that fulfilled the AMSII criteria and/or the Bethesda guidelines and/or other criteria. The range of the mean age at diagnosis was 35–45 years for CRC and 41–49 years for endometrial cancer in the different databases (Table 2). Of the 389 path_MMR carriers, MLH1 was affected in 52.4% (204/389), MSH2 in 42.7% (166/389), MSH6 in 3.6% (14/389), PMS2 in 0.8% (3/389) and EPCAM in 0.5% (2/389) (Table 2).
Latin America MMR variants
In total, 220 unique alterations were identified, including 71 frameshift variants, 50 missense variants, 40 nonsense variants, 36 intronic variants and 23 large deletions/duplications. Frameshift and missense variants were the most common alterations (32% and 23%, respectively), followed by nonsense variants (18%), intronic variants (16%) and large deletions/duplications (11%) (Fig. 2, Table 3).
By the MaxEntScan algorithm, we found that 12% of the variants in our cohort are expected to have a negative impact on RNA splicing (Table 3). Indeed, for 27 out of the 220 variants, the MaxEntScan algorithm predicts a significant decrease in splice site strength (>15% decrease in MaxEntScan scores relative to corresponding wild-type splice sites). These include 23 intronic variants (7 within acceptor sites and 16 at donor sites) and 4 exonic variants (located either at the penultimate or at the last position of the exon). Among these variants, 24 are already considered pathogenic (either Class 4 or Class 5, with MaxEntScan scores ranging from −23% to −100% of WT), including 15 variants located at the most conserved positions of the consensus splice sites, i.e. IVS ± 1 or IVS ± 2, and a nonsense mutation located at the penultimate position of MLH1 exon 8. The three-remaining potential splicing mutations are either currently considered as Class 3 (MLH1 c.588G + 5G > C, and PMS2 c.1144G > C) or have not yet been reported (MLH1 c.588 + 5G > T). Further studies will be necessary to determine if these three variants cause splicing alterations as predicted by MaxEntScan (decrease in donor splice site strength, MaxEntScan scores ranging from −27% to −55% of WT), and if they are pathogenic or not.
Our in-silico assessment of potential variant-induced de novo splice sites (data not shown) indicates that 3 out of the 220 variants analyzed in this study are likely to create new splice sites. More precisely, MLH1 c.117-1G > T is predicted to destroy the acceptor site of MLH1 exon 2 and to concomitantly create a potential new and stronger acceptor site 5 nucleotides downstream, within the exon; MSH2 c.645 + 1_645 + 10delins15 is expected to destroy the donor site of MSH2 exon 3 and to create a new donor site 14 nucleotides downstream the reference site, within intron 8; and PMS2 c.804-1G > T is predicted to destroy the acceptor site of PMS2 exon 8 and to concurrently create a new and stronger acceptor site, 8 nucleotides downstream, within the exon. These in silico predictions support the classification of MLH1 c.117-1G > T, MSH2 c.645 + 1_645 + 10delins15 and PMS2 c.804-1G > T as pathogenic (Table 3).
Though the single nucleotide variants (SNV) were spread over the genes, most frequently affected regions included exons 11 of MLH1 (15%), exon 3 and 7 of MSH2 (17 and 15%), exon 4 of MSH6 (65%) and exons 11 and 13 of PMS2 (31% and 23%).
We found that the Latin America LS variant spectrum was broad with 80% (175/220) alterations being private i.e., observed in a single family, 15% (33/220) observed in 2–3 families and 6% (12/220) variants observed in ≥4 families. Forty-one variants (19%) had not previously been reported in LS, and thus herein represent novel genetic variants in the MMR genes (including 10 in MLH1, 13 in MSH2, 11 in MSH6, 5 in PMS2 and 2 in EPCAM). The classification of the remaining 179 variants is indicated in Table 3, 37 variants being currently considered as Class 3, 10 as Class 4, 131 as Class 5 and 1 has conflicting interpretations of pathogenicity (Table 3, Fig. 3). The variants have been submitted to the InSiGHT locus-specific database (https://www.insight-group.org).
In total, 45 MMR variants identified in at least two families were classified as recurrent. Among these, the MLH1 c.1276C > T and the MSH2 c.2152C > T were identified in ≥7 families from different Brazilian cities and the MLH1 c.665del was identified in 4 unrelated Uruguayan families. Recurrent pathogenic variants shared by more than one South American country, include: the MLH1 c.350C > T, c.1852_1854del and the c.2041G > A. More precisely, the MLH1 c.350C > T was identified in 5 unrelated families from Uruguay and Argentina, the MLH1 c.1852_1854del was detected in 6 unrelated families from Argentina, Brazil, El Salvador and Mexico, and the MLH1 c.2041G > A was observed in 7 unrelated families from Chile, Colombia and Brazil. These variants may thus represent frequent MLH1 variants in South American population. Moreover, we found a high incidence of intronic and not previously reported MSH6 and PMS2 variants in Argentina (Table 3).
Founder variants
Here, we identified 16 international founder variants: 8 in MLH1,7 in MSH2 and 1 in MSH6 pathogenic variants in 27 LS families [23, 34, 36, 59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74] (Table 4). International founder pathogenic variants detected in >2 unrelated LS families included e.g. MLH1 c.545 + 3A > G identified as an Italian founder pathogenic variant [75], MSH2 c.388_389del as a Portuguese founder variant identified in Argentina [69]. The MSH2 c.942 + 3A > T was found in 2 unrelated Brazilian families and widely described as a Newfoundland founder variant. It had been identified in different populations and could be considered as a world-wide MSH2 variant [26, 64]. The MLH1 c.1039-8T_1558 + 896Tdup has been suggested to represent a founder MMR variant in Colombia [23]. In line with the Portuguese influence in Brazil, the MLH1 c.1897-?_2271 +?del encompassing exons 17 to 19 have been identified in 4 unrelated Brazilian families [69, 70]. The MLH1 c.2044_2045del have been recently described as a founder variant in Puerto Rico [34, 36] and the MSH2 c.1077-?_1276 +?del as a Spanish founder Alu-mediated rearrangement which have been identified in Argentina, Uruguay and Brazil [67].
Update of the MMR variants from the previous South America LS study
Due to changes in InSIGHT classification of variants, 14 variants were altered for the MLH1 gene and 2 for the MSH2 gene, relative to our previous classification in Dominguez-Valentin et al. [32]. For MLH1, 3 previously classified Class 5 variants were downgraded to Class 4, while 4 previously classified Class 5 were moved to Class 3 and 3 previously classified Class 5 were moved to Class 1 (MLH1: c.1558 + 14G > A, c.1852_1853delinsGC, c.1853A > C). Three MLH1 variants were updated in their nomenclature. For MSH2 gene, two variants were updated in their nomenclature (Table 3).
Differences between LS patients according to the path_MMR gene
The clinicopathological characteristics evaluated were similar between path_MLH1, path_MSH2, path_MSH6, path_PMS2 and path_EPCAM carriers, except for the mean age at CRC diagnosis for MLH1 (39.6 years) and MSH2 carriers (41.5 years) (p ≤ 0.05) (Table 5). For path_MLH1 carriers, we observed that the probands had more family history of CRC (56.4%) than LS-associated cancers (20.1%) and 97% fulfilled the AMSII criteria. LS individuals with path_MSH2, path_MSH6 and path_PMS2 were mostly females (63.5%, 90% and 77.8% respectively). Path_MSH2 carriers fulfilled AMSII criteria (100%) while path_MSH6 and path_PMS2 carriers had more family history of CRC (30% and 75%, respectively) than LS-associated cancers (10% and 25%, respectively). Path_EPCAM carriers had a lower number for each clinical characteristic (Table 5). Deviating distributions of the parameters discussed above for path_MSH6 and especially path_PMS2 carriers may have escaped significance due to limited number of carriers included.
Tumor testing results
Tumors specimens from 83 individuals from Peru, 6 from Argentina, 61 from Bolivia, and 60 from Mexico were analyzed either by IHC and MSI-testing, MSI-testing only, or IHC only, respectively, (Table 6). Of these, 69 (32.8%) were found to have MMR-deficient tumors as determined by IHC or MSI analysis (Table 6). The range of the mean age at diagnosis was 27–43 years for CRC and 37–52 years for endometrial cancer in the different registries. The prevalence of deficient MMR protein expression (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2) among Peruvian, Argentinean and Mexican patients was 48%, 50% and 38%, respectively, with most cases having absence of MLH1 protein (data available upon request). Regardless of their MMR proficiency status (proficient vs. deficient), patients had similar ages at CRC diagnosis and gender (Table 7). As shown in Table 7, family history of CRC was increased in MMR-deficient individuals compared to MMR proficient (P ≤ 0.05). Interestingly, AMSII criteria were more frequently fulfilled among MMR deficient (42.4%) than MMR-proficient (10.9%) individuals and this difference was statistically significant (P ≤ 0.05) (Table 7).
Compilation of IHC and MSI data from reports on Latin America LS cases (published results and/or database entries) revealed that 21% had MMR deficiency based on IHC and/or MSI analysis (2.5%–60%). No information was available for the mean age at CRC and endometrial cancer diagnosis (Table 8). This data highlights the importance of genetic testing for LS in these populations.
Family history
Since there are no premonitory signs of susceptibility to LS, family history has been the primary method for identifying patients at risk in Brazil, Mexico, Peru and Paraguay. Four published reports showed that 11.5% (107/931) were selected as likely LS on the basis of a positive family history (Table 9).
Discussion
Progress has been achieved throughout the past years regarding a better molecular and clinical characterization of LS in Latin America, which is important for the surveillance and management of high-risk patients and their families [2].
Here, we present the first thorough LS investigation in Latin America by taking into account 15 different countries. We found that germline genetic testing for LS is already available in six of these countries (Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Uruguay and Puerto Rico). Moreover, in three countries (Bolivia, Peru and Mexico), where genetic testing is not yet implemented, tumor analyses are already performed for identifying patients most likely to carry a path_MMR variant.
According to our data, the contribution from the different MMR genes is apparently slightly higher for MLH1 and MSH2 and lower for MSH6 and PMS2 when comparing to the InSIGHT database and international reports. It is possible that this pattern reflects the recent inclusion of MSH6, PMS2 and EPCAM in LS genetic testing in Latin America molecular diagnostic laboratories but could also reflect population structure [32, 48, 76, 77]. Interestingly, the clinicopathological features of path_MMR carriers described in Latin America families are in accordance with other studies, e.g. the AMSII criteria were fulfilled by 64% of the path_MMR carriers [37, 77].
This study revealed that the Latin America spectrum of MMR variants is broad with a total of 220 different variants, of which 80% are currently considered as private, whereas 20% are deemed as recurrent. Our data support evidence on a significant contribution from large deletions/duplications in EPCAM and frameshift variants in MLH1 and MSH2. Of the 220 MMR variants, 178 were already listed in the InSiGHT database or previous studies [78, 79], whereas 41 have not been previously reported in LS [80]. In addition, we observed that MSH2 variants most frequently caused disease in Argentinean LS families. Further studies are needed to elucidate the ancestral origin of MMR variants in this population, which may increase the knowledge on the inheritance of LS among affected Latin America individuals [10, 14, 17, 40].
Differences in the spectrum of path_MMR variants between populations could be due to differences in the sample size, clinical criteria, selection bias, as well as, genetic ancestry of the individual populations. For instance, Caribbean Hispanics have higher percentage of African ancestry compared to Argentineans and Uruguay nationals [36]. Puerto Ricans are an admixed population of three ancestral populations, including European, Africans and Taínos [36]. The South American population is ethnically mixed from American Indian, European, and other ancestries, but the proportions may vary between countries. For instance, European ancestry predominates in Uruguay and Argentina, whereas Brazil includes a more heterogeneous population, which is the result of interethnic crosses between the European colonizers (mainly Portuguese), African slaves, and the autochthonous Amerindians [15]. The Peruvian population is a multi-ethnic population with Amerindian (45%), Mestizo (37%), white Spanish influence (15%), as well as other minority ethnic groups, such as African-American, Japanese, and Chinese (3%) [24]. In Chile, Colombia and Bolivia, Spanish colonist and American Indian ancestry influence the populations [20, 32].
It is well established that awareness of founder variants in a specific geographic area or population can be very helpful in designing cost-effective molecular diagnostic approaches [70, 81, 82]. Founder mutations provide molecular diagnostic centers the benefit of unambiguous results and thereby, do not demand high skilled professional training.
The other aim of the study was to investigate if the previously MMR variants identified in South American LS families [32] are in accordance with the 5-tier classification system [55]. We were able to refine the classification of 16 MLH1 and MSH2 variants.
When the tumor MMR data from original and published studies were combined, up to 33% of suspected LS individuals had MMR deficiency. The frequency of MMR deficiency was lower than that reported in studies focusing in American, Spanish and Australian LS families (56%–72%) but is in line to the reported prevalence of MSI in sporadic CRC among Hispanic patients [34, 83,84,85,86]. These differences could also be a reflect of the differences in the tumor testing methodologies across the countries, e.g. MSI analysis is not widely available in the majority of routine pathology service laboratories, the number of MSI mononucleotide markers varies between laboratories as well as the limitation in the number of MMR proteins analyzed by IHC. Moreover, even if MMR deficiency is a good predictor of carrying a germline path_MMR variant, MMR deficiency can also result from somatic inactivation, most commonly due to methylation of the MLH1 promoter [86]. IHC and MSI testing will, however, combined identify most LS patients with high sensitivity and specificity.
In Latin America, low budgets make the issue of integrating genetics into clinical practice a challenge, a situation in which the use of family history becomes important for patient care, as it is a low-cost strategy and a risk assessment tool [19]. In this scenario, published family history data from Paraguay, Peru, Brazil and Mexico suggest its use as a triage tool together with IHC and MSI to identify and stratify genetic risk in these populations [19]. However, awareness of hereditary cancer among clinicians involved in diagnosis and treatment of CRC is currently low, and families actually meeting the clinical criteria may not be identified [77]. In addition, the average life expectancy in Latin America and the Caribbean is 75 years and inequalities persist among and within the countries (www.paho.org). These countries are mainly represented by a young population where family history could be less informative and insensitive for assessing genetic screening for LS.
Limitation on genetic testing has an impact in the evaluation of the patients at risk of hereditary cancer and their relatives, and ultimately increases the burden of cancer for this minority population [35]. As mentioned, in Latin America, genetic testing is not routinely available at the public health system, with exception of few studies conducted in research institutes or private institutions. For instance, until recently the coverage of oncogenetic services in Brazil, was restricted to less than 5% of the population. However, a significant advance took place in 2012, when the coverage of genetic testing by private health care plans became mandatory in Brazil, currently covering around 20–30% of the population [19, 87].
This work provides a snapshot view of the current LS-associated diagnostics practice/output in Latin America. The limitations of this study include the selection of patients recruited from selected reference centers and/or from a nation-wide public reference hospital for cancer patients that cannot renders a representative sample. Furthermore, the diagnostic methodologies may vary between the countries regarding the coverage of the coding region of the genes tested and the clinical criteria for referral to genetic counseling and testing, thus causing an even larger knowledge gap. Finally, several countries are not represented; for instance, we could not find any reports from Venezuela, Honduras, Nicaragua or Ecuador. It will be important to pursue additional studies on LS in Latin America countries to both increase the knowledge of MMR variants in different populations and to bring additional awareness of this condition to medical professionals and public health leaders in Latin America.
Conclusions
The Latin America LS MMR variants spectrum included new MMR variants, genetic frequent regions and potential founder effect. The present study provides support to set or improve LS genetic testing in these countries. Improving the accessibility, including tertiary care, is vital in low-income and middle-income countries that face an increasing burden of CRC. An early diagnosis and intensive screening may predict the disease and/or improve the disease prognosis. Low cost approaches to reach these ends are discussed.
Abbreviations
- AMS:
-
Amsterdam
- AMSII:
-
Amsterdam II criteria
- CRC:
-
colorectal cancer
- HGMD:
-
Human Gene Mutation Database
- HGVS:
-
Human Genome Variation Society
- IHC:
-
immunohistochemical
- InSIGHT:
-
International Society of Gastrointestinal Hereditary Tumors
- LOVD:
-
Leiden Open Variation Database
- LS:
-
Lynch syndrome
- MMR:
-
mismatch-repair gene
- MSI:
-
microsatellite instability
- MSI-H:
-
MSI high
- MSI-L:
-
MSI low
- MSS:
-
microsatellite stable
- path_MLH1 :
-
Pathogenic (disease-causing) variant of the MLH1 gene
- Path_MMR:
-
Pathogenic (disease-causing) variant of an MMR gene.
- path_MSH2 :
-
Pathogenic (disease-causing) variant of the MSH2 gene
- path_MSH6 :
-
Pathogenic (disease-causing) variant of the MSH6 gene
- path_PMS2 :
-
Pathogenic (disease-causing) variant of the PMS2 gene
- UMD:
-
Universal Mutation Database
References
Kuiper RP, Vissers LE, Venkatachalam R, Bodmer D, Hoenselaar E, Goossens M, Haufe A, Kamping E, Niessen RC, Hogervorst FB, et al. Recurrence and variability of germline EPCAM deletions in Lynch syndrome. Hum Mutat. 2011;32(4):407–14.
Moller P, Seppala T, Bernstein I, Holinski-Feder E, Sala P, Evans DG, Lindblom A, Macrae F, Blanco I, Sijmons R, et al. Cancer incidence and survival in Lynch syndrome patients receiving colonoscopic and gynaecological surveillance: first report from the prospective Lynch syndrome database. Gut. 2015;66(3):464–72.
Moller P, Seppala T, Bernstein I, Holinski-Feder E, Sala P, Evans DG, Lindblom A, Macrae F, Blanco I, Sijmons R, et al. Incidence of and survival after subsequent cancers in carriers of pathogenic MMR variants with previous cancer: a report from the prospective Lynch syndrome database. Gut. 2016;
Vasen HF, Mecklin JP, Khan PM, Lynch HT. The international collaborative group on hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (ICG-HNPCC). Dis Colon Rectum. 1991;34(5):424.
Vasen HF, Watson P, Mecklin JP, Lynch HT. New clinical criteria for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC, Lynch syndrome) proposed by the international collaborative group on HNPCC. Gastroenterology. 1999;116(6):1453–6.
RodriguezBigas MA, Boland CR, Hamilton SR, Henson DE, Jass JR, Khan PM, Lynch H, Perucho M, Smyrk T, Sobin L, et al. A National Cancer Institute workshop on hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer syndrome: meeting highlights and Bethesda guidelines. J Natl Cancer I. 1997;89(23):1758–62.
Umar A, Srivastava S. The promise of biomarkers in colorectal cancer detection. Dis Markers. 2004;20(2):87–96.
Evaluation of Genomic Applications in P, Prevention Working G. Recommendations from the EGAPP working group: genetic testing strategies in newly diagnosed individuals with colorectal cancer aimed at reducing morbidity and mortality from Lynch syndrome in relatives. Genet Med. 2009;11(1):35–41.
Kobayashi H, Ohno S, Sasaki Y, Matsuura M. Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility genes (review). Oncol Rep. 2013;30(3):1019–29.
Roque M, Pusiol E, Giribet G, Perinetti H, Mayorga LS. Diagnosis of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer by site directed mutagenesis in a family with a mutation at the hMSH2 gene. Medicina-Buenos Aire. 2000;60(2):188–94.
Rossi BM, Lopes A, Oliveira Ferreira F, Nakagawa WT, Napoli Ferreira CC. Casali Da Rocha JC, Simpson CC, Simpson AJ: hMLH1 and hMSH2 gene mutation in Brazilian families with suspected hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9(6):555–61.
Giraldo A, Gomez A, Salguero G, Garcia H, Aristizabal F, Gutierrez O, Angel LA, Padron J, Martinez C, Martinez H, et al. MLH1 and MSH2 mutations in Colombian families with hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome)--description of four novel mutations. Familial Cancer. 2005;4(4):285–90.
Sarroca C, Valle AD, Fresco R, Renkonen E, Peltomaki P, Lynch H. Frequency of hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer among Uruguayan patients with colorectal cancer. Clin Genet. 2005;68(1):80–7.
Chialina SG, Fornes C, Landi C, Elena CDD, Nicolorich MV, Dourisboure RJ, Solano A, Solis EA. Microsatellite instability analysis in hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer using the Bethesda consensus panel of microsatellite markers in the absence of proband normal tissue. Bmc Med Genet. 2006;7
Clarizia AD, Bastos-Rodrigues L, Pena HB, Anacleto C, Rossi B, Soares FA, Lopes A, Rocha JC, Caballero O, Camargo A, et al. Relationship of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism with microsatellite instability and promoter hypermethylation in sporadic colorectal cancer. Genet Mol Res. 2006;5(2):315–22.
Montenegro Y, Ramirez-Castro JL, Isaza LF, Bedoya G, Muneton-Pena CM. Microsatellite instability among patients with colorectal cancer. Rev Med Chile. 2006;134(10):1221–9.
Vaccaro CA, Bonadeo F, Roverano AV, Peltomaki P, Bala S, Renkonen E, Redal MA, Mocetti E, Mullen E, Ojea-Quintana G, et al. Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome) in Argentina: report from a referral hospital register. Dis Colon Rectum. 2007;50(10):1604–11.
Vaccaro CA, Carrozzo JE, Mocetti E, Berho M, Valdemoros P, Mullen E, Oviedo M. Redal MA: [Immunohistochemical expression and microsatellite instability in Lynch syndrome]. Medicina (B Aires). 2007;67(3):274–8.
Viana DV, Goes JRN, Coy CSR, Ayrizono MDS, Lima CSP, Lopes-Cendes I. Family history of cancer in Brazil: is it being used? Familial Cancer. 2008;7(3):229–32.
Alvarez K, Hurtado C, Hevia MA, Wielandt AM, de la Fuente M, Church J, Carvallo P, Lopez-Kostner F. Spectrum of MLH1 and MSH2 mutations in Chilean families with suspected Lynch syndrome. Dis Colon Rectum. 2010;53(4):450–9.
De Jesus-Monge WE, Gonzalez-Keelan C, Zhao RH, Hamilton SR, Rodriguez-Bigas M, Cruz-Correa M. Mismatch repair protein expression and colorectal cancer in Hispanics from Puerto Rico. Familial Cancer. 2010;9(2):155–66.
Leite SMO, Gomes KB, Pardini VC, Ferreira ACS, Oliveira VC, Cruz GMG. Assessment of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer patients from Brazil. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37(1):375–80.
Alonso-Espinaco V, Giraldez MD, Trujillo C, van der Klift H, Munoz J, Balaguer F, Ocana T, Madrigal I, Jones AM, Echeverry MM, et al. Novel MLH1 duplication identified in Colombian families with Lynch syndrome. Genet Med. 2011;13(2):155–60.
Egoavil CM, Montenegro P, Soto JL, Casanova L, Sanchez-Lihon J, Castillejo MI, Martinez-Canto A, Perez-Carbonell L, Castillejo A, Guarinos C, et al. Clinically important molecular features of Peruvian colorectal tumours: high prevalence of DNA mismatch repair deficiency and low incidence of KRAS mutations. Pathology. 2011;43(3):228–33.
Koehler-Santos P, Izetti P, Abud J, Pitroski CE, Cossio SL, Camey SA, Tarta C, Damin DC, Contu PC, Rosito MA, et al. Identification of patients at-risk for Lynch syndrome in a hospital-based colorectal surgery clinic. World J Gastroentero. 2011;17(6):766–73.
Valentin MD, da Silva FC, dos Santos EMM, Lisboa BG, de Oliveira LP, Ferreira FD, Gomy I, Nakagawa WT, Aguiar S, Redal M, et al. Characterization of germline mutations of MLH1 and MSH2 in unrelated south American suspected Lynch syndrome individuals. Familial Cancer. 2011;10(4):641–7.
Ramirez-Ramirez MA, Sobrino-Cossio S, de la Mora-Levy JG, Hernandez-Guerrero A, Macedo-Reyes Vde J, Maldonado-Martinez HA, Alonso-Larraga JO, Ramirez-Solis ME. Loss of expression of DNA mismatch repair proteins in aberrant crypt foci identified in vivo by magnifying colonoscopy in subjects with hereditary nonpolyposic and sporadic colon rectal cancer. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2012;43(2):209–14.
Rasuck CG, Leite SMO, Komatsuzaki F, Ferreira ACS, Oliveira VC, Gomes KB. Association between methylation in mismatch repair genes, V600E BRAF mutation and microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer patients. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(3):2553–60.
Santos EMM, Valentin MD, Carneiro F, de Oliveira LP, Ferreira FD, Aguiar S, Nakagawa WT, Gomy I, Ferraz VED, da Silva WA, et al. Predictive models for mutations in mismatch repair genes: implication for genetic counseling in developing countries. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:1–9.
Valentin MD, Da Silva FC, Santos EM, Da Silva SD, De Oliveira FF, Aguiar Junior S, Gomy I, Vaccaro C, Redal MA, Della Valle A, et al. Evaluation of MLH1 I219V polymorphism in unrelated south American individuals suspected of having Lynch syndrome. Anticancer Res. 2012;32(10):4347–51.
Wielandt AM, Zarate AJ, Hurtado C, Orellana P, Alvarez K, Pinto E, Contreras L, Corvalan A, Kronberg U, Lopez-Kostner F. Lynch syndrome: selection of families by microsatellite instability and immunohistochemistry. Rev Med Chil. 2012;140(9):1132–9.
Dominguez-Valentin M, Nilbert M, Wernhoff P, Lopez-Kostner F, Vaccaro C, Sarroca C, Palmero EI, Giraldo A, Ashton-Prolla P, Alvarez K, et al. Mutation spectrum in South American Lynch syndrome families. Hered Cancer Clin Pr. 2013;11
Castro-Mujica Mdel C, Sullcahuaman-Allende Y, Barreda-Bolanos F, Taxa-Rojas L. Inherited colorectal cancer predisposition syndromes identified in the Instituto Nacional de Enfermedades Neoplasicas (INEN), Lima, Peru. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2014;34(2):107–14.
Marques-Lespier JM, Diaz-Algorri Y, Gonzalez-Pons M, Cruz-Correa M. Report of a novel mutation in MLH1 gene in a Hispanic family from Puerto Rico fulfilling classic Amsterdam criteria for Lynch syndrome. Gastroent Res Pract. 2014;
Nique Carbajal C, Sanchez Renteria F, Lettiero B, Wernhoff P. Dominguez-Valentin M: [molecular characterization of hereditary colorectal cancer in Peru]. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2014;34(4):299–303.
Cruz-Correa M, Diaz-Algorri Y, Perez-Mayoral J, Suleiman-Suleiman W, Gonzalez-Pons Mdel M, Bertran C, Casellas N, Rodriguez N, Pardo S, Rivera K, et al. Clinical characterization and mutation spectrum in Caribbean Hispanic families with Lynch syndrome. Familial Cancer. 2015;14(3):415–25.
da Silva FC, Ferreira JRD, Torrezan GT, Figueiredo MCP, Santos EMM, Nakagawa WT, Brianese RC, de Oliveira LP, Begnani MD, Aguiar S, et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of Brazilian patients suspected to have Lynch syndrome. PLoS One. 2015;10:10.
de Freitas IN, de Campos FG, Alves VA, Cavalcante JM, Carraro D, Coudry Rde A, Diniz MA, Nahas SC, Ribeiro U Jr. Proficiency of DNA repair genes and microsatellite instability in operated colorectal cancer patients with clinical suspicion of Lynch syndrome. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015;6(6):628–37.
Garcia GH, Riechelmann RP, Hoff PM. Adherence to colonoscopy recommendations for first-degree relatives of young patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2015;70(10):696–9.
Cajal AR, Pinero TA, Verzura A, Santino JP, Solano AR, Kalfayan PG, Ferro A. Vaccaro C: [founder mutation in Lynch syndrome]. Medicina (B Aires). 2016;76(3):180–2.
Castro-Mujica Mdel C, Barletta-Carrillo C, Acosta-Aliaga M, Montenegro-Garreaud X. Lynch syndrome, Muir Torre variant: 2 cases. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2016;36(1):81–5.
Dominguez-Valentin M, Wernhoff P, Cajal AR, Kalfayan PG, Pinero T, Gonzalez ML, Ferro A, Sammartino I, Causada NS, Vaccaro CA. MLH1 Ile219Val polymorphism in Argentinean families with suspected Lynch syndrome. Front Oncol. 2016;6:189.
Germini DE, Mader AM, Gomes LG, Teodoro TR, Franco MI, Waisberg J. Detection of DNA repair protein in colorectal cancer of patients up to 50 years old can increase the identification of Lynch syndrome? Tumour Biol. 2016;37(2):2757–64.
Moreno-Ortiz JM, Ayala-Madrigal MD, Corona-Rivera JR, Centeno-Flores M, Maciel-Gutierrez V, Franco-Topete RA, Armendariz-Borunda J, Hotchkiss E, Perez-Carbonell L, Rhees J, et al. Novel mutations in MLH1 and MSH2 genes in Mexican patients with Lynch syndrome. Gastroent Res Pract. 2016;2016:1–6.
Ortiz C, Dongo-Pflucker K, Martin-Cruz L, Barletta Carrillo C, Mora-Alferez P. Arias a: [microsatellite instability in patients with diagnostic of colorectal cancer]. Rev Gastroenterol Peru. 2016;36(1):15–22.
Rossi BM, Sarroca C, Vaccaro C, Lopez F, Ashton-Prolla P, Ferreira Fde O, Santos EM. The development of the study of hereditary cancer in South America. Genet Mol Biol. 2016;39(2):166–7.
Vaccaro CA, Sarroca C, Rossi B, Lopez-Kostner F, Dominguez M, Calo NC, Cutait R, Valle AD, Nunez L, Neffa F, et al. Lynch syndrome in South America: past, present and future. Familial Cancer. 2016;15(3):437–45.
Gomez A, Salguero G, Garcia H, Aristizabal F, Gutierrez O, Angel LA, Padron J, Martinez C, Martinez H, Malaver O, et al. Detection mutations in the DNA mismatch repair genes of hMLH1 and hMSH2 genes in Colombian families with suspicion of hereditary non-polyposis colorectal carcinoma (Lynch syndrome). Biomedica. 2005;25(3):315–24.
Mendoza Sanchez A, Sobrino Cossio S, Hernandez Guerrero A, Cordova Pluma VH, Alonso Larraga O. Sanchez del Monte D: [utility of diagnostic scales for hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer in the Mexican population]. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2005;70(4):411–5.
Recalde A. Colon cancer. Prevalence and staging in a Paraguayan university hospital. Cirugía Paraguaya. 2005;28(1):3.
Ricker C KN, Ault G, Roman L, Spicer D, Heinz-Josef L: Characteristics of Lynch syndrome in 13 Hispanic Families. Hered Cancer Clin Pract 2010, 8 (Supppl 1):19.
Risco J, Maldonado H, Luna L, Osada J, Ruiz P, Juarez A, Vizcarra D. Latitudinal prevalence gradient of multiple sclerosis in Latin America. Mult Scler. 2011;17(9):1055–9.
Plazzer JP, Sijmons RH, Woods MO, Peltomaki P, Thompson B, Den Dunnen JT, Macrae F. The InSiGHT database: utilizing 100 years of insights into Lynch syndrome. Familial Cancer. 2013;12(2):175–80.
den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE. Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion. Hum Mutat. 2000;15(1):7–12.
Thompson BA, Spurdle AB, Plazzer JP, Greenblatt MS, Akagi K, Al-Mulla F, Bapat B, Bernstein I, Capella G, den Dunnen JT, et al. Application of a 5-tiered scheme for standardized classification of 2,360 unique mismatch repair gene variants in the InSiGHT locus-specific database. Nat Genet. 2014;46(2):107–15.
Yeo G, Burge CB. Maximum entropy modeling of short sequence motifs with applications to RNA splicing signals. J Comput Biol. 2004;11(2–3):377–94.
Houdayer C, Caux-Moncoutier V, Krieger S, Barrois M, Bonnet F, Bourdon V, Bronner M, Buisson M, Coulet F, Gaildrat P, et al. Guidelines for splicing analysis in molecular diagnosis derived from a set of 327 combined in silico/in vitro studies on BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants. Hum Mutat. 2012;33(8):1228–38.
Soukarieh O, Gaildrat P, Hamieh M, Drouet A, Baert-Desurmont S, Frebourg T, Tosi M, Martins A. Exonic splicing mutations are more prevalent than currently estimated and can be predicted by using in Silico tools. PLoS Genet. 2016;12:1.
Aarnio M, Mecklin JP, Aaltonen LA, Nystrom-Lahti M, Jarvinen HJ. Life-time risk of different cancers in hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC) syndrome. Int J Cancer. 1995;64(6):430–3.
Borelli I, Barberis MA, Spina F, Cavalchini GCC, Vivanet C, Balestrino L, Micheletti M, Allavena A, Sala P, Carcassi C, et al. A unique MSH2 exon 8 deletion accounts for a major portion of all mismatch repair gene mutations in Lynch syndrome families of Sardinian origin. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013;21(2):154–61.
Borras E, Pineda M, Blanco I, Jewett EM, Wang F, Teule A, Caldes T, Urioste M, Martinez-Bouzas C, Brunet J, et al. MLH1 founder mutations with moderate penetrance in Spanish Lynch syndrome families. Cancer Res. 2010;70(19):7379–91.
Chong G, Jarry J, Marcus V, Thiffault I, Winocour S, Monczak Y, Drouin R, Latreille J, Australie K, Bapat B, et al. High frequency of exon deletions and putative founder effects in French Canadian Lynch syndrome families. Hum Mutat. 2009;30(8):E797–812.
Clendenning M, Baze ME, Sun S, Walsh K, Liyanarachchi S, Fix D, Schunemann V, Comeras I, Deacon M, Lynch JF, et al. Origins and prevalence of the American founder mutation of MSH2. Cancer Res. 2008;68(7):2145–53.
Froggatt NJ, Green J, Brassett C, Evens DGR, Bishop DT, Kolodner R, Maher ER. A common MSH2 mutation in English and north American HNPCC families: origin, phenotypic expression, and sex specific differences in colorectal cancer. J Med Genet. 1999;36(2):97–102.
Lastella P, Patruno M, Forte G, Montanaro A, Di Gregorio C, Sabba C, Suppressa P, Piepoli A, Panza A, Andriulli A, et al. Identification and surveillance of 19 Lynch syndrome families in southern Italy: report of six novel germline mutations and a common founder mutation. Familial Cancer. 2011;10(2):285–95.
Moisio AL, Sistonen P, Weissenbach J, de la Chapelle A, Peltomaki P. Age and origin of two common MLH1 mutations predisposing to hereditary colon cancer. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;59(6):1243–51.
Perez-Cabornero L, Borras Flores E, Infante Sanz M, Velasco Sampedro E, Acedo Becares A, Lastra Aras E, Cuevas Gonzalez J, Pineda Riu M, Ramon y Cajal Asensio T, Capella Munar G, et al. Characterization of new founder Alu-mediated rearrangements in MSH2 gene associated with a Lynch syndrome phenotype. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2011;4(10):1546–55.
Pinheiro M, Pinto C, Peixoto A, Veiga I, Mesquita B, Henrique R, Baptista M, Fragoso M, Sousa O, Pereira H, et al. A novel exonic rearrangement affecting MLH1 and the contiguous LRRFIP2 is a founder mutation in Portuguese Lynch syndrome families. Genet Med. 2011;13(10):895–902.
Pinheiro M, Pinto C, Peixoto A, Veiga I, Mesquita B, Henrique R, Lopes P, Sousa O, Fragoso M, Dias LM, et al. The MSH2 c.388_389del mutation shows a founder effect in Portuguese Lynch syndrome families. Clin Genet. 2013;84(3):244–50.
Ponti G, Castellsague E, Ruini C, Percesepe A, Tomasi A. Mismatch repair genes founder mutations and cancer susceptibility in Lynch syndrome. Clin Genet. 2015;87(6):507–16.
Stella A, Surdo NC, Lastella P, Barana D, Oliani C, Tibiletti MG, Viel A, Natale C, Piepoli A, Marra G, et al. Germline novel MSH2 deletions and a founder MSH2 deletion associated with anticipation effects in HNPCC. Clin Genet. 2007;71(2):130–9.
Nystrom-Lahti M, Kristo P, Nicolaides NC, Chang SY, Aaltonen LA, Moisio AL, Jarvinen HJ, Mecklin JP, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, et al. Founding mutations and Alu-mediated recombination in hereditary colon cancer. Nat Med. 1995;1(11):1203–6.
Wagner A, Barrows A, Wijnen JT, van der Klift H, Franken PF, Verkuijlen P, Nakagawa H, Geugien M, Jaghmohan-Changur S, Breukel C, et al. Molecular analysis of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer in the United States: high mutation detection rate among clinically selected families and characterization of an American founder genomic deletion of the MSH2 gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;72(5):1088–100.
Vahteristo P, Ojala S, Tamminen A, Tommiska J, Sammalkorpi H, Kiuru-Kuhlefelt S, Eerola H, Aaltonen LA, Aittomaki K, Nevanlinna H. No MSH6 germline mutations in breast cancer families with colorectal and/or endometrial cancer. J Med Genet. 2005;42:4.
Thiffault I, Foulkes WD, Marcus VA, Farber D, Kasprzak L, MacNamara E, Wong N, Hutter P, Radice P, Bertario L, et al. Putative common origin of two MLH1 mutations in Italian-Quebec hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer families. Clin Genet. 2004;66(2):137–43.
Lagerstedt-Robinson K, Rohlin A, Aravidis C, Melin B, Nordling M, Stenmark-Askmalm M, Lindblom A, Nilbert M. Mismatch repair gene mutation spectrum in the Swedish Lynch syndrome population. Oncol Rep. 2016;36(5):2823–835.
Sjursen W, McPhillips M, Scott RJ, Talseth-Palmer BA. Lynch syndrome mutation spectrum in new South Wales, Australia, including 55 novel mutations. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2016;4(2):223–31.
Casey G, Lindor NM, Papadopoulos N, Thibodeau SN, Moskow J, Steelman S, Buzin CH, Sommer SS, Collins CE, Butz M, et al. Conversion analysis for mutation detection in MLH1 and MSH2 in patients with colorectal cancer. JAMA. 2005;293(7):799–809.
Song H, Cicek MS, Dicks E, Harrington P, Ramus SJ, Cunningham JM, Fridley BL, Tyrer JP, Alsop J, Jimenez-Linan M, et al. The contribution of deleterious germline mutations in BRCA1, BRCA2 and the mismatch repair genes to ovarian cancer in the population. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(17):4703–9.
Tanyi M, Olasz J, Lukacs G, Tanyi JL, Toth L, Antal-Szalmas P, Ress Z, Buban T, Andras C, Damjanovich L. A new mutation in Muir-Torre syndrome associated with familiar transmission of different gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2009;35(10):1128–30.
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 2016;0:1–9.
Norum J, Hagen AI, Maehle L, Apold J, Burn J, Moller P. Prophylactic bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (PBSO) with or without prophylactic bilateral mastectomy (PBM) or no intervention in BRCA1 mutation carriers: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44(7):963–71.
Buchanan DD, Rosty C, Clendenning M, Spurdle AB, Win AK. Clinical problems of colorectal cancer and endometrial cancer cases with unknown cause of tumor mismatch repair deficiency (suspected Lynch syndrome). Appl Clin Genet. 2014;7:183–93.
Gupta S, Ashfaq R, Kapur P, Afonso BB, Nguyen TPT, Ansari F, Boland CR, Goel A, Rockey DC. Microsatellite instability among individuals of Hispanic origin with colorectal cancer. Cancer-Am Cancer Soc. 2010;116(21):4965–72.
Hampel H, Frankel WL, Martin E, Arnold M, Khanduja K, Kuebler P, Nakagawa H, Sotamaa K, Prior TW, Westman J, et al. Screening for the Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer). N Engl J Med. 2005;352(18):1851–60.
Rodriguez-Soler M, Perez-Carbonell L, Guarinos C, Zapater P, Castillejo A, Barbera VM, Juarez M, Bessa X, Xicola RM, Clofent J, et al. Risk of cancer in cases of suspected Lynch syndrome without Germline mutation. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(5):926.
Ashton-Prolla P, Seuanez HN. The Brazilian hereditary cancer network: historical aspects and challenges for clinical cancer genetics in the public health care system in Brazil. Genet Mol Biol. 2016;39(2):163–5.
Acknowledgements
We thank the families for their participation and contribution to this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Radium Hospital Foundation (Oslo, Norway) in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript, Helse Sør-Øst (Norway) in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript, the French Association Recherche contre le Cancer (ARC) in the analysis, and interpretation of data, the Groupement des Entreprises Françaises dans la Lutte contre le Cancer (Gefluc) in the analysis, and interpretation of data, the Association Nationale de la Recherche et de la Technologie (ANRT, CIFRE PhD fellowship to H.T.) in the analysis, and interpretation of data and by the OpenHealth Institute in the analysis, and interpretation of data. Barretos Cancer Hospital received financial support by FINEP-CT-INFRA (02/2010).
Availability of data and materials
Data from the Latin America hereditary cancer registers, this is indeed available for researchers following direct contact with the register (thus not freely available online).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BMR, MDV: Designed the study. BMR, EIP, FLK, CS, CAV, FS, PAP, YR, HCRG, RMR, AEP, LGCR, KA, ADV, FN, PGK, ES, SC, MGA, MCCM, JSM, RQ, SDS, NTR, CB, SR, XT, LML, HT, EMMS, TAP, CDB, PW, AM, EH, PM, MDV: managed and interpreted the data. SDS, HT, AM: calculated the results. MDV, PM, SDS, AM, HT and BMR wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All patients provided an informed consent for inclusion into the Latin America registers during genetic counseling sessions and is in compliance with the Helsinki Declaration. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants during genetic counseling sessions.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Rossi, B.M., Palmero, E.I., López-Kostner, F. et al. A survey of the clinicopathological and molecular characteristics of patients with suspected Lynch syndrome in Latin America. BMC Cancer 17, 623 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3599-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3599-4