Abstract
Bacteriocins are bacterial antimicrobial peptides that, unlike classical peptide antibiotics, are products of ribosomal synthesis and usually have a narrow spectrum of antibacterial activity against species closely related to the producers. Pediocin-like bacteriocins (PLBs) belong to the class IIa of the bacteriocins of Gram-positive bacteria. PLBs possess high activity against pathogenic bacteria from Listeria and Enterococcus genera. Molecular target for PLBs is a membrane protein complex — bacterial mannose-phosphotransferase. PLBs can be synthesized by components of symbiotic microflora and participate in the maintenance of homeostasis in various compartments of the digestive tract and on the surface of epithelial tissues contacting the external environment. PLBs could give a rise to a new group of antibiotics of narrow spectrum of activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GI:
-
gastrointestinal (tract)
- Man-PTS:
-
mannose phosphotransferase
- MIC:
-
minimal inhibitory concentration
- PLBs:
-
pediocin-like bacteriocins
- PTS:
-
phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase system
References
Cotter, P. D., Ross, R. P., and Hill, C. (2013) Bacteriocins — a viable alternative to antibiotics? Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 11, 95–105.
Kemperman, R., Kuipers, A., Karsens, H., Nauta, A., Kuipers, O., and Kok, J. (2003) Identification and characterization of two novel clostridial bacteriocins, circularin A and closticin 574, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 69, 1589–1597.
Svetoch, E. A., Eruslanov, B. V., Perelygin, V. V., Mitsevich, E. V., Mitsevich, I. P., Borzenkov, V. N., Levchuk, V. P., Svetoch, O. E., Kovalev, Y. N., Stepanshin, Y. G., Siragusa, G. R., Seal, B. S., and Stern, N. J. (2008) Diverse antimicrobial killing by Enterococcus faecium E 50–52 bacteriocin, J. Agric. Food Chem., 56, 1942–1948.
Cotter, P. D., Hill, C., and Ross, R. P. (2005) Bacteriocins: developing innate immunity for food, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 3, 777–788.
Svetoch, E. A., and Stern, N. J. (2010) Bacteriocins to control Campylobacter spp. in poultry — a review, Poult. Sci., 89, 1763–1768.
Desriac, F., Defer, D., Bourgougnon, N., Brillet, B., Le Chevalier, P., and Fleury, Y. (2010) Bacteriocin as weapons in the marine animal-associated bacteria warfare: inventory and potential applications as an aquaculture probiotic, Mar. Drugs, 8, 1153–1177.
Gharsallaoui, A., Oulahal, N., Joly, C., and Degraeve, P. (2016) Nisin as a food preservative. Part 1: Physicochemical properties, antimicrobial activity, and main uses, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr., 56, 1262–1274.
Shin, J. M., Gwak, J. W., Kamarajan, P., Fenno, J. C., Rickard, A. H., and Kapila, Y. L. (2016) Biomedical applications of nisin, J. Appl. Microbiol., 120, 1449–1465.
Panteleev, P. V., Balandin, S. V., Ivanov, V. T., and Ovchinnikova, T. V. (2017) A therapeutic potential of animal β-hairpin antimicrobial peptides, Curr. Med. Chem., 24, 1724–1746.
Maxson, T, and Mitchell, D. A. (2016) Targeted treatment for bacterial infections: prospects for pathogen-specific antibiotics coupled with rapid diagnostics, Tetrahedron, 72, 3609–3624.
Melander, R. J., Zurawski, D. V., and Melander, C. (2018) Narrow-spectrum antibacterial agents, Medchemcomm, 9, 12–21.
Klaenhammer, T. R. (1993) Genetics of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 12, 39–85.
Drider, D., Fimland, G., Hechard, Y., McMullen, L. M., and Prevost, H. (2006) The continuing story of class IIa bacteriocins, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 70, 564–582.
Papagianni, M., and Anastasiadou, S. (2009) Pediocins: the bacteriocins of pediococci. Sources, production, properties and applications, Microb. Cell Fact., 8, 3.
Rhos Colombo, N. S., Chalon, M. C., Navarro, S. A., and Bellomio, A. (2018) Pediocin-like bacteriocins: new perspectives on mechanism of action and immunity, Curr. Genet., 64, 345–351.
Bhunia, A. K., Johnson, M. C., and Ray, B. (1988) Purification, characterization and antimicrobial spectrum of a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici, J. Appl. Bacteriol., 65, 261–268.
Hastings, J. W., Sailer, M., Johnson, K., Roy, K. L., Vederas, J. C., and Stiles, M. E. (1991) Characterization of leucocin A-UAL 187 and cloning of the bacteriocin gene from Leuconostoc gelidum, J. Bacteriol., 173, 7491–7500.
Motlagh, A. M., Bhunia, A. K., Szostek, F., Hansen, T. R., Johnson, M. C., and Ray, B. (1992) Nucleotide and amino acid sequence of pap-gene (pediocin AcH production) in Pediococcus acidilactici H, Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 15, 45–48.
Henderson, J. T., Chopko, A. L., and van Wassenaar, P. D. (1992) Purification and primary structure of pediocin PA-1 produced by Pediococcus acidilactici PAC-1.0, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 295, 5–12.
Cui, Y., Zhang, C., Wang, Y., Shi, J., Zhang, L., Ding, Z., Qu, X., and Cui, H. (2012) Class IIa bacteriocins: diversity and new developments, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 13, 16668–16707.
Yildirim, Z., and Johnson, M. G. (1998) Characterization and antimicrobial spectrum of bifidocin B, a bacteriocin produced by Bifidobacterium bifidum NCFB 1454, J. Food Prot., 61, 47–51.
Cheikhyoussef, A., Cheikhyoussef, N., Chen, H., Zhao, J., Tang, J., Zhang, H., and Chen, W. (2010) Bifidin I — a new bacteriocin produced by Bifidobacterium infantis BCRC 14602: purification and partial amino acid sequence, Food Control, 21, 746–753.
Le Marrec, C., Hyronimus, B., Bressollier, P., Verneuil, B., and Urdaci, M. C. (2000) Biochemical and genetic characterization of coagulin, a new antilisterial bacteriocin in the pediocin family of bacteriocins, produced by Bacillus coagulans I(4), Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 66, 5213–5220.
Kalmokoff, M. L., Banerjee, S. K., Cyr, T., Hefford, M. A., and Gleeson, T. (2001) Identification of a new plasmid-encoded Sec-dependent bacteriocin produced by Listeria innocua 743, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 67, 4041–4047.
Zheng, J., Ganzle, M. G., Lin, X. B., Ruan, L., and Sun, M. (2015) Diversity and dynamics of bacteriocins from human microbiome, Environ. Microbiol., 17, 2133–2143.
Cleveland, J., Montville, T. J., Nes, I. F., and Chikindas, M. L. (2001) Bacteriocins: safe, natural antimicrobials for food preservation, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 71, 1–20.
Dabour, N., Zihler, A., Kheadr, E., Lacroix, C., and Fliss, I. (2009) In vivo study on the effectiveness of pediocin PA-1 and Pediococcus acidilactici UL5 at inhibiting Listeria monocytogenes, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 133, 225–233.
Charpentier, E., and Courvalin, P. (1999) Antibiotic resistance in Listeria spp., Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 43, 2103–2108.
Bertsch, D., Muelli, M., Weller, M., Uruty, A., Lacroix, C., and Meile, L. (2014) Antimicrobial susceptibility and antibiotic resistance gene transfer analysis of foodborne, clinical, and environmental Listeria spp. isolates including Listeria monocytogenes, Microbiologyopen, 3, 118–127.
Cintas, L. M., Casaus, P., Fernandez, M. F., and Hernandez, P. E. (1998) Comparative antimicrobial activity of enterocin L50, pediocin PA-1, nisin A and lactocin S against spoilage and foodborne pathogenic bacteria, Food Microbiol., 15, 289–298.
Millette, M., Cornut, G., Dupont, C., Shareck, F., Archambault, D., and Lacroix, M. (2008) Capacity of human nisin- and pediocin-producing lactic acid bacteria to reduce intestinal colonization by vancomycin-resistant enterococci, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 74, 1997–2003.
McClintock, M. K., Kaznessis, Y. N., and Hackel, B. J. (2016) Enterocin A mutants identified by saturation mutagenesis enhance potency towards vancomycin-resistant enterococci, Biotechnol. Bioeng., 113, 414–423.
Jimenez, J. J., Borrero, J., Gutiez, L., Arbulu, S., Herranz, C., Cintas, L. M., and Hernandez, P. E. (2014) Use of synthetic genes for cloning, production and functional expression of the bacteriocins enterocin A and bacteriocin E 50–52 by Pichia pastoris and Kluyveromyces lactis, Mol. Biotechnol., 56, 571–583.
Arbulu, S., Jimenez, J. J., Gutiez, L., Cintas, L. M., Herranz, C., and Hernandez, P. E. (2015) Cloning and expression of synthetic genes encoding the broad antimicrobial spectrum bacteriocins SRCAM 602, OR-7, E-760, and L-1077 by recombinant Pichia pastoris, Biomed. Res. Int., 2015, 767183.
Wachsman, M. B., Castilla, V., de Ruiz Holgado, A. P., de Torres, R. A., Sesma, F., and Coto, C. E. (2003) Enterocin CRL35 inhibits late stages of HSV-1 and HSV-2 replication in vitro, Antiviral Res., 58, 17–24.
Todorov, S. D., Wachsman, M., Tome, E., Dousset, X., Destro, M. T., Dicks, L. M. T., Franco, B. D. G. de M., Vaz-Velho, M., and Drider, D. (2010) Characterization of an antiviral pediocin-like bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus faecium, Food Microbiol., 27, 869–879.
Lohans, C. T., and Vederas, J. C. (2012) Development of class IIa bacteriocins as therapeutic agents, Int. J. Microbiol., 2012, 386410.
Corr, S. C., Li, Y., Riedel, C. U., O’Toole, P. W., Hill, C., and Gahan, C. G. M. (2007) Bacteriocin production as a mechanism for the antiinfective activity of Lactobacillus salivarius UCC118, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 104, 7617–7621.
Dobson, A., Cotter, P. D., Ross, R. P., and Hill, C. (2012) Bacteriocin production: a probiotic trait? Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 78, 1–6.
O’Shea, E. F., Cotter, P. D., Stanton, C., Ross, R. P., and Hill, C. (2012) Production of bioactive substances by intestinal bacteria as a basis for explaining probiotic mechanisms: bacteriocins and conjugated linoleic acid, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 152, 189–205.
Nissen-Meyer, J., Rogne, P., Oppegard, C., Haugen, H. S., and Kristiansen, P. E. (2009) Structure-function relationships of the non-lanthionine-containing peptide (class II) bacteriocins produced by gram-positive bacteria, Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol., 10, 19–37.
Zouhir, A., Hammami, R., Fliss, I., and Hamida, J. B. (2010) A new structure-based classification of gram-positive bacteriocins, Protein J., 29, 432–439.
Casaus, P., Nilsen, T., Cintas, L. M., Nes, I. F., Hernandez, P. E., and Holo, H. (1997) Enterocin B, a new bacteriocin from Enterococcus faecium T136 which can act synergistically with enterocin A, Microbiology (Reading, Engl.), 143, 2287–2294.
Fregeau Gallagher, N. L., Sailer, M., Niemczura, W. P., Nakashima, T. T., Stiles, M. E., and Vederas, J. C. (1997) Three-dimensional structure of leucocin A in trifluoroethanol and dodecylphosphocholine micelles: spatial location of residues critical for biological activity in type IIa bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria, Biochemistry, 36, 15062–15072.
Wang, Y, Henz, M. E., Gallagher, N. L., Chai, S., Gibbs, A. C., Yan, L. Z., Stiles, M. E., Wishart, D. S., and Vederas, J. C. (1999) Solution structure of carnobacteriocin B2 and implications for structure-activity relationships among type IIa bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria, Biochemistry, 38, 15438–15447.
Uteng, M., Hauge, H. H., Markwick, P. R. L., Fimland, G., Mantzilas, D., Nissen-Meyer, J., and Muhle-Goll, C. (2003) Three-dimensional structure in lipid micelles of the pediocin-like antimicrobial peptide sakacin P and a sakacin P variant that is structurally stabilized by an inserted C-terminal disulfide bridge, Biochemistry, 42, 11417–11426.
Haugen, H. S., Fimland, G., Nissen-Meyer, J., and Kristiansen, P. E. (2005) Three-dimensional structure in lipid micelles of the pediocin-like antimicrobial peptide curvacin A, Biochemistry, 44, 16149–16157.
Arbulu, S., Lohans, C. T., van Belkum, M. J., Cintas, L. M., Herranz, C., Vederas, J. C., and Hernandez, P. E. (2015) Solution structure of enterocin HF, an antilisterial bacteriocin produced by Enterococcus faecium M3K31, J. Agric. Food Chem., 63, 10689–10695.
Sit, C. S., Lohans, C. T., van Belkum, M. J., Campbell, C. D., Miskolzie, M., and Vederas, J. C. (2012) Substitution of a conserved disulfide in the type IIa bacteriocin, leucocin A, with L-leucine and L-serine residues: effects on activity and three-dimensional structure, Chembiochem, 13, 35–38.
Bedard, F., Hammami, R., Zirah, S., Rebuffat, S., Fliss, I., and Biron, E. (2018) Synthesis, antimicrobial activity and conformational analysis of the class IIa bacteriocin pediocin PA-1 and analogs thereof, Sci. Rep., 8, 9029.
Fimland, G., Pirneskoski, J., Kaewsrichan, J., Jutila, A., Kristiansen, P. E., Kinnunen, P. K. J., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2006) Mutational analysis and membrane-interactions of the beta-sheet-like N-terminal domain of the pediocin-like antimicrobial peptide sakacin P, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1764, 1132–1140.
Haugen, H. S., Kristiansen, P. E., Fimland, G., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2008) Mutational analysis of the class IIa bacteriocin curvacin A and its orientation in target cell membranes, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 74, 6766–6773.
Johnsen, L., Fimland, G., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2005) The C-terminal domain of pediocin-like antimicrobial peptides (class IIa bacteriocins) is involved in specific recognition of the C-terminal part of cognate immunity proteins and in determining the antimicrobial spectrum, J. Biol. Chem., 280, 9243–9250.
Fimland, G., Jack, R., Jung, G., Nes, I. F., and NissenMeyer, J. (1998) The bactericidal activity of pediocin PA-1 is specifically inhibited by a 15-mer fragment that spans the bacteriocin from the center toward the C-terminus, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64, 5057–5060.
Yan, L. Z., Gibbs, A. C., Stiles, M. E., Wishart, D. S., and Vederas, J. C. (2000) Analogues of bacteriocins: antimicrobial specificity and interactions of leucocin A with its enantiomer, carnobacteriocin B2, and truncated derivatives, J. Med. Chem., 43, 4579–4581.
Haugen, H. S., Fimland, G., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2011) Mutational analysis of residues in the helical region of the class IIa bacteriocin pediocin PA-1, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 77, 1966–1972.
Oppegard, C., Fimland, G., Anonsen, J. H., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2015) The pediocin PA-1 accessory protein ensures correct disulfide bond formation in the antimicrobial peptide pediocin PA-1, Biochemistry, 54, 2967–2974.
Quadri, L. E., Yan, L. Z., Stiles, M. E., and Vederas, J. C. (1997) Effect of amino acid substitutions on the activity of carnobacteriocin B2. Overproduction of the antimicrobial peptide, its engineered variants, and its precursor in Escherichia coli, J. Biol. Chem., 272, 3384–3388.
Miller, K. W., Schamber, R., Osmanagaoglu, O., and Ray, B. (1998) Isolation and characterization of pediocin AcH chimeric protein mutants with altered bactericidal activity, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64, 1997–2005.
Tominaga, T., and Hatakeyama, Y. (2006) Determination of essential and variable residues in pediocin PA-1 by NNK scanning, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 72, 1141–1147.
Kanatani, K., Oshimura, M., and Sano, K. (1995) Isolation and characterization of acidocin A and cloning of the bacteriocin gene from Lactobacillus acidophilus, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 61, 1061–1067.
Stern, N. J., Svetoch, E. A., Eruslanov, B. V., Perelygin, V. V., Mitsevich, E. V., Mitsevich, I. P., Pokhilenko, V. D., Levchuk, V. P., Svetoch, O. E., and Seal, B. S. (2006) Isolation of a Lactobacillus salivarius strain and purification of its bacteriocin, which is inhibitory to Campylobacter jejuni in the chicken gastrointestinal system, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 50, 3111–3116.
Chen, Y., Ludescher, R. D., and Montville, T. J. (1997) Electrostatic interactions, but not the YGNGV consensus motif, govern the binding of pediocin PA-1 and its fragments to phospholipid vesicles, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 63, 4770–4777.
Kazazic, M., Nissen-Meyer, J., and Fimland, G. (2002) Mutational analysis of the role of charged residues in target-cell binding, potency and specificity of the pediocin-like bacteriocin sakacin P, Microbiology, 148, 2019–2027.
Simon, L., Fremaux, C., Cenatiempo, Y., and Berjeaud, J. M. (2002) Sakacin G, a new type of antilisterial bacteriocin, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 68, 6416–6420.
Derksen, D. J., Stymiest, J. L., and Vederas, J. C. (2006) Antimicrobial leucocin analogues with a disulfide bridge replaced by a carbocycle or by noncovalent interactions of allyl glycine residues, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 128, 14252–14253.
Fleury, Y., Dayem, M. A., Montagne, J. J., Chaboisseau, E., Le Caer, J. P., Nicolas, P., and Delfour, A. (1996) Covalent structure, synthesis, and structure-function studies of mesentericin Y 105(37), a defensive peptide from gram-positive bacteria Leuconostoc mesenteroides, J. Biol. Chem., 271, 14421–14429.
Derksen, D. J., Boudreau, M. A., and Vederas, J. C. (2008) Hydrophobic interactions as substitutes for a conserved disulfide linkage in the type IIa bacteriocins, leucocin A and pediocin PA-1, Chembiochem, 9, 1898–1901.
Mor, A., and Nicolas, P. (1994) The NH2-terminal alpha-helical domain 1–18 of dermaseptin is responsible for antimicrobial activity, J. Biol. Chem., 269, 1934–1939.
Skerlavaj, B., Gennaro, R., Bagella, L., Merluzzi, L., Risso, A., and Zanetti, M. (1996) Biological characterization of two novel cathelicidin-derived peptides and identification of structural requirements for their antimicrobial and cell lytic activities, J. Biol. Chem., 271, 28375–28381.
Shin, S. Y., Park, E. J., Yang, S. T., Jung, H. J., Eom, S. H., Song, W. K., Kim, Y., Hahm, K. S., and Kim, J. I. (2001) Structure-activity analysis of SMAP-29, a sheep leukocytes-derived antimicrobial peptide, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 285, 1046–1051.
Xiao, Y., Dai, H., Bommineni, Y R., Soulages, J. L., Gong, Y.-X., Prakash, O., and Zhang, G. (2006) Structure-activity relationships of fowlicidin-1, a cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide in chicken, FEBS J., 273, 2581–2593.
Zhang, Y., Zhao, H., Yu, G.-Y., Liu, X.-D., Shen, J.-H., Lee, W.-H., and Zhang, Y. (2010) Structure-function relationship of king cobra cathelicidin, Peptides, 31, 1488–1493.
Fimland, G., Blingsmo, O. R., Sletten, K., Jung, G., Nes, I. F., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (1996) New biologically active hybrid bacteriocins constructed by combining regions from various pediocin-like bacteriocins: the C-terminal region is important for determining specificity, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 62, 3313–3318.
Saavedra, L., Minahk, C., de Ruiz Holgado, A. P., and Sesma, F. (2004) Enhancement of the enterocin CRL35 activity by a synthetic peptide derived from the NH2-terminal sequence, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 48, 2778–2781.
Richard, C., Canon, R., Naghmouchi, K., Bertrand, D., Prevost, H., and Drider, D. (2006) Evidence on correlation between number of disulfide bridge and toxicity of class IIa bacteriocins, Food Microbiol., 23, 175–183.
Fimland, G., Johnsen, L., Axelsson, L., Brurberg, M. B., Nes, I. F., Eijsink, V. G., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2000) A C-terminal disulfide bridge in pediocin-like bacteriocins renders bacteriocin activity less temperature dependent and is a major determinant of the antimicrobial spectrum, J. Bacteriol., 182, 2643–2648.
Kaur, K., Andrew, L. C., Wishart, D. S., and Vederas, J. C. (2004) Dynamic relationships among type IIa bacteriocins: temperature effects on antimicrobial activity and on structure of the C-terminal amphipathic alpha helix as a receptor-binding region, Biochemistry, 43, 9009–9020.
Fimland, G., Eijsink, V. G. H., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2002) Mutational analysis of the role of tryptophan residues in an antimicrobial peptide, Biochemistry, 41, 9508–9515.
Chikindas, M. L., Garcia-Garcera, M. J., Driessen, A. J., Ledeboer, A. M., Nissen-Meyer, J., Nes, I. F., Abee, T., Konings, W. N., and Venema, G. (1993) Pediocin PA-1, a bacteriocin from Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0, forms hydrophilic pores in the cytoplasmic membrane of target cells, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 59, 3577–3584.
Bruno, M. E., and Montville, T. J. (1993) Common mechanistic action of bacteriocins from lactic acid bacteria, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 59, 3003–3010.
Minahk, C. J., Farias, M. E., Sesma, F., and Morero, R. D. (2000) Effect of enterocin CRL35 on Listeria monocytogenes cell membrane, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 192, 79–83.
Wu, M., Maier, E., Benz, R., and Hancock, R. E. (1999) Mechanism of interaction of different classes of cationic antimicrobial peptides with planar bilayers and with the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli, Biochemistry, 38, 7235–7242.
Minahk, C. J., Dupuy, F., and Morero, R. D. (2004) Enhancement of antibiotic activity by sub-lethal concentrations of enterocin CRL35, J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 53, 240–246.
Venema, K., Kok, J., Marugg, J. D., Toonen, M. Y., Ledeboer, A. M., Venema, G., and Chikindas, M. L. (1995) Functional analysis of the pediocin operon of Pediococcus acidilactici PAC1.0: PedB is the immunity protein and PedD is the precursor processing enzyme, Mol. Microbiol., 17, 515–522.
Chen, Y., Ludescher, R. D., and Montville, T. J. (1998) Influence of lipid composition on pediocin PA-1 binding to phospholipid vesicles, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64, 3530–3532.
Ramnath, M., Beukes, M., Tamura, K., and Hastings, J. W. (2000) Absence of a putative mannose-specific phosphotransferase system enzyme IIAB component in a leucocin A-resistant strain of Listeria monocytogenes, as shown by two-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 66, 3098–3101.
Dalet, K., Briand, C., Cenatiempo, Y, and Hechard, Y. (2000) The RpoN gene of Enterococcus faecalis directs sensitivity to subclass IIa bacteriocins, Curr. Microbiol., 41, 441–443.
Dalet, K., Cenatiempo, Y., Cossart, P., Hechard, Y., and European Listeria Genome Consortium (2001) A sigma(54)-dependent PTS permease of the mannose family is responsible for sensitivity of Listeria monocytogenes to mesentericin Y105, Microbiology, 147, 3263–3269.
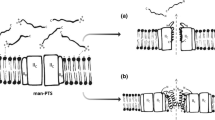
Diep, D. B., Skaugen, M., Salehian, Z., Holo, H., and Nes, I. F. (2007) Common mechanisms of target cell recognition and immunity for class II bacteriocins, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 104, 2384–2389.
Kjos, M., Salehian, Z., Nes, I. F., and Diep, D. B. (2010) An extracellular loop of the mannose phosphotransferase system component IIC is responsible for specific targeting by class IIa bacteriocins, J. Bacteriol., 192, 5906–5913.
Barraza, D. E., Rios Colombo, N. S., Galvan, A. E., Acuna, L., Minahk, C. J., Bellomio, A., and Chalon, M. C. (2017) New insights into enterocin CRL35: mechanism of action and immunity revealed by heterologous expression in Escherichia coli, Mol. Microbiol., 105, 922–933.
Stevens, K. A., Sheldon, B. W., Klapes, N. A., and Klaenhammer, T. R. (1991) Nisin treatment for inactivation of Salmonella species and other gram-negative bacteria, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 57, 3613–3615.
Chalon, M. C., Acuna, L., Morero, R. D., Minahk, C. J., and Bellomio, A. (2012) Membrane-active bacteriocins to control Salmonella in foods: are they the definite hurdle? Food Res. Int., 45, 735–744.
Kjos, M., Nes, I. F., and Diep, D. B. (2009) Class II one-peptide bacteriocins target a phylogenetically defined subgroup of mannose phosphotransferase systems on sensitive cells, Microbiology, 155, 2949–2961.
Opsata, M., Nes, I. F., and Holo, H. (2010) Class IIa bacteriocin resistance in Enterococcus faecalis V583: the mannose PTS operon mediates global transcriptional responses, BMC Microbiol., 10, 224.
Kjos, M., Borrero, J., Opsata, M., Birri, D. J., Holo, H., Cintas, L. M., Snipen, L., Hernandez, P. E., Nes, I. F., and Diep, D. B. (2011) Target recognition, resistance, immunity and genome mining of class II bacteriocins from gram-positive bacteria, Microbiology, 157, 3256–3267.
Vadyvaloo, V., Hastings, J. W., van der Merwe, M. J., and Rautenbach, M. (2002) Membranes of class IIa bacteriocin-resistant Listeria monocytogenes cells contain increased levels of desaturated and short-acyl-chain phosphatidylglycerols, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 68, 5223–5230.
Tessema, G. T., Moretro, T., Kohler, A., Axelsson, L., and Naterstad, K. (2009) Complex phenotypic and genotypic responses of Listeria monocytogenes strains exposed to the class IIa bacteriocin sakacin P, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 75, 6973–6980.
Masias, E., Dupuy, F. G., da Silva Sanches, P. R., Farizano, J. V., Cilli, E., Bellomio, A., Saavedra, L., and Minahk, C. (2017) Impairment of the class IIa bacteriocin receptor function and membrane structural changes are associated to enterocin CRL35 high resistance in Listeria monocytogenes, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1861, 1770–1776.
Kundig, W., Ghosh, S., and Roseman, S. (1964) Phosphate bound to histidine in a protein as an intermediate in a novel phospho-transferase system, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 52, 1067–1074.
Postma, P. W., Lengeler, J. W., and Jacobson, G. R. (1993) Phosphoenolpyruvate: carbohydrate phosphotransferase systems of bacteria, Microbiol. Rev., 57, 543–594.
Deutscher, J., Francke, C., and Postma, P. W. (2006) How phosphotransferase system-related protein phosphorylation regulates carbohydrate metabolism in bacteria, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 70, 939–1031.
Deutscher, J., Ake, F. M. D., Derkaoui, M., Zebre, A. C., Cao, T. N., Bouraoui, H., Kentache, T., Mokhtari, A., Milohanic, E., and Joyet, P. (2014) The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: carbohydrate phosphotransferase system: regulation by protein phosphorylation and phosphorylation-dependent protein—protein interactions, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 78, 231–256.
Galinier, A., and Deutscher, J. (2017) Sophisticated regulation of transcriptional factors by the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system, J. Mol. Biol., 429, 773–789.
Saier, M. H., and Paulsen, I. T. (1999) Paralogous genes encoding transport proteins in microbial genomes, Res. Microbiol., 150, 689–699.
Saier, M. H., Hvorup, R. N., and Barabote, R. D. (2005) Evolution of the bacterial phosphotransferase system: from carriers and enzymes to group translocators, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 33, 220–224.
Nguyen, T X., Yen, M.-R., Barabote, R. D., and Saier, M. H. (2006) Topological predictions for integral membrane permeases of the phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system, J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 11, 345–360.
Cao, Y., Jin, X., Levin, E. J., Huang, H., Zong, Y, Quick, M., Weng, J., Pan, Y., Love, J., Punta, M., Rost, B., Hendrickson, W. A., Javitch, J. A., Rajashankar, K. R., and Zhou, M. (2011) Crystal structure of a phosphorylation-coupled saccharide transporter, Nature, 473, 50–54.
McCoy, J. G., Ren, Z., Stanevich, V., Lee, J., Mitra, S., Levin, E. J., Poget, S., Quick, M., Im, W., and Zhou, M. (2016) The structure of a sugar transporter of the glucose EIIC superfamily provides insight into the elevator mechanism of membrane transport, Structure, 24, 956–964.
Ren, Z., Lee, J., Moosa, M. M., Nian, Y., Hu, L., Xu, Z., McCoy, J. G., Ferreon, A. C. M., Im, W., and Zhou, M. (2018) Structure of an EIIC sugar transporter trapped in an inward-facing conformation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 115, 5962–5967.
Luo, P., Yu, X., Wang, W., Fan, S., Li, X., and Wang, J. (2015) Crystal structure of a phosphorylation-coupled vitamin C transporter, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol., 22, 238–241.
Stock, J. B., Ninfa, A. J., and Stock, A. M. (1989) Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria, Microbiol. Rev., 53, 450–490.
Fujita, Y. (2009) Carbon catabolite control of the metabolic network in Bacillus subtilis, Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 73, 245–259.
Zuniga, M., Comas, I., Linaje, R., Monedero, V., Yebra, M. J., Esteban, C. D., Deutscher, J., Perez-Martinez, G., and Gonzalez-Candelas, F. (2005) Horizontal gene transfer in the molecular evolution of mannose PTS transporters, Mol. Biol. Evol., 22, 1673–1685.
Eijsink, V. G., Skeie, M., Middelhoven, P. H., Brurberg, M. B., and Nes, I. F. (1998) Comparative studies of class IIa bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64, 3275–3281.
Diep, D. B., Godager, L., Brede, D., and Nes, I. F. (2006) Data mining and characterization of a novel pediocin-like bacteriocin system from the genome of Pediococcus pentosaceus ATCC 25745, Microbiology, 152, 1649–1659.
Erni, B. (2006) The mannose transporter complex: an open door for the macromolecular invasion of bacteria, J. Bacteriol., 188, 7036–7038.
Fimland, G., Eijsink, V. G. H., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2002) Comparative studies of immunity proteins of pediocin-like bacteriocins, Microbiology, 148, 3661–3670.
Fimland, G., Johnsen, L., Dalhus, B., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2005) Pediocin-like antimicrobial peptides (class IIa bacteriocins) and their immunity proteins: biosynthesis, structure, and mode of action, J. Pept. Sci., 11, 688–696.
Johnsen, L., Fimland, G., Mantzilas, D., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2004) Structure-function analysis of immunity proteins of pediocin-like bacteriocins: C-terminal parts of immunity proteins are involved in specific recognition of cognate bacteriocins, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 70, 2647–2652.
Sprules, T., Kawulka, K. E., and Vederas, J. C. (2004) NMR solution structure of ImB2, a protein conferring immunity to antimicrobial activity of the type IIa bacteriocin, carnobacteriocin B2, Biochemistry, 43, 11740–11749.
Johnsen, L., Dalhus, B., Leiros, I., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2005) 1.6-angstroms crystal structure of EntA-Im. A bacterial immunity protein conferring immunity to the antimicrobial activity of the pediocin-like bacteriocin enterocin A, J. Biol. Chem., 280, 19045–19050.
Zhou, W., Wang, G., Wang, C., Ren, F., and Hao, Y. (2016) Both IIC and IID components of mannose phosphotransferase system are involved in the specific recognition between immunity protein PedB and bacteriocin—receptor complex, PLoS ONE, 11, e0164973.
Nissen-Meyer, J., Havarstein, L. S., Holo, H., Sletten, K., and Nes, I. F. (1993) Association of the lactococcin A immunity factor with the cell membrane: purification and characterization of the immunity factor, J. Gen. Microbiol., 139, 1503–1509.
Quadri, L. E., Sailer, M., Terebiznik, M. R., Roy, K. L., Vederas, J. C., and Stiles, M. E. (1995) Characterization of the protein conferring immunity to the antimicrobial peptide carnobacteriocin B2 and expression of carnobacteriocins B2 and BM1, J. Bacteriol., 177, 1144–1151.
Murinda, S. E., Rashid, K. A., and Roberts, R. F. (2003) In vitro assessment of the cytotoxicity of nisin, pediocin, and selected colicins on simian virus 40-transfected human colon and Vero monkey kidney cells with trypan blue staining viability assays, J. Food Prot., 66, 847–853.
Jasniewski, J., Cailliez-Grimal, C., Chevalot, I., Milliere, J.-B., and Revol-Junelles, A.-M. (2009) Interactions between two carnobacteriocins Cbn BM1 and Cbn B2 from Carnobacterium maltaromaticum CP5 on target bacteria and Caco-2 cells, Food Chem. Toxicol., 47, 893–897.
Ju, X., Chen, X., Du, L., Wu, X., Liu, F., and Yuan, J. (2015) Alanine-scanning mutational analysis of durancin GL reveals residues important for its antimicrobial activity, J. Agric. Food Chem., 63, 6402–6409.
Song, D. F., Li, X., Zhang, Y. H., Zhu, M. Y., and Gu, Q. (2014) Mutational analysis of positively charged residues in the N-terminal region of the class IIa bacteriocin pediocin PA-1, Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 58, 356–361.
Tominaga, T., and Hatakeyama, Y. (2007) Development of innovative pediocin PA-1 by DNA shuffling among class IIa bacteriocins, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 73, 5292–5299.
Acuna, L., Picariello, G., Sesma, F., Morero, R. D., and Bellomio, A. (2012) A new hybrid bacteriocin, Ent35-MccV, displays antimicrobial activity against pathogenic gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, FEBS Open Bio, 2, 12–19.
Johnsen, L., Fimland, G., Eijsink, V., and Nissen-Meyer, J. (2000) Engineering increased stability in the antimicrobial peptide pediocin PA-1, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 66, 4798–4802.
Quadri, L. E., Sailer, M., Roy, K. L., Vederas, J. C., and Stiles, M. E. (1994) Chemical and genetic characterization of bacteriocins produced by Carnobacterium piscicola LV17B, J. Biol. Chem., 269, 12204–12211.
Jasniewski, J., Cailliez-Grimal, C., Gelhaye, E., and Revol-Junelles, A.-M. (2008) Optimization of the production and purification processes of carnobacteriocins Cbn BM1 and Cbn B2 from Carnobacterium maltaromaticum CP5 by heterologous expression in Escherichia coli, J. Microbiol. Methods, 73, 41–48.
Bernbom, N., Jelle, B., Brogren, C.-H., Vogensen, F. K., Norrung, B., and Licht, T R. (2009) Pediocin PA-1 and a pediocin producing Lactobacillus plantarum strain do not change the HMA rat microbiota, Int. J. Food Microbiol., 130, 251–257.
Umu, O. C. O., Bauerl, C., Oostindjer, M., Pope, P. B., Hernandez, P. E., Perez-Martinez, G., and Diep, D. B. (2016) The potential of class II bacteriocins to modify gut microbiota to improve host health, PLoS ONE, 11, e0164036.
Salvucci, E., Saavedra, L., Hebert, E. M., Haro, C., and Sesma, F. (2012) Enterocin CRL35 inhibits Listeria monocytogenes in a murine model, Foodborne Pathog. Dis., 9, 68–74.
Sosunov, V., Mischenko, V., Eruslanov, B., Svetoch, E., Shakina, Y., Stern, N., Majorov, K., Sorokoumova, G., Selishcheva, A., and Apt, A. (2007) Antimycobacterial activity of bacteriocins and their complexes with liposomes, J. Antimicrob. Chemother., 59, 919–925.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balandin, S.V., Sheremeteva, E.V. & Ovchinnikova, T.V. Pediocin-Like Antimicrobial Peptides of Bacteria. Biochemistry Moscow 84, 464–478 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791905002X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791905002X