Abstract
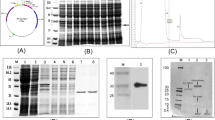
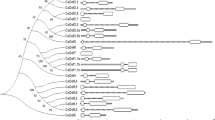
Gerbera (Gerbera hybrida), a major fresh cut flower crop, is very susceptible to root rot disease. Although plant defensins (PDFs), a major group of plant antimicrobial peptides, display broad-spectrum antifungal and antibacterial activities, PDF genes in gerbera have not been systematically characterized. Here, we identified and cloned nine PDF genes from gerbera and divided them into two classes based on phylogenetic analysis. Most Class I GhPDF genes were highly expressed in petioles, whereas all Class II GhPDF genes were highly expressed in roots. Phytophthora cryptogea inoculation strongly upregulated all Class II GhPDF genes in roots and upregulated all Class I GhPDF genes in petioles. Transient overexpression of GhPDF1.5 and GhPDF2.4 inhibited P. cryptogea infection in tobacco (Nicotiana benthamiana) leaves. Transient overexpression of GhPDF2.4, but not GhPDF1.5, significantly upregulated ACO and LOX gene expression in tobacco leaves, indicating that overexpressing GhPDF2.4 activated the jasmonic acid/ethylene defense pathway and that the two types of GhPDFs have different modes of action. Prokaryotically expressed recombinant GhPDF2.4 inhibited mycelial growth and delayed the hyphal swelling of P. cryptogea, in vitro, indicating that GhPDF2.4 is a morphogenetic defensin. Moreover, the addition of GhPDF2.4 to plant culture medium alleviated the root rot symptoms of in vitro-grown gerbera seedlings and greatly reduced pathogen titer in P. cryptogea-inoculated gerbera roots in the early stages of treatment. Our study provides a basis for the use of GhPDFs, especially GhPDF2.4, for controlling root rot disease in gerbera.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al KN, Abulreesh HH, El-Sheikh IA et al (2020) Utilization of a recombinant defensin from Maize (Zea mays L.) as a potential antimicrobial peptide. AMB Express 10(1):208. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-020-01146-9
Broekaert WF, Terras F, Cammue B et al (1995) Plant Defensins: novel antimicrobial peptides as components of the host defense system. Plant Physiol 108(4):1353–1358. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.4.1353
Ceballo Y, Gonzalez C, Ramos O et al (2022) Production of soluble bioactive NmDef02 plant defensin in Escherichia coli. Int J Pept Res Ther 28(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-021-10338-1
Chen L, Zhong H, Kuang J et al (2011) Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR studies of gene expression in banana fruit under different experimental conditions. Planta 234(2):377–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1410-3
Cheng C, Yang R, Yin L et al (2023) Characterization of carotenoid cleavage oxygenase genes in Cerasus humilis and functional analysis of ChCCD1. Plants (basel) 12(11):2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12112114
de Oliveira MÉ, Taveira GB, de Oliveira CA et al (2019) Improved smallest peptides based on positive charge increase of the γ-core motif from PvD1 and their mechanism of action against Candida species. Int J Nanomedicine 14:407–420. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S187957
de Paula VS, Razzera G, Medeiros L et al (2008) Evolutionary relationship between defensins in the Poaceae family strengthened by the characterization of new sugarcane defensins. Plant Mol Biol 68(4):321–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9372-y
de Paula VS, Razzera G, Barreto-Bergter E et al (2011) Portrayal of complex dynamic properties of sugarcane defensin 5 by NMR: multiple motions associated with membrane interaction. Structure 19(1):26–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2010.11.011
de Zelicourt A, Letousey P, Thoiron S et al (2007) Ha-DEF1, a sunflower defensin, induces cell death in Orobanche parasitic plants. Planta 226(3):591–600. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0507-1
Dracatos PM, Weerden NL, Carroll KT et al (2013) Inhibition of cereal rust fungi by both classI and II defensins derived from the flowers of Nicotiana alata. Mol Plant Pathol 15(1):67–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.12066
Dracatos PM, Payne J, Di Pietro A et al (2016) Plant defensins NaD1 and NaD2 induce different stress response pathways in fungi. Int J Mol Sci 17(9):1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091473
Emamifar S, Abolmaali S, Mohsen Sohrabi S et al (2021) Molecular characterization and evaluation of the antibacterial activity of a plant defensin peptide derived from a gene of oat (Avena sativa L.). Phytochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2020.112586
Ghag SB, Shekhawat UK, Ganapathi TR (2012) Petunia floral defensins with unique prodomains as novel candidates for development of fusarium wilt resistance in transgenic banana plants. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039557
Hanks JN, Snyder AK, Graham MA et al (2005) Defensin gene family in Medicago truncatula: structure, expression and induction by signal molecules. Plant Mol Biol 58(3):385–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-005-5567-7
Houben M, Van de Poel B (2019) 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase (ACO): The enzyme that makes the plant hormone ethylene. Front Plant Sci 10:695. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00695
Ishaq N, Bilal M, Iqbal H (2019) Medicinal potentialities of plant defensins: a review with applied perspectives. Medicines (basel) 6(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines6010029
Jha S, Chattoo BB (2010) Expression of a plant defensin in rice confers resistance to fungal phytopathogens. Transgenic Res 19(3):373–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-009-9315-7
Kaewklom S, Wongchai M, Petvises S et al (2018) Structural and biological features of a novel plant defensin from Brugmansia x candida. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201668
Kaur J, Fellers J, Adholeya A et al (2017) Expression of apoplast-targeted plant defensin MtDef4.2 confers resistance to leaf rust pathogen Puccinia triticina but does not affect mycorrhizal symbiosis in transgenic wheat. Transgenic Res 26(1):37–49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-016-9978-9
Kerenga BK, Mckenna JA, Harvey PJ et al (2019) Salt-tolerant antifungal and antibacterial activities of the corn defensin ZmD32. Front Microbiol 10:795. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00795
Kovaleva V, Bukhteeva I, Kit OY et al (2020) Plant defensins from a structural perspective. Int J Mol Sci 21(15):5307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21155307
Kraszewska J, Beckett MC, James TC et al (2016) Comparative analysis of the antimicrobial activities of plant defensin-like and ultrashort peptides against food-spoiling bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 82(14):4288–4298. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00558-16
Lacerda AF, Vasconcelos EA, Pelegrini PB et al (2014) Antifungal defensins and their role in plant defense. Front Microbiol 5:116. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00116
Lay FT, Brugliera F, Anderson MA (2003) Isolation and properties of floral defensins from ornamental tobacco and petunia. Plant Physiol 131(3):1283–1293. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.102.016626
Lay FT, Poon S, Mckenna JA et al (2014) The C-terminal propeptide of a plant defensin confers cytoprotective and subcellular targeting functions. BMC Plant Biol 14(1):41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-14-41
Lee H, Kim J, Hoang QT et al (2018) Root-specific expression of defensin in transgenic tobacco results in enhanced resistance against Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae. Eur J Plant Pathol 151(3):811–823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-018-1419-6
Li N, Euring D, Cha JY et al (2020) Plant hormone-mediated regulation of heat tolerance in response to global climate change. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.627969
Liu Y, Hua YP, Chen H et al (2021) Genome-scale identification of plant defensin (PDF) family genes and molecular characterization of their responses to diverse nutrient stresses in allotetraploid rapeseed. PeerJ. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.12007
Liu J, Wang R, Li G et al (2022a) Cloning and prokaryotic expression of WRKY48 from Caragana intermedia. Open Life Sci 17(1):131–138. https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2022-0016
Liu Y, Liu L, Yang C et al (2022b) Molecular identification and antifungal activity of a defensin (PaDef) from Spruce. J Plant Growth Regul 41(2):494–506. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-021-10316-3
Mulla JA, Kibe AN, Deore DD et al (2021) Molecular characterization of diverse defensins (γ-thionins) from Capsicum annuum flowers and their effects on the insect pest Helicoverpa armigera. Plant Gene. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plgene.2021.100284
Munir N, Cheng CZ, Xia CS et al (2019) RNA-Seq analysis reveals an essential role of tyrosine metabolism pathway in response to root-rot infection in Gerbera hybrida. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0223519
Nanni V, Zanetti M, Bellucci M et al (2013) The peach (Prunus persica) defensin PpDFN1 displays antifungal activity through specific interactions with the membrane lipids. Plant Pathol 62(2):393–403. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3059.2012.02648.x
Nawrot R, Barylski J (2014) Nowicki G et al Plant antimicrobial peptides. Folia Microbiol (praha) 59(3):181–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-013-0280-4
Ntui VO, Thirukkumaran G, Azadi P et al (2010) Stable integration and expression of wasabi defensin gene in “Egusi” melon (Colocynthis citrullus L.) confers resistance to Fusarium wilt and Alternaria leaf spot. Plant Cell Rep 29(9):943–954. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-010-0880-2
Safaiefarahani B, Mostowfizadeh-Ghalamfarsa R, Hardy GESJ et al (2016) Species from within the Phytophthora cryptogea complex and related species, P. erythroseptica and P. sansomeana, readily hybridize. Fungal Biol 120(8):975–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2016.05.002
Sagaram US, Pandurangi R, Kaur J et al (2011) Structure-activity determinants in antifungal plant defensins MsDef1 and MtDef4 with different modes of action against Fusarium graminearum. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0018550
Sathoff AE, Velivelli S, Shah DM et al (2019) Plant defensin peptides have antifungal and antibacterial activity against human and plant pathogens. Phytopathology 109(3):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-09-18-0331-R
Seo MD, Won HS, Kim JH et al (2012) Antimicrobial peptides for therapeutic applications: a review. Molecules (basel) 17(10):12276–12286. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules171012276
Sher KR, Iqbal A, Malak R et al (2019) Plant defensins: types, mechanism of action and prospects of genetic engineering for enhanced disease resistance in plants. 3 Biotech 9(5):192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1725-5
Soto N, Hernandez Y (2020) Delgado C et al Field resistance to Phakopsora pachyrhizi and Colletotrichum truncatum of transgenic soybean expressing the NmDef02 plant defensin gene. Front Plant Sci 11:562. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00562
Spelbrink RG, Dilmac N, Allen A et al (2004) Differential antifungal and calcium channel-blocking activity among structurally related plant defensins. Plant Physiol 135(4):2055–2067. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00562
Sun T, Chen Y, Feng A et al (2023) The allene oxide synthase gene family in sugarcane and its involvement in disease resistance. Ind Crops Prod 192:116136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.116136
Tetorya M, Li H, Djami-Tchatchou AT et al (2023) Plant defensin MtDef4-derived antifungal peptide with multiple modes of action and potential as a bio-inspired fungicide. Mol Plant Pathol 24(8):896–913. https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.13336
Thomma B, Cammue B, Thevissen K (2002) Plant defensins. Planta 216(2):193–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-002-0902-6
Velivelli S, Islam KT, Hobson E et al (2018) Modes of action of a bi-domain plant defensin MtDef5 against a bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas campestris. Front Microbiol 9:934. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00934
Verly C, Djoman A, Rigault M et al (2020) Plant defense stimulator mediated defense activation Is affected by nitrate fertilization and developmental stage in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 11:583. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00583
Viswanath KK, Varakumar P, Pamuru RR et al (2020) Plant lipoxygenases and their role in plant physiology. J Plant Biol 63(2):83–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12374-020-09241-x
Wang B, Yu J, Zhou D et al (2011) Maize defensin ZmDEF1 is involved in plant response to fungal phytopathogens. AFR J Biotechnol 10(72):16128–16137. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.1456
Wang B, Xu Y, Xu S et al (2023) Characterization of banana SNARE genes and their expression analysis under temperature stress and mutualistic and pathogenic fungal colonization. Plants (basel) 12(8):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12081599
Wu H, Wang B, Hao X et al (2022) Piriformospora indica promotes the growth and enhances the root rot disease resistance of gerbera. Sci Hort. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2022.110946
Xu R, Tang J, Hadianamrei R et al (2023) Antifungal activity of designed alpha-helical antimicrobial peptides. Biomate Sci 11(8):2845–2859. https://doi.org/10.1039/d2bm01797k
Zhang Y, Liu F, Wang B et al (2021) Identification, characterization and expression analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis-related bHLH genes in blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.). Int J Mol Sci 22(24):13274. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413274
Zhao K, Ren R, Ma XL et al (2021) Genome-wide investigation of defensin genes in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) reveals AhDef2.2 conferring resistance to bacterial wilt. Crop J 10(3):809–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.11.002
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Construction Project for Shanxi Key Laboratory of Germplasm Resources Innovation and Utilization of Vegetables and Flowers (202204010931019), the Reward Fund for PhDs and Postdoctors of Shanxi Province (SXBYKY2022004), and the Fund for High-level Talents of Shanxi Agricultural University (2021XG010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CC: conceptualization, funding acquisition, writing- original draft preparation, writing- reviewing and editing. HW: methodology, software, data curation, writing- original draft preparation. YZ: methodology, data curation, investigation, writing- reviewing and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, C., Wu, H. & Zhang, Y. Characterization and functional analysis of gerbera plant defensin (PDF) genes reveal the role of GhPDF2.4 in defense against the root rot pathogen Phytophthora cryptogea. aBIOTECH (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42994-024-00146-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42994-024-00146-8