Abstract
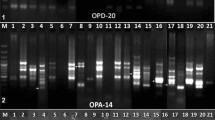
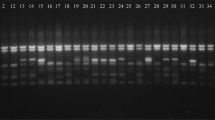
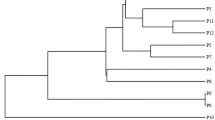
Banana belonging to the family Musaceae is the fourth most important staple food crop after rice, wheat, and maize. Genomic composition and genetic variation among 25 Musaceae genotypes, collected from different regions of Manipur, were evaluated using PCR–RFLP and RAPD and ISSR markers. Restriction-site variations in the internal transcribed spacers (ITS) of the nuclear ribosomal RNA genes were used to distinguish the genotypes and their genomic constitutions. PCR amplification using specific primers produced a 700-bp fragment in all the genotypes studied. This fragment that is equivalent in size to the ITS of most plants was digested with RsaI, revealing 530-bp fragment that is unique to ‘A’ genome and 350 bp and 180-bp fragments that were unique to ‘B’ genome alone, and thus, the genotypes were differentiated as constituting of either the A or B genome alone or having both the A and B genomic compositions. In the wild and semi-wild genotypes, unique restriction fragments were observed. Genetic variations among the genotypes were determined using 15 RAPD and 15 ISSR markers. The respective percentage of polymorphisms for RAPD and ISSR markers was 99.79% and 99.70%. Similarity coefficients in RAPD analysis ranged from 0.14 to 0.95 and in ISSR analysis from 0.30 to 0.96. The polymorphism information content (PIC) scores for RAPD markers ranged from 0.20 to 0.29 and that of ISSR markers was 0.25 to 0.36. The Mantel Z-test between the two Jaccard’s similarity matrices gave r ≥ 0.93, indicating a very good fit correlation between RAPD- and ISSR-based similarities. The RAPD and ISSR analyses could identify distinctive cultivars and wild species that remained conspicuously distinct in both marker systems.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajibade SR, Weeden NF, Michite S (2000) Inter-simple sequence repeat analysis of genetic relationships in the genus Vigna. Euphytica 111:47–55
Arif M, Zaidi NW, Singh YP, Haq QMR, Singh US (2009) A comparative analysis of ISSR and RAPD markers for the study of genetic diversity in shisham (Dalbergia sissoo). Plant Mol Biol Rep 27:488–495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0097-0
Becker J, Heun M (1995) Barley microsatellites: allele variation and mapping. Plant Mol Biol 27:835–845
Bhat KV, Jarret RL (1995) Random amplified polymorphic DNA and genetic diversity in Indian Musa germplasm. Genet Resour Crop Evol 42:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02539514
Bhat KV, Jarret RL, Liu ZW (1994) RFLP characterization of Indian Musa germplasm for clonal identification and classification. Euphytica 80:95–103
Bhat KV, Jarret RL, Rana RS (1995) DNA profiling of banana and plantain cultivars using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) markers. Electrophoresis 16:1736–1745
Bhattachaya S, Bandopadhyay TK, Ghosh PD (2010) Efficiency of RAPD and ISSR markers in assessment of molecular diversity in elite germplasms of Cymbopogon winterianus across West Bengal, India. Emir J Food Agric 221:13–24
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32:314–331
Bradeen JM, Bach IC, Briard M et al (2002) Molecular diversity analysis of cultivated carrot (Daucus carota L.) and wild Daucus populations reveals a genetically non-structured composition. J Am Soc Hort Sci 127:383–391
Brown N, Venkatasamy S, Khittoo G, Bahorun T, Jawaheer S (2009) Evaluation of genetic diversity between 27 banana cultivars (Musa spp.) in Mauritius using RAPD markers. Afr J Biotechnol 8:1834–1840
Cheesman EE (1947) Classification of the bananas II the Genus Musa l. Kew Bull 2:106–117. https://doi.org/10.2307/4109207
Crouch HK, Crouch JH, Madsen S, Vuylsteke DR, Ortiz R (2000) Comparative analysis of phenotypic and genotypic diversity among plantain landraces (Musa spp., AAB group). Theor Appl Genet 101:1056–1065. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220051580
D’Hont A, Paget-Goy A, Escoute J, Carreel F (2000) The inter-specific genome structure of cultivated banana, Musa spp., revealed by genomic DNA in situ hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 100:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-009-0097-0
Dolezel J, Bartos J (2005) Plant flow cytometry and estimation of nuclear genome size. Ann Bot 95:99–100
Dolezel J, Deolzelova M, Novak FJ (1994) Flow cytometry estimation of nuclear DNA amount in diploid bananas (Musa acuminata and M. balbisiana). Biol Plant 36:351–357
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) A rapid total DNA preparation procedure for fresh plant tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Friedt W, Snowdon R, Ordon F, Ahlemeyer J (2007) Plant Breeding: Assessment of Genetic Diversity in Crop Plants and its Exploitation in Breeding. In: Esser K, Löttge U, Beyschlag W, Murata J (eds) Progress in Botany. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, p 68. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-36832-8_7
Galvan MZ, Bornet B, Balatti PA, Branchard M (2003) Inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers as a tool for assessment of both genetic diversity and gene pool origin in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Euphytica 132:297–301. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025032622411
Ghislain M, Zhang D, Fajardo D, Huamann Z, Hijmans R (1999) Marker-assisted sampling of the cultivated Andean potato Solanum phureja collection using RAPD markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 46:547–555
Grajal-Martin M, Siverio-Grillo G, Marrero-Dominguez A (1998) The use of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) for the study of genetic diversity and somaclonal variation in Musa. Sci Horti 490:445–454
Henry R (1997) Molecular markers in plant improvement. Practical applications of plant molecular biology. Chapman & Hall, London, UK, pp 99–132
Howell EC, Newbury HJ, Swennen RL, Withers LA, Ford-Lloyd BV (1994) The use of RAPD for identifying and classifying Musa germplasm. Genome 37:328–332
Hsiao C, Chatterton NJ, Asay KH, Jensen KB (1994) Phylogenetic relationships of ten grass species: an assessment of Phylogenetic utility of the internal transcribed spacer region in the nuclear ribosomal DNA in monocots. Genome 37:112–120
IPGRI-INIBAP and CIRAD (1996) Descriptors for banana (Musa spp.), 3rd ed International Plant Genetic Resources Institute, Rome, INIBAP, Montpellier, France, pp 59
Jain PK, Saini ML, Pathak H, Gupta PK (2000) Analysis of genetic variation in different banana (Musa species) variety using random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPDs). Afr J Biotechnol 6:1987–1989
Kaemmer D, Afza R, Weising K, Kahl G, Novak FJ (1992) Oligonucleotide and amplification fingerprinting of wild species and cultivars of banana (Musa spp.). Biotechnol 10:1030–1035. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0992-1030
Kuras A, Korbin M, Zuramicz E (2004) Comparison of suitability of RAPD and ISSR techniques for determination of strawberry (Fragaria_anassa Duch.) relationship. Plan Cell Tiss Org Cult 79:183–194
Lai J, Yang WC, Hsiao JY (2001) An assessment of genetic relationships in cultivated tea clones and native wild tea in Taiwan using RAPD and ISSR markers. Bot Bull Acad Sin 42:93–100
Lakshmanan V, Venkataramareddy SR, Neelwarne B (2007) Molecular analysis of genetic stability in long-term micropropagated shoots of banana using RAPD and ISSR markers. Electron J Biotechnol 10:106–113. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol10-issue5-fulltext-12
Loarce Y, Gallego R, Ferrer E (1996) A comparative analysis of genetic relationships between rye cultivars using RFLP and RAPD markers. Euphytica 88:107–115
Lopez-Sese A, Staub JE, Gomez-Guillamon ML (2003) Genetic analysis of Spanish melon (Cucumis melo L.) germplasm using a standardized molecular marker array and reference accessions. Theor Appl Genet 108:41–52
Mantel NA (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Mattioni C, Casasoli M, Gonzalez M, Ipiza R, Villani F (2002) Comparison of ISSR and RAPD markers to characterize three Chilean Nothofagus species. Theor Appl Genet 104:1064–1070
Nair AS, Teo CH, Schwarzacher T, Harrison PH (2005) Genome classification of banana cultivars from South India using IRAP markers. Euphytica 144:285–290
Ning SP, Xu LB, Lu Y, Huang BZ, Ge XJ (2007) Genome composition and genetic diversity of Musa germplasm from China revealed by PCR-RFLP and SSR markers. Sci Hort 114:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2007.07.002
Nsabimana A, van Staden J (2006) Ploidy investigation of bananas (Musa spp.) from the National Banana Germplasm Collection at Rubona-Rwanda by flow cytometry. South Afr J Bot 72:302–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2005.10.004
Nwakanma DC, Pillay M, Okoli BE, Tenkouano A (2003) PCR-RFLP of the ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacers (ITS) provides markers for the A and B genomes in Musa L. Theor Appl Genet 108:154–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1402-1
Osuji JO, Crouch J, Harrison G, Heslop-Harrison JS (1997) Identification of the genomic constitution of Musa L. lines (bananas, plantains and hybrids) using molecular cytogenetics. Ann Bot 80:787–793
Pamidimarri DVNS, Singh S, Mastan SG, Patel J, Reddy MP (2009) Molecular characterization and identification of markers for toxic and non-toxic varieties of Jatropha curcus L. using RAPD, AFLP and SSR markers. Mol Biol Rep 36:1357–1364
Parab GV, Krishnan S (2008) Assessment of genetic variation among populations of Rhynchostylis retusa an epiphytic orchid from Goa, India using ISSR and RAPD markers. J Biotech 7:313–319
Paterson AH, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME (1991) DNA markers in plant improvement. Adv Agron 46:36–90
Patzak J (2001) Comparison of RAPD, STS, ISSR and AFLP molecular methods used for assessment of genetic diversity in hop (Humulus lupulus L.). Euphytica 121:9–18
Pillay M, Nwakanma DC, Tenkouano A (2000) Identification of RAPD markers linked to A and B genome sequences in Musa L. Genome 43:763–767. https://doi.org/10.1139/g00-038
Ray T, Dutta I, Saha P, Das S, Roy SC (2006) Genetic stability of three economically important micropropagated banana (Musa spp.) cultivars of lower Indo-Gangetic plains, as assessed by RAPD and ISSR markers. Plan Cell Tiss Org Cult 85:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-005-9044-4
Rohlf FJ (2000) NTSYS-pc: Numerical Taxonomy System. Ver. 2.1 Exeter Publishing Ltd., Setauket, New York.
Sahu PK, Sao R, Mondal S, Vishwakarma G, Gupta SK, Kumar V, Singh S, Sharma D, Das BK (2020) Next generation sequencing based forward genetic approaches for identification and mapping of causal mutations in crop plants: a comprehensive review. Plants 9:1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9101355
Saraladevi M, Selvaraju K, Shanmugasundaram P (2008) Efficiency of RAPD and ISSR markers system in accessing genetic variation of rice bean (Vigna umbellata) landraces. Electron J Biotechnol 11:1–10. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol11
Simmonds NW (1962) The evolution of bananas. Longman, London
Simmonds NW, Shepherd K (1955) The taxonomy and origins of the cultivated bananas. Bot J Linn Soc 55:302–312. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.1955.tb00015.x
Singh HP,Uma S (1996) Genetic diversity of banana in India. In the proceedings of the conference on “Challenges for banana production and utilization in 21st century” held at Trichy, 24–25 Sept
Singh WA, Bharat SG, Gourshyam T, Handique PJ, Sunitibala HD (2013) DEBDOM: database exploring banana diversity of manipur. Bioinformation 9:270–273
Smith JSC, Chin ECL, Smith OS, Wall SJ, Senior ML, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Ziegle J (1997) An evaluation of the utility of SSR loci as molecular markers in maize (Zea mays L.): comparisons with data from RFLPS and pedigree. Theor Appl Genet 95:163–173
Soller M, Beckmann JS (1983) Genetic polymorphism in varietal identification and genetic improvement. Theor Appl Genet 67:25–33
Souframanien J, Gopalakrishna T (2004) A comparative analysis of genetic diversity in black gram genotypes using RAPD and ISSR markers. Theor Appl Genet 109:1687–1693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1797-3
Staub JE, Dane F, Reitsma K, Fazio G, Lopez-Sese A (2002) The formation of test arrays and a core collection in (Cucumis sativus L.) using phenotypic and molecular marker data. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 127:558–567
Teo CH, Tan SH, Ho CL, Faridah QZ, Othman YR, Heslop-Harrison JS, Kalendar R, Schulman AH (2005) Genome constitution and classification using retrotransposon-based markers in the orphan crop banana. J Plant Biol 48:96–105
Uma S, Sudha S, Saraswathi MS, Manickavasagam M, Selvarajan R, Durai P, Sathiamoorthy S, Siva SA (2004) Analysis of genetic diversity and phylogenetic relationship among indigenous and exotic Silk (AAB) group of bananas using RAPD markers. J Hort Sci Biotech 79:523–527
Uma S, Siva SA, Saraswathi MS, Durai P, Sharma TVRS, Singh DB, Selvarajan R, Sathiamoorthy S (2005) Studies on the origin and diversification of Indian wild banana (Musa balbisiana) using arbitrarily amplified DNA markers. J Hort Sci Biotech 80:575–580
Uma S, Siva SA, Saraswathi MS, Manickavasagam M, Durai P, Selvarajan R, Sathiamoorthy S (2006) Variation and intra-specific relationships in Indian wild Musa balbisiana (BB) population as evidenced by random amplified polymorphic DNA. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:349–355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-004-0576-y
Venkatachalam L, Sreedhar RV, Bhagyalakshmi N (2007a) Genetic analysis of micropropagated and regenerated plantlets of banana as assessed by RAPD and ISSR markers. Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:267–274
Venkatachalam L, Sreedhar RV, Bhagyalakshmi N (2007b) Molecular analysis of genetic stability in long-term micropropagated shoots of banana using RAPD and ISSR markers. Electron J Biotechnol 10:1–8
Venkatachalam L, Sreedhar RV, Bhagyalakshmi N (2008) The use of genetic markers for detecting DNA polymorphism, genotype identification and phylogenetic relationships among banana cultivars. Mol Phylogenet Evol 47:974–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2008.03.017
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M et al (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23(21):4407–4414. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/23.21.4407
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenies. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, California, USA, pp 315–322
Williams JG, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl Acids Res 18:6531–6535. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/18.22.6531
Wu CJ, Cheng ZQ, Huang XQ, Yin SH, Cao KM, Sun CR (2004) Genetic diversity among and within pupations of Oryza granulata from yunnan of China revealed by RAPD and ISSR markers: implications for conservation of the endangered species. Plant Sci 167:35–42
Wu W, Zheng YL, Chen L, Wei YM, Yang RW, Yan ZH (2005) Evaluation of genetic relationships in the genus Houttuynia Thunb. in China based on RAPD and ISSR markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 33:1141–1157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bse.2005.02.010
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1994.1151
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Institute of Bioresources and Sustainable Development (IBSD) for the grant of fellowship and would also like to express gratitude to Markku Häkkinen (Botanic Garden, University of Helsinki, Finland) for identification of the species. The IBSD communication number of the manuscript is IBSD/2020/01/036.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Huidrom Sunitibala Devi; Methodology: Warepam Amuchou Singh, Nandeibam Samarjit Singh; Formal analysis and investigation: Warepam Amuchou Singh, Nandeibam Samarjit Singh; Writing—original draft preparation: Warepam Amuchou Singh; Writing—review and editing: Nandeibam Samarjit Singh, Elangbam Julia Devi; Funding acquisition: Huidrom Sunitibala Devi; Resources: Huidrom Sunitibala Devi; Supervision: Pratap Jyoti Handique, Huidrom Sunitibala Devi; Project administration: Huidrom Sunitibala Devi
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Human and animal right
This work does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, W.A., Singh, N.S., Devi, E.J. et al. Collection and characterization of banana gene pools (Musa spp.) in Manipur (N.E. India) using PCR–RFLP and RAPD and ISSR markers. Braz. J. Bot 44, 671–684 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-021-00722-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40415-021-00722-y