Abstract
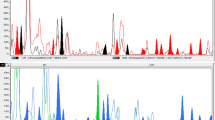
Sixteen collections of the wild Musa species, Musa balbisiana Colla collected from different regions of India were studied for their intraspecific relationships using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Out of 80 primers screened, 34 primers produced reproducible bands and four primers among them showing polymorphic bands were used. In all, 43 DNA fragments were amplified averaging 10.75 per primer. Of these, 31 amplified fragments showed polymorphism (averaging of 7.75 per primer). The extent of polymorphism (74.6%) has indicated the existence of considerable variation at the DNA level within the species. The 16 accessions were clustered into four as against seven clusters obtained through morphotaxonomic characterization. The inter relationships based on geographical origin in comparison with molecular characterization have been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous 2002. Recommendations of the promusa workshop of M. balbisiana diversity held at Bangkok, Thailand, 8–10 July 2002.
K.V. Bhat R.L. Jarret (1995) ArticleTitleRandom Amplified Polymorphic DNA and genetic diversity in Indian Musa germplasm Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 42 107–118
K.V. Bhat S.R. Bhat K.P.S. Chandel (1992a) ArticleTitleSurvey of isozyme polymorphism for clonal identification in Musa. I. Esteraseacid phosphatase and catalase J. Hort. Sci. 67 501–507 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XmtV2jsLk%3D
K.V. Bhat S.R. Bhat K.P.S. Chandel (1992b) ArticleTitleSurvey of isozyme polymorphism for clonal identification in Musa.II. Peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, shikimate dehydrogenase and malate dehydrogenase J. Hort. Sci. 67 737–744 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhsVent7s%3D
F. Carreel (1994) Etude de la diversité des bananiers (genre Musa) à l aide des marqueurs RFLP Thèse de la Institut National Agronomique Paris–Grignon 90
N.J. Gawal R.L. Jarret (1991) ArticleTitleCytoplasmic genetic diversity in banana and plantain Euphytica 52 19–23
E.C. Howell H.J. Newbury R.L. Swennen L.A. Withers B.V. Ford Lioyd (1994) ArticleTitleThe use of RAPD for identifying and classifying Musa germplasm Genome 37 328–332 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmvFeru70%3D Occurrence Handle8200520
IPGRI–INIBAP/CIRAD 1996. Descriptor for Banana (Musa ssp.).
D. Kaemmer R. Afza G. Kaw F.J. Novak (1992) ArticleTitleOligonucleotide and amplification fingerprinting of wild species and cultivars of banana Musa spp.) Biotechnology 10 1030–1035 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXhslSmtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1369000
F.J. Rohlf (1990) NTSYS-PC. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system Exeter Software New York
N.W. Simmonds (1959) Bananas Longmans, Green and Co. Ltd. London
N.W. Simmonds (1962) The Evolution of the Bananas Longmans, Green and Co. Ltd. London
Singh H.P. and Uma S. 2000. Genetic diversity of banana in India. In: Singh H.P and Chadha K.L. (eds), The Proceedings of the Conference on Challenges for Banana Production and Utilization in 21st Century. pp. 136–156.
R.C. Sotto R.C. Rabara (2000) ArticleTitleMorphological diversity of Musa balbisiana Colla in the Philippines Infomusa 9 IssueID2 28–30
S. Uma S. Sathiamoorthy (2002) Names and Synonyms of Bananas and Plantains in India National Research Centre for Banana Tiruchirappalli, India 60
J.G.K. Williams A.R. Kubelik K.J. Livak J.A. Rafalski S.V. Tingey (1990) ArticleTitleDNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers Nucleic Acid Res. 18 6531–6536 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXjslWmsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle1979162
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uma, S., Siva, S.A., Saraswathi, M.S. et al. Variation and Intraspecific Relationships in Indian Wild Musa balbisiana (BB) Population as Evidenced by Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53, 349–355 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-004-0576-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-004-0576-y