Abstract
Background
Overactive adenosine triphosphate signaling via P2X3 homotrimeric receptors is implicated in multiple conditions. To fully understand the metabolism and elimination pathways of eliapixant, a study was conducted to assess the pharmacokinetics, mass balance, and routes of excretion of a single oral dose of the selective P2X3 receptor antagonist eliapixant, in addition to an in vitro characterization.
Methods
In this single-center open-label non-randomized non-placebo-controlled phase I study, healthy male subjects (n = 6) received a single dose of 50 mg eliapixant blended with 3.7 MBq [14C]eliapixant as a PEG 400-based oral solution. Total radioactivity and metabolites excreted in urine and feces, and pharmacokinetics of total radioactivity, eliapixant, and metabolites in plasma were assessed via liquid scintillation counting and high-performance liquid chromatography-based methods coupled to radiometric and mass spectrometric detection. Metabolite profiles of eliapixant in human in vitro systems and metabolizing enzymes were also investigated.
Results
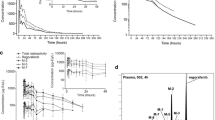
After administration as an oral solution, eliapixant was rapidly absorbed, reaching maximum plasma concentrations within 2 h. Eliapixant was eliminated from plasma with a mean terminal half-life of 48.3 h. Unchanged eliapixant was the predominant component in plasma (72.6% of total radioactivity area under the curve). The remaining percentage of drug-related components in plasma probably represented the sum of many metabolites, detected in trace amounts. Mean recovery of total radioactivity was 97.9% of the administered dose (94.3–99.4%) within 14 days, with 86.3% (84.8–88.1%) excreted via feces and 11.6% (9.5–13.1%) via urine. Excretion of parent drug was minimal in feces (0.7% of dose) and urine (≈ 0.5%). In feces, metabolites formed by oxidation represented > 90% of excreted total radioactivity. The metabolites detected in the in vitro experiments were similar to those identified in vivo.
Conclusion
Complete recovery of administered eliapixant-related radioactivity was observed in healthy male subjects with predominant excretion via feces. Eliapixant was almost exclusively cleared by oxidative biotransformation (> 90% of dose), with major involvement of cytochrome P450 3A4. Excretion of parent drug was of minor importance (~ 1% of dose).
Clinical trial registration
ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT04487431 (registered 27 July 2020)/EudraCT number: 2020-000519-54 (registered 3 February 2020), NCT02817100 (registered 26 June 2016), NCT03310645 (registered 16 October 2017).
Plain Language Summary
Eliapixant is a drug that acts on structures in the body called P2X3 receptors that are involved in several conditions, including chronic cough, overactive bladder, and endometriosis-related pain. When evaluating a new drug, it is important to know how it is being removed from the body by natural mechanisms. We performed a study in which six healthy male volunteers took a single dose of eliapixant, and we investigated what happened to the drug after it was taken. We measured the amount of eliapixant in the volunteers’ blood, urine, and feces, and also measured the compounds formed when eliapixant was broken down naturally by the body (“metabolites”). We also used human cells in the laboratory to investigate how the different metabolites of eliapixant are formed. Almost three-quarters of eliapixant in the blood had not been broken down at all, while the remaining one-quarter had been converted into many different metabolites. A total of 2 weeks after taking eliapixant, almost all of it had been converted to metabolites and eliminated from the body (mostly in feces, but also a small amount in urine). The most important organ for breaking down eliapixant is the liver. The information from this study will help doctors determine whether eliapixant is likely to interfere with other drugs taken simultaneously, and whether patients with liver or kidney problems might take longer than healthy people to remove it from their bodies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnstock G. Purinergic mechanosensory transduction and visceral pain. Mol Pain. 2009;5:69.
Bernier LP, Ase AR, Seguela P. P2X receptor channels in chronic pain pathways. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175(12):2219–30.
Cockayne DA, Dunn PM, Zhong Y, Rong W, Hamilton SG, Knight GE, Ruan HZ, Ma B, Yip P, Nunn P, McMahon SB, Burnstock G, Ford AP. P2X2 knockout mice and P2X2/P2X3 double knockout mice reveal a role for the P2X2 receptor subunit in mediating multiple sensory effects of ATP. J Physiol. 2005;567(Pt 2):621–39.
Ding S, Yu Q, Wang J, Zhu L, Li T, Guo X, Zhang X. Activation of ATF3/AP-1 signaling pathway is required for P2X3-induced endometriosis pain. Hum Reprod. 2020;35(5):1130–44.
Fabbretti E. ATP P2X3 receptors and neuronal sensitization. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013;7:236.
Ford AP. In pursuit of P2X3 antagonists: novel therapeutics for chronic pain and afferent sensitization. Purinergic Signal. 2012;8(Suppl 1):3–26.
Song WJ, Morice AH. Cough hypersensitivity syndrome: a few more steps forward. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(5):394–402.
Morice A, Smith JA, McGarvey L, Birring SS, Parker SM, Turner A, Hummel T, Gashaw I, Fels L, Klein S, Francke K, Friedrich C. Eliapixant (BAY 1817080), a P2X3 receptor antagonist, in refractory chronic cough: a randomised, placebo-controlled, crossover phase 2a study. Eur Respir J. 2021;58(5):2004240.
Fletcher MC. Selectivity of the P2X3 receptor antagonist eliapixant, and its potential use in the treatment of endometriosis. Purinergic Signal. 2022;18(1):1–3.
Dicpinigaitis PV, Morice AH, Smith JA, Sher MR, Vaezi M, Guilleminault L, Niimi A, Gude K, Krahn U, Saarinen R, Pires PV, Wosnitza M, McGarvey L, on behalf of the PAGANINI Investigators. Efficacy and safety of eliapixant in refractory chronic cough: the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2b PAGANINI study. Lung. 2023;1–12.
Klein S, Gashaw I, Baumanna S, Chang X, Hummel T, Thuss U, Friedrich C. First-in-human study of eliapixant (BAY 1817080), a highly selective P2X3 receptor antagonist, in healthy volunteers: tolerability, safety and pharmacokinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;88(10):4552–64.
Francke K, Chattopadhyay N, Klein S, Rottmann A, Krickau D, van de Wetering J, Friedrich C. Preclinical and clinical pharmacokinetics and bioavailability in healthy volunteers of a novel formulation of the selective P2X3 receptor antagonist eliapixant. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2023;48(1):75–87.
Friedrich C, Francke K, Gashaw I, Scheerans C, Klein S, Fels L, Smith JA, Hummel T, Morice A. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of P2X3 receptor antagonist eliapixant (BAY 1817080) in healthy subjects: double-blind randomized study. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2022;61(8):1143–56.
Klein S, Gashaw I, Baumann S, Chang X, Hummel T, Thuß U, Friedrich C. First-in-human study of eliapixant (BAY 1817080), a highly selective P2X3 receptor antagonist: tolerability, safety and pharmacokinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2022;88(10):4552–64.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank all the volunteers who participated in the study and the investigator team at PRA Health Science (now ICON), Groningen, for their assistance in conducting the study. Thanks are also due to the following (all employees of Bayer AG): Detlef Obst and Sabine Backhus for conducting in vitro experiments and exploratory analyses; Alexandra Neumann and Daniela Schaefer for conducting in vitro experiments; Martina Blombach and Dirk Gäfke for technical support in analyzing the mass balance study samples; Klaudia Grunenberg for analysis of human in vivo samples; and Ercan Sükür for pharmacokinetic evaluation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was funded by Bayer AG.
Conflicts of interest
Antje Rottmann, Isabel Piel, Karsten Denner, Marcus-Hillert Schultze-Mosgau, Klaus Francke, Stefanie Reif, and Stefan Klein are employees of Bayer AG. Anna Engelen was an employee of Bayer AG at the time the study was designed and conducted and is now an employee of Boehringer Ingelheim, Drug Discovery Sciences, Germany. Renger Tiessen and Ad Roffel are employees of ICON plc., Groningen, the Netherlands, formerly PRA Health Sciences, Groningen, the Netherlands. PRA Health Sciences were contracted by Bayer AG to perform the study.
Ethics approval
Both parts of the mass balance study were approved by the Medical Research Ethics Committee of the Beoordeling Ethiek Biomedisch Onderzoek (BEBO) Foundation, Assen, the Netherlands and conducted in accordance with the ethical principles that have their origins in the Declaration of Helsinki and the International Council for Harmonisation guidelines on Good Clinical Practice. The Central Committee on Research Involving Human Subjects [Centrale Commissie Mensgebonden Onderzoek (CCMO)] number was NL7431.056.20, and the EudraCT number was 2020-000519-54. The study was approved by the accredited ethics committee on 27 July 2020.
Consent to participate
All subjects in both study parts provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Data availability
Availability of the data underlying this publication will be determined according to Bayer’s commitment to the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations and Pharmaceutical Research and Manufacturers of America principles for responsible clinical trial data sharing, pertaining to scope, timepoint, and process of data access. Bayer commits to sharing, upon request from qualified scientific and medical researchers, patient-level clinical trial data, study-level clinical trial data, and protocols from clinical trials in patients for medicines and indications approved in the USA and European Union as necessary for performing legitimate research. This commitment applies to data on new medicines and indications that have been approved by the European Union and US regulatory agencies on or after 1 January 2014. Interested researchers can use https://www.clinicalstudydatarequest.com to request access to anonymized patient-level data and supporting documents from clinical studies to perform further research that can help advance medical science or improve patient care. Information on the Bayer criteria for listing studies and other relevant information is provided in the study sponsors’ section of the portal. Access will be granted to anonymized patient-level data, protocols, and clinical study reports after approval by an independent scientific review panel. Bayer is not involved in the decisions made by the independent review panel. Bayer will take all necessary measures to ensure that patient privacy is safeguarded.
Author contributions
Antje Rottmann, Isabel Piel, Anna Engelen, Karsten Denner, and Klaus Francke made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work and the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of the data. Marcus-Hillert Schultze-Mosgau and Stefanie Reif made significant contributions to the conception or design of the work, and analysis and interpretation of data. Stefan Klein made significant contributions to conception of the work and analysis of data. Ad Roffel and Renger Tiessen made significant contributions to the conception of the work and the acquisition and analysis of data. All authors drafted the manuscript or revised it critically for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript and agreed that it should be published. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Medical writing support
Medical writing services were provided by Richard Murphy, PhD of Adelphi Communications Ltd, Macclesfield, UK and funded by Bayer AG, Berlin, Germany in accordance with the Good Publication Practice guidelines, 2022.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Reif, S., Schultze-Mosgau, MH., Engelen, A. et al. Mass Balance and Metabolic Pathways of Eliapixant, a P2X3 Receptor Antagonist, in Healthy Male Volunteers. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 49, 71–85 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-023-00866-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13318-023-00866-0