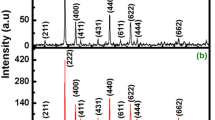
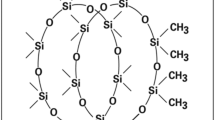
Abstract
The prolonged exposure of high-energy ionizing radiations during treatment of cancer/tumour and radiological examinations is hazardous to occupational workers and patients. Lead-incorporated composite materials are traditionally used as radiopaque fabrics, but are heavy, bulky and hence often cause inconvenience to users. Therefore, superior radiopaque protective wears that are preferably lead-free, light weight and flexible are being explored. Towards this goal, we study here the synergistic effect of graphene nanoplatelets and multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) on the X-ray attenuation property of polymer nanocomposites containing β-Bi2O3 nanofillers. The effect of graphene and MWCNT at different concentrations on Bi2O3-based polymer nanocomposites is studied to attain optimal compositions with respect to its X-ray attenuation property and thermal stability. Surface topography and surface roughness of the nanocomposite blocks are studied using an atomic force microscope (AFM). The effect of the density of polymer on the curing, thermal stability and X-ray attenuation property is also studied by using silicone polymers of density 1.7 (G1) and 1.04 g/cm3 (G2). The X-ray attenuation property of nanocomposites with G1 polymer matrix is found to be better than that of G2. The G1-based nanocomposite containing β-Bi2O3 and graphene is found to be better than the one with G1 polymer containing β-Bi2O3 and MWCNT. Thermal stability of multifiller nanocomposites is found to be better than the one without nanofillers. AFM topography images show a variation in surface roughness of nanocomposites with different fillers, which contributes to the different micro- and nano-structural architectures due to polymer–nanofiller interaction, thereby, affecting the X-ray attenuation of the nanocomposites. Our study shows that the multifiller nanocomposite containing β-Bi2O3 and graphene nanoplatelets offer greater potential for the development of efficient radiopaque fabric materials.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre FMA, Becerra RH (2015) New synthesis of bismuth oxide nanoparticles Bi2O3 assisted by tannic acid. Appl Phys A 119:909–915. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-015-9039-x
Aqel A, Nour KMMAE, Ammar RAA, Warthan AA (2012) Carbon nanotubes, science and technology part (I) structure, synthesis and characterisation. Arab J Chem 5:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2010.08.022
Aral N, Nergis FB, Candan C (2016) An alternative X-ray shielding material based on coated textiles. Text Res J 86:803–811. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517515590409
Azman NZN, Musa NFL, Razak NNANA, Ramli RM, Mustafa IS, Rahman AA, Yahaya NZ (2016) Effect of Bi2O3 particle sizes and addition of starch into Bi2O3-PVA composites for X-ray shielding. Appl Phys A 122:818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-016-0329-8
Bychkov AN, Dzhardimalieva GI, Fetisov GP, Valskiy VV, Golubeva ND, Pomogailo AD (2016) Synthesis and characterization of metal-polymer nanocomposites with radiation-protective properties. Russ Metall 2016:1207–1213. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0036029516130024
Chen S et al (2019) Bismuth oxide-based nanocomposite for high-energy electron radiation shielding. J Mater Sci 54:3023–3034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-3063-0
Cui H, Yan X, Monasterio M, Xing F (2017) Effects of various surfactants on the dispersion of MWCNTs-OH in aqueous solution. Nanomaterials (Basel) 7:262. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090262
Dai H, Hafner JH, Rinzler AG, Colbert DT, Smalley RE (1996) Nanotubes as nanoprobes in scanning probe microscopy. Nature 384:147–150. https://doi.org/10.1038/384147a0
Erol A, Pocan I, Yanbay E, Ersoz OA, Lambrecht FY (2016) Radiation shielding of polymer composite materials with wolfram carbide and boron carbide. Radiat Prot Environ 39:3–6. https://doi.org/10.4103/0972-0464.185147
Ersan G, Apul OG, Perreault F, Karanfil T (2017) Adsorption of organic contaminants by graphene nanosheets: A review. Water Res 126:385–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.08.010
Fan X, Wang L (2015) Graphene with outstanding anti-irradiation capacity as multialkylated cyclopentanes additive toward space application. Sci Rep 5:12734. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep12734
Fujimori T et al (2011) Enhanced X-ray shielding effects of carbon nanotubes. Mater Express 1:273–278. https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2011.1043
Guenther G, Guillon O (2014) Solid state transitions of Bi2O3 nanoparticles. J Mater Res 29:1383–1392. https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.124
Guenther G, Kruis FE, Guillon O (2014) Size-dependent phase transformations in bismuth oxide nanoparticles. I. Synthesis and evaporation. J Phys Chem C 118:27010–27019. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp412531t
Guo L et al (2018) Direct formation of wafer-scale single-layer graphene films on the rough surface substrate by PECVD. Carbon 129:456–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2017.12.023
Hashemi SA, Mousavi SM, Faghihi R, Arjmand M, Sina S, Amani AM (2018) Lead oxide-decorated graphene oxide/epoxy composite towards X-Ray radiation shielding. Radiat Phys Chem 146:77–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.01.008
Herrera CAR, Gonzalez JP, Feria OS, Partida NR, Vela AF, Moreno JGC (2018) Highest recorded electrical conductivity and microstructure in polypropylene-carbon nanotubes composites and the effect of carbon nanofibers addition. Appl Nanosci 8:1221–1232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0750-8
Ilunga K (2011) The effect of the Si-Bi2O3 system on the ignition of the Al-CuO thermite. M. Sc. Thesis, University of Pretoria
Jayakumar S, Saravanan T, Philip J (2017) Preparation, characterization and X-ray attenuation property of Gd2O3-based nanocomposites. Appl Nanosci 7:919–931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0631-6
Jayakumar S, Saravanan T, Philip J (2018) Thermal stability and X-ray attenuation studies of α-Bi2O3, β-Bi2O3 and Bi based nanocomposites for radiopaque fabrics. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18:3969–3981. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.15237
Johansen S, Hauge IHR, Hogg P, England A, Lanca L, Gunn C, Sanderud A (2018) Are antimony-bismuth aprons as efficient as lead rubber aprons in providing shielding against scattered radiation? J Med Imaging Radiat Sci 49:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmir.2018.02.002
Kanakia S et al (2013) Physicochemical characterization of a novel graphene-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. Int J Nanomedicine 8:2821–2833. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S47062
Kang JH, Oh SH, Oh JI, Kim SH, Choi YS, Hwang EH (2018) Protection evaluation of non-lead radiation-shielding fabric: preliminary exposure-dose study. Oral Radiology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-018-0338-8 (In Press)
Kharissova OV, Kharisov BI (2014) Variations of interlayer spacing in carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv 4:30807–30815. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA04201H
Kim Y, Park S, Seo Y (2015) Enhanced X-ray shielding ability of polymer-nonleaded metal composites by multilayer structuring. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:5968–5973. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.5b00425
Kyzas GZ, Deliyanni EA, Bikiaris DN, Mitropoulos AC (2018) Graphene composites as dye adsorbents: review. Chem Eng Res Des 129:75–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.11.006
Labouriau A et al (2015) The effects of gamma irradiation on RTV polysiloxane foams. Polym Degrad Stab 117:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2015.03.021
Li L, Zeng Z, Zou H, Liang M (2015) Curing characteristics of an epoxy resin in the presence of functional graphite oxide with amine-rich surface. Thermochim Acta 614:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2015.06.006
Li Z, Chen S, Nambiar S, Sun Y, Zhang M, Zheng W, Yeow JTW (2016) PMMA/MWCNT nanocomposite for proton radiation shielding applications. Nanotechnology 27:234001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/23/234001
Li Q, Wei Q, Zheng W, Zheng Y, Okosi N, Wang Z, Su M (2018) Enhanced radiation shielding with conformal light-weight nanoparticle-polymer composite. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:35510–35515. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b10600
Liu Y, Chi W, Duan H, Zou H, Yue D, Zhang L (2016) Property improvement of room temperature vulcanized silicone elastomer by surface-modified multi-walled carbon nanotube inclusion. J Alloys Compd 657:472–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.10.129
Maghrabi HA, Vijayan A, Deb P, Wang L (2016a) Bismuth oxide-coated fabrics for X-ray shielding. Text Res J 86:649–658. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517515592809
Maghrabi HA, Vijayan A, Mohaddes F, Deb P, Wang L (2016b) Evaluation of X-ray radiation shielding performance of barium sulphate-coated fabrics. Fibers Polym 17:2047–2054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-016-5850-z
Mayavan S, Sim JB, Choi SM (2012) Simultaneous reduction, exfoliation and functionalization of graphite oxide into a graphene-platinum nanoparticle hybrid for methanol oxidation. J Mater Chem 22:6953–6958. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM15566D
McCaffrey JP, Shen H, Downton B, Hing EM (2007) Radiation attenuation by lead and nonlead materials used in radiation shielding garments. Med Phys 34:530–537. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.2426404
Meghzifene A, Dance DR, McLean D, Kramer HM (2010) Dosimetry in diagnostic radiology. Eur J Radiol 76:11–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2010.06.032
Mirzaei M, Zarrebini M, Shirani A, Shanbeh M, Borhani S (2017) X-ray shielding by a novel garment woven with melt-spun monofilament weft yarn containing lead and tin particles. Text Res J. https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517517736475 (in press)
Mohan VB, Lau KT, Hui D, Bhattacharyya D (2018) Graphene-based materials and their composites: a review on production, applications and product limitations. Composites Part B 142:200–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.01.013
Momen G, Farzaneh M, Jafari R (2011) Wettability behaviour of RTV silicone rubber coated on nanostructured aluminium surface. Appl Surf Sci 257:6489–6493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.02.049
Nag A, Mitra A, Mukhopadhyay SC (2018) Graphene and its sensor-based applications: a review. Sens Actuators A Phys 270:177–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2017.12.028
Nambiar S, Yeow JTW (2012) Polymer-composite materials for radiation protection. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:5717–5726. https://doi.org/10.1021/am300783d
Nambiar S, Osei EK, Yeow JTW (2013) Polymer nanocomposite-based shielding against diagnostic X-rays. J Appl Polym Sci 127:4939–4946. https://doi.org/10.1002/APP.37980
Papageorgiou DG, Kinloch IA, Young RJ (2015) Graphene/elastomer nanocomposites. Carbon 95:460–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.08.055
Pinero ER, Amoros DC, Solano AL, Delpeux S, Frackowiak E, Szostak K, Beguin F (2002) High surface area carbon nanotubes prepared by chemical activation. Carbon 40:1614–1617. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(02)00134-3
Poltabtim W, Wimolmala E, Saenboonruang K (2018) Properties of lead-free gamma-ray shielding materials from metal oxide/EPDM rubber composites. Radiat Phys Chem 153:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2018.08.036
Qiu SL et al (2011) Effects of graphene oxides on the cure behaviors of a tetrafunctional epoxy resin. Express Polym Lett 5:809–818. https://doi.org/10.3144/expresspolymlett.2011.79
Quinn KJ, Courtney JM (1988) Silicones as biomaterials. Br Polym J 20:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.4980200106
Randviir EP, Brownson DAC, Banks CE (2014) A decade of graphene research: production, applications and outlook. Mater Today 17:426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2014.06.001
Rathod VT, Kumar JS, Jain A (2017) Polymer and ceramic nanocomposites for aerospace applications. Appl Nanosci 7:519–548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-017-0592-9
Rubinsztajn S, Smith LS, Baumgartner CE (2013) Silicone rubber compositions comprising bismuth oxide and articles made therefrom. US Patent 8(389):627 B2
Russell JGB (1984) How dangerous are diagnostic X-rays? Clin Radiol 35:347–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-9260(84)80170-1
Schlattl H, Zankl M, Eder H, Hoeschen C (2007) Shielding properties of lead-free protective clothing and their impact on radiation doses. Med Phys 34:4270–4280. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.2786861
Schroder F, Bagdassarov N, Ritter F, Bayarjargal L (2010) Temperature dependence of Bi2O3 structural parameters close to α–δphase transition. Phase Transit 83:311–325. https://doi.org/10.1080/01411591003795290
Scuderi GJ, Brusovanik GV, Campbell DR, Henry RP, Kwon B, Vaccaro AR (2006) Evaluation of non-lead-based protective radiological material in spinal surgery. Spine J 6:577–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2005.09.010
Seabra AB, Duran N (2015) Nanotoxicology of metal oxide nanoparticles. Metals 5:934–975. https://doi.org/10.3390/met5020934
Seibert JA, Boone JM (2005) X-Ray imaging physics for nuclear medicine technologists. Part 2: X-ray interactions and image formation. J Nucl Med Technol 33:3–18 (PMID: 15731015)
Shahriary L, Ghourchian H, Athawale AA (2014) Graphene-multiwalled carbon nanotube hybrids synthesized by gamma radiations: application as a glucose sensor. J Nanotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/903872 (Article ID 903872)
Shik NA, L.Gholamzadeh (2018) X-ray shielding performance of the EPVC composites with micro- or nanoparticles of WO3, PbO or Bi2O3. Appl Radiat Isot 139:61–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2018.03.025
Shit SC, Shah P (2013) A review on silicone rubber. Natl Acad Sci Lett 36:355. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-013-0150-2
Singh BP, Bharadwaj P, Choudhary V, Mathur RB (2014) Enhanced microwave shielding and mechanical properties of multiwall carbon nanotubes anchored carbon fiber felt reinforced epoxy multiscale composites. Appl Nanosci 4:421–428. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-013-0214-0
Soylu HM, Lambrecht FY, Ersoz OA (2015) Gamma radiation shielding efficiency of a new lead-free composite material. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 305:529–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-015-4051-3
Stewart C et al (2016) First proof of bismuth oxide nanoparticles as efficient radiosensitisers on highly radioresistant cancer cells. Phys Med 32:1444–1452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmp.2016.10.015
Tang X, Bansaruntip S, Nakayama N, Yenilmez E, Chang Yl, Wang Q (2006) Carbon nanotube DNA sensor and sensing mechanism. Nano Lett 6:1632–1636. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl060613v
Tugui C, Cazacu M, Sacarescu L, Bele A, Stiubianu G, Ursu C, Racles C (2015) Full silicone interpenetrating bi-networks with different organic groups attached to the. Silicon Atoms Polym 77:312–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2015.09.042
Viegas J, Silva LA, Batista AMS, Furtado CA, Nascimento JP, Faria LO (2017) Increased X-ray attenuation efficiency of graphene-based nanocomposite. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:11782–11790. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b02711
Wall BF, Kendall GM, Edwards AA, Bouffler S, Muirhead CR, Meara JR (2006) What are the risks from medical X-rays and other low dose radiation? Br J Radiol 79:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/55733882
Wang B et al (2018) New deformation-induced nanostructure in silicon. Nano Lett 18:4611–4617. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b01910
Wozniak AI, Ivanov VS, Zhdanovich OA, Nazarov VI, Yegorov AS (2017) Modern approaches to polymer materials protecting from ionizing radiation. Orient J Chem 33:2148–2163. https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/330502
Wu C, Li W, Gao D, Jia M (2009) Study of resistance of silicone resin to heat and irradiation. Polym Plast Technol Eng 48:1094–1100. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602550903147213
Wu X, Mu F, Wang Y, Zhao H (2018) Application of atomic simulation methods on the study of graphene nanostructure fabrication by particle beam irradiation: a review. Comput Mater Sci 149:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2018.03.022
Zhang Z, Huo F, Zhang X, Guo D (2012a) Fabrication and size prediction of crystalline nanoparticles of silicon induced by nanogrinding with ultrafine diamond grits. Scr Mater 67:657–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2012.07.016
Zhang Z, Song Y, Huo F, Guo D (2012b) Nanoscale material removal mechanism of soft-brittle HgCdTe single crystals under nanogrinding by ultrafine diamond grits. Tribol Lett 46:95–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-012-9924-9
Zhang Z, Song Y, Xu C, Guo D (2012c) A novel model for undeformed nanometer chips of soft-brittle HgCdTe films induced by ultrafine diamond grits. Scr Mater 67:197–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2012.04.017
Zhang Z, Wang B, Kang R, Zhang B, Guo D (2015) Changes in surface layer of silicon wafers from diamond scratching. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 64:349–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cirp.2015.04.005
Zhang W, Xiong H, Wang S, Li M, Gu Y, Li R (2016a) Gamma-ray shielding performance of carbon nanotube film material. Mater Express 6:456–460. https://doi.org/10.1166/mex.2016.1326
Zhang Z et al (2016b) A novel approach to fabricating a nanotwinned surface on a ternary nickel alloy. Mater Des 106:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2016.06.004
Zhang Z, Wang B, Zhou P, Guo D, Kang R, Zhang B (2016c) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing using environment-friendly slurry for mercury cadmium telluride semiconductors. Sci Rep 6:22466. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22466
Zhang Z, Wang B, Zhou P, Kang R, Zhang B, Guo D (2016d) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for cadmium zinc telluride wafers. Sci Rep 6:26891. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26891
Zhang Z, Cui J, Wang B, Wang Z, Kang R, Guo D (2017a) A novel approach of mechanical chemical grinding. J Alloys Compd 726:514–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.024
Zhang Z, Huang S, Chen L, Wang B, Wen B, Zhang B, Guo D (2017b) Ultrahigh hardness on a face-centered cubic metal. Appl Surf Sci 416:891–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.04.223
Zhang Z, Shi Z, Du Y, Yu Z, Guo L, Guo D (2018) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for a titanium alloy using an environment-friendly slurry. Appl Surf Sci 427:409–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.08.064
Zhang Z, Cui J, Zhang J, Liu D, Yu Z, Guo D (2019) Environment friendly chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Appl Surf Sci 467–468:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.133
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. G. Amarendra and Dr. A. K. Bhaduri for their constant support and encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jayakumar, S., Saravanan, T., Vadivel, M. et al. Synergistic effect of β-Bi2O3 and graphene/MWCNT in silicone-based polymeric matrices on diagnostic X-ray attenuation. Appl Nanosci 9, 1891–1913 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-00972-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-019-00972-z