Abstract
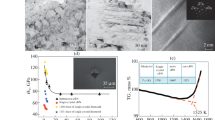
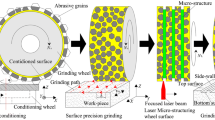
Damage-free subsurfaces of soft-brittle HgCdTe (MCT) single crystals were directly achieved after nanogrinding by a developed ultrafine diamond wheel. This is different from those of hard-brittle semiconductors, where there is usually a damaged layer found after mechanical machining. Two chips induced by nanogrinding with thicknesses varying from 23 to 27.1 nm attached on the ground MCT surface were observed, which is consistent well with a proposed model of chip thickness. Nanoscale material removal mechanism was investigated using high resolution transmission electron microscopy. Twins and nanocrystals were observed within the chips found.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan, J.W., Takahashi, H., Tamaki, J., Gai, X., Kuriyagawa, T.: Transmission electron microscopic observation of nanoindentations made on ductile-machined silicon wafers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 211901 (2005)
Zarudi, I., Nguyen, T., Zhang, L.C.: Effect of temperature and stress on plastic deformation in monocrystalline silicon induced by scratching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 011922 (2005)
Bradby, J.E., Williams, J.S., Leung, J.W., Swain, M.V., Munroe, P.: Nanoindentation-induced deformation of Ge. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 2353–2651 (2002)
Wasmer, K., Wojtan, M.P., Gassilloud, R., Pouvreau, C., Tharian, J., Micher, J.: Plastic deformation modes of gallium arsenide in nanoindentation and nanoscratching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 031902 (2007)
Zhang, Z.Y., Guo, D.M., Kang, R.K., Gao, H., Jin, Z.J., Meng, Y.W.: Subsurface crystal lattice deformation machined by ultraprecision grinding of soft-brittle CdZnTe crystals. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 47, 1065–1081 (2010)
Zhang, Z.Y., Meng, Y.W., Guo, D.M., Wu, L.L., Tian, Y.J., Liu, R.P.: Material removal mechanism of precision grinding of soft-brittle CdZnTe wafers. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 46, 563–569 (2010)
Rogalski, A.: HgCdTe infrared detector material: history, status and outlook. Rep. Prog. Phys. 68, 2267–2336 (2005)
Martyniuk, M., Sewell, R.H., Musca, C.A., Dell, J.M., Faraone, L.: Nanoindentation of HgCdTe prepared by molecular beam epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 251905 (2005)
Gopal, A.V., Rao, P.V.: A new chip-thickness model for performance assessment of silicon carbide grinding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 24, 816–820 (2004)
Snoeys, R., Peters, J.: Significance of chip thickness in grinding. Ann. CIRP 23, 227–237 (1974)
Reichenbach, G.S., Mayer, J.E., Kalpakcioglu, S., Shaw, M.C.: Role of chip thickness in grinding. Trans. ASME 78, 847–859 (1956)
Malkin, S.: Grinding technology, theory and applications of machining with abrasives. Ellis Horwood, Chichester (1989)
Tomlinson, W.J., Stapley, D.: Thermal conductivity of epoxy resin-aluminium (0–50%) composites. J. Mater. Sci. 12, 1689–1690 (1977)
Inasaki, I.: Creep feed grinding with continuous dressing. Ann. CIRP 36, 227–230 (1987)
Eberg, E., Monsen, A.F., Tybell, T., van Helvoort, A.T.J., Holmestad, R.: Comparison of TEM specimen preparation of perovskite thin films by tripod polishing and conventional ion milling. J. Electron Microsc. 57, 175–179 (2008)
Agarwal, S., Rao, P.V.: Grinding characteristics, material removal and damage formation mechanisms in high removal rate grinding of silicon carbide. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 50, 1077–1087 (2010)
Xu, L.M., Shen, B., Shih, A.J.: Vitreous bond silicon carbide wheel for grinding of silicon nitride. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 46, 631–639 (2006)
Fan, S.W., Zhang, L.T., Cheng, L.F., Tian, G.L., Yang, S.J.: Effect of braking pressure and braking speed on the tribological properties of C/SiC aircraft brake materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 70, 959–965 (2010)
Goswami, A.P., Das, G.C.: Role of fabrication route and sintering on wear and mechanical properties of liquid-phase-sintered alumina. Ceram. Int. 26, 807–819 (2000)
Avalos, J.C.R., Ramirez, A.M., Limon, J.M.Y., Garcia, M.E.C., Guzman, E.M.A., Hernandez, J.G.: Development and characterization of an inorganic foam obtained by using sodium bicarbonate as a gas generator. Constr. Build. Mater. 19, 543–549 (2005)
Xu, H.H.K., Jahanmir, S., Ives, L.K.: Effect of grinding on strength of tetragonal zirconia and zirconia-toughened alumina. Mach. Sci. Technol. 1, 49–66 (1997)
Renault, P.O., Barbot, J.F., Girault, P., Declemy, A., Rivaud, G., Blanchard, C.: Properties of dislocations in HgCdTe crystals. J. Phys. III. 5, 1383–1389 (1995)
Foll, H., Carter, C.B.: Direct TEM determination of intrinsic and extrinsic stacking fault energies of silicon. Philos. Mag. A 40, 497–510 (1979)
Ray, I.L.F., Cockayne, D.J.H.: Investigation of dislocation geometries in the diamond cubic structure. J. Microsc. 98, 170–173 (1973)
Gomez, A.M., Hirsch, P.B.: The dissociation of dislocations in GaAs. Philos. Mag. A 38, 733–737 (1978)
Gogotsi, Y.G., Domnich, V., Dub, S.N., Kailer, A., Nickel, K.G.: Cyclic nanoindentation and Raman microspectroscopy study of phase transformations in semiconductors. J. Mater. Res. 15, 871–879 (2000)
Sabinina, I.V., Gutakovsky, A.K., Sidorov, Y.G., Latyshev, A.: Nature of V-shaped defects in HgCdTe epilayers grown by molecular beam epitaxy. J. Cryst. Growth 274, 339–346 (2005)
Material Safety Dada Sheet for MCT. Spitfire Semiconductors Inc. http://www.spitfirenz.com/ (2004)
Material Safety Dada Sheet for Si, Ge and GaAs. Sciencelab.com, Inc. http://www.sciencelab.com/ (2005)
Sanjay, A., Venkateswara, R.P.: Experimental investigation of surface/subsurface damage formation and material removal mechanisms in SiC grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 48, 689–710 (2008)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91123013), and the Science and Technology Project of Dalian City of China (2009A18GX014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Song, Y., Huo, F. et al. Nanoscale Material Removal Mechanism of Soft-Brittle HgCdTe Single Crystals Under Nanogrinding by Ultrafine Diamond Grits. Tribol Lett 46, 95–100 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-012-9924-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-012-9924-9