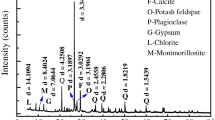
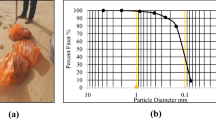
Abstract
In recent years, with the development of geothermal resources, the thermal conductivity of soil has become a research hotspot. In this study, the thermal conductivity measured by the transient plane heat source method was used to evaluate five common thermal conductivity models from the previous literature. The influences of water content and salt content on the internal heat transfer mode of this soil are explored. It was found that the presence of water in soil changes the conventional mode of point-to-point heat transfer between solid soil particles. With increases in water content, “liquid bridges” are formed between particles. During their formation, NaCl brine can transfer heat in a similar way to water. In this experiment, the model of Usowicz et al. (Intern J Heat Mass Transfer 57:536–571, 2006) was found to best describe the thermal conductivity of soil with salt contents of 0%, 2%, 4% and 6%. This study provides a valuable reference for the development of geothermal resources in the Guanzhong area and for engineering projects in loess areas.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Hamdeh NH, Reeder CR, Khdair AI, Al-Jalil HF (2000) Thermal conductivity of disturbed soils under laboratory conditions. Transactions of the ASAE 43:855–860. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.2980
Akrouch GA, Sánchez M, Briaud J-L (2014) Thermo-mechanical behavior of energy piles in high plasticity clays. Acta Geotech 9:399–412. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-014-0312-5
Al-Ajlan SA (2006) Measurements of thermal properties of insulation materials by using transient plane source technique. Appl Therm Eng 26:2184–2191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2006.04.006
Astm SD (2010) Standard Test Methods for Laboratory Determination of Water (Moisture) Content of Soil and Rock by Mass. Astm.
Barry-Macaulay D, Bouazza A, Wang B, Singh RM (2015) Evaluation of soil thermal conductivity models. Can Geotech J 52:1892–1900. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2014-0518
Bovesecchi G, Coppa P (2013) Basic Problems in thermal-conductivity measurements of soils. Int J Thermophys 34:1962–1974. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-013-1503-2
Bovesecchi G, Coppa P, Potenza M (2017) A numerical model to explain experimental results of effective thermal conductivity measurements on unsaturated soils. Int J Thermophys 38:68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-017-2202-1
Campbell GS (1985) Soil physics with BASIC. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 221–234
Chu Y, Liu S, Bate B, Xu L (2018) Evaluation on expansive performance of the expansive soil using electrical responses. J Appl Geophys 148:265–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2017.12.001
Cohen E, Glicksman L (2014) Analysis of the transient hot-wire method to measure thermal conductivity of silica aerogel: influence of wire length, and radiation properties. J Heat Transfer 136:041301. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4025921
Corasaniti S, Gori F (2002) Theoretical prediction of the soil thermal conductivity at moderately high temperatures. J Heat Transfer 124:1001–1008. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1513573
Cosenza P, Guérin R, Tabbagh A (2003) Relationship between thermal conductivity and water content of soils using numerical modelling. Eur J Soil Sci 54:581–588. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2003.00539.x
Dehghanpoor Abyaneh S, Wong HS, Buenfeld NR (2013) Modelling the diffusivity of mortar and concrete using a three-dimensional mesostructure with several aggregate shapes. Comput Mater Sci 78:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.05.024
Dong Y, McCartney JS, Lu N (2015) Critical review of thermal conductivity models for unsaturated soils. Geotech Geol Eng 33:207–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-015-9843-2
Duan Z, Cheng WC, Peng JB, Wang QY, Chen W (2019) Investigation into the triggering mechanism of loess landslides in the south Jingyang platform, Shaanxi province. Bull Eng Geol Env 78:4919–4930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-01432-8
Duan Z, Cheng WC, Peng JB, Rahman MM, Tang H (2020a) Interactions of landslide deposit with terrace sediments: perspectives from velocity of deposit movement and apparent friction angle. Eng Geol 105913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105913
Duan Z, Wu YB, Tang H, Ma JQ, Zhu XH (2020b) An analysis of factors affecting flowslide deposit morphology using taguchi method. Advances in Civil Engineering 2020:8844722. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8844722
Gangadhara Rao M, Singh DN (1999) A generalized relationship to estimate thermal resistivity of soils. Can Geotech J 36:767–773. https://doi.org/10.1139/t99-037
Gautam PK, Verma AK, Singh TN, Hu W, Singh KH (2019) Experimental investigations on the thermal properties of Jalore granitic rocks for nuclear waste repository. Thermochim Acta 681:178381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2019.178381
Gustafsson SE (1991) Transient plane source techniques for thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity measurements of solid materials. Rev Sci Instrum 62:797–804. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1142087
He H, Zhao Y, Dyck MF, Si B, Jin H, Lv J, Wang J (2017) A modified normalized model for predicting effective soil thermal conductivity. Acta Geotech 12:1281–1300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-017-0563-z
Hiraiwa Y, Kasubuchi T (2000) Temperature dependence of thermal conductivity of soil over a wide range of temperature (5–75 °C). Eur J Soil Sci 51:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2389.2000.00301.x
Jia GS, Tao ZY, Meng XZ, Ma CF, Chai JC, Jin LW (2019) Review of effective thermal conductivity models of rock-soil for geothermal energy applications. Geothermics 77:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.08.001
Johansen O (1977) Thermal Conductivity of Soils. Dissertation, University of Trondheim
Ju Z, Ren T, Hu C (2011) Soil thermal conductivity as influenced by aggregation at intermediate water contents. Soil Sci Soc Am J 75:26–29. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2010.0050N
Kang M, Lee JS (2015) Evaluation of the freezing–thawing effect in sand–silt mixtures using elastic waves and electrical resistivity. Cold Reg Sci Technol 113:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2015.02.004
Kersten MS (1949) Laboratory research for the determination of the thermal properties of soils: final report. University of Minnesota Engineering Experiment Station. Bulletin 1949. No. 28
Kosior-Kazberuk M, Ezerskiy V (2011) Mathematical modelling of thermal conductivity process in salt-contaminated wall materials. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:86–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.10.004
Li D, Sun X, Khaleel M (2013) Comparison of different upscaling methods for predicting thermal conductivity of complex heterogeneous materials system: application on nuclear waste forms. Metall Mater Trans A 44:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1269-3
Likos WJ (2015) Pore-scale model for thermal conductivity of unsaturated sand. Geotech Geol Eng 33:179–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9744-9
Lu S, Ren T, Gong Y, Horton R (2007) An improved model for predicting soil thermal conductivity from water content at room temperature. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71:8–14. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2006.0041
Lyu C, Sun Q, Zhang W (2020) Effects of NaCl concentration on thermal conductivity of clay with cooling. Bull Eng Geol Environ 79:1449–1459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01624-w
Ma G, Ran F, Yang Q, Feng E, Lei Z (2015) Eco-friendly superabsorbent composite based on sodium alginate and organo-loess with high swelling properties. RSC Adv 5:53819–53828. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA07206A
Malinarič S, Dieška P (2015) Concentric circular strips model of the transient plane source-sensor. Int J Thermophys 36:692–700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-015-1848-9
McCombie ML, Tarnawski VR, Bovesecchi G, Coppa P, Leong WH (2016) Thermal conductivity of pyroclastic soil (pozzolana) from the environs of rome. Int J Thermophys 38:21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-016-2161-y
Munoz-Castelblanco J, Pereira J-M, Delage P, Cui Y-J (2012) The influence of changes in water content on the electrical resistivity of a natural unsaturated loess. Geotech Test J 35:11–17. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ103587
Nagasaka Y, Nakazawa N, Nagashima A (1992) Experimental determination of the thermal diffusivity of molten alkali halides by the forced Rayleigh scattering method. I. Molten LiCl, NaCl, KCl, RbCl, and CsCl. Int J Thermophys 13:555–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00501941
Nikoosokhan S, Nowamooz H, Chazallon C (2016) Effect of dry density, soil texture and time-spatial variable water content on the soil thermal conductivity. Geomech Geoeng 11:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1080/17486025.2015.1048313
Noborio K, Mcinnes KJ (1993) Thermal conductivity of salt-affected soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 57:329–334. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1993.03615995005700020057x
Nusier O, Abu-Hamdeh N (2003) Laboratory techniques to evaluate thermal conductivity for some soils. Heat Mass Transf 39:119–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-002-0295-x
Radhakrishna HS, Chan HT, Crawford AM, Lau KC (1989) Thermal and physical properties of candidate buffer–backfill materials for a nuclear fuel waste disposal vault. Can Geotech J 26:629–639. https://doi.org/10.1139/t89-076
Rahib Y, Sarh B, Chaoufi J, Bonnamy S, Elorf A (2020) Physicochemical and thermal analysis of argan fruit residues (AFRs) as a new local biomass for bioenergy production. J Therm Anal Calorim. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-020-09804-7
Ren J, Men L, Zhang W, Yang J (2019) A new empirical model for the estimation of soil thermal conductivity. Environ Earth Sci 78:361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8360-7
Saito T, Hamamoto S, Ei Mon E, Takemura T, Saito H, Komatsu T, Moldrup P (2014) Thermal properties of boring core samples from the Kanto area, Japan: development of predictive models for thermal conductivity and diffusivity. Soils Found 54:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2014.02.004
Sattler P, Fredlund DG (1989) Use of thermal conductivity sensors to measure matric suction in the laboratory. Can Geotech J 26:491–498. https://doi.org/10.1139/t89-063
Seladji S, Cosenza P, Tabbagh A, Ranger J, Richard G (2010) The effect of compaction on soil electrical resistivity: a laboratory investigation. Eur J Soil Sci 61:1043–1055. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01309.x
Shan W, Liu Y, Hu Z, Xiao J (2015) A model for the electrical resistivity of frozen soils and an experimental verification of the model. Cold Reg Sci Technol 119:75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2015.07.010
Siddiqua S, Tabiatnejad B, Siemens G (2017) Impact of pore fluid chemistry on the thermal conductivity of bentonite–sand mixture. Environ Earth Sci 77:8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7182-8
Slegel D, Davis L (1977) Transient heat and mass transfer in soils in the vicinity of heated porous pipes. J Heat Transfer 99:541. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3450739
Song X, Fan H, Liu J, Yang X (2020) An improved thermal conductivity model for unsaturated clay. KSCE J Civil Eng 24:2364–2371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1812-5
Sun Q, Lu C (2019) Semiempirical correlation between thermal conductivity and electrical resistivity for silt and silty clay soils. Geophysics 84:MR99–MR105. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2018-0549.1
Tarnawski VR, Leong WH (2012) A series–parallel model for estimating the thermal conductivity of unsaturated soils. Int J Thermophys 33:1191–1218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-012-1282-1
Tarnawski VR, Momose T, Leong WH, Bovesecchi G, Coppa P (2009) Thermal conductivity of standard sands. Part I. Dry-State Conditions. Intern J Thermophys 30:949–968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-009-0596-0
Tarnawski VR, McCombie ML, Leong WH, Wagner B, Momose T, Schönenberger J (2012) Canadian field soils II. Modeling of quartz occurrence. Int J Thermophys 33:843–863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-012-1184-2
Tarnawski VR, Momose T, McCombie ML, Leong WH (2015) Canadian field soils III. Thermal-conductivity data and modeling. Int J Thermophys 36:119–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-014-1793-z
Tarnawski VR, McCombie ML, Leong WH, Coppa P, Corasaniti S, Bovesecchi G (2018) Canadian field soils IV: modeling thermal conductivity at dryness and saturation. Int J Thermophys 39:35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-017-2357-9
Tarnawski VR, Tsuchiya F, Coppa P, Bovesecchi G (2019) Volcanic soils: inverse modeling of thermal conductivity data. Int J Thermophys 40:14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-018-2480-2
Tarnawski VR, Coppa P, Leong WH, McCombie M, Bovesecchi G (2020) On modelling the thermal conductivity of soils using normalized-multi-variable pedotransfer functions. Int J Therm Sci 156:106493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2020.106493
Usowicz B, Lipiec J, Ferrero A (2006) Prediction of soil thermal conductivity based on penetration resistance and water content or air-filled porosity. Int J Heat Mass Transf 49:5010–5017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2006.05.023
Usowicz B, Lipiec J, Usowicz JB, Marczewski W (2013) Effects of aggregate size on soil thermal conductivity: comparison of measured and model-predicted data. Int J Heat Mass Transf 57:536–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.10.067
Wagner R, Clauser C (2005) Evaluating thermal response tests using parameter estimation for thermal conductivity and thermal capacity. J Geophys Eng 2:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-2132/2/4/S08
Wang J, Hayakawa KI (1993) Maximum slope method for evaluating thermal conductivity probe data. J Food Sci 58:1340–1345. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1993.tb06179.x
Wang S, Ai Q, Tq Z, Sun C, Xie M (2020) Analysis of radiation effect on thermal conductivity measurement of semi-transparent materials based on transient plane source method. Appl Therm Eng 177:115457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2020.115457
Xu P, Zhang Q, Qian H, Qu W (2020) Effect of sodium chloride concentration on saturated permeability of remolded loess. Minerals 10:199. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10020199
Yun TS, Jeong YJ, Han TS, Youm KS (2013) Evaluation of thermal conductivity for thermally insulated concretes. Energy Build 61:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2013.01.043
Yusufova VD, Pepinov RI, Nikolaev VA, Guseinov GM (1975) Thermal conductivity of aqueous solutions of NaCl. J Eng Phys 29:1225–1229. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00867119
Zhang N, Wang Z (2017) Review of soil thermal conductivity and predictive models. Int J Therm Sci 117:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.03.013
Zhang H, Li MJ, Fang WZ, Dan D, Li ZY, Tao WQ (2014) A numerical study on the theoretical accuracy of film thermal conductivity using transient plane source method. Appl Therm Eng 72:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2014.01.058
Zhang X, Li P, Li ZB, Yu GQ (2017) Soil water-salt dynamics state and associated sensitivity factors in an irrigation district of the loess area: a case study in the Luohui Canal Irrigation District China. Environ Earth Sci 76:715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-7066-y
Zhang Y-H, Feng B, Tu J, Fan LW (2019) Transient determination on the bulk thermal conductivity of sub-millimeter thin films of composite phase change thermal interfacial materials. In: ASME 2019 Heat Transfer Summer Conference collocated with the ASME 2019 13th International Conference on Energy Sustainability, 2019. V001T14A001. https://doi.org/10.1115/ht2019-3520
Zheng Q, Kaur S, Dames C, Prasher RS (2020) Analysis and improvement of the hot disk transient plane source method for low thermal conductivity materials. Int J Heat Mass Transf 151:119331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119331
Acknowledgements
The financial supports from the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 41702298, 41790442 and 41972288 from the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China under Grant No. 2017JQ4020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, X., Duan, Z. & Sun, Q. Influences of water and salt contents on the thermal conductivity of loess. Environ Earth Sci 80, 52 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09335-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-09335-2