Abstract
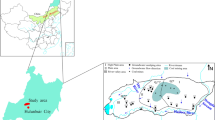
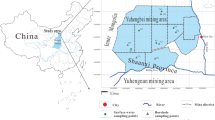
This study explores the hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality of different aquifers in the Caojiatan coal mine in the Ordos Basin, northwestern China, using classical graphical methods and multivariate analysis. The study found that surface water and groundwater in the Quaternary unconsolidated aquifer (UA) and weathered bedrock zone (WZ) have a HCO3–Ca·Mg hydrochemical type, while the groundwater in the Jurassic Zhiluo aquifer (ZA) and Jurassic Yanan aquifer (YA) are predominantly of the HCO3–Na type. Rock weathering, silicate dissolution, and reverse cation exchange are the dominant hydrogeochemical processes controlling the water chemical variables in the study area. In addition, variations in the hydraulic conductivities and TDS in different aquifers indicate that groundwater residence time is also the main factor controlling the chemical variables. Groundwater in the UA and WZ is suitable for drinking and irrigation, with low ion concentrations. However, the groundwater in ZA and YA must be treated before drinking, because of the high pH value. The excessive concentrations of F-, and high sodium adsorption ratio Na%, and residual sodium carbonate values also make the water unsuitable for irrigation. Mining activities can significantly impact the circulation and occurrence of natural groundwater. Once the groundwater in WZ becomes mine water, it becomes contaminated because of the mixing process with groundwater in ZA and YA. Further, undissolved coal slime and large quantities of oil leaking from fully mechanized mining equipment increase the CODMn levels in the mine water, making the levels higher than in natural groundwater and beyond permissible limits for drinking.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adimalla N, Li P (2019) Occurrence, health risks and geochemical mechanisms of fluoride and nitrate in groundwater of the rock-dominant semi-arid region, Telangana State, India. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):81–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1480353
Adimalla N, Li P, Qian H (2019) Evaluation of groundwater contamination for fluoride and nitrate in semi-arid region of Nirmal Province, South India: a special emphasis on human health risk assessment (HHRA). Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(5):1107–1124. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1460579
Bierkens MF, De Graaf IEM, Van Beek LP, Wada Y (2014) Global depletion of groundwater resources: past and future analyses. Agu Fall Meeting. AGU Fall Meeting Abstracts
Blake S, Henry T, Murray J, Flood R, Muller MR, Jones AG et al (2016) Compositional multivariate statistical analysis of thermal groundwater provenance: a hydrogeochemical case study from ireland. Appl Geochem 75:171–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.05.008
Cerling TE, Pederson BL (1989) Sodium-calcium ionexchange in the weathering of shales: implications for global weathering budgets. Geology 17:552–554. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1989)017<0552:scieit>2.3.co;2
Cidu R, Biddau R, Fanfani L (2009) Impact of past mining activity on the quality of groundwater in sw sardinia (italy). J Geochem Explor 100(2):125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2008.02.003
Cloutier V, René L, René T, Savard MM (2008) Multivariate statistical analysis of geochemical data as indicative of the hydrogeochemical evolution of groundwater in a sedimentary rock aquifer system. J Hydrol (Amsterdam) 353(3–4):294–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.02.015
Collins R, Jenkins A (1996) The impact of agricultural land use on stream chemistry in the middle hills of the Himalayas, Nepal. J Hydrol 185:71–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(95)03008-5
Ghesquière O, Walter J, Chesnaux R, Rouleau A (2015) Scenarios of groundwater chemical evolution in a region of the Canadian Shield based on multivariate statistical analysis. J Hydrol Reg Stud 4:246–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2015.06.004
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 170(3962):1088–1090. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
He S, Li P (2019) A MATLAB based graphical user interface (GUI) for quickly producing widely used hydrogeochemical diagrams. Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2019.125550
He X, Li P (2020) Surface water pollution in the middle Chinese Loess Plateau with special focus on hexavalent chromium (Cr6+): occurrence, sources and health risks. Expo Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-020-00344-x
He S, Wu J (2019a) Hydrogeochemical characteristics, groundwater quality and health risks from hexavalent chromium and nitrate in groundwater of Huanhe Formation in Wuqi County, northwest China. Expo Health 11(2):125–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0289-7
He S, Wu J (2019b) Relationships of groundwater quality and associated health risks with land use/land cover patterns: a case study in a loess area, northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):354–373. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1570463
He X, Wu J, He S (2019a) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in terms of health risks in Luohe aquifer in Wuqi County of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):32–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1531693
He S, Li P, Wu J, Elumalai V, Adimalla N (2019b) Groundwater quality under land use/land cover changes: a temporal study from 2005 to 2015 in Xi’an, northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1684186
Johnson AI (1972) Symposium on planning and design of groundwater data programs: introduction. Water Resour Res 8(1):177. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr008i001p00177
Kumar M, Ramanathan A, Rao MS, Kumar B (2006) Identification and evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Delhi, India. Environ Geol 50(7):1025–1039. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0275-4
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2013a) Major ion chemistry of shallow groundwater in the Dongsheng Coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. Mine Water Environ 32(3):195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-013-0234-8
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2013b) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County, China. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2211–2225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2049-5
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2014) Occurrence and hydrogeochemistry of fluoride in shallow alluvial aquifer of Weihe River, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(7):3133–3145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2691-6
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J (2015) Building a new and sustainable “Silk Road economic belt”. Environ Earth Sci 74(10):7267–7270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4739-2
Li P, Li X, Meng X, Li M (2016a) Zhang Y (2016a) Appraising groundwater quality and health risks from contamination in a semiarid region of northwest China. Expos Health 8(3):361–379. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0205-y
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Zhang Y, Yang N, Jing L, Yu P (2016b) Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger Desert, Northwest China. Expo Health 8(3):331–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0193-y
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016c) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab J Geosci 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2059-1
Li P, Zhang Y, Yang N, Jing L, Yu P (2016d) Major ion chemistry and quality assessment of groundwater in and around a mountainous tourist town of China. Expo Health 8(2):239–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0198-6
Li P, Tian R, Xue C, Wu J (2017a) Progress, opportunities and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(15):13224–13234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8753-7
Li P, Qian H, Zhou W (2017b) Finding harmony between the environment and humanity: an introduction to the thematic issue of the Silk Road. Environ Earth Sci 76(3):105. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6428-9
Li J, Depaolo DJ, Wang Y, Xie X (2018a) Calcium isotope fractionation in a silicate dominated cenozoic aquifer system. J Hydrol 559:523–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.02.039
Li P, He S, He X, Tian R (2018b) Seasonal hydrochemical characterization and groundwater quality delineation based on matter element extension analysis in a paper wastewater irrigation area, northwest China. Expo Health 10(4):241–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-17-0258-6
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2018c) Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, North-West China. Int J Water Resour Dev 34(3):337–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2018.1443059
Li P, Wu J, Tian R, He S, He X, Xue C, Zhang K (2018d) Geochemistry, hydraulic connectivity and quality appraisal of multilayered groundwater in the Hongdunzi Coal Mine, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(2):222–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0507-8
Li P, He S, Yang N, Xiang G (2018e) Groundwater quality assessment for domestic and agricultural purposes in Yan’an City, northwest China: implications to sustainable groundwater quality management on the Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 77(23):775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7968-3
Li P, He X, Guo W (2019a) Spatial groundwater quality and potential health risks due to nitrate ingestion through drinking water: a case study in Yan’an City on the Loess Plateau of northwest China. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25(1–2):11–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1553612
Li P, Tian R, Liu R (2019b) Solute geochemistry and multivariate analysis of water quality in the Guohua phosphorite mine, Guizhou Province, China. Expo Health 11(2):81–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0277-y
Li P, He X, Li Y, Xiang G (2019c) Occurrence and health implication of fluoride in groundwater of loess aquifer in the Chinese Loess Plateau: a case study of Tongchuan, northwest China. Expo Health 11(2):95–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0278-x
Mahato MK, Singh PK, Singh AK, Tiwari AK (2018) Assessment of hydrogeochemical processes and mine water suitability for domestic, irrigation, and industrial purposes in East Bokaro Coalfield, India. Mine Water Environ 37(1):493–504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0508-7
Meybeck M (1987) Global chemical weathering of surficial rocks estimated from river dissolved loads. Am J Sci 287(5):401–428. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.287.5.401
Ministry of Health of the P. R. China, Standardization Administration of the P. R. China (2006) Standards for drinking water quality (GB5749–2006). China Standard Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Montcoudiol N, Molson J, Lemieux JM (2014) Groundwater geochemistry of the outaouais region (Québec, Canada): a regional-scale study. Hydrogeol J 23(2):377–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-014-1190-5
Nordstrom DK, Ball JW, Donahoe RJ, Whittemore D (1989) Groundwater chemistry and water-rock interactions at stripa. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53(8):1727–1740. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(89)90294-9
Piña A, Donado LD, Blake S, Cramer T (2018) Compositional multivariate statistical analysis of the hydrogeochemical processes in a fractured massif: la línea tunnel project, colombia. Appl Geochem 95:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.05.012
Piper (1944) A graphical procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analysis. Am Geophys Union Trans 25:914–928. https://doi.org/10.1029/tr025i006p00914
Qian H, Li P, Wu J, Zhou Y (2013) Isotopic Characteristics of Precipitation, Surface and Ground Waters in the Yinchuan Plain, Northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 70(1):57–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2103-3
Qian H, Wu J, Zhou Y, Li P (2014) Stable oxygen and hydrogen isotopes as indicators of lake water recharge and evaporation in the lakes of the Yinchuan Plain. Hydrol Process 28:3554–3562. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.9915
Scanlon BR (1989) Physical controls on hydrochemical variability in the inner bluegrass karst region of central kentuckya. Groundwater 27(5):639–646. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1989.tb00477.x
Schoeller H (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development. Water Research, Series-33. UNESCO, Delft, pp 54–83
Scott AC, Whittal RM, Fedorak PM (2009) Coal is a potential source of naphthenic acids in groundwater. Sci Total Environ 407(7):2451–2459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.12.028
Shi B (2011) Research on water-preserved-mining in shallow seam covered with rock soil and sand in Northern Shaanxi. J Min Saf Eng 28(4):548–552 (in Chinese)
Stiff HA (1951) The interpretation of chemical water analysis by means of patterns. J Petrol Technol 3(10):15–30. https://doi.org/10.2118/951376-g
Tiwari AK, Ghione R, De MM, Lavy M (2017) Evaluation of hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality for suitability of drinking and irrigation purposes: a case study in the aosta valley region, italy. Arab J Geosci 10(12):264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-017-3031-z
Turner JV, Macpherson DK (1990) Mechanisms affecting streamflow and stream water quality: an approach via stable isotope, hydrogeochemical, and time series analysis. Water Resour Res 26(12):3005–3019. https://doi.org/10.1029/90wr01514
USSL (US Salinity Laboratory) (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. US Dept of Agriculture Hand Book, No 60
Wada Y, Beek LPHV, Kempen CMV, Reckman JWTM, Vasak S, Bierkens MFP (2010) Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophys Res Lett 37:L20402. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010gl044571
Wang X, Ji H, Qi W, Liu X, Dan H, Yao X et al (2016) Divisions based on groundwater chemical characteristics and discrimination of water inrush sources in the pingdingshan coalfield. Environ Earth Sci 75(10):872. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5616-3
Wang D, Wu J, Wang Y, Ji Y (2019a) Finding high-quality groundwater resources to reduce the hydatidosis incidence in the Shiqu County of Sichuan Province, China: Analysis, Assessment, and Management. Expo Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-019-00314-y
Wang Q, Jin D, Wang W, Liu J, Yang J et al (2019b) Joint effects of groundwater and aridity index on the transpiration of vegetation: a case study in the Yushen mining area. J China Coal Soc 44(3):840–846 (in Chinese)
Webster JG, Brown KL, Vincent WF (1994) Geochemical processes affecting meltwater chemistry and the formation of saline ponds in the victoria valley and bull pass region, antarctica. Hydrobiologia 281(3):171–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00028680
WHO (2017) Guidelines for drinking-water quality: fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. World Health Organization, Geneva, p 631
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters. US Dept of Agriculture, Washington, DC (Circular 969)
Wu J, Li P, Qian H, Duan Z, Zhang X (2014) Using correlation and multivariate statistical analysis to identify hydrogeochemical processes affecting the major ion chemistry of waters: case study in Laoheba phosphorite mine in Sichuan, China. Arab J Geosci 7(10):3973–3982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-1057-4
Wu J, Li P, Qian H (2015) Hydrochemical characterization of drinking groundwater with special reference to fluoride in an arid area of China and the control of aquifer leakage on its concentrations. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8575–8588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4018-2
Wu J, Zhou H, He S, Zhang Y (2019a) Comprehensive understanding of groundwater quality for domestic and agricultural purposes in terms of health risks in a coal mine area of the Ordos basin, north of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 78(15):446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8471-1
Wu J, Li P, Wang D, Ren X, Wei M (2019b) Statistical and multivariate statistical techniques to trace the sources and affecting factors of groundwater pollution in a rapidly growing city on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Hum Ecol Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2019.1594156
Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhou H (2020) Groundwater chemistry and groundwater quality index incorporating health risk weighting in Dingbian County, Ordos basin of northwest China. Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125607
Yang Z, Wang W, Wang Z, Jiang G, Li W (2016) Ecology-oriented groundwater resource assessment in the tuwei river watershed, Shaanxi province, china. Hydrogeol J 24(8):1939–1952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1446-3
Yang J, Liu J, Jin D, Wang Q (2018a) Method of determining mine water inrush source based on combination of organic–inorganic water chemistry. J China Coal Soc 43(10):2886–2894 (in Chinese)
Yang J, Wang Q, Liu J, Wang TT, Zhang XY (2018b) Fluorescence characteristics of dissolved organic matter in underground different position of coal mine. J China Coal Soc 43(S2):546–552 (in Chinese)
Zhang Y, Wu J, Xu B (2018) Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Jinghui canal irrigation area of the loess region, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 77(7):273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7456-9
Zhao C, Jin D, Geng J, Sun Q (2018) Numerical simulation of the groundwater system for mining shallow buried coal seams in the ecologically fragile areas of western china. Mine Water Environ 38(1):158–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-018-0551-z
Zhao C, Jin D, Wang H, Wang Q, Wang S, Liu Y (2019) Construction and application of overburden damage and aquifer water loss model in medium-deep buried coal seam mining in Yushen mining area. J China Coal Soc 44(7):2227–2235 (in Chinese)
Zheng Y, Geen AV, Stute M, Dhar R, Mo Z, Cheng Z et al (2005) Geochemical and hydrogeological contrasts between shallow and deeper aquifers in two villages of araihazar, bangladesh: implications for deeper aquifers as drinking water sources. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69(22):5203–5218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.06.001
Zhou Y, Li P, Xue L, Dong Z, Li D (2020) Solute geochemistry and groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes: a case study in Xinle City, North China. Geochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemer.2020.125609
Zhu B, Yang X, Rioual P, Qin X, Liu Z, Xiong H, Yu J (2011) Hydrogeochemistry of three watersheds (the Erlqis, Zhungarer and Yili) in northern Xinjiang, NW China. Appl Geochem 26(8):1535–1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.06.018
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Chinese 13th Five-Year Key Research and Development Program (Grant no. 2017YFC0804100), Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Grant no. 2019JQ-009), China National Natural Science Foundation (Grant no. 41907264), and Science and Technology Innovation Fund of Xi’an Research Institute of CCTEG (Grant no. 2018XAYZD11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is a part of the Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on “Water in Large Basins” guest edited by Peiyue Li and Jianhua Wu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Dong, S., Wang, H. et al. Hydrogeochemical processes and groundwater quality assessment for different aquifers in the Caojiatan coal mine of Ordos Basin, northwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 79, 199 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-08942-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-08942-3