Abstract
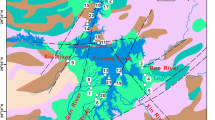
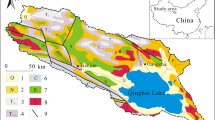
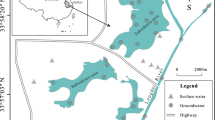
The isotopic characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen of various water bodies in the Yinchuan plain were investigated. A total of 131 water samples were collected and another 99 water samples collected by other scholars and the International Atomic Energy Agency were referred to in the study. The stable isotopic compositions of precipitation and lake waters are influenced by dry climate and strong evaporation of the area, and the slope of local meteoric water line and lake water line are smaller than that of global meteoric water line. The isotopic compositions of the Yellow River water are significantly lower than the weighted averages of local atmospheric precipitation and are controlled by the runoff of upstream areas. The isotopes of phreatic water suggest that the single phreatic water is predominantly recharged by the bedrock fissure water of Helan Mountain, while the phreatic water in multilayer structure area is recharged by multiple sources. The confined waters in the area may be recharged under cooler climate conditions than the present, which makes the heavy isotopes depleted. The 3H contents of various water bodies are in the following order: the Yellow River water > multilayer phreatic water > single phreatic water > lake water > drainage ditch water > upper confined water > lower confined water. This is in accordance with the recharge, discharge and circulation conditions of the specific water bodies. The isotope compositions of waters in the Yinchuan plain are mainly affected by external water recharge rather than local precipitation. This study is meaningful and helpful in understanding the groundwater flow systems and water cycle in the area.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark I, Fritz P (1997) Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology. Lewis, New York
Craig H (1961) Isotope variations in meteoric waters. Science 133:1702–1703
Craig H, Gordon LI (1965) Deuterium and oxygen-18 variations in the ocean and the marine atmosphere. In: Tongiorgi E (ed) Stable isotopes in oceanographic studies and paleotemperatures. C. N. R. laboratorio di Geologia Nuclear, Pisa, pp 9–130
Exploration and Development Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Ningxia (1990) Groundwater resources management model of Yinchuan City. Yinchuan (in Chinese)
Gat JR (1996) Oxygen and hydrogen isotopes in the hydrologic cycle. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 24:225–262
Gibson JJ, Prepas EE, McEachern P (2002) Quantitative comparison of lake through flow, residency and catchment runoff using stable isotopes: modeling and results from a regional survey of Boreal lakes. J Hydrol 262:128–144. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(02)00022-7
Gonfiantini R (1978) Standards for stable isotope measurements in natural compounds. Nature 271:534–536
Gonfiantini R (1986) Environmental isotopes in lake studies. In: Fritz P, Fontes JC (eds) Handbook of environmental isotope geochemistry, vol 2., The Terrestrial Environment B. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 113–168
IAEA (2006) Isotope hydrology information system. The ISOHIS database. http://www.iaea.org/water
Jin XM, Xue ZQ, Yu QS, Yu YQ (2007) Groundwater resources development and variation in vegetation and in the Yinchuan Plain. Hydrogeol Eng Geol 34(3):33–36 (in Chinese)
Jin XM, Hu GC, Shi XJ (2009) Relationship between soil salinization and the vegetation growing, groundwater depth in the Yinchuan plain. Geoscience 23(1):23–27 (in Chinese)
Kebede S, Travi Y, Rozanski K (2009) The δ 18O and δ 2H enrichment of Ethiopian lakes. J Hydrol 365:173–182. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.11.027
Mayr C, Lücke A, Stichler W et al (2007) Precipitation origin and evaporation of lakes in semi-arid Patagonia (Argentina) inferred from stable isotopes (δ 18O, δ 2H). J Hydrol 334:53–63. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.09.025
Ningxia Institute of Geologic Engineering Investigation (1995) Report on groundwater resources and the geo-environmental investigation in agricultural production base of the Yinchuan plain, Yinchuan (in Chinese)
Qian H, Li PY (2011) Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater in Yinchuan plain and their control factors. Asian J Chem 23(7):2927–2938
Qian H, Li MY, Ji YD, Yang BC, Zhao ZH (2007) Changes of δ 18O and δD along the Dousitu River, Inner Mongolia, China, and their evidence of river water evaporation. Aquat Geochem 13(2):127–142. doi:10.1007/s10498-007-9011-2
Qian H, Li PY, Howard KWF, Yang C, Zhang XD (2012) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability in the Yinchuan Plain, Northwest China using OREADIC. Environ Monit Assess 184(6):3613–3628. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2211-7
Su XS, Lin XY, Liao ZS, Wang JS (2003) Variation of isotopes in the Yellow River along the flow path and its affecting factors. Geochimica 4:349–357 (in Chinese)
Sun XC, Jin XM, Wan L (2008) Effect of groundwater on vegetation growth in Yinchuan plain. Geoscience 22(2):321–324 (in Chinese)
Wang L, Yu FL (2001) Shallow groundwater resources and water salinity control in Yinchuan plain. Resour Sci 23(3):82–87 (in Chinese)
Wang WK, Han JP, Zhao YQ, Yu DM, Wang HY (2004) Optimal allocation of water resources in Yinchuan plain. Resour Sci 26(2):36–45 (in Chinese)
Wu XH, Qian H, Yu DM et al (2008) Investigation and assessment on the rational allocation of groundwater resources in the Yinchuan plain. Geology Publishing House, Beijing
Zhang L, Wang L (2003) Groundwater resources in Ningxia. Ningxia Publishing House, Yinchuan (in Chinese)
Zhang Q, Zhang L (2010) Main water-related environmental problems in Yinchuan plain and the corresponding countermeasure. J Earth Sci Environ 32(4):392–397 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This research project was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41172212), the Doctor Postgraduate Technical Project of Chang’an University (CHD2011ZY025 and CHD2011ZY022) and the Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research of Central Colleges (CHD2012TD003). We would like to thank the editor and anonymous reviewers for their useful comments that have lead to the greatly improved version of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qian, H., Li, P., Wu, J. et al. Isotopic characteristics of precipitation, surface and ground waters in the Yinchuan plain, Northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 70, 57–70 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2103-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2103-3