Abstract
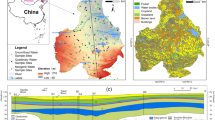
Groundwater is critical for the sustainable development of the Loess Plateau, while groundwater quality is generally poor in this area due to natural factors and anthropogenic pollution. This study was carried out to investigate the suitability of groundwater for domestic and agricultural purposes in Yan’an City on the Chinese Loess Plateau and to assess its implications to sustainable groundwater management on the plateau. The index levels were compared with the threshold values established by the national and the WHO drinking water guidelines, and the suitability of groundwater for irrigation purposes was assessed using multiple agricultural water quality indicators. An entropy-weighted Technique for Order Preference by Similarity to an Ideal Solution (entropy-weighted TOPSIS) was adopted for overall groundwater quality assessment. The results indicate that the study area is characterized by saline, hard, and slightly alkaline groundwater, mainly of the HCO3–Ca·Mg type, accompanied by some minor SO4·Cl–Ca·Mg type. The dissolution of carbonates and gypsum and the leaching of soluble salts are important natural processes influencing the groundwater ion chemistry. The parameters TH, TDS, and SO42− are major indices, while Fe, Mn, F−, and NH4+ are minor contaminants affecting groundwater quality. The overall groundwater quality is generally acceptable for irrigation, and most of the water is suitable for drinking. Rainwater harvesting, water quality improvement programs, regular water quality monitoring, and multidisciplinary water research programs are suggested as measures for sustainable groundwater management on the Loess Plateau.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adimalla N, Li P, Venkatayogi S (2018a) Hydrogeochemical evaluation of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and integrated interpretation with water quality index studies. Environ Process. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-018-0297-4
Adimalla N, Li P, Qian H (2018b) Evaluation of groundwater contamination for fluoride and nitrate in semi-arid region of Nirmal Province, South India: a special emphasis on human health risk assessment (HHRA). Human Ecol Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.146057
Adimalla N, Vasa SK, Li P (2018c) Evaluation of groundwater quality, Peddavagu in Central Telangana (PCT), South India: an insight of controlling factors of fluoride enrichment. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0443-z
Ai N, Wei T, Zhu Q, Qiang F, Ma H, Qin W (2017) Impacts of land disturbance and restoration on runoff production and sediment yield in the Chinese Loess Plateau. J Arid Land 9(1):76–86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-016-0088-6
Ako AA, Eyong GET, Shimada J, Koike K, Hosono T, Ichiyanagi K, Richard A, Tandia BK, Nkeng GE, Roger NN (2014) Nitrate contamination of groundwater in two areas of the Cameroon Volcanic Line (Banana Plain and Mount Cameroon area). Appl Water Sci 4:99–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0134-x
Amalraj A, Pius A (2018) Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and agricultural purposes of a few selected areas in Tamil Nadu South India: a GIS-based study. Sustain Water Resour Manag 4:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0113-8
Awasthi A, Chauhan SS, Goyal SK (2010) A fuzzy multicriteria approach for evaluating environmental performance of suppliers. Int J Prod Econ 126(2):370–378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2010.04.029
Brantley SL, Goldhaber MB, Vala Ragnarsdottir K (2007) Crossing disciplines and scales to understand the critical zone. Elements 3(5):307–314. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.3.5.307
Campisano A, Butler D, Ward S, Burns MJ, Friedler E, DeBusk K, Fisher-Jeffes LN, Ghisi E, Rahman A, Furumai H, Han M (2017) Urban rainwater harvesting systems: research, implementation and future perspectives. Water Res 115:195–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.02.056
Chadha DK (1999) A proposed new diagram for geochemical classification of natural waters and interpretation of chemical data. Hydrogeol J 7:431–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100400050216
Chen J, Qian H, Wu H (2017) Nitrogen contamination in groundwater in an agricultural region along the New Silk Road, northwest China: distribution and factors controlling its fate. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(15):13154–13167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8881-0
Chen J, Wu H, Qian H, Li X (2018a) Challenges and prospects of sustainable groundwater management in an agricultural plain along the Silk Road Economic Belt, north-west China. Int J Water Resour Dev 34(3):354–368. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2016.1238348
Chen D, Li J, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Li T, Liu J (2018b) Simulating and mapping the spatial and seasonal effects of future climate and land -use changes on ecosystem services in the Yanhe watershed, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(2):1115–1131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0499-8
Cheong J-Y, Hamm S-Y, Lee J-H, Lee K-S, Woo N-C (2012) Groundwater nitrate contamination and risk assessment in an agricultural area, South Korea. Environ Earth Sci 66:1127–1136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-1320-5
Elisante E, Muzuka ANN (2017) Occurrence of nitrate in Tanzanian groundwater aquifers: a review. Appl Water Sci 7(1):71–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0269-z
Esmaeili A, Moore F, Keshavarzi B (2014) Nitrate contamination in irrigation groundwater, Isfahan, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 72:2511–2522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3159-z
Falkenmark M (2005) Water usability degradation: economist wisdom or societal madness? Water Int 30(2):136–146. https://doi.org/10.1080/02508060508691854
Ferchichi H, Ben Hamouda MF, Farhat B, Ben Mammou A (2018) Assessment of groundwater salinity using GIS and multivariate statistics in a coastal Mediterranean aquifer. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1767-y
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection & quarantine of China, Standardization Administration of China (2017) standards for groundwater quality, (GB/T 14848—2017). Standards Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Gilabert-Alarcón C, Daesslé LW, Salgado-Méndez SO, Pérez-Flores MA, Knöller K, Kretzschmar TG, Stumpp C (2018) Effects of reclaimed water discharge in the Maneadero coastal aquifer, Baja California, Mexico. Appl Geochem 92:121–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.03.006
Gnecco I, Palla A, La Barbera P (2017) The role of domestic rainwater harvesting systems in storm water runoff mitigation. Eur Water 58:497–503
He S, Wu J (2018) Hydrogeochemical characteristics, groundwater quality and health risks from hexavalent chromium and nitrate in groundwater of Huanhe Formation in Wuqi County, northwest China. Exposure Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0289-7
He X, Wu J, He S (2018) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality evaluation of groundwater in terms of health risks in Luohe aquifer in Wuqi County of the Chinese Loess Plateau, northwest China. Human Ecol Risk Assess. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807039.2018.1531693
Hou Y, Lü Y, Chen W, Fu B (2017) Temporal variation and spatial scale dependency of ecosystem service interactions: a case study on the central Loess Plateau of China. Landscape Ecol 32(6):1201–1217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-017-0497-8
Hwang CL, Yoon K (1981) Multiple attribute decision making methods and applications. Springer–Heidelberg, Berlin
IAH (International Association of Hydrogeologists) (2015) World Water Day 2015—embracing groundwater. https://iah.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/2015WWD.pdf. Accessed 15 April 2018
IAH (International Association of Hydrogeologists) (2016) Global change and groundwater. https://iah.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/IAH-Global-Change-Groundwater-14-June-2016.pdf. Accessed 15 April 2018
Jain CK, Vaid U (2018) Assessment of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes using hydrochemical studies in Nalbari district of Assam, India. Environ Earth Sci 77:254. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7422-6
Kalaivanan K, Gurugnanam B, Pourghasemi HR, Suresh M, Kumaravel S (2017) Spatial assessment of groundwater quality using water quality index and hydrochemical indices in the Kodavanar sub-basin, Tamil Nadu, India. Sustain Water Resour Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-017-0148-x
Kelemenis A, Askounis D (2010) A new TOPSIS-based multi-criteria approach to personnel selection. Expert Syst Appl 37:4999–5008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2009.12.013
Kelley WP (1963) Use of saline irrigation water. Soil Sci 95(6):385–391. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-196306000-00003
Kumar M, Kumari K, Ramanathan AL, Saxena R (2007) A comparative evaluation of groundwater suitability for irrigation and drinking purposes in two intensively cultivated districts of Punjab, India. Environ Geol 53:553–574. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-0672-3
Lapworth DJ, Nkhuwa DCW, Okotto-Okotto J, Pedley S, Stuart ME, Tijani MN, Wright J (2017) Urban groundwater quality in sub-Saharan Africa: current status and implications for water security and public health. Hydrogeol J 25:1093–1116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-016-1516-6
Lasagna M, De Luca DA, Franchino E (2016) Nitrate contamination of groundwater in the western Po Plain (Italy): the effects of groundwater and surface water interactions. Environ Earth Sci 75:240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5039-6
Li P, Qian H (2018a) Water resources research to support a sustainable China. Int J Water Resour Dev 34(3):327–336. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2018.1452723
Li P, Qian H (2018b) Water in loess. In: Meyers RA (ed) Encyclopedia of sustainability science and technology. Springer, New York, pp 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-2493-6_968-1
Li PY, Wu JH, Qian H (2012) Groundwater quality assessment based on rough sets attribute reduction and TOPSIS method in a semi-arid area. China Environ Monit Assess 184(8):4841–4854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2306-1
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2013) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County, China. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2211–2225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-2049-5
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2014) Accelerate research on land creation. Nature 510(7503):29–31. https://doi.org/10.1038/510029a
Li X, Li J, Xi B, Yuan Z, Zhu X, Zhang X (2015a) Effects of groundwater level variations on the nitrate content of groundwater: a case study in Luoyang area, China. Environ Earth Sci 74(5):3969–3983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4016-4
Li P, Qian H, Howard KWF, Wu J (2015b) Building a new and sustainable “Silk Road economic belt”. Environ Earth Sci 74(10):7267–7270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4739-2
Li P, Wu J, Qian H, Zhang Y, Yang N, Jing L, Yu P (2016a) Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger Desert, Northwest China. Expo Health 8(3):331–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0193-y
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016b) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab J Geosci 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2059-1
Li P, Tian R, Xue C, Wu J (2017a) Progress, opportunities and key fields for groundwater quality research under the impacts of human activities in China with a special focus on western China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(15):13224–13234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8753-7
Li P, Feng W, Xue C, Tian R, Wang S (2017b) Spatiotemporal variability of contaminants in lake water and their risks to human health: a case study of the Shahu Lake tourist area, northwest China. Expo Health 9(3):213–225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0237-3
Li P, He X, Li Y, Xiang G (2018a) Occurrence and health implication of fluoride in groundwater of loess aquifers in the Chinese Loess Plateau: a case study of Tongchuan, northwest China. Expo Health. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-018-0278-x
Li P, Wu J, Tian R, He S, He X, Xue C, Zhang K (2018b) Geochemistry, hydraulic connectivity and quality appraisal of multilayered groundwater in the Hongdunzi coal mine, Northwest China. Mine Water Environ 37(2):222–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-017-0507-8
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2018c) Conjunctive use of groundwater and surface water to reduce soil salinization in the Yinchuan Plain, north-west China. Int J Water Resour Dev 34(3):337–353. https://doi.org/10.1080/07900627.2018.1443059
Lin H (2010) Earth’s critical zone and hydropedology: concepts, characteristics, and advances. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 14:25–45. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-14-25-2010
McKinley DC, Miller-Rushing AJ, Ballard HL, Bonney R, Brown H, Cook-Patton SC, Evans DM, French RA, Parrish JK, Phillips TB, Ryan SF, Shanley LA, Shirk JL, Stepenuck KF, Weltzin JF, Wiggins A, Boyle OD, Briggs RD, Soukup MA (2017) Citizen science can improve conservation science, natural resource management, and environmental protection. Biol Cons 208:15–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2016.05.015
Ministry of Health of China, Standardization Administration of China (2006) Standard Examination methods for drinking water (GB/T 5750 – 2006). Standards Press of China, Beijing (in Chinese)
Morris BL, Lawrence ARL, Chilton PJC, Adams B, Calow RC, Klinck BA (2003) Groundwater and its susceptibility to degradation: a global assessment of the problem and options for management. Early warning and assessment report series 03–3, United Nations Environment Programme, pp 126, Nairobi, Kenya. Available at http://nora.nerc.ac.uk/id/eprint/19395/1/Groundwater_INC_cover.pdf. Accessed 22 Nov 2018
Nagaraju A, Thejaswi A, Sharifi Z (2016) Assessment of groundwater quality and its suitability for agricultural usage in and around Rangampeta Area, Andhra Pradesh, South India. J Water Chem Technol 38(6):358–365. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1063455X16060102
Peng J, Fan Z, Wu D, Zhuang J, Dai F, Chen W, Zhao C (2015) Heavy rainfall triggered loess–mudstone landslide and subsequent debris flow in Tianshui, China. Eng Geol 186:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.08.015
Peng J, Wang G, Wang Q, Zhang F (2017) Shear wave velocity imaging of landslide debris deposited on an erodible bed and possible movement mechanism for a loess landslide in Jingyang, Xi’an, China. Landslides 14(4):1503–1512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0827-6
Qian J, Wang L, Liu Y, Wu B, Wang X (2015) Distribution of nitrate and its implication for the contaminant source in groundwater of Huaibei Plain, Anhui Province. Geosci J 19(3):537–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-014-0051-5
Rezaei M, Nikbakht M, Shakeri A (2017) Geochemistry and sources of fluoride and nitrate contamination of groundwater in Lar area, south Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(18):15471–15487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9108-0
Sadi-Nezhad S, Damghani KK (2010) Application of a fuzzy TOPSIS method base on modified preference ratio and fuzzy distance measurement in assessment of traffic police centers performance. Appl Soft Comput 10:1028–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2009.08.036
Seibert SL, Holt T, Reckhardt A, Ahrens J, Beck M, Pollmann T, Giani L, Waska H, Böttcher ME, Greskowiak J, Massmann G (2018) Hydrochemical evolution of a freshwater lens below a barrier island (Spiekeroog, Germany): the role of carbonate mineral reactions, cation exchange and redox processes. Appl Geochem 92:196–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.03.001
Singh AL, Singh VK (2018) Assessment of groundwater quality of Ballia district, Uttar Pradesh, India, with reference to arsenic contamination using multivariate statistical analysis. Appl Water Sci 8:95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0737-3
Srinivas Y, Aghil TB, Oliver DH, Nair CN, Chandrasekar N (2017) Hydrochemical characteristics and quality assessment of groundwater along the Manavalakurichi coast, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl Water Sci 7(3):1429–1438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0325-8
Tiwari AK, Maio MD, Amanzio G (2017) Evaluation of metal contamination in the groundwater of the Aosta Valley Region, Italy. Int J Environ Res 11(3):291–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-017-0027-1
USSL (US Salinity Laboratory) (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of salinity and alkaline soil. USDA Hand Book no. 60, Washington
Vandanapu R, Omer JR, Attom MF (2017) Laboratory simulation of irrigation-induced settlement of collapsible desert soils under constant surcharge. Geotech Geol Eng 35(6):2827–2840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0282-0
Vetrimurugan E, Elango L (2015) Groundwater chemistry and quality in an intensively cultivated river delta. Water Qual Expo Health 7(2):125–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-014-0133-7
Vikas C, Kushwaha R, Ahmad W, Prasannakumar V, Dhanya PV, Reghunath R (2015) Hydrochemical appraisal and geochemical evolution of groundwater with special reference to nitrate contamination in aquifers of a semi-arid terrain of NW India. Water Qual Expo Health 7(3):347–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-014-0155-1
Vystavna Y, Diadin D, Yakovlev V, Hejzlar J, Vadillo I, Huneau F, Lehmann MF (2017) Nitrate contamination in a shallow urban aquifer in East Ukraine: evidence from hydrochemical, stable isotopes of nitrate and land use analysis. Environ Earth Sci 76:463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6796-1
Wang X, Jiao F, Li X, An S (2017) The Loess Plateau. In: Zhang L, Schwärzel K (eds) Multifunctional land-use systems for managing the nexus of environmental resources. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-54957-6_2
Wasana HMS, Aluthpatabendi D, Kularatne WMTD, Wijekoon P, Weerasooriya R, Bandara J (2016) Drinking water quality and chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu): synergic effects of fluoride, cadmium and hardness of water. Environ Geochem Health 38(1):157–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-015-9699-7
WHO (2017) Guidelines for drinking water quality: fourth edition incorporating the first addendum. World Health Organization, Geneva
Wilcox LV (1955) Classification and use of irrigation waters. USDA, Washington, DC (Circular 969)
Wu J (2015) Evolution and regulation of groundwater environment affected by land creation project in loess area: a case study from the construction of Yan’an New District. Ph.D. Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, pp 143 (in Chinese)
Wu J, Sun Z (2016) Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, mid-west China. Expo Health 8(3):311–329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x
Wu J, Li P, Qian H (2011) Groundwater quality in Jingyuan County, a semi-humid area in Northwest China. E-J Chem 8(2):787–793. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/163695
Wu J, Li P, Qian H, Fang Y (2014) Assessment of soil salinization based on a low-cost method and its influencing factors in a semi-arid agricultural area, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 71(8):3465–3475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-013-2736-x
Wu J, Li P, Qian H, Chen J (2015) On the sensitivity of entropy weight to sample statistics in assessing water quality: statistical analysis based on large stochastic samples. Environ Earth Sci 74(3):2185–2195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4208-y
Wu J, Wang L, Wang S, Tian R, Xue C, Feng W, Li Y (2017) Spatiotemporal variation of groundwater quality in an arid area experiencing long-term paper wastewater irrigation, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 76(13):460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6787-2
Xiao J, Jin Z, Zhang F (2015) Geochemical controls on fluoride concentrations in natural waters from the middle Loess Plateau, China. J Geochem Explor 159:252–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.018
Xu Y, Leung CF, Yu J, Chen W (2018) Numerical modelling of hydro-mechanical behaviour of ground settlement due to rising water table in loess. Nat Hazards. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-018-3385-x
Yan’an Local Chronicles Committee (2000) Yan’an area chronicles. Xi’an Publishing House, Xi’an. http://fzbz.yanan.gov.cn/info/iList.jsp?cat_id=10439&tm_id=136. Accessed 16 June 2018 (in Chinese)
Yang Z, Kong F, Zhang M (2016) Groundwater contamination by microcystin from toxic cyanobacteria blooms in Lake Chaohu, China. Environ Monit Assess 188:280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5289-0
Yin X, Chen L, He J, Feng X, Zeng W (2016) Characteristics of groundwater flow field after land creation engineering in the hilly and gully area of the Loess Plateau. Arab J Geosci 9:646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2672-7
Yue BJ, Shi ZH, Fang NF (2014) Evaluation of rainfall erosivity and its temporal variation in the Yanhe River catchment of the Chinese Loess Plateau. Nat Hazards 74(2):585–602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1199-z
Zhang Y, Wu J, Xu B (2018) Human health risk assessment of groundwater nitrogen pollution in Jinghui canal irrigation area of the loess region, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 77(7):273. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7456-9
Zhuang J, Peng J, Xu Y, Xu Q, Zhu X, Li W (2016) Assessment and mapping of slope stability based on slope units: a case study in Yan’an, China. J Earth Syst Sci 125(7):1439–1450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-016-0741-7
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the various agencies and institutes that provided financial support for the research presented in this paper. They are the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41502234, 41602238, 41572236 and 41761144059), the Research Funds for Young Stars in Science and Technology of Shaanxi Province (2016KJXX-29), the Special Funds for Basic Scientific Research of Central Colleges (300102298301), the Fok Ying Tong Education Foundation (161098), the General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M580804), the Special Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016T090878), the Special Financial Grant from the Shaanxi Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015BSHTDZZ09), the Innovation Training Program for Undergraduate Students of Chang’an University (201710710099 and 201710710100) and the Ten Thousand Talents Program. The anonymous reviewers and the editor are also sincerely acknowledged for their useful and constructive comments which have helped us improve the quality of the paper. In addition, the first author thanks his wife and his new baby boy who bring him a lot of joy which is very helpful to relieve his mental stress.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is a part of a Topical Collection in Environmental Earth Sciences on Water resources development and protection in loess areas of the world, edited by Drs. Peiyue Li and Hui Qian.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., He, S., Yang, N. et al. Groundwater quality assessment for domestic and agricultural purposes in Yan’an City, northwest China: implications to sustainable groundwater quality management on the Loess Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 77, 775 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7968-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7968-3