Abstract
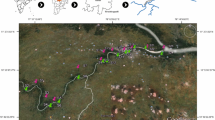
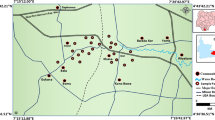
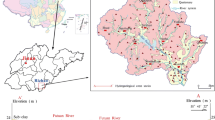
Groundwater is widely used for various purposes over the world. To investigate the quality of groundwater for domestic and agricultural purposes in a mountainous tourist town of China, nine groundwater and three river water samples were collected during June 2015 for analysis of major ions (K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3 −, SO4 2−, Cl−, and CO3 2−), pH, total dissolved solids, electric conductivity, and total hardness. The sources of major ions were discussed in detail by correlation analysis and bivariate diagrams. Sodium adsorption ratio, residual sodium carbonate, soluble sodium percentage, permeability index, and Kelley’s ratio were applied for irrigation water quality assessment. Physiochemical parameters were also compared with the WHO and national standards for domestic purpose. The results demonstrate that both groundwater and river water are fresh water. The abundance of cations in collected water samples is Ca2+ > Na+ > Mg2+ > K+, while that of anions is HCO3 − > SO4 2− > Cl−. All major ion concentrations except CO3 2− in groundwater are higher than those in the river water because of more contacts with rocks and more mineral dissolution in the groundwater. Groundwater in the study area is mainly of SO4·Cl–Ca·Mg type and HCO3–Ca·Mg type, and river water is of SO4·Cl–Ca·Mg type. Groundwater and river water in the study area are both controlled mainly by rock weathering. The dissolutions of halite, carbonates, and silicates, as well as cation exchange and human activities such as fertilizer application in agriculture, geothermal bathing, and tourism are drivers for the variation of major ions in the water. Groundwater is generally suitable for domestic uses except some local samples experiencing low pH and high hardness. Both groundwater and river water in the study area are suitable for irrigation. Land irrigated rationally with such water will have no salinity and alkali hazards.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdesselam S, Halitim A, Jan A, Trolard F, Bourrie G (2013) Anthropogenic contamination of groundwater with nitratein arid region: case study of southern Hodna (Algeria). Environ Earth Sci 70:2129–2141. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1834-5
Alam F (2014) Evaluation of hydrogeochemical parameters of groundwater for suitability of domestic and irrigational purposes: a case study from central Ganga Plain, India. Arab J Geosci 7:4121–4131. doi:10.1007/s12517-013-1055-6
Almasri MN, Kaluarachchi JJ (2007) Modeling nitrate contamination of groundwater in agricultural watersheds. J Hydrol 343:211–229. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2007.06.016
Anantha RV, Chandrakanta G (2014) Major ion chemistry, hydro-geochemical studies and mapping of variability in ground water quality of Sitanadi basin, Southern Karnataka. Octa J Environ Res 2(2):178–196
Chen J, Wang F, Xia X, Zhang L (2002) Major element chemistry of the Changjiang (Yangtze River). Chem Geol 187:231–255. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00032-3
Chen J, Taniguchi M, Liu G, Miyaoka K, Onodera S, Tokunaga T, Fukushima Y (2007) Nitrate pollution of groundwater in the Yellow River delta, China. Hydrogeol J 15:1605–1614. doi:10.1007/s10040-007-0196-7
Davraz A, Özdemir A (2014) Groundwater quality assessment and its suitability in Çeltikçi plain (Burdur/Turkey). Environ Earth Sci 72:1167–1190. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-3036-1
Ding J, Qian H, Li P, Zheng F, Wang C (2009) Geochemical characteristics and medical values of geothermal water in Xi’an. In: The 3rd international conference on bioinformatics and biomedical engineering, 2009 (ICBBE 2009). IEEE, pp 1–4. doi:10.1109/ICBBE.2009.5162884
Doneen LD (1962) The influence of crop and soil on percolating waters. In: Schiff L (ed.) Proceedings of the 1961 Biennial conference on Groundwater recharge, pp 156–163
Doneen LD (1975) Water quality for irrigated agriculture. In: Poljakoff-Mayber A. (ed.) Plants in saline environments, pp 56–76
Eiswirth M, Hötzl H (1997) The impact of leaking sewers on urban groundwater. In: Chilton J (ed.) Groundwater in the urban environment, pp 399–404
Elbaz-Poulichet F, Favreau G, Leduc C, Seidel JL (2002) Major ion chemistry of groundwaters in the Continental Terminal water table of southwestern Niger (Africa). Appl Geochem 17:1343–1349. doi:10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00024-0
Esmaeili A, Moore F, Keshavarzi B (2014) Nitrate contamination in irrigation groundwater, Isfahan, Iran. Environ Earth Sci 72:2511–2522. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3159-z
Gibbs RJ (1970) Mechanisms controlling world water chemistry. Science 17:1088–1090. doi:10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
Griffioen J (2001) Potassium adsorption ratios as an indicator for the fate of agricultural potassium in groundwater. J Hydrol 254(1–4):244–254. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00503-0
Han Y, Wang GC, Cravotta CA III, Hu WY, Bian YY, Zhang ZW, Liu YY (2012) Hydrogeochemical evolution of Ordovician limestone groundwater in Yanzhou. Hydrol Process, North China. doi:10.1002/hyp.9297
Joshi DM, Kumar A, Agrawal N (2009) Assessment of the irrigation water quality of river Ganga in Haridwar district. Rasayan J Chem 2(2):285–292
Khairy H, Janardhana MR (2014) Hydrogeochemistry and quality of groundwater of coastal unconfined aquifer in Amol-Ghaemshahr plain, Mazandaran Province, Northern Iran. Environ Earth Sci 71:4767–4782. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2868-z
Kolahchi Z, Jalali M (2007) Effect of water quality on the leaching of potassium from sandy soil. J Arid Environ 68:624–639. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2006.06.010
Krishnakumar P, Lakshumanan C, Kishore VP, Sundararajan M, Santhiya G, Chidambaram S (2014) Assessment of groundwater quality in and around Vedaraniyam, South India. Environ Earth Sci 71:2211–2225. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2626-2
Lee B, Zhu L, Zhang G, Guo B, Gong H, Yao A (2010) Geological characteristics, metallogenic background, and genesis of the Tongyu VHMS copper deposit in the west part of the North Qinling, Shaanxi Province. Sci China Earth Sci 53(10):1460–1485. doi:10.1007/s11430-010-4054-4
Li P-Y, Qian H, Wu J-H, Ding J (2010) Geochemical modeling of groundwater in southern plain area of Pengyang County, Ningxia, China. Water Sci Eng 3(3):282–291. doi:10.3882/j.issn.1674-2370.2010.03.004
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2011) Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution laws of drinking groundwater in Pengyang County, Ningxia, northwest China. E-J Chem 8(2):565–575. doi:10.1155/2011/472085
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2013a) Major ion chemistry of shallow groundwater in the Dongsheng coalfield, Ordos Basin, China. Mine Water Environ 32(3):195–206. doi:10.1007/s10230-013-0234-8
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2013b) Assessment of groundwater quality for irrigation purposes and identification of hydrogeochemical evolution mechanisms in Pengyang County, China. Environ Earth Sci 69(7):2211–2225. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-2049-5
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2013c) Occurrence and hydrogeochemistry of fluoride in alluvial aquifer of Weihe River. China Environ Earth Sci 71:3133–3145. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2691-6
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2014a) Hydrogeochemistry and quality assessment of shallow groundwater in the southern part of the Yellow River alluvial plain (Zhongwei Section), China. Earth Sci Res J 18(1):27–38. doi:10.15446/esrj.v18n1.34048
Li P, Qian H, Wu J, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang H (2014b) Occurrence and hydrogeochemistry of fluoride in shallow alluvial aquifer of Weihe River, China. Environ Earth Sci 71(7):3133–3145. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2691-6
Li P, Qian H, Wu J (2014c) Origin and assessment of groundwater pollution and associated health risk: a case study in an industrial park, northwest China. Environ Geochem Health 36(4):693–712. doi:10.1007/s10653-013-9590-3
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016a) Hydrochemical appraisal of groundwater quality for drinking and irrigation purposes and the major influencing factors: a case study in and around Hua County, China. Arab J Geosci 9(1):15. doi:10.1007/s12517-015-2059-1
Li P, Wu J, Qian H (2016b) Hydrogeochemical characterization of groundwater in and around a wastewater irrigated forest in the southeastern edge of the Tengger Desert, Northwest China. Expo Health. doi:10.1007/s12403-016-0193-y
Ma Z, Yu J, Su Y, Xie J, Jia X, Hu Y (2010) δ 18O shifts of geothermal waters in the central of Weihe Basin, NW China. Environ Earth Sci 59:995–1008. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0092-7
Maharana C, Gautam SK, Singh AK, Tripathi JK (2015) Major ion chemistry of the Son River, India: weathering processes, dissolved fluxes and water quality assessment. J Earth Syst Sci 124(6):1293–1309. doi:10.1007/s12040-015-0599-0
Marghade D, Malpe DB, Zade AB (2012) Major ion chemistry of shallow groundwater of a fast growing city of Central India. Environ Monit Assess 184:2405–2418. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2126-3
Marghade D, Malpe DB, Subba Rao N (2015) Identification of controlling processes of groundwater quality in a developing urban area using principal component analysis. Environ Earth Sci 74:5919–5933. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4616-z
Ministry of Health of the PRC, Standardization Administration of the PRC (2006) Standards for drinking water quality (GB5749–2006). China Standard Press (in Chinese), Beijing
Mondal D, Gupta S (2015) Fluoride hydrogeochemistry in alluvial aquifer: an implication to chemical weathering and ion-exchange phenomena. Environ Earth Sci 73:3537–3554. doi:10.1007/s12665-014-3639-1
Naseem S, Rafique T, Bashir E, Bhanger MI, Laghari A, Usmani TH (2010) Lithological influences on occurrence of high-fluoride groundwater in Nagar Parkar area, Thar Desert, Pakistan. Chemosphere 78:1313–1321. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.01.010
Neumann RB, Ashfaque KN, Badruzzaman ABM, Ali MA, Shoemaker JK, Harvey CF (2010) Anthropogenic influences on groundwater arsenic concentrations in Bangladesh. Nat Geosci 3:46–52. doi:10.1038/ngeo685
Pastén-Zapata E, Ledesma-Ruiz R, Harter T, Ramírez AI, Mahlknecht J (2014) Assessment of sources and fate of nitrate in shallow groundwater of an agricultural area by using a multi-tracer approach. Sci Total Environ 470–471:855–864. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.10.043
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water-analyses. Trans Am Geophys Union 25(6):914–928. doi:10.1029/TR025i006p00914
Qian H, Ma Z, Li P (2012) Hydrogeochemistry, 2nd edn. Geologic Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Rice EW, Baird RB, Eaton AD, Clesceri LS (2012) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Sawyer CN, McCarty PL (1967) Chemistry for sanitary engineers, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, p 518
Schoeller H (1965) Qualitative evaluation of groundwater resources. In: Methods and techniques of groundwater investigation and development. Water Research Series 33: UNESCO, pp 54–83
Shanyengana ES, Seely MK, Sanderson RD (2004) Major-ion chemistry and ground-water salinization in ephemeral floodplains in some arid regions of Namibia. J Arid Environ 57:71–83. doi:10.1016/S0140-1963(03)00095-8
Subba Rao N, Rao PS (2010) Major ion chemistry of groundwater in a river basin: a study from India. Environ Earth Sci 61:757–775. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0389-6
Trusdell AH, Jones BF (1973) WATEQ: a computer program for calculating chemical equilibria of natural waters. J Res US Geol Surv 2(2):233–248
United States Salinity Laboratory (USSL) (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Agriculture handbook 60, US Department of Agriculture (USDA), Washington, pp 69–81
Vasanthavigar M, Srinivasamoorthy K, Prasanna MV (2012) Evaluation of groundwater suitability for domestic, irrigational, and industrial purposes: a case study from Thirumanimuttar river basin, Tamilnadu, India. Environ Monit Assess 184:405–420. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-1977-y
Vetrimurugan E, Elango L (2015) Groundwater chemistry and quality in an intensively cultivated river delta. Water Qual Expo Health 7(2):125–141. doi:10.1007/s12403-014-0133-7
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking water quality, 4th edn. World Health Organization, Geneva. ISBN 978-92-4-154815-1
Wilcox LV (1948) The quality of water for irrigation use. US Department of Agriculture, Washington, Tech Bull 1962
Wu J, Sun Z (2015) Evaluation of shallow groundwater contamination and associated human health risk in an alluvial plain impacted by agricultural and industrial activities, Mid-west China. Expo Health. doi:10.1007/s12403-015-0170-x
Wu J, Li P, Qian H, Fang Y (2014) Assessment of soil salinization based on a low-cost method and its influencing factors in a semi-arid agricultural area, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 71(8):3465–3475. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2736-x
Wu J, Li P, Qian H (2015) Hydrochemical characterization of drinking groundwater with special reference to fluoride in an arid area of China and the control of aquifer leakage on its concentrations. Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8575–8588. doi:10.1007/s12665-015-4018-2
Zhang L, Song X, Xia J, Yuan R, Zhang Y, Liu X, Han D (2011) Major element chemistry of the Huai River basin, China. Appl Geochem 26:293–300. doi:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.12.002
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to the funds granted by the Innovation Training Program for Undergraduate Students of Chang’an University (201510710072), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41502234), the Foundation of Outstanding Young Scholar of Chang’an University (310829153509), the General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M580804), the Special Financial Grant from the Shaanxi Postdoctoral Science Foundation, the Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research of Central Colleges (310829151072), and the Special Fund for Scientific Research on Public Interest of the Ministry of Water Resources (201301084). We are also grateful to Tao Qian who has helped us a lot in the sample analysis. The anonymous reviewers and the editors are sincerely acknowledged for their constructive comments which have helped us in improving the quality of the original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Zhang, Y., Yang, N. et al. Major Ion Chemistry and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in and Around a Mountainous Tourist Town of China. Expo Health 8, 239–252 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0198-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12403-016-0198-6