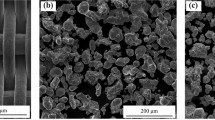
Abstract
Direct energy deposition (DED) has great potential for the production of stainless steel matrix nanocomposite parts. However, the propensity of nanoparticle agglomeration leads to the difficulty in realizing homogenous dispersion of nanoparticles in the matrix. In this study, a series of agglomeration-free nano-WC-Co-reinforced 420 stainless steel matrix nanocomposite powders with high flowability were prepared by ball milling under the optimal parameters. The effect of ball milling time on the properties of the composite powders was investigated. Excellent powder properties ensure the DED processing performance. Furthermore, the corresponding composites were fabricated by DED, and the effects of nano-WC-Co content on the properties of the composites were comprehensively investigated. The contact angles between the single pass cladding layer and the substrate change with increasing nano-WC-Co content (decrease from 127.38° to 113.07°). The different contact angles will significantly influence the quality of the multi-pass cladding layer. Furthermore, the addition of nano-WC-Co leads not only to further grain refinement but also to more pronounced isotropy of the microstructure. With the increase in nano-WC-Co content, the corrosion resistance is significantly improved (62.28% lower corrosion current for 420–15 wt% nano-WC-Co than for 420).
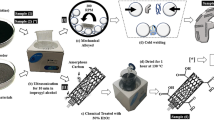
Graphical abstract

摘要
直接能量沉积法(DED)在不锈钢基纳米复合材料的制备中具有很大的潜力。然而,纳米颗粒的团聚会导致纳米颗 粒难以在基体中实现均匀分散。本研究采用球磨法,在最佳工艺条件下制备了一系列高流动性的无团聚纳米WCCo 增强420 基纳米复合粉体。研究了球磨时间对复合粉体性能的影响。优良的粉末性能保证了DED 的加工性能。 采用DED 法制备了相应的复合材料,并综合研究了纳米WC-Co 含量对复合材料性能的影响。随着纳米WC-Co 含量的增加,单道次熔覆层与基体的接触角发生变化(从127.38°减小到113.07°)。不同的接触角对多道次熔覆层 的质量有显著影响。此外,纳米WC-Co 的加入不仅使晶粒进一步细化,而且使微观结构具有更明显的各向同性。 随着纳米WC-Co 含量的增加,纳米WC-Co 的耐蚀性显著提高(420-15 wt%纳米WC-Co 的腐蚀电流比420 低 62.28%)。








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nath SD, Clinning E, Gupta G, Poirier VW, Espérance G, Gulsoy O, Kearns M. Effects of Nb and Mo on the microstructure and properties of 420 stainless steel processed by laser-powder bed fusion. Addit Manuf. 2019;28:682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2019.06.016.
Sadoun AM, Najjar IR, Alsoruji GS, Abd-Elwahed MS, Elaziz MA, Fathy A. Utilization of improved machine learning method based on artificial hummingbird algorithm to predict the tribological behavior of Cu-Al2O3 nanocomposites synthesized by in situ method. Mathematics. 2022;10(8):1266. https://doi.org/10.3390/math10081266.
Zhang RY, Li JX, Yang S, Yan H, Liu H, Zhao G. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of TiB2(p)/ZL205 composites with different TiB2 conten. Chin J Rare Met. 2021;45(2):194. https://doi.org/10.13373/j.cnki.cjrm.xy19060027.
Wang T, Liu XY, Chen SY, Lei JB, Song XL. Study on microstructure and tribological properties of nano/micron TiC/TC4 composites fabricated by laser melting deposition. J Manuf Process. 2022;82:296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.07.068.
Sadoun AM, Najjar IMR, Abd-Elwahed MS, Meselhy A. Experimental study on properties of Al-Al2O3 nanocomposite hybridized by graphene nanosheets. J Mater Res Technol. 2020;9(6):14708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.10.011.
Shi J, Wang Y. Development of metal matrix composites by laser-assisted additive manufacturing technologies: a review. J Mater Sci. 2020;55:9883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-020-04730-3.
Chen HY, Gu DD, Zhang HM. Novel WC-reinforced iron-based composites with excellent mechanical properties synthesized by laser additive manufacturing: underlying role of reinforcement weight fraction. J Mater Process Tech. 2021;289:116959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116959.
Wang X, Zhang ZH, Men YZ, Li XJ, Liang YH, Ren LQ. Fabrication of nano-TiC functional gradient wear-resistant composite coating on 40Cr gear steel using laser cladding under starved lubrication conditions. Opt Laser Technol. 2020;126:106136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106136.
Hao XN, Liu X. Molecular dynamics study on microscale residual stress of graphene/aluminum nanocomposites by selective laser sintering. Rare Met. 2022;41(11):3677. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-022-02079-x.
Ertugrul O, Enrici TM, Paydas H. Laser cladding of TiC reinforced 316L stainless steel composites: feedstock powder preparation and microstructural evaluation. Powder Technol. 2020;375:384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.07.100.
Wang RQ, Xi LX, Gökce B, Barcikowski S, Gu DD. Powder preparation during ball milling and laser additive manufacturing of aluminum matrix nanocomposites: powder properties, processability and mechanical property. Adv Powder Technol. 2022;8(33):103687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2022.103687.
Bartkowski D, Bartkowska A, Jurči P. Laser cladding process of Fe/WC metal matrix composite coatings on low carbon steel using Yb: YAG disk laser. Opt Laser Technol. 2021;136:106784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106784.
Chen H, Lu YY, Sun YS. Coarse TiC particles reinforced H13 steel matrix composites produced by laser cladding. Surf Coat Tech. 2020;395:125867. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.125867.
Zhang Z, Kovacevic R. Laser cladding of iron-based erosion resistant metal matrix composites. J Manuf Process. 2019;38:63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.01.001.
Tian ZH, Zhao YT, Jiang YJ, Ren HP. Microstructure and properties of Inconel 625 + WC composite coatings prepared by laser cladding. Rare Met. 2021;40(8):2281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01507-0.
Chen LY, Zhao Y, Meng FW, Yu TB, Ma ZL, Qu S, Sun ZY. Effect of TiC content on the microstructure and wear performance of in situ synthesized Ni-based composite coatings by laser direct energy deposition. Surf Coat Technol. 2022;444:128678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128678.
Wang Z, Tan MX, Wang J, Zeng J, Zhao FJ, Xiao XY, Xu SR, Liu B, Gong L, Sui QX, Zhang RZ, Han B, Liu J. Core–shell structural iron based metal matrix composite powder for laser cladding. J Alloys Compd. 2021;878:160127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.160127.
Zhu HM, Ouyang MN, Hu JP. Design and development of TiC-reinforced 410 martensitic stainless steel coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Ceram Int. 2021;9(47):12505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.01.108.
Zhou SW, Xu TY, Hu C. Utilizing carbon nanotubes in ceramic particle reinforced MMC coatings deposited by laser cladding with Inconel 625 wire. J Mater Res Technol. 2021;13:2026. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.06.028.
Oliveira U, Ocelík V, De Hosson JThM. Analysis of coaxial laser cladding processing conditions. Surf Coat Tech. 2005;197(2–3):127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2004.06.029.
Wang Z, Wang J, Xu SR, Liu B, Sui QX, Zhao FJ, Gong L, Liu J. Influence of powder characteristics on microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 718 superalloy manufactured by direct energy deposition. Appl Surf Sci. 2022;583:152545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.152545.
Zhai WG, Zhu ZG, Zhou W, Nai SML, Wei J. Selective laser melting of dispersed TiC particles strengthened 316L stainless steel. Compos Part B Eng. 2020;199:108291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108291.
Chen HY, Gu DD, Kosiba K, Lu TW, Deng L, Xi LX, Kühn U. Achieving high strength and high ductility in WC-reinforced iron-based composites by laser additive manufacturing. Addit Manuf. 2020;35:101195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addma.2020.101195.
Benarji K, Ravikumar Y, Jinoop AN, Paul CP, Bindra KS. Effect of WC composition on the microstructure and surface properties of laser directed energy deposited SS 316-WC composites. J Mater Eng Perform. 2021;30:6732. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-021-05971-2.
Hosseini-Tayeb H, Rafiaei SM. Enhanced microstructural and mechanical properties of stellite/wc nanocomposite on Inconel 718 deposited through vibration-assisted laser cladding. Int J Miner Metall Mater. 2022;29:327. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2211-0.
Wang T, Zhu L, Song HY, Wang H. Effect of WC-17Co content on microstructure and properties of IN718 composites prepared by laser cladding. Opt Laser Technol. 2022;148:107780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107780.
Liu SF, Li YZ, Wang Y, Yk W, Zhang LL, Wang JY, Yang X. Selective laser melting of WC-Co reinforced AISI 1045 steel composites: microstructure characterization and mechanical properties. J Mater Res Technol. 2022;19:1821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.05.158.
Mola J, Seo EJ, Cho L. Correlation between mechanical stability and hardness of austenite in martensite/austenite mixtures. Mater Sci Eng A. 2021;822:141687. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.141687.
Xu SP, Shi CS, Zhao NQ, He CN. Microstructure and tensile properties of A356 alloy with different Sc/Zr additions. Rare Met. 2021;40(9):2514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-020-01529-8.
Chen W, Xu LY, Hao KD, Han YD, Zhao L, Jing HY. Additive manufacturing of 15–5PH/WC composites with the synergistic enhancement of strength and ductility. Mater Sci Eng A. 2022;840:142926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2022.142926.
Chen HY, Lu TW, Wang YG, Liu Y, Shi TY, Prashanth KG, Kosiba K. Laser additive manufacturing of nano-TiC particles reinforced CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy matrix composites with high strength and ductility. Mater Sci Eng A. 2022;833:142512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.142512.
Gu DD, Ma J, Chen HY, Lin KJ, Xi LX. Laser additive manufactured WC reinforced Fe-based composites with gradient reinforcement/matrix interface and enhanced performance. Compos Struct. 2018;192:387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.03.008.
Zhu CB, Fordyce L, Sun SD, Annasamy M, Fabijanic D, Short K, Paradowska A, Leary M, Brandt M, Easton M. Effect of Ti and TiC additions on the microstructure and wear resistance of high chromium white irons produced by laser directed energy deposition. Wear. 2022;510–511:204519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2022.204519.
Yi JL, Niu B, Pan LL, Zou XD, Cao Y, Wang X, Luo JW, Hu YJ. Influence of WC grain size on the microstructure and wear property enhancement of 18Ni300 coatings. Surf Coat Technol. 2022;447:128823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128823.
Zhou L, Zhang JW, Li SQ, Tian Y, Wang JP, Huang MY, Yuan Q, Li X, Kou ZL, Zhan GD, He DW. Effects of hardness and grain size on wear resistance of polycrystalline cubic boron nitride. Int J Refract Hard Meter. 2022;836:142574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2021.142574.
Xie HB, Zhang JL, Li FL, Yuan GQ, Zhu Q, Jia QL, Zhang HJ, Zhang SW. Selective laser melting of SiCp/Al composites: densification, microstructure, and mechanical and tribological properties. Ceram Int. 2021;21(47):30826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.263.
Chen L, Sun YZ, Li L, Ren YP, Ren XD. In situ TiC/Inconel 625 nanocomposites fabricated by selective laser melting: densification behavior, microstructure evolution, and wear properties. Appl Surf Sci. 2020;518:145981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145981.
Xie HB, Zhang JL, Li FL, Yuan GQ, Zhu Q, Jia QL, Zhang HJ, Zhang SW. Selective laser melting of SiCp/Al composites: densification, microstructure, and mechanical and tribological properties. Ceram Int. 2021;47(21):30826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2021.07.263.
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by Gansu Science and Technology Department (No. 21ZD3GC001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Xu, SR., Sui, QX. et al. High-performance martensitic stainless steel nanocomposite powder for direct energy deposition prepared by ball milling. Rare Met. 42, 2419–2432 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02267-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-023-02267-3