Abstract
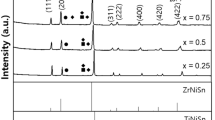
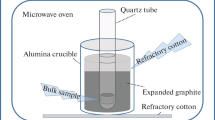
We obtained TiNiSn-based half-Heusler HfxTi1−xNiSn0.97Sb0.03 bulks with 85%–96% relative densities via 5-min microwave synthesis and 20-min microwave sintering in sealed vacuum. The phase composition and microstructure of samples were characterized by X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Thermoelectric (TE) properties were measured, i.e., Seebeck coefficient (S), electrical resistivity (ρ), and thermal conductivity (κ) through Seebeck coefficient/resistance analysis system (S/RAs) and laser flash thermal analyzer (LFT). The results show that the nearly single phase exists after microwave sintering. The grain sizes and the number of grain boundaries decrease with increase in Hf-doping amount due to an increase in point defects. The matrix grains for Hf0.1Ti0.9NiSn0.97Sb0.03 are ~ 10 μm. The nanoscle pores and precipitates are present as second phases in matrix grain. The real composition for Hf0.1Ti0.9NiSn0.97Sb0.03 matrix grain is Hf3.51Ti28.76Ni34.76Sn31.55Sb1.43. The variation trends of electrical resistivity, Seebeck coefficient, power factor, and thermal conductivity were analyzed in detail. The maximum figure of merit (ZT) of 0.46 is obtained for Hf0.1Ti0.9NiSnSn0.97Sb0.03 at 723 K. The innovation route exhibits advantages for predation of TE bulks when compared to the conventional methods, especially in terms of efficiency while it still maintains TE performance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu R, Tan X, Liu YC, Ren GK, Lan JL, Zhou ZF, Nan CW, Lin YH. BiCuSeO as state-of-the-art thermoelectric materials for energy conversion: from thin films to bulks. Rare Met. 2018;37(4):5.
Kosuga A, Fujii Y, Horie A. High-temperature formation phases and crystal structure of hot-pressed thermoelectric compounds with chalcopyrite-type structure. Rare Met. 2018;37(4):360.
Aliev FG, Brandt NB, Moshchalkov VV, Kozyrkov VV, Skolozdra RV, Belogorokhov AI. Gap at the Fermi level in the intermetallic vacancy system RBiSn (R = Ti, Zr, Hf). Z Phys B Condens Matter. 1989;75(2):167.
Aliev FG, Kozyrkov VV, Moshchalkov VV, Skolozdra RV, Durczewski K. Narrow band in the intermetallic compounds MNiSn (M = Ti, Zr, Hf). Z Phys B Condens Matter. 1990;80(3):353.
Uher C, Yang J, Hu S, Morelli DT, Meisner GP. Transport properties of pure and doped MNiSn(M = Zr, Hf). Phys Rev B. 1999;50(59):8615.
Populoh S, Aguirre MH, Brunko OC, Galazka K, Lu Y, Weidenkaff A. High figure of merit in (Ti, Zr, Hf)NiSn half-Heusler alloys. Scripta Mater. 2012;66(12):1073.
Gürth M, Rogl G, Romaka VV, Grytsiv A, Bauer E, Rogl P. Thermoelectric high ZT half-Heusler alloys Ti1−x−yZrxHfyNiSn (0 ≤ x ≤ 1; 0 ≤ y ≤ 1). Acta Mater. 2016;104:210.
Rausch E, Castegnaro MV, Bernardi F, Alves MCM, Morais J, Balke B. Short and long range order of half-Heusler phases in (Ti, Zr, Hf)CoSb thermoelectric compounds. Acta Mater. 2016;115:308.
Makongo JPA, Misra DK, Zhou XY, Pant A, Shabetai MR, Su XL. Simultaneous large enhancements in thermopower and electrical conductivity of bulk nanostructured half-Heusler alloys. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133(46):18843.
Birkel CS, Zeier WG, Douglas JE, Lettiere BR, Mills CE, Seward G. Rapid microwave preparation of thermoelectric TiNiSn and TiCoSb half-Heusler compounds. Chem Mater. 2012;24(13):2558.
Birkel CS, Douglas JE, Lettiere BR, Seward G, Verma N, Zhang YC. Improving the thermoelectric properties of half-Heusler TiNiSn through inclusion of a second full-Heusler phase: microwave preparation and spark plasma sintering of TiNi(1+x)Sn. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2013;15(18):6990.
Lei Y, Li Y, Xu L, Yang JY, Wan RD, Long HM. Microwave synthesis and sintering of TiNiSn thermoelectric bulk. J Alloy Compd. 2015;660:166.
Li Y, Cheng C, Lei Y, Wang M, Wan RD. Ultra-fast preparation of high-performance thermoelectric bulk TiNiSb0.05Sn0.95 by microwave synthesis. Dalton Trans. 2017;46(1):33.
Lei Y, Li Y, Xu L, Cheng C, Wang M, Wan RD. Rapid microwave synthesis and sintering of ZrNiSn half-Heusler thermoelectric alloy. Rare Met Mater Eng. 2016;45(6):1565.
Biswas K, Muir S, Subramanian MA. Rapid microwave synthesis of indium filled skutterudites: an energy efficient route to high performance thermoelectric materials. Mater Res Bull. 2011;46(12):2288.
Hmood A, Kadhim A, Hassan HA. Influence of Yb-doping on the thermoelectric properties of Pb1−xYbxTe alloy synthesized using solid-state microwave. J Alloys Compd. 2012;520:1.
Kadhim A, Hmood A, Hassan HA. Structural and electrical transport properties of Se-substituted p-type Bi2Se3xTe3(1−x)(x = 0–1.0) alloys prepared by solid-state microwave synthesis. Mater Sci Semicond Proc. 2014;26:379.
Kadhim A, Hmood A, Hassan HA. Characterizations of solid-state microwave-synthesized Sb2Te3-based alloys with various compositions of bismuth in Bi2xSb2(1−x)Te3. Mater Sci Semicond Proc. 2012;15(5):549.
Kadhim A, Hmood A, Hassan HA. Characterization of PbSe1−xTex synthesized by solid-state microwave plasma assisted. Chalcogenide Lett. 2011;8(9):579.
Fan XA, Yang F, Rong ZZ, Cai XZ, Li GQ. Characterization and thermoelectric properties of Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 nanostructured bulk prepared by mechanical alloying and microwave activated hot pressing. Ceram Int. 2015;41(5):6817.
Kim-Hak O, Soulier M, Szkutnik PD, Saunier S, Simon J, Goeuriot D. Microwave sintering and thermoelectric properties of p-type (Bi0.2Sb0.8)2Te3 powder. Powder Technol. 2012;226(8):231.
Delaizir G, Bernard-Granger G, Monnier J, Grodzki R, Kim-Hak O, Szkutnik PD. A comparative study of spark plasma sintering (sps), hot isostatic pressing (hip) and microwaves sintering techniques on p-type Bi2Te3, thermoelectric properties. Mater Res Bull. 2012;47(8):1954.
Rong Z, Fan X, Yang F, Cai X, Han X, Li G. Microwave activated hot pressing: a new opportunity to improve the thermoelectric properties of n–type Bi2Te3−xSex bulks. Mater Res Bull. 2016;83:122.
Yang F, Fan X, Rong Z, Cai X, Li G. Lattice thermal conductivity reduction due to in situ-generated nano-phase in Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 alloys by microwave-activated hot pressing. J Electron Mater. 2014;43(11):4327.
Rong Z, Fan X, Yang F, Cai X, Li G. Microwave activated hot pressing: a new consolidation technique and its application to fine crystal bismuth telluride based compounds. Powder Technol. 2014;267(267):119.
Fan X, Rong Z, Yang F, Cai X, Han X, Li G. Effect of process parameters of microwave activated hot pressing on the microstructure and thermoelectric properties of Bi2Te3-based alloys. J Alloys Compd. 2015;630:282.
Xie H, Wang H, Pei Y, Fu C, Liu X, Snyder GJ. Beneficial contribution of alloy disorder to electron and phonon transport in half-Heusler thermoelectric materials. Adv Funct Mater. 2013;23(41):5123.
Zou T, Xie W, Widenmeyer M, Xiao X, Qin X, Weidenka A. Enhancing point defect scattering in copper antimony selenides via Sm and S co-doping. Rare Met. 2018;37(4):290.
Zhang S, Yang D, Shaheen N, Shen X, Xie D, Yan Y, Lu X, Zhou X. Enhanced thermoelectric performance of CoSbS0.85Se0.15 by point defect. Rare Met. 2018;37(4):316.
Bhattacharya S, Tritt TM, Xia Y. Grain structure effects on the lattice thermal conductivity of Ti-based half-Heusler alloys. Appl Phys Lett. 2002;81(1):43.
Bhattacharya S, Skove MJ, Russell M. Effect of boundary scattering on the thermal conductivity of TiNiSn-based half-Heusler alloys. Phys Rev B. 2008;77(18):998.
Douglas JE, Birkel CS, Miao MS, Torbet CJ. Enhanced thermoelectric properties of bulk TiNiSn via formation of a TiNi2Sn second phase. Appl Phys Lett. 2012;101(18):8616.
Chen LD, Huang XY, Zhou M, Shi X, Zhang WB. The high temperature thermoelectric performances of Zr0.5Hf0.5Ni0.8Pd0.2Sn0.99Sb0.01 alloy with nanophase inclusions. J Appl Phys. 2006;99(6):064305.
Chai YW, Kimura Y. Nanosized precipitates in half-Heusler TiNiSn alloy. Appl Phys Lett. 2012;100(3):033114.
Kim SW, Kimura Y, Mishima Y. High temperature thermoelectric properties of TiNiSn-based half-Heusler compounds. Intermetallics. 2007;15:349.
Zhang H, Wang YM, Dahal K, Mao J, Huang LH, Zhang QY. Thermoelectric properties of n-type half-Heusler compounds (Hf0.25Zr0.75)1−xNbxNiSn. Acta Mater. 2016;113:41.
Misra DK, Rajput A, Bhardwaj A, Chauhan NS, Singh S. Enhanced power factor and reduced thermal conductivity of a half-Heusler derivative Ti9Ni7Sn8: a bulk nanocomposite thermoelectric material. Appl Phys Lett. 2015;106(79):103901.
Bhardwaj A, Misra DK. Improving the thermoelectric performance of TiNiSn half-Heusler via incorporating submicron lamellae eutectic phase of Ti70.5Fe29.5: a new strategy for enhancing the power factor and reducing the thermal conductivity. J Mater Chem A. 2014;2(48):20980.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51574134 and 51574042), the Joint Fund between Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science and State Key Laboratory of Advanced Processing and Recycling of Nonferrous Metals (No. 18LHPY016) and Anhui University Outstanding Young Talent Support Program (Key Project) (No. gxyqZD2017039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, Y., Li, Y., Wan, RD. et al. Microwave synthesis and enhancement of thermoelectric performance in HfxTi1−xNiSn0.97Sb0.03 half-Heusler bulks. Rare Met. 42, 3780–3786 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01290-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-019-01290-7