Abstract
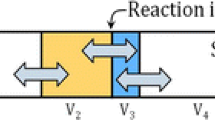
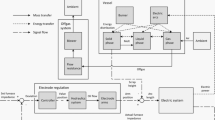
The development of a kinetic process model for the electric arc furnace (EAF) based on the effective equilibrium reaction zone approach is presented. The model combines kinetic expressions with accurate thermodynamic databases to predict the evolution of the mass, temperature and composition of the scrap, liquid metal, slag and gas phase during the process. The model addresses all the main phenomena occurring during the EAF process using empirical relations linked to process conditions: charge heating by arc and burners, scrap melting, C and O2 injection, slag-metal-gas reactions and post-combustion. The model can effectively reproduce measured endpoint temperature and composition of the slag and liquid metal in industrial EAF and illustrates the benefits of the hot heel practice. The model serves as a tool to assist in the optimization of the process operation conditions and in the design and evaluation of new process scenarios.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Madias, Treatise on Process Metallurgy - Volume 3: Industrial Processes, ed. S. Seetharaman (Elsevier, Oxford, UK, ), pp. 271–300
International Energy Agency, Iron and Steel Technology Roadmap (International Energy Agency, Paris, 2020).
H.J. Odenthal, A. Kemminger, F. Krause, L. Sankowski, N. Uebber, and N. Vogl, Steel Res. Int. 89, 1700098. (2018).
J.G. Bekker, I.K. Craig, and P.C. Pistorius, ISIJ Int. 39, 23–32. (1999).
R.D. Morales, H. Rodríguez-Hernández, and A.N. Conejo, ISIJ Int. 41, 426–435. (2001).
R.D. Morales, A.N. Conejo, and H.H. Rodriguez, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 33, 187–199. (2002).
R.D.M. MacRosty, and C.L.E. Swartz, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 44, 8067–8083. (2005).
H. Matsuura, C.P. Manning, R.A.F.O. Fortes, and R.J. Fruehan, ISIJ Int. 48, 1197–1205. (2008).
V. Logar, D. Dovžan, and I. Škrjanc, ISIJ Int. 52, 402–412. (2012).
V. Logar, D. Dovžan, and I. Škrjanc, ISIJ Int. 52, 413–423. (2012).
F. Opitz, and P. Treffinger, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 47, 1489–1503. (2016).
F. Opitz, P. Treffinger, and J. Wöllenstein, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48, 3301–3315. (2017).
T. Meier, K. Gandt, T. Hay, and T. Echterhof, Steel Res. Int. 89, 1700487. (2018).
T. Hay, A. Reimann, and T. Echterhof, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 50, 2377–2388. (2019).
A. Fathi, Y. Saboohi, I. Škrjanc, and V. Logar, Steel Res. Int. 88, 1600083. (2017).
Y. Saboohi, A. Fathi, I. Skrjanc, and V. Logar, IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66, 8030–8039. (2019).
T. Hay, V.V. Visuri, M. Aula, and T. Echterhof, Steel Res. Int. 92, 2000395. (2021).
M.A. Van Ende, Y.M. Kim, M.K. Cho, J. Choi, and I.H. Jung, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 42, 477–489. (2011).
E. Moosavi-Khoonsari, M.A. Van Ende and I.H. Jung, Kinetic model for hot metal pretreatment using lime and magnesium. Paper presented at the ICS 2018 - 7th International Congress on Science and Technology of Steelmaking, Venice, Italy, June 13-15 2018
M.A. Van Ende, and I.H. Jung, CAMP-ISIJ 28, 527–530. (2015).
M.A. Van Ende and I.H. Jung, A kinetic BOF process simulation model. Paper presented at the Asia Steel International Conference, Yokohama, Japan, October 5–8 2015.
D. You, C. Bernhard, P. Mayer, J. Fasching, G. Kloesch, R. Rössler, and R. Ammer, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 52, 1854–1865. (2021).
M.A. Van Ende, and I.H. Jung, ISIJ Int. 54, 489–495. (2014).
M.A. Van Ende, and I.H. Jung, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48, 28–36. (2017).
I.H. Jung, and M.A. Van Ende, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 51, 1851–1874. (2020).
D. Kumar, K.C. Ahlborg, and P.C. Pistorius, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 50, 2163–2174. (2019).
D. You, S.K. Michelic, and C. Bernhard, Steel Res. Int. 91, 2000045. (2020).
Y. Ren, L. Zhang, H. Ling, Y. Wang, D. Pan, Q. Ren, and X. Wang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48, 1433–1438. (2017).
S.P.T. Piva, D. Kumar, and P.C. Pistorius, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48, 37–45. (2017).
J.H. Shin, Y. Chung, and J.H. Park, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 48, 46–59. (2017).
C. Xuan, E.S. Persson, J. Jensen, R. Sevastopolev, and M. Nzotta, J. Alloys Compd. 812, 152149. (2020).
C.W. Bale, E. Bélisle, P. Chartrand, S.A. Decterov, G. Eriksson, A.E. Gheribi, K. Hack, I.H. Jung, Y.B. Kang, J. Melançon, A.D. Pelton, S. Petersen, C. Robelin, J. Sangster, P. Spencer, and M.A. Van Ende, Calphad 54, 35–53. (2016).
S. Petersen, and K. Hack, Int. J. Mat. Res. 98, 935–945. (2007).
H. Gaye, M. Wanin, P. Gugliermina and P. Schittly, Kinetics of scrap dissolution in the converter, theoretical model and plant experimentation. Paper presented at the Steelmaking Conference Proceedings, Detroit, MI, April 14–17 1985.
D.A. Goldstein, and R.J. Fruehan, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 30, 945–956. (1999).
G.H. Li, B. Wang, Q. Liu, X.Z. Tian, R. Zhu, L.N. Hu, and G.G. Cheng, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 17, 715–722. (2010).
N. Dogan, G.A. Brooks, and M.A. Rhamdhani, ISIJ Int. 51, 1102–1109. (2011).
J. Peter, K.D. Peaslee, D.G.C. Robertson and B.G. Thomas, Experimental study of kinetic processes during the steel treatment at two LMF's. Paper presented at the AISTech 2005, Charlotte, N.C., May 9–12 2005.
K.J. Graham, and G.A. Irons, Iron Steel Technol. 6, 164–173. (2009).
A. Harada, N. Maruoka, H. Shibata, and S.Y. Kitamura, ISIJ Int. 53, 2110–2117. (2013).
J. Li, G. Brooks, and N. Provatas, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 36, 293–302. (2005).
R. Inoue, and H. Suito, ISIJ Int. 46, 174–179. (2006).
F. Pahlevani, K. Shinya, H. Shibata, and N. Maruoka, ISIJ Int. 50, 822–829. (2010).
Acknowledgements
Financial support from Tata Steel Europe, Posco, Hyundai Steel, Nucor Steel, RioTionto Iron and Titanium, Nippon Steel Corp., JFE Steel, Voestalpine, RHI Magnesita, SeAH Besteel, Doosan Heavy Industry and Construction, and SCHOTT AG is gratefully acknowledged. This work was also partially supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) grant funded by the Korean government (MOTIE) (20217510100080, Development of critical metal recovery technologies (capacity of 200 kg/day) from low-grade solid wastes for the foundation of open access recycling platform).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The present author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Ende, MA. Development of an Electric Arc Furnace Simulation Model Using the Effective Equilibrium Reaction Zone (EERZ) Approach. JOM 74, 1610–1623 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05186-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-022-05186-3