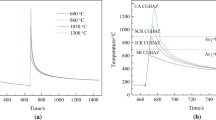
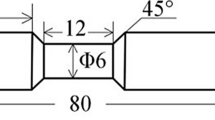
Abstract
The effect of heat input on the microstructure and toughness of simulated subregions was investigated by welding thermal simulations and Charpy impact tests. The results indicate that the microstructures of the simulated coarse and fine grain heat affected zone (CGHAZ and FGHAZ) gradually changed from lath martensite to a mixture of lath martensite/lath bainite and finally to granular bainite with the increase in heat input. The microstructure of the simulated intercritical heat affected zone (ICHAZ) was mainly composed of granular bainite and blocky martensite regardless of heat input. When the heat input increased, the toughness of the simulated CGHAZ and ICHAZ continuously decreased. Nevertheless, the simulated FGHAZ still displayed good toughness (53.16 J) due to its fine structure. The occurrence of martensite-austenite (M-A) constituents was the main reason for the decrease in crack initiation energy of the simulated CGHAZ and ICHAZ at high values of heat input, and the toughness deteriorated as the size of M-A constituents increased. It should be noted that high-misorientation packet and block boundaries can effectively deviate or arrest the propagation of microcracks. When the heat input was in the approximate range of 8.63-14.95 kJ cm−1, all of the simulated subregions exhibited good toughness.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.D.K. Misra, H. Nathani, J.E. Hartmann, and F. Siciliano, Microstructural Evolution in a New 770 MPa Hot Rolled Nb-Ti Microalloyed Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 394(1), p 339–352
A. Ghosh, R. Shukla, S. Das, and S. Chatterjee, The Structure And Properties of a Thermo-Mechanically Processed Low Carbon High Strength Steel, Steel Res. Int., 2016, 77(4), p 276–283
G. Magudeeswaran, V. Balasubramanian, and G. Madhusudhan Reddy, Effect of Welding Consumables on Fatigue Performance of Shielded Metal Arc Welded High Strength, Q&T Steel Joints, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2009, 18(1), p 49–56
M. Shome, O.P. Gupta, and O.N. Mohanty, Effect of Simulated Thermal Cycles on the Microstructure of the Heat-affected Zone in HSLA-80 and HSLA-100 Steel Plates, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, 35(13), p 985–996
J.H. Chen, Y. Kikuta, T. Araki, M. Yoneda, and Y. Matsuda, Micro-fracture Behaviour Induced by M-A Constituent (Island Martensite) in Simulated Welding Heat Affected Zone of HT80 High Strength Low Alloyed Steel, Acta Metall., 1984, 32(10), p 1779–1788
W. Meng, Z. Li, X. Jiang, J. Huang, Y. Wu, and S. Katayama, Microstructure and Toughness of Simulated Heat-Affected Zone of Laser Welded Joint for 960 MPa Grade High Strength Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, 23(10), p 3640–3648
B. Hutchinson, J. Komenda, G.S. Rohrer, and H. Beladi, Heat Affected Zone Microstructures and Their Influence on Toughness in Two Microalloyed HSLA Steels, Acta Mater., 2015, 97, p 380–391
R. Cao, J. Li, D.S. Liu, J.Y. Ma, and J.H. Chen, Micromechanism of Decrease of Impact Toughness in Coarse-Grain Heat-Affected Zone of HSLA Steel with Increasing Welding Heat Input, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, 46(7), p 2999–3014
F.Y. Song, M.H. Shi, P. Wang, F.X. Zhu, and R.D.K. Misra, Effect of Mn Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Weld Metal During High Heat Input Welding Processes, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26(6), p 2947–2953
P. Mohseni, J.K. Solberg, M. Karlsen, O.M. Akselsen, and E. Østby, Investigation of Mechanism of Cleavage Fracture Initiation in Intercritically Coarse Grained Heat Affected Zone of HSLA Steel, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2012, 28(11), p 1261–1268
J.A. Gianetto, J.E.M. Braid, J.T. Bowker, and W.R. Tyson, Heat-Affected Zone Toughness of a TMCP Steel Designed for Low-Temperature Applications, J. Offshore Mech. Arct., 1997, 119(2), p 134–144
J. Yang, K. Zhu, R. Wang, and J. Shen, Improving the Toughness of Heat Affected Zone of Steel Plate by Use of Fine Inclusion Particles, Steel Res. Int., 2011, 82(5), p 552–556
Z.R. Shi, C.F. Yang, R.Z. Wang, H. Su, F. Chai, J.F. Chu, and Q.F. Wang, Effect of Nitrogen on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties in Simulated CGHAZ of Vanadium Microalloyed Steel Varied with Different Heat Inputs, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2016, 649, p 270–281
Z.X. Zhu, J. Han, H.J. Li, and C. Lu, High Temperature Processed High Nb X80 Steel with Excellent Heat-Affected Zone Toughness, Mater. Lett., 2016, 163, p 171–174
H.H. Wang, K.M. Wu, X.W. Lei, and Y. Qian, Effect of Fast Cooling Process on Microstructure and Toughness of Heat Affected Zone in High Strength Pipeline Steel X120, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2013, 17(4), p 309–313
Y. Terada, H. Tamehiro, H. Morimoto, T. Hara, E. Tsuru, H. Asahi, M. Sugiyama, N. Doi, M. Murata, and N. Ayukawa, X100 Linepipe with Excellent HAZ Toughness and Deformability, in 22nd International Conference on Offshore Mechanics & Arctic Engineering ASME, 2003, p 287–294
S. Moeinifar, A.H. Kokabi, and H.R.M. Hosseini, Role of Tandem Submerged Arc Welding Thermal Cycles on Properties of the Heat Affected Zone in X80 Microalloyed Pipe Line Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2011, 211(3), p 368–375
W. Wang, W. Zhao, and J. Qu, Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 2.25Cr–1Mo Steel, Steel Res. Int., 2013, 84(2), p 178–183
J. Lee and Y. Pan, The Formation of Intragranular Acicular Ferrite in Simulated Heat-Affected Zone, ISIJ Int., 1995, 35(8), p 1027–1033
N.N. Rykalin, Calculations of Heat Processes in Welding, Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Moscow, 1960, p 183–201
L. Lan, C. Qiu, D. Zhao, X. Gao, and L. Du, Microstructural Characteristics and Toughness of the Simulated Coarse Grained Heat Affected Zone of High Strength Low Carbon Bainitic Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 529, p 192–200
E. Bouyne, H.M. Flower, T.C. Lindley, and A. Pineau, Use of EBSD Technique to Examine Microstructure and Cracking in a Bainite Steel, Scr. Mater., 1998, 39(3), p 295–300
X. Yue, Investigation on Heat-affected Zone Hydrogen-Induced Cracking of High-strength Naval Steels Using the Granjon Implant Test, Weld. World, 2015, 59(1), p 77–89
V. Biss and R.L. Cryderman, Martensite and Retained Austenite in Hot-Rolled, Low-Carbon Bainitic Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1971, 2(8), p 2267–2276
Y. Li and T.N. Baker, Effect of Morphology of Martensite-Austenite Phase on Fracture of Weld Heat Affected Zone in Vanadium and Niobium Microalloyed Steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, 26(9), p 1029–1040
Y. Sakuma, O. Matsumura, and H. Takechi, Mechanical Properties and Retained Austenite in Intercritically Heat-Treated Bainite-Transformed Steel and Their Variation with Si and Mn Additions, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1991, 22(2), p 489–498
S. Lee, B.C. Kim, and D.Y. Lee, Fracture Mechanism in Coarse Grained HAZ of HSLA Steel Welds, Scr. Metall., 1989, 23(6), p 995–1000
J.Y. Koo and G. Thomas, Metallurgical Factors Controlling Impact Properties of Two Phase Steels, Scr. Metall., 1979, 13(12), p 1141–1145
M. Shi, X. Yuan, H. Huang, and S. Zhang, Effect of Zr Addition on the Microstructure and Toughness of Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone with High-Heat Input Welding Thermal Cycle in Low-Carbon Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2017, 26(7), p 3160–3168
D.A. Curry and J.F. Knott, Effect of Microstructure on Cleavage Fracture Toughness of Quenched and Tempered Steels, Met. Sci. J., 1979, 13(6), p 341–345
M.J. Santofimia, C. Kwakernaak, W.G. Sloof, L. Zhao, and J. Sietsma, Experimental Study of the Distribution of Alloying Elements after the Formation of Epitaxial Ferrite upon Cooling in a Low-Carbon Steel, Mater. Charact., 2010, 61(10), p 937–942
A. Lambert-Perlade, A.F. Gourgues, and A. Pineau, Austenite to Bainite Phase Transformation in the Heat-Affected Zone of a High Strength Low Alloy Steel, Acta Mater., 2004, 52(8), p 2337–2348
A. Lambert-Perlade, X. Garat, T. Sturel, A.F. Gourgues, and A. Gingell, Application of Acoustic Emission to the Study of Cleavage Fracture Mechanism in a HSLA Steel, Scr. Mater., 2000, 43(2), p 161–166
A.F. Gourgues, Electron Backscatter Diffraction and Cracking, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2002, 18(2), p 119–133
M. Díaz-Fuentes, A. Iza-Mendia, and I. Gutiérrez, Analysis of Different Acicular Ferrite Microstructures in Low-Carbon Steels by Electron Backscattered Diffraction. Study of their toughness behavior, Metall. Mater.Trans. A, 2003, 34(11), p 2505–2516
H. Kitahara, R. Ueji, N. Tsuji, and Y. Minamino, Crystallographic Features of Lath Martensite in Low-Carbon steel, Acta Mater., 2006, 54(5), p 1279–1288
C. Wang, M. Wang, J. Shi, W. Hui, and H. Dong, Effect of Microstructural Refinement on the Toughness of Low Carbon Martensitic steel, Scr. Mater., 2008, 58(6), p 492–495
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016 YFB 0300601), National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51504064, 51474064, 51234002), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M591443) and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (N160704002, N160708001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, C., Deng, X., Tian, Y. et al. Microstructural Evolution and Toughness of the Various HAZs in 1300-MPa-Grade Ultrahigh-Strength Structural Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 1301–1311 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-3869-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-3869-1