Abstract
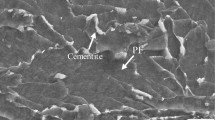
To obtain the correlation of microstructural characteristics and toughness in a novel high-strength low-carbon bainitic structural steel with medium and heavy plate after multipass welding, a welding thermal simulation experiment was conducted to simulate different subregions in the reheated coarse-grained heat-affected zones (CGHAZ). The microstructure evolution was then analyzed and factors that influence the fracture behavior were studied. The results show that the brittle zone appeared in subcritical reheated CGHAZ, and the fractured morphology was cleavage fracture. Supercritical reheated CGHAZ had the highest impact toughness, and the fractured morphology was primarily the ductile fracture with dimples formed via the micropore polycondensation mechanism. With an increase in the secondary pass welding thermal cycle peak temperature (tp2), the average length size of martensite and austenite (M-A) decreased from 9 to 2 μm. The coarsening of M-A constituents was the main reason for decrease in the crack initiation absorbed energy. A large number of retained austenite and cementite precipitates in subcritical reheated CGHAZ clearly worsened the impact toughness, and the massive austenite and cementite precipitates more than offset the beneficial effects of high-angle boundaries. This phenomenon led to disappearance of the effect of high-angle grain boundary of prior austenite and lath bainite on arresting crack propagation. In supercritical reheated CGHAZ, crack propagation absorbed energy was increased because of grain refinement, fine precipitates, lamellar residual austenite at corners, and high-angle grain boundary.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Aleksić, L. Milović, I. Blačić, T. Vuherer, and S. Bulatović: Eng. Failure Anal., 2019, vol. 104, pp. 1094-106.
J.J. Cui, W.T. Zhu, Z.Y. Chen, and L.Q. Chen: Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 2020, vol. 25, pp. 169-77.
X.H. Yu, J.L. Caron, S.S. Babu, J.C. Lippold, D. Isheim, and D.N. Seidman: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42, pp. 3669-79.
P. Mohseni, J.K. Solberg, M. Karlsen, O.M. Akselsen, and E. Østby: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2012, vol. 28, pp. 1261-68.
S. Moeinifar, A.H. Kokabi, and H.R.M. Hosseini: Mater. Des., 2010, vol. 31, pp. 2948-55.
J. Hu, L.X. Du, J.J. Wang, H. Xie, C.R. Gao, and R.D.K. Misra: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, vol. 590, pp. 323-28.
Y.L. Zhou, T. Jia, X.J. Zhang, and R.D.K. Misra: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2015, vol. 219, pp. 314-20.
L.Y. Lan, C.L. Qiu, H.Y. Song, and D.W. Zhao: Mater. Lett., 2014, vol. 125, pp. 86-88.
Q.M. Jiang, X.Q. Zhang, S. Hu, L.Q. Chen, and W.H. Sun: Welding Technology (In Chinese), 2015, vol. 44, pp. 5-9.
Y. You, C.J. Shang, L. Chen, and S. Subramanian: Mater. Des., 2013, vol. 43, pp. 485-91.
L.Y. Lan, C.L. Qiu, D.W. Zhao, C.M. Li, X.H. Gao, and L.X. Du: Acta Metall. Sin. (in Chinese), 2011, vol. 47, pp. 1046-54.
A.M. Guo, R.D.K. Misra, J.B. Liu, L. Chen, X.L. He, and S.J. Jansto: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 6440-48.
P.A. Lambert, A.F. Gourgues, J. Besson, T. Sturel, and A. Pinear: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35, pp. 1039-53.
N.N. Rykalin: Calculation of Heat Processes in Welding, Translation at the European Commission: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Moscow, 1960, pp. 28–35.
A.F. Gourgues: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2002, vol. 18, pp. 119-33.
M. Yang, Y.J. Chao, X.D. Li, D. Immel, and J.Z. Tan: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 497, pp. 462-70.
A.F. Gourgues, H.M. Flower, and T.C. Lindley: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2000, vol. 16, pp. 26-40.
X.L. Yang, Y.B. Xu, X.D. Tan, and D. Wu: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, vol. 641, pp. 96-106.
T. Kobayashi: Eng. Fract. Mech., 1984, vol. 19, pp. 49-65.
P.R. Sreenivasan, A. Moitra, S.K. Ray, S.L. Mannan, and R. Chandramohan: Int. J. Pressure Vessels Piping, 1996, vol. 69, pp. 149-59.
A.A. Griffith: Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London, 1921, vol. 221, pp. 163-98.
D.A. Curry, J.F. Knott: Met. Sci., 1978, vol. 12, pp. 511-14.
W.W. B. Filho, A.L. Carvalho, and P. Bowen: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, vol. 452-453, pp. 401-10.
K. Zhang, Q.L. Yong, X.J. Sun, Z.D. Li, P.L. Zhao, and S.D. Chen: Acta Metall. Sin. (in Chinese), 2014, vol. 50, pp. 913-20.
A. Lambert, J. Drillet, A.F. Gourgues, T. Sturel, and A. Pineau: Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining, 2000, vol. 5, pp. 168-73.
J.D. Chen, W.L. Mo, P. Wang, and S.P. Lu: Acta Metall. Sin. (in Chinese), 2012, vol. 48, pp. 1186-93.
Y. Shao, B.Y. Yan, Y.H. Liu, C.L. Mao, C. Wei, Y.C. Liu, Z.S. Yan, H.J. Li, and C.X. Liu: J. Manuf. Process., 2019, vol. 43, pp. 9-16.
W. Zhang, L.Z. Jiang, J.C. Hu, and H.M. Song: Mater. Charact., 2009, vol. 60, pp. 50-55.
K. Kocatepe, M. Cerah, and M. Erdogan: Mater. Des., 2007, vol. 28, pp. 172-81.
Y.S. Ahn, H.D. Kim, T.S. Byun, Y.J. Oh, G.M. Kim, and J.H. Hong: Nucl. Eng. Des., 1999, vol. 194, pp. 161-77.
C.K. Syn, B. Fultz, and J.W. Morris: Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9, pp. 1635-40.
G. Thomas: Metall. Trans. A, 1978, vol. 9, pp. 439-50.
M. Diaz-Fuentes, A. Iza-Mendia, and I. Gutierrez: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34, pp. 2505-16.
J. Kang, C. Wang, and G.D. Wang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, vol. 553, pp. 96-104.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51904071), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. N180703011), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Northeastern University (Grant No. 20190302), the PhD Start-up Fund of Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (Grant No. 2020-BS-271), the Key Research and Development Program of Hebei Province of China (Grant No. 18211019D), and Technical Development Program between HBIS Company Limited and NEU (Contract No. 2019040200044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted July 19, 2020.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, J., Zhu, W., Chen, Z. et al. Microstructural Characteristics and Impact Fracture Behaviors of a Novel High-Strength Low-Carbon Bainitic Steel with Different Reheated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zones. Metall Mater Trans A 51, 6258–6268 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-06017-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-06017-3